Published online Sep 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i9.3832
Revised: August 13, 2024
Accepted: August 14, 2024
Published online: September 15, 2024
Processing time: 55 Days and 20.7 Hours
Early diagnosis of colorectal cancer (CRC) is of great significance to improve the survival rate and quality of life of patients, but early diagnosis of CRC requires more sensitive techniques. Peripheral blood UL16-binding protein 2 (ULBP2) and human fibrinogen degradation products (DR-70) are the main indicators for the diagnosis of malignant tumors.
To assess ULBP2 and DR-70 potential for the early diagnosis and prognostic evaluation of CRC to provide a reference.
This study involved 60 patients with early-stage CRC (CRC group), 50 patients with benign colorectal tumors (benign group), and 50 healthy patients (control group) enrolled at the Affiliated Hospital of Jiangnan University and Jiangsu Province Official Hospital between January, 2020 and January, 2022. ULBP2 and DR-70 levels in the blood were determined and differences among the three groups and early diagnostic values for CRC were determined. Patients with CRC were divided into the good prognosis and poor prognosis groups, and ULBP2 and DR-70 levels in the blood and diagnostic values were compared.
ULBP2 and DR-70 serum levels were significantly higher in the CRC group than in the control and benign groups (P < 0.05); however, no significant differences were observed between the benign and control groups (P > 0.05). Among the 60 patients with CRC followed up for two years, two died (3.33%) and 15 exhibited tumor metastasis, progression, or recurrence (25.00%). ULBP2 and DR-70 serum levels were significantly higher in the poor prognosis group than in the good prognosis group (P < 0.05). A receiver operating characteristic curve was plotted. Area under the curve, sensitivity, and specificity of serum ULBP2 with DR-70 for the early diagnosis of CRC were higher than those of the single serum indices (P < 0.05) in both the good and poor prognosis groups.
ULBP2 and DR-70 serum levels were significantly high in patients with early-stage CRC. They improved the diagnostic rate of early-stage CRC and predicted patient prognosis, thereby showing clinical application potential.
Core Tip: The combination of Peripheral blood UL16-binding protein 2 (ULBP2) and human fibrinogen degradation products (DR-70) can obviously improve the diagnostic value of early colorectal cancer (CRC), which is very important for the early diagnosis and treatment of CRC. This study confirmed the diagnostic value of serum ULBP2 and DR-70 levels in early CRC patients by observing their serum ULBP2 and DR-70 levels.
- Citation: Zong ZP, Wu C. Clinical significance of peripheral blood UL16 and DR-70 for the early diagnosis and prognostic evaluation of colorectal cancer. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2024; 16(9): 3832-3838
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v16/i9/3832.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v16.i9.3832
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is a common malignant tumor, with the third highest incidence rate and second highest mortality rate among all malignant tumors. Moreover, approximately 1.9 million new CRC cases are reported annually, accounting for 10% of all new cancer cases worldwide[1]. Therefore, effective screening methods are necessary to improve the early diagnosis and reduce the disease burden of CRC. CRC progresses rapidly, and the five-year survival rate of patients with metastatic CRC is approximately 14%[2]. Selection of effective indicators is important to assess the patient prognosis and provide a reference for treatment. UL16-binding protein 2 (ULBP2), an activated receptor on the surface of natural killer cells that is involved in anti-tumor and anti-infection immunity, is highly expressed in many malignant tumors[3]. Human fibrinogen degradation products (DR-70) are proteolytic enzymes secreted by tumor cells. DR-70 is named after the American blood scientist, Donald Rounds, who first discovered it in 1970. DR-70 is obtained by detecting all degradation products of fibrin and fibrinogen in the serum; therefore, it is also known as the fibrin degradation complex[4]. However, only a few clinical studies have investigated the expression levels and diagnostic value of ULBP2 and DR-70 for patients with CRC. Therefore, in this study, we aimed to analyze the application value of ULBP2 and DR-70 for the early diagnosis and prognostic assessment of CRC to provide a reference for its clinical diagnosis and treatment.
This study included 60 patients with early-stage CRC (CRC group), including 32 males and 28 females [age: 40–75 (60.83 ± 5.86) years old] treated at the Affiliated Hospital of Jiangnan University and Jiangsu Province Official Hospital between January, 2020 and January, 2022. In total, 21 cases of colon cancer and 39 cases of rectal cancer were included in this study. As per the TNM staging, 26 cases were of stage I and 34 cases were of stage II. In terms of tumor types, this study included 44 cases of adenocarcinoma, 13 cases of signet-ring cell carcinoma, and 3 cases of mucinous carcinoma. Additionally, this study involved 50 cases of colorectal benign tumors (benign group), including 26 males and 24 females [age: 40-75 (61.04 ± 5.92) years old], and 50 control cases (control group), including 24 males and 26 females [age: 40–75 (59.92 ± 6.04) years old]. Basic data of all three groups were compared (P > 0.05).
