Published online May 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i5.2060
Revised: February 26, 2024
Accepted: April 1, 2024
Published online: May 15, 2024
Processing time: 161 Days and 10.5 Hours
Targeting DNA damage response (DDR) pathway is a cutting-edge strategy. It has been reported that Schlafen-11 (SLFN11) contributes to increase chemosen
To investigate the role of SLFN11 in DDR and the application of synthetic lethal in esophageal cancer with SLFN11 defects.
To reach the purpose, eight esophageal squamous carcinoma cell lines, 142 eso
Methylation of SLFN11 was exhibited in 9.15% of (13/142) ED and 25.62% of primary (258/1007) ESCC cases, and its expression was regulated by promoter region methylation. SLFN11 methylation was significantly associated with tumor differentiation and tumor size (both P < 0.05). However, no significant associations were observed between promoter region methylation and age, gender, smoking, alcohol consumption, TNM stage, or lymph node metastasis. Utilizing DNA damaged model induced by low dose cisplatin, SLFN11 was found to activate non-homologous end-joining and ATR/CHK1 signaling pathways, while inhibiting the ATM/CHK2 signaling pathway. Epigenetic silencing of SLFN11 was found to sensitize the ESCC cells to ATM inhibitor (AZD0156), both in vitro and in vivo.
SLFN11 is frequently methylated in human ESCC. Methylation of SLFN11 is sensitive marker of ATM inhibitor in ESCC.
Core Tip: Targeting DNA damage repair (DDR) is a novel strategy for cancer therapy. Epigenetic-based synthetic lethality studies have been conducted recently. Schlafen-11 (SLFN11) has been reported to sensitize cancer cells by involving DDR. However, the detailed regulatory network in DDR remains controversial. This study explored the mechanism of SLFN11 in DDR, and further investigated the synthetic lethal efficiency of epigenetic silencing SLFN11 and ATM inhibitor. The results demonstrated that SLFN11 activated non-homologous end-joining and ATR/CHK1, while inhibiting the ATM/CHK2 signaling pathway. Epigenetic silencing SLFN11 sensitized esophageal cancer cells to ATM inhibitor both in vitro and in vivo.
- Citation: Zhou J, Zhang MY, Gao AA, Zhu C, He T, Herman JG, Guo MZ. Epigenetic silencing schlafen-11 sensitizes esophageal cancer to ATM inhibitor. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2024; 16(5): 2060-2073
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v16/i5/2060.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v16.i5.2060
Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) is the most common esophageal carcinoma, accounting for over 90%[1]. Surgical resection is the sole curable approach for early-stage cancer patients, but most cases were diagnosed at the late stage. Despite the efforts of oncologists using different regimens for a long time, chemo-radiotherapy remains inefficient[2]. Targeting therapeutics were validated almost unsuccessful in ESCC, despite advancements made in other types of cancer[3]. It is desirable to discover novel therapeutic strategy for ESCC.
The discovery of synthetic lethality in BRCA1/2 mutated cancer has ushered in a new era of inhibition of DNA da
Defects of high-fidelity DDR will result in increased genomic instability and force cells to primarily depend on the compensatory survival pathways to evade cell death[11]. Synthetic lethality is applied to cancer therapy by selectively targeting compensatory pathways[11,12]. Currently, the majority of studies and ongoing clinical trials are focused on a limited number of DDR mutants, as the exhausting of genomic resources[13-15]. The application of DDR defects caused by aberrant epigenetic changes will expand synthetic lethal rationale in cancer therapy. Epigenetic abnormalities occur more frequently than mutations for tumor suppressor and DDR-related genes in cancer[16,17].
The Schlafen (SLFN) gene family was identified by screening growth regulatory genes from lymphocytes, which are present only in mammals. The mouse genome contains 10 members of the Schlafen family, and the human genome contains 6 members[18,19]. Human SLFN11 was identified by comparing the structural similarity with mouse[20]. SLFN11 protein contains an N-terminal ATPases associated domain and a C-terminal DNA/RNA helicase domain[20,21]. By utilizing 60 human cancer cell lines derived from nine distinct tissues, it was observed that cells exhibiting elevated levels of SLFN11 displayed heightened sensitivity to various cytotoxic agents, including topoisomerase inhibitors and cisplatin[22]. Previous research has indicated that SLFN11 directly interacts with replication protein A (RPA) and is recruited to DNA damage sites to inhibit homologous recombination repair by destabilizing the RPA-single-strand DNA complex[23]. Another study revealed that SLFN11 impeded stressed replication forks independently of ATR[24]. Moreover, high level expression of SLFN11 sensitized different cancer cells to poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitors, single strand DNA damage repair inhibitors[25-27]. The exact regulatory network of SLFN11 in DDR remains elusive.
In this study, we explored the epigenetic regulation and the role of SLFN11 in DDR to pave the way for synthetic lethal therapy in human ESCC.
Eight ESCC cells were used in this study, including KYSE30, KYSE140, KYSE150, KYSE180, KYSE450, KYSE510, KYSE520, and colo680n. These cells were derived from primary ESCC and cultured in RPMI-1640 medium (Gibco, No. 31800089) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum and 1% penicillin/streptomycin. HEK293 cell line was used for lentivirus production and was maintained in DMEM (Gibco, No. 12100061).