For this study, the inclusion criteria were: (1) Patients meeting the diagnostic criteria for CRC[5]; (2) Patients with stage I–II tumors, with no metastasis; (3) Patients who underwent surgical treatment in the hospital; and (4) Patients with complete clinical data.
Exclusion criteria were: (1) Patients who received anti-tumor treatment before blood collection; (2) Patients with advanced tumors; (3) Patients with recurrent tumors; (4) Patients with other malignant tumors; (5) Patients with autoimmune deficiency or acute/chronic infection; and (6) Patients with deep vein thrombosis, liver and renal insufficiency, rheumatoid arthritis, sepsis, or other diseases that affect DR-70 expression.
Fasting elbow venous blood (5 mL) samples were collected from the CRC and benign groups one day before surgery and from the control group on the day of physical examination. Blood samples were allowed to stand for 10 minutes and centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 10 minutes with a centrifugal radius of 8 cm to obtain the supernatant. Then, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (Liangrunbio Biomedical Technology Co, Ltd.) was used to measure the serum ULBP2 and DR-70 levels, according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
We compared the serum ULBP2 and DR-70 levels among the CRC, benign, and control groups.
Patients with CRC were followed-up for two years after operation. Follow-up data was mainly collected via telephone, WeChat, and outpatient visits, and the patient conditions were tracked and recorded. Patients with tumor metastasis, progression, or recurrence and those who died were classified into the poor prognosis group, whereas those without tumor progression, recurrence, or metastasis and those who stayed alive were classified into the good prognosis group. Serum ULBP2 and DR-70 levels were compared between these two groups.
Serum ULBP2 and DR-70 levels and their predictive values for the diagnosis and prognosis of early-stage CRC were assessed and compared.
SPSS 26.0 software was used for the statistical analyses of data. Measurement data were described as mean ± SD, Shapiro-Wilk test is used to test the normality of continuous variables, and independent sample t tests were performed if the data exhibited normal distribution. Measurement data that did not conform to a normal distribution were described using the rank-sum test with median and interquartile range. Repeated variance F for the data test among multiple groups and count data was expressed as a rate (%), and χ2 tests were conducted. A receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was plotted to determine the early diagnosis and prognostic values of serum indicators. Area under the curve (AUC) was calculated, and the difference in clinical values was considered statistically significant when P < 0.05.