Esophageal tissue samples, including 142 esophageal dysplasia (ED) and 1007 primary ESCC tissue samples, were collected from the Chinese PLA General Hospital. These samples were not subjected to chemo-radiotherapy prior to surgical resection. Sample collection adhered to the guidelines authorized by the Chinese PLA General Hospital Institutional Review Board (IRB number: 20090701-015). Tumor classification was performed using the TNM staging system (AJCC 8th).
For cell treatment, 5-aza-2’-deoxycytidine (5-aza, Sigma-Aldrich, No. A3656) was added to RPMI-1640 medium at a concentration of 2 μmol/L. RNA isolation and semi-quantitative RT-PCR procedures were conducted in accordance with our previously described methods[28]. RT-PCR primers for SLFN11 were designed as follows: 5′-AACGCCC
The methods for DNA extraction, bisulfite modification, and methylation-specific PCR (MSP) were described as previously[28]. The primer sequences for MSP targeting SLFN11 were designed as below: 5′-TTTGGAAGGTGGGATCGTAGGTATC-3′ (MF) and 5′-ACCCAAACAACTATCGACTCCTACG-3′ (MR); 5′-TATTTGGAAGGTGGGATTGTAGGTATT-3′ (UF) and 5′-AAACCCAAACAACTATCAACTCCTACA-3′ (UR).
The PCDH-CMV-MCS-puro vector was employed to construct a full-length cDNA (GenBank accession number: NM_91607) expression vector for human SLFN11. The lentiviral supernatant was obtained after transfection into HEK293 cells by lipofectamine 3000 growing for 48 h and 72 h following the instructions of the manufacturer (Invitrogen, No. L3000008). Subsequently, the lentiviral supernatant was added into the culture medium. Puromycin (MCE, No. HY-15695) was then used to screen for SLFN11 expressing KYSE30 (2.5 μg/mL) and KYSE450 (1.0 μg/mL) cells 48 h after lentiviral transfection, with a duration of 3 d for the screening process. The monoclonal SLFN11 expression cells were obtained through limited dilution in 96 well plates, and further validated via Western blot.
The CRISPR/Cas9 technique was employed to generate SLFN11 deleted KYSE510 cells. Single guide RNA (sgRNA) was designed using Guide Design Resources from http://crispr.mit.edu. The LentiCRISPRv2 vector was utilized to construct the CRISPR/Cas9 knockout system with sgRNA1 5′-CACCGCAGCCTGACAACCGAGAAAT-3′ and sgRNA2 5′-AAACATTTCTCGGTTGTCAGGCTGC-3′. SLFN11 knockout KYSE510 cell clones were selected following above procedure with puromycin (0.5 μg/mL), and validated by DNA sequencing and Western blot.
Anti-SLFN11 (No. 34858), anti-p-ATM Ser1981 (No. 13050S), anti-ATR (No. 2790S), anti-p-ATR Ser428 (No. 2853S), and anti- γ-H2AX Ser139 (No. 9718) antibodies were ordered in the Cell Signaling Technology. Anti-DNA-PKcs (No. 200618-6D1), anti-p-DNA-PKcs Ser2056 (No. 380800), anti-CHK2 (No. R23921), anti-p-CHK2 Thr68 (No. 240766) and anti-CHK1 (No. 380200) antibodies were ordered from ZENBIO. Anti-ATM (No. HX12561) and anti-XRCC4 (No. HX19688) antibodies were obtained from Huaxingbio. Anti-β-actin (No. 66009-1-Ig) and anti-p-CHK1 Ser345 (No. GTX100065) antibodies were from Proteintech and Genetex, respectively. The procedures were performed as described previously[28].
For assessment of the sensitivity of ESCC cells to different reagents, MTT assay was employed. Cells were grown in 96-well plates with 2000 cells for each well, and treatment was performed after seeding for 24 h. The IC50 was evaluated by treatment with gradient dilution of cisplatin (Selleck, No. S1166) for 48 h. The sensitivity of three different cell lines to AZD0156 (MCE, No. HY-100016), an ATM inhibitor, was tested using DNA damaging cell models induced by low dose cisplatin with gradient dilution of AZD0156 for 48 h. GraphPad Prism software was employed for data analysis.
Colony formation assays were performed using 35 mm dishes. For chemosensitivity detection, KYSE30, KYSE450, and KYSE510 cells were inoculated with the density of 3 × 103 cells each well. They were cultured in medium supplemented with 1 μmol/L and 2 μmol/L of cisplatin for 24 h. Then the medium was changed for growing 14 d. To assess the impact of SLFN11 on DDR, ESCC cell models induced with 0.05 μmol/L cisplatin were treated with 0.20 μmol/L AZD0156. The medium was changed after 24 h of growth for a total of 14 d. The cell colonies were then fixed with 75.0% ethanol and stained with 0.2% crystal violet (Solarbio, No. G1063) for 30 min. The relative efficiency of colony formation was determined by normalizing the colony areas to the control. This process was repeated in three independent experiments.
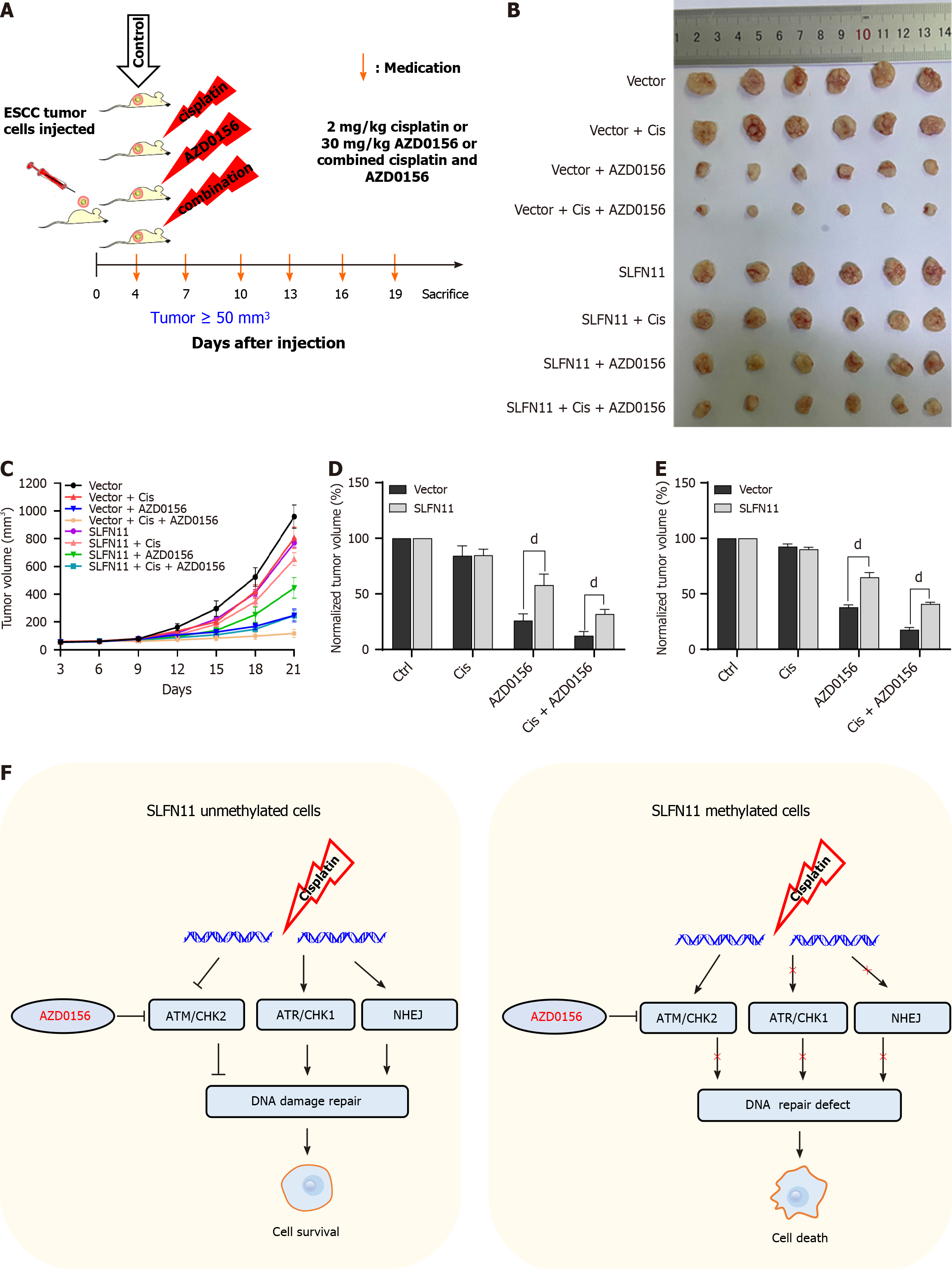
Four-week-old BALB/c nude mice weighing around 20 g were procured from SPF Company (Beijing, China) and housed under conditions that met standard pathogen-free requirements. SLFN11 silenced and re-expressed KYSE30 cells (6 × 106 cells in 0.15 mL sterilized PBS) were injected subcutaneously into the mice. A caliper was used for tumor size measuring. The volume was calculated as the formula: V = length × width2/2. Once the average tumor volume reached 50 mm3, both SLFN11 unexpressed and re-expressed xenograft mice were randomly divided into four groups (six mice per group). Mice were administrated with 0.9% saline, cisplatin (2 mg/kg), AZD0156 (30 mg/kg) or combined cisplatin and AZD0156 for every three days in different groups. Cisplatin was administered via intraperitoneal injection, and AZD0156 was administered orally. The Animal Ethics Committee of the Chinese PLA General Hospital (approval number: 2022-X18-72) approved the animal experimental procedures, with strict adherence to protocols aimed at minimizing the discomfort of mice.
SPSS 21.0 (NY, United States) and GraphPad Prism 8.0 (CA, United States) were used for statistical analysis. P < 0.05 was regarded significantly difference. The association between methylation status and clinical-pathological factors was examined with the χ2 test. Quantitative data were described as mean ± SD and analyzed using the student’s two-tailed t test.
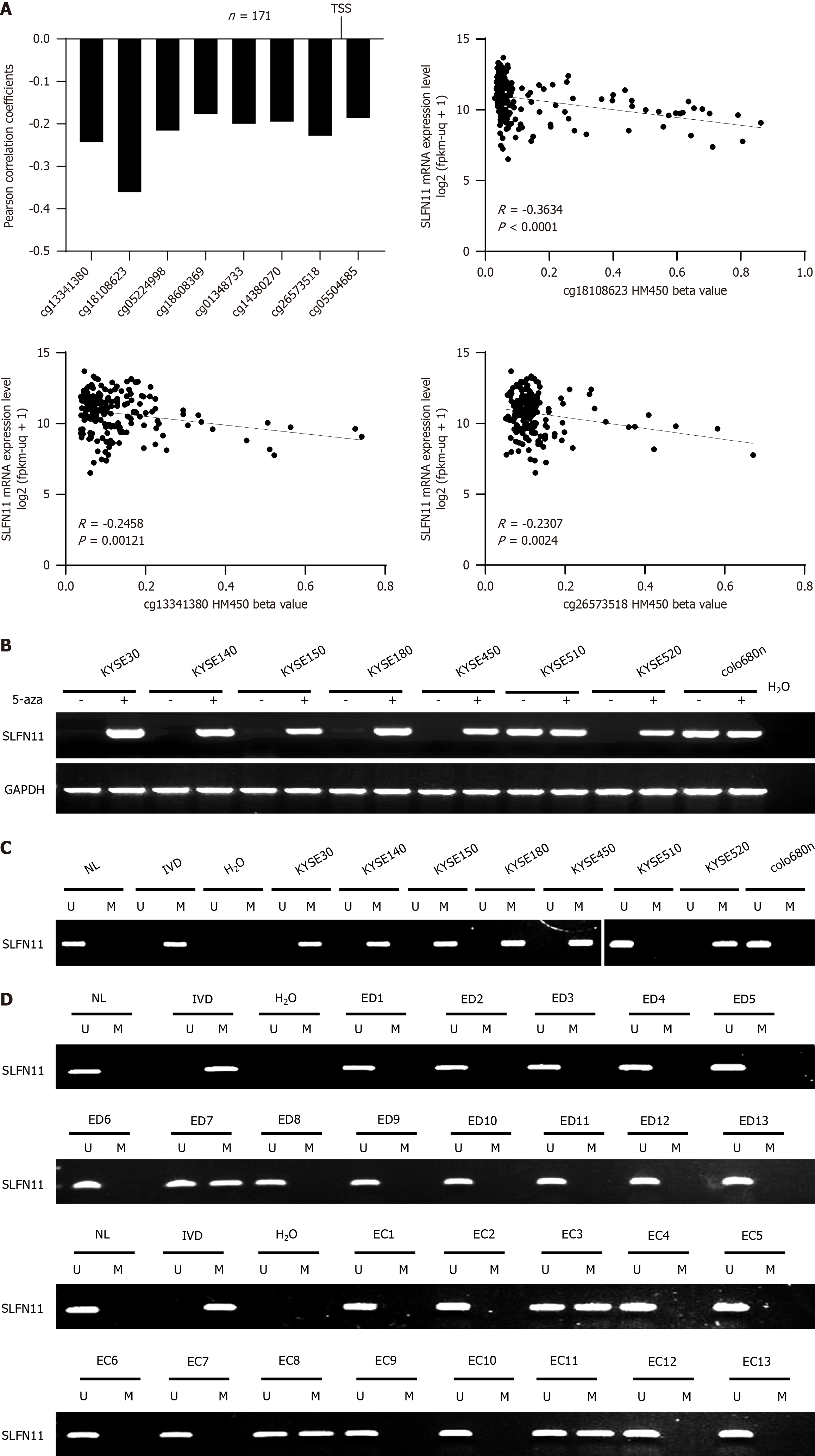
To assess the relation between the expression of SLFN11 and its methylation status in the promoter region, 171 cases of ESCC data were extracted from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database (http://xena.ucsc.edu/). The reverse association between SLFN11 mRNA levels and CpG sites (cg13341380, cg18108623, cg05224998, cg18608369, cg01348733, cg14380270, cg26573518, and cg05504685, all P < 0.05) methylation around the transcript start sites was observed, as depicted in Figure 1A.
The expression and promoter region methylation were detected by semi-quantitative RT-PCR and MSP. SLFN11 was highly expressed in KYSE510 and colon680n cells whereas SLFN11 was silenced in KYSE520, KYSE450, KYSE180, KYSE150, KYSE140, and KYSE30 cell lines (Figure 1B). SLFN11 was unmethylated in KYSE510 and colo680n cells, and completely methylated in KYSE520, KYSE450, KYSE180, KYSE150, KYSE140, and KYSE30 cell lines (Figure 1C), indicating the correlation between loss of expression and promoter region hypermethylation. To further validate the regulatory role of DNA methylation in SLFN11 expression, 5-aza, an inhibitor of DNA methyltransferase, was employed. The induction of SLFN11 expression by 5-aza was observed in methylated ESCC cells (Figure 1B), suggesting that DNA methylation regulates the expression of SLFN11.
To explore the epigenetic changes of SLFN11 during esophageal carcinogenesis, methylation status was detected in 142 cases of ED and 1007 cases of primary ESCC tissues. Methylation of SLFN11 was found in 9.15% (13/142) of ED and 25.62% (258/1007) of ESCC samples, indicating a progressive tendency during carcinogenesis (Figure 1D). Furthermore, SLFN11 methylation was significantly associated with poor tumor differentiation and tumor size (both P < 0.05, Table 1). However, no significant association was observed between methylation and age, gender, smoking, alcohol consumption, TNM stage or lymph node metastasis (Table 1).
| Clinical factor | No. | SLFN11 methylation status | P value | |
| Unmethylated, n = 749 (74.37%) | Methylated, n = 258 (25.62%) | |||
| Age (yr) | 0.512 | |||
| < 60 | 317 | 240 | 77 | |
| ≥ 60 | 690 | 509 | 181 | |
| Gender | 0.823 | |||
| Male | 677 | 505 | 172 | |
| Female | 330 | 244 | 86 | |
| Smoking | 0.883 | |||
| No | 562 | 417 | 145 | |
| Yes | 445 | 332 | 113 | |
| Alcohol consumption | 0.743 | |||
| No | 730 | 545 | 185 | |
| Yes | 277 | 204 | 73 | |
| Tumor size (cm) | 0.012a | |||
| ≤ 4 | 633 | 454 | 179 | |
| > 4 | 374 | 295 | 79 | |
| Differentiation | 0.002b | |||
| Well | 173 | 147 | 26 | |
| Moderate | 526 | 383 | 143 | |
| Poor | 308 | 219 | 89 | |
| TNM stage | 0.567 | |||
| I + II | 531 | 391 | 140 | |
| III + IV | 476 | 358 | 118 | |
| Lymph node metastasis | 0.973 | |||
| Negative | 526 | 391 | 135 | |
| Positive | 481 | 358 | 123 | |
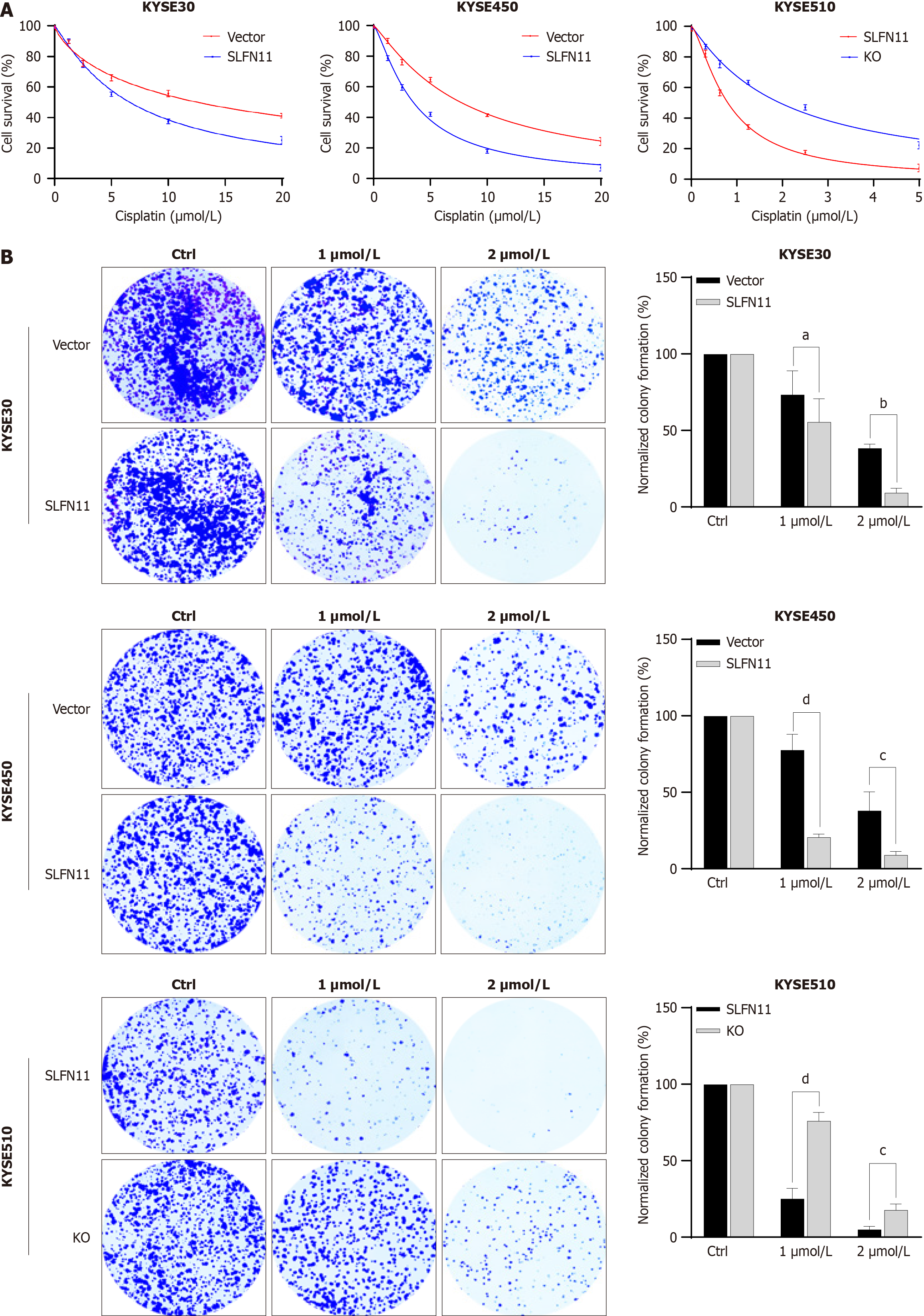
To evaluate the impact of SLFN11 on cisplatin sensitivity, we utilized SLFN11 epigenetic silenced and knockout ESCC cell models. As shown in Figure 2A, the IC50 value of cisplatin was 12.45 μmol/L ± 1.16 μmol/L vs 7.03 μmol/L ± 0.69 μmol/L in KYSE30 cells (P < 0.01) and 8.57 μmol/L ± 0.87 μmol/L vs 4.30 μmol/L ± 0.71 μmol/L in KYSE450 cells (P < 0.01) before and after re-expressing SLFN11, indicating that SLFN11 increased the sensitivity of ESCC cells to cisplatin. In SLFN11 highly expressed KYSE510 cells, the IC50 value was 0.79 μmol/L ± 0.12 μmol/L vs 1.93 μmol/L ± 0.09 μmol/L (P < 0.001) before and after deletion of SLFN11, demonstrating that deletion of SLFN11 reduced sensitivity to cisplatin.
To further investigate the impact of SLFN11 on cisplatin sensitivity, colony formation assay was performed. Before and after the restoration of SLFN11 expression in KYSE30 cells, the normalized colony efficiency was 73.59% ± 12.51% vs 55.73% ± 12.18% (1 μmol/L cisplatin), and 38.52% ± 2.13% vs 9.49% ± 2.25% (2 μmol/L cisplatin), respectively (both P < 0.05, Figure 2B). The normalized colony efficiency was 77.86% ± 8.26% vs 20.79% ± 1.54% (1 μmol/L cisplatin) and 38.15% ± 9.95% vs 9.16% ± 1.79% (2 μmol/L cisplatin) in KYSE450 cells before and after the expression of SLFN11, respectively (both P < 0.05, Figure 2B). In KYSE510 cells, the normalized colony efficiency was 25.30% ± 5.40% vs 76.24% ± 4.34% (1 μmol/L cisplatin) and 5.15% ± 1.55% vs 17.92% ± 3.05% (2 μmol/L cisplatin) before and after knockout of SLFN11, respectively (both P < 0.01, Figure 2B). Above results validated the chemo-sensitive role of SLFN11 in human ESCC.
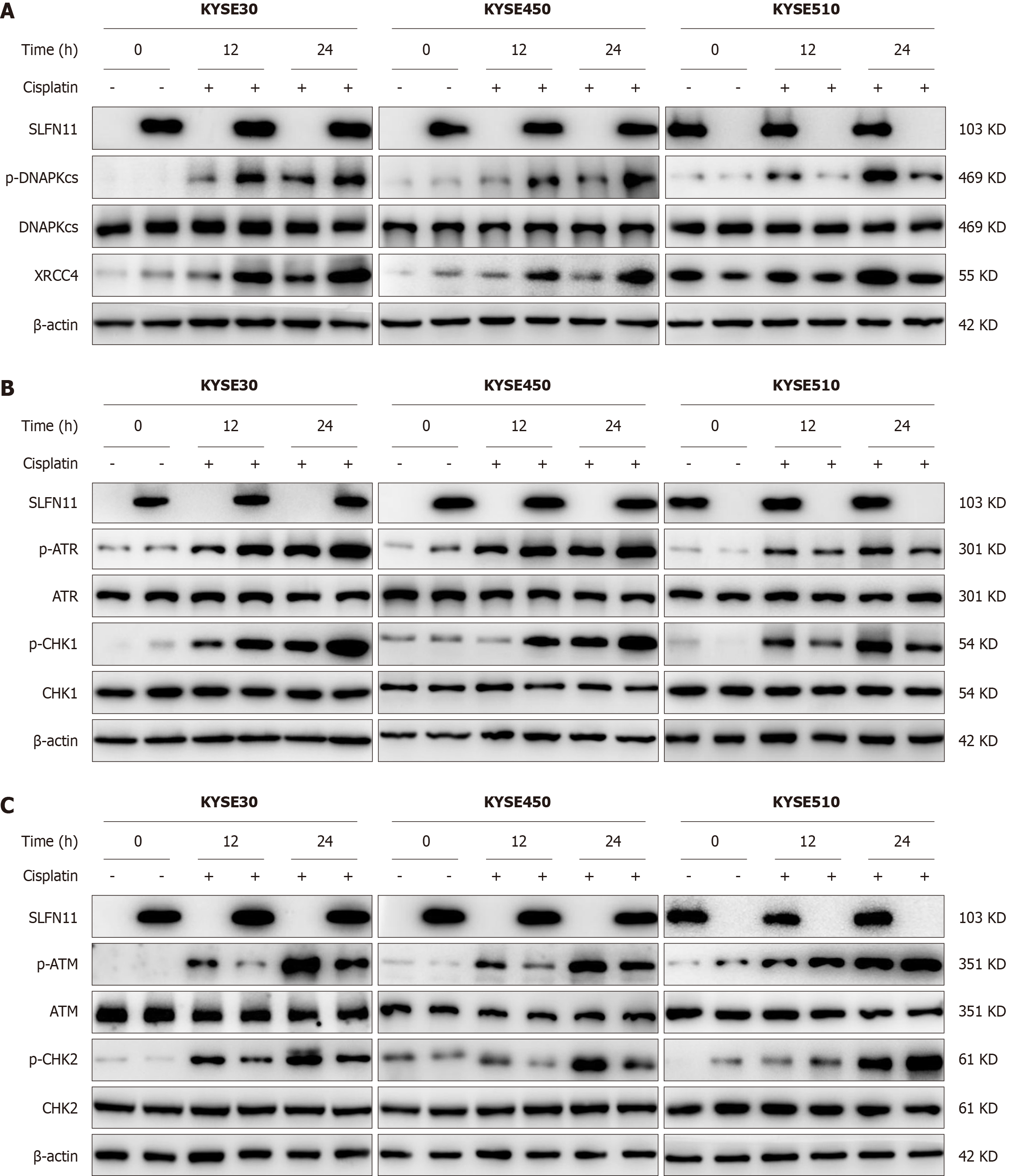
To elucidate the mechanism of SLFN11 in ESCC, low dose cisplatin induced DNA damage cell models were employed. The majority of chemotherapeutic reagents primarily induce DNA double strand breaks (DSBs), which are the most harmful DNA lesions. DSBs are repaired through two major signaling pathways, namely homologous recombination repair (HR) and non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ). Subsequently, the expression levels of ATM, ATR, p-CHK1, p-CHK2, DNAPKcs, and XRCC4 were examined in SLFN11 expressed and unexpressed ESCC cells. Under the treatment of low dose cisplatin, the expression of p-DNAPKcs and XRCC4 was elevated in KYSE30 and KYSE450 cells by re-expressing SLFN11, indicating that the NHEJ pathway was activated by SLFN11 (Figure 3A). The involvement of SLFN11 in NHEJ signaling pathway was then further demonstrated through SLFN11 knockout in KYSE510 cell lines (Figure 3A). As shown in Figure 3B and C, the expression of p-ATR and p-CHK1 was elevated, while the expression of p-ATM and p-CHK2 was suppressed after re-expression of SLFN11 in KYSE30 and KYSE450 cell lines, suggesting that SLFN11 activates ATR/CHK1 signaling and inhibits ATM/CHK2 signaling in ESCC cells. These results were further validated by deletion of SLFN11 in KYSE510 cell lines.
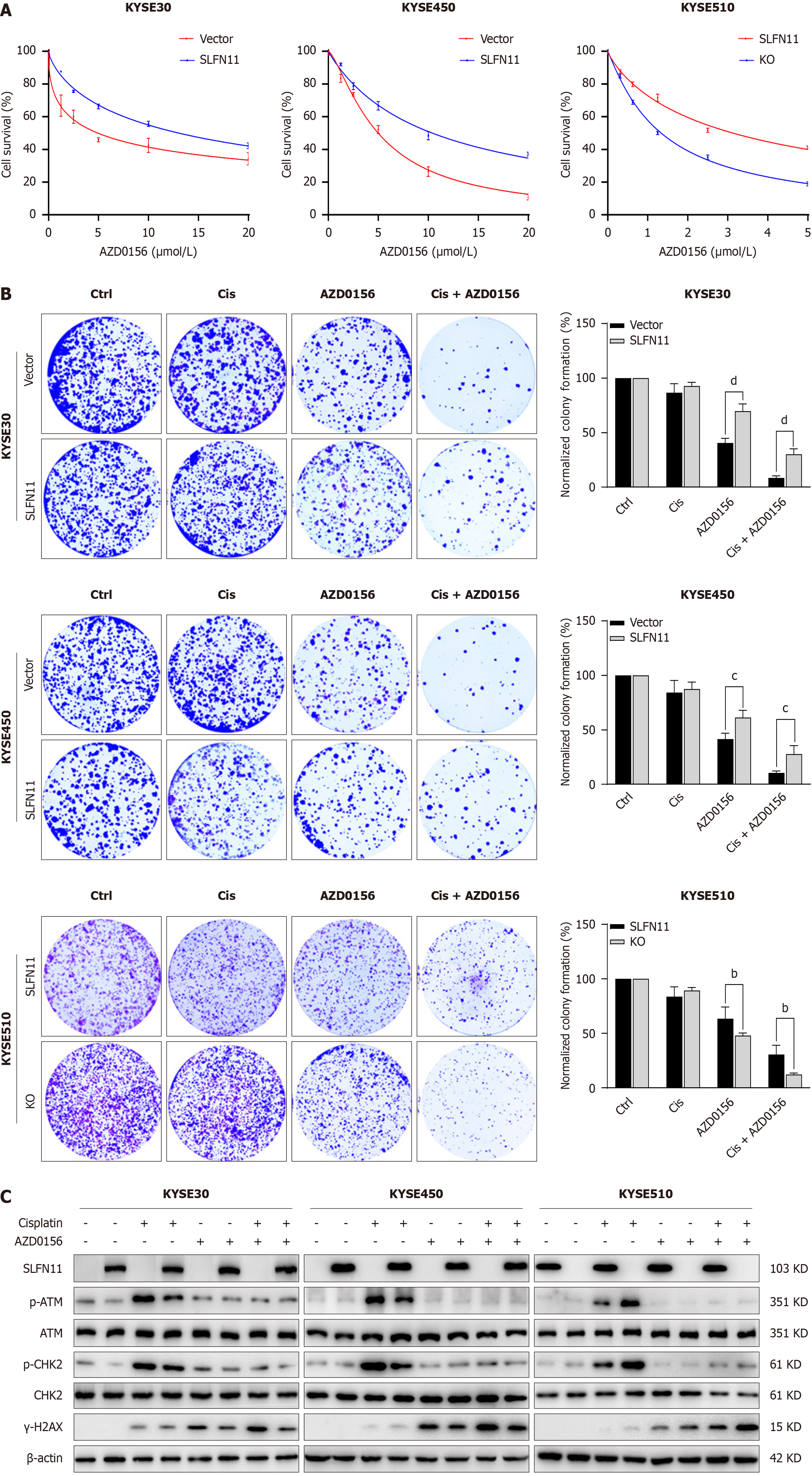
SLFN11 is regulated by promoter region methylation, and its expression suppresses ATM signaling. Then, the effects of AZD0156 were assessed in SLFN11 deficient ESCC cells. As shown in Figure 4A, the IC50 value was 5.91 μmol/L ± 1.35 μmol/L vs 13.04 μmol/L ± 2.54 μmol/L (P < 0.05) in KYSE30 cells and 5.79 μmol/L ± 0.83 μmol/L vs 10.77 μmol/L ± 1.08 μmol/L (P < 0.01) in KYSE450 cells before and after re-expressing SLFN11, respectively, demonstrating that epigenetic silencing of SLFN11 sensitizes ESCC cells to AZD0156. The IC50 value was 3.52 μmol/L ± 0.48 μmol/L vs 1.62 μmol/L ± 0.29 μmol/L (P < 0.01) in SLFN11 highly expressed and deleted KYSE510 cells, respectively (Figure 4A), further supporting the notion that SLFN11 deficiency sensitizes ESCC cells to AZD0156.
To further evaluate the sensitivity of SLFN11 to AZD0156, colony formation assay was applied. Under the treatment of low dose cisplatin and AZD0156, the normalized colony efficiency was 8.67% ± 1.93% vs 30.36% ± 5.01% (P < 0.001) in KYSE30 cells and 10.72% ± 1.78% vs 27.94% ± 7.76% (P < 0.01) in KYSE450 cells before and after re-expressing SLFN11, hinting that the relative colony formation efficiency was inhibited by SLFN11 (Figure 4B). The relative colony formation efficiency was 30.53% ± 8.56% vs 12.18% ± 1.42% (P < 0.01) in KYSE510 cells before and after deleting SLFN11, respectively, providing further evidence for the role of SLFN11 in sensitizing AZD0156. The levels of γ-H2AX, a DNA damage marker, were detected in these cells with or without SLFN11 expression (Figure 4C). The levels of γ-H2AX were elevated by administration of AZD0156 in ESCC cells without SLFN11, further validating above results.
To further investigate the impact of SLFN11 on ATM inhibitor in vivo, KYSE30 cell xenograft models were employed. The tumor volume and weight in control groups, which did not receive cisplatin or AZD0156 treatment, were normalized as 100%. When subjected to low dose cisplatin, AZD0156 or a combination of both, the relative normalized tumor volumes were 84.33% ± 8.87% vs 84.83% ± 5.33% (P > 0.05), 26.07% ± 6.00% vs 57.90 ± 9.92% (P < 0.0001), and 12.43% ± 3.81% vs 31.95% ± 4.17% (P < 0.0001) in SLFN11 silenced and re-expressed xenografts, respectively (Figure 5C and D).
The results showed that in the cisplatin, AZD0156, and combined cisplatin with AZD0156 treatment groups, the normalized tumor weight was 92.62% ± 2.36% vs 90.25% ± 1.65% (P > 0.05), 37.98% ± 2.13% vs 64.93% ± 4.20% (P < 0.001), and 17.67% ± 1.97% vs 40.92% ± 1.56% (P < 0.0001) in SLFN11 silenced and re-expressed xenografts, respectively (Figure 5E). The combined cisplatin and AZD0156 treatment led to a significant reduction in tumor volume and weight in SLFN11 silenced KYSE30 cell xenografts, demonstrating that the loss of SLFN11 expression increased the sensitivity of ESCC cells to AZD0156 in vivo.
Human SLFN11 is a putative DNA/RNA helicase and recently more studies were focused on its chemosensitivity in various cancers by combination of different therapeutic reagents, including PARP inhibitor and PD1 antibody[27,29,30]. The expression of SLFN11 was shown to correlate with chemosensitivity broadly[29-32]. While a majority of tumors exhibit low levels or lack of SLFN11 expression, which varies depending on the cancer types[22,33]. And recent reports demonstrated that expression of SLFN11 did not exhibit sensitivity to all chemo-therapeutic agents, as evidenced by the analysis of multiple cancer types[30]. The mechanism of SLFN11 in chemosensitivity was mainly recognized to involve in DDR[34]. An early study found that the inhibition of ATR had substantial effect on DDR in SLFN11-negative cells[26]. Another investigation suggested that SLFN11 involved in ATR signaling by downregulation of type II tRNAs[35]. However, Murai et al[24] illustrated that the guarding of the genome by SLFN11 is independent of ATR. Additional stu
Our findings revealed that methylation of SLFN11 is in an accumulating tendency during esophageal carcinogenesis. Methylation of SLFN11 is a sensitive marker for ATM inhibitor both in vitro and in vivo in ESCC.
The authors