Serum ULBP2 and DR-70 levels were significantly higher in the CRC group than in the control and benign groups (P < 0.05); however, no significant differences were observed between the benign and control groups (P > 0.05; Table 1).
Among the 60 patients with CRC followed up for two years, two died (3.33%) and 15 exhibited tumor metastasis, progression, or recurrence (25.00%). Serum levels of ULBP2 and DR-70 were significantly higher in the poor prognosis group than in the good prognosis group (P > 0.05; Table 2).
| Group | ULBP2 (ng/L) | DR-70 (μg/mL) |
| Good prognosis (n = 43) | 76.91 ± 15.28 | 1.10 ± 0.36 |
| Poor prognosis (n = 17) | 95.67 ± 17.05 | 1.49 ± 0.45 |
| t value | 4.147 | 3.518 |
| P value | 0.001 | 0.001 |
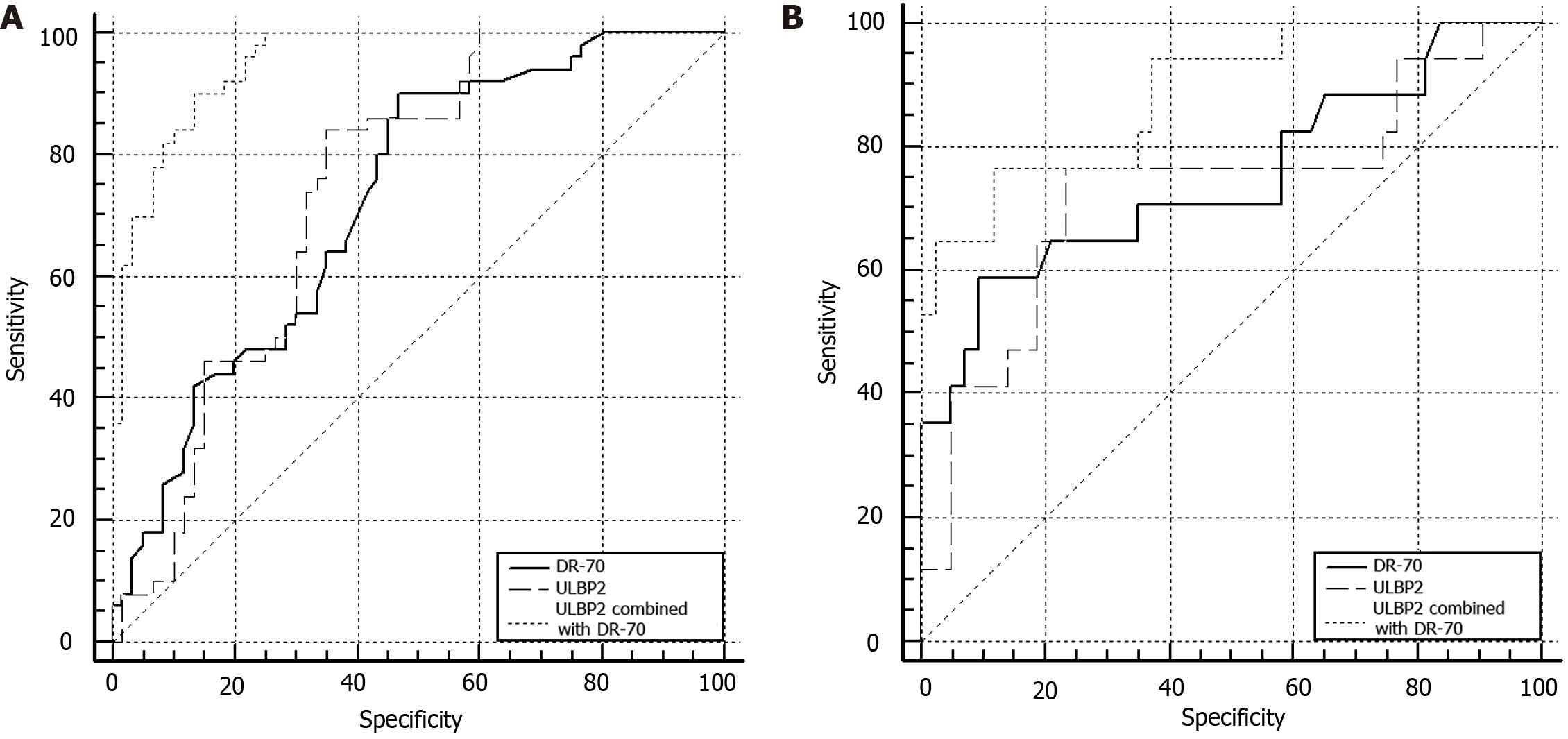
In the ROC curve, the AUC, sensitivity, and specificity of serum ULBP2 with DR-70 for the early diagnosis of CRC were higher than those of the single serum indices (P < 0.05; Table 3; Figure 1A).
| Index | AUC | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | Youden's index | SE | 95%CI |
| ULBP2 | 0.743 | 84.00 | 65.00 | 0.490 | 0.0472 | 0.651-0.821 |
| DR-70 | 0.725 | 90.00 | 53.33 | 0.433 | 0.0477 | 0.632-0.806 |
| ULBP2 combined with DR-70 | 0.952 | 92.00 | 86.67 | 0.767 | 0.0178 | 0.894-0.984 |
In the ROC curve, the AUC, sensitivity, and specificity of serum ULBP2 with DR-70 for the assessment of poor prognosis in CRC were higher than those of the single serum indices (P < 0.05; Table 4; Figure 1B).
| Index | AUC | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | Youden's index | SE | 95%CI |
| ULBP2 | 0.731 | 76.50 | 76.70 | 0.532 | 0.0807 | 0.600–0.837 |
| DR-70 | 0.748 | 64.71 | 81.40 | 0.495 | 0.0782 | 0.619–0.851 |
| ULBP2 combined with DR-70 | 0.885 | 82.35 | 88.37 | 0.648 | 0.0485 | 0.776–0.953 |
Incidence and mortality rates of CRC are increasing annually, and its overall development period is approximately 10 years. Diagnostic screening within this period is crucial to reduce the mortality rate and improve the patient prognosis[6]. However, early onset CRC has no specific manifestations, and most patients are diagnosed during physical examination. However, as the patients already exhibit abnormal manifestations at the time of diagnosis, the disease is mostly in the intermediate and advanced stages, thus affecting their five-year survival rate. Colonoscopy and pathological examinations are complex, invasive, and expensive; hence, they are not widely used as screening tools[7]. Serum indicators are important for the clinical auxiliary diagnosis of malignant tumors. However, conventional tumor markers exhibit low sensitivity and specificity. Therefore, more effective markers need to be explored to improve the detection of early-stage tumors.
ULBP family, consisting of 1–4 members, acts as an important active ligand for the D receptor, a member of NKG2. ULBP expression is significantly increased in viral infections or malignant lesions. NKG2D mediates the resistance of immune cells to tumor cells by regulating the binding of immune cells to tumor cells with the corresponding ligands[8]. ULBP2 is an important member of the ULBP family. In this study, we observed significantly increased ULBP2 Levels in the peripheral blood of patients with CRC, correlating with a poor prognosis. Consistently, Kegasawa et al[9] reported that blood ULBP2 levels are closely related to the prognosis of patients with pancreatic cancer and that high ULBP2 expression is an independent risk factor for poor overall survival of patients with pancreatic cancer. Yang et al[10] revealed that ULBP2 is related to the T-stage, N-stage, and pathological stage of colon cancer and acts as an independent predictor of the overall survival of patients with colon cancer. Therefore, ULBP2 in the peripheral blood may be a major marker for the diagnosis and prognosis of CRC. Under normal conditions, ULBP is only expressed in highly active cells; however, ULBP levels are sharply elevated by any abnormal increase in cell proliferation and differentiation or morphology changes. CRC cells are highly active cells that undergo rapid proliferation and differentiation and exhibit abnormal morphological changes, thus promoting an increase in ULBP2 Levels. ULBP2 induces tumor cell apoptosis and mediates the toxic effects of immune mechanisms on tumor cells; it is highly expressed in the serum and tissues of patients with malignant tumors[11]. Moreover, ULBP2 expression is associated with the tumor stage, malignancy, and tumor replication; the higher its expression, the faster is the tumor cell proliferation and replication, resulting in the poor prognosis of patients.
DR-70 is a novel marker for the diagnosis of malignant tumors. Unlike conventional tumor cell adhesion molecules, DR-70 freely floats in the blood and is highly expressed in the serum of patients with malignant tumors[12]. Here, serum DR-70 levels were significantly high in patients with CRC, exhibiting an abnormal upward trend in patients with poor prognosis compared to that in patients with a good prognosis. Our results suggest that DR-70 levels can be used to diagnose early-stage CRC and predict the prognosis and outcomes of affected patients. Ke et al[13] reported that DR-70 levels are significantly high in patients with malignant tumors, suggesting it as an ideal tumor marker. Sakai et al[14] revealed that fibrinogen degradation products are closely associated with the TNM stage and poor prognosis of patients with esophageal cancer and that their preoperative levels affect the poor prognosis of patients post-surgery. Formation and proliferation of malignant tumors are often accompanied by angiogenesis and production of various coagulation factors, resulting in a high coagulation rate. Simultaneously, the exogenous coagulation cascade is activated, further promoting the invasion, metastasis, and proliferation of tumor cells. As a fibrin hydrolase, DR-70 degrades fibrin into coagulation fragments D, E, and D-dimer, whose expression levels indicate the degree of coagulation in the body; high levels indicate an active coagulation system, with the body in a hypercoagulable state. The higher the malignancy of the tumor, the higher is the risk of tumor cell metastasis and proliferation, resulting in the poor prognosis of patients after surgery[15].
Here, ROC curve revealed that the AUC, sensitivity, and specificity of serum ULBP2 with DR-70 for the early diagnosis of CRC and prediction of postoperative patient prognosis were higher than those of single serum indices (P < 0.05). These results indicate that serum ULBP2 and DR-70 levels can individually predict the prognosis of patients with CRC, but their combination is more effective and has a higher application value. Serum ULBP2 and DR-70 are highly expressed in various types of malignant tumors, and their detection is affected by other diseases, drugs, and factors. Hence, their specificity and sensitivity are limited in individual applications. However, in combination, these indicators play synergistic and complementary roles and exhibit better clinical value. However, due to the limited sample size included in this study, the research results may be biased. In the future, it is necessary to expand the sample size and further discuss such as assay variability and potential confounders to obtain more accurate research results.
In summary, serum levels of ULBP2 and DR-70 were significantly elevated in patients with early-stage CRC. ULBP2 combined with DR-70 improved the diagnosis of early-stage CRC and effectively predicted the patient prognosis, thereby showing high clinical application potential.
Malignant CRC tumor cells are highly active cells that promote the expression of ULBP2. These proliferating and invading malignant tumor cells further affect the coagulation system, leading to the increased production of plasminogen activator, which causes fibrinogen dissolution and increased DR-70 expression. Here, serum ULBP2 and DR-70 levels were significantly increased in patients with early-stage CRC. Our findings suggest that ULBP2 combined with DR-70 can be used as an ideal tumor marker for the diagnosis and prognostic evaluation of patients with CRC, highlighting their clinical value.
| 1. | Ionescu VA, Gheorghe G, Bacalbasa N, Chiotoroiu AL, Diaconu C. Colorectal Cancer: From Risk Factors to Oncogenesis. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023;59. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 60] [Cited by in RCA: 64] [Article Influence: 32.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Klimeck L, Heisser T, Hoffmeister M, Brenner H. Colorectal cancer: A health and economic problem. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2023;66:101839. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 65] [Article Influence: 32.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Shin AE, Giancotti FG, Rustgi AK. Metastatic colorectal cancer: mechanisms and emerging therapeutics. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2023;44:222-236. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in RCA: 279] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Köklü H, Köklü S, Öztürk Ö. DR-70 immunoassay in gastric cancer. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2016;27:88. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Dekker E, Tanis PJ, Vleugels JLA, Kasi PM, Wallace MB. Colorectal cancer. Lancet. 2019;394:1467-1480. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1570] [Cited by in RCA: 3008] [Article Influence: 501.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (3)] |
| 6. | Baidoun F, Elshiwy K, Elkeraie Y, Merjaneh Z, Khoudari G, Sarmini MT, Gad M, Al-Husseini M, Saad A. Colorectal Cancer Epidemiology: Recent Trends and Impact on Outcomes. Curr Drug Targets. 2021;22:998-1009. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 26] [Cited by in RCA: 154] [Article Influence: 38.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (2)] |
| 7. | Kastrinos F, Kupfer SS, Gupta S. Colorectal Cancer Risk Assessment and Precision Approaches to Screening: Brave New World or Worlds Apart? Gastroenterology. 2023;164:812-827. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 7] [Cited by in RCA: 51] [Article Influence: 25.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Lopez KJ, Spence JP, Li W, Zhang W, Wei B, Cross-Najafi AA, Butler JR, Cooper DKC, Ekser B, Li P. Porcine UL-16 Binding Protein 1 Is Not a Functional Ligand for the Human Natural Killer Cell Activating Receptor NKG2D. Cells. 2023;12. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 2] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Kegasawa T, Tatsumi T, Yoshioka T, Suda T, Ikezawa K, Nakabori T, Yamada R, Kodama T, Shigekawa M, Hikita H, Sakamori R, Takehara T. Soluble UL16-binding protein 2 is associated with a poor prognosis in pancreatic cancer patients. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;517:84-88. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 17] [Article Influence: 2.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Yang X, Su X, Wang Z, Yu Y, Wu Z, Zhang D. ULBP2 is a biomarker related to prognosis and immunity in colon cancer. Mol Cell Biochem. 2023;478:2207-2219. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Feng R, Xu J, Huang J, Liu J, Wang X, Wang J, Zhang C, Li H, Wei Y, Ren G. An immune-related prognostic gene ULBP2 is correlated with immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment and immunotherapy in breast cancer. Heliyon. 2024;10:e23687. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Cai L, Tu M, Yin X, Zhang S, Zhuang W, Xia Y, Zhang Y, Zhang L, Yu L, Chi L, Huang Y. Combination of serum CST4 and DR-70 contributes to early diagnosis of colorectal cancer. Clin Chim Acta. 2022;531:318-324. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in RCA: 13] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Ke CH, Sio KM, Wu CH, Xia YY, Lee JJ, Hu CH, Liu CC, Lu CL, Cheng CL, Lin KH, Tomiyasu H, Wang YS, Lin CS. Increased plasma DR-70 (fibrinogen-fibrin degradation products) concentrations as a diagnostic biomarker in dogs with neoplasms. J Vet Intern Med. 2023;37:2391-2401. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Sakai M, Sohda M, Uchida S, Yamaguchi A, Watanabe T, Saito H, Ubukata Y, Nakazawa N, Kuriyama K, Sano A, Ogawa H, Yokobori T, Shirabe K, Saeki H. Fibrin/fibrinogen Degradation Products Are Associated With Tumor Stage and Prognosis in Patients Undergoing Resection of Esophageal Cancer. Anticancer Res. 2021;41:4523-4527. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Poole LG, Kopec AK, Flick MJ, Luyendyk JP. Cross-linking by tissue transglutaminase-2 alters fibrinogen-directed macrophage proinflammatory activity. J Thromb Haemost. 2022;20:1182-1192. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 11] [Article Influence: 3.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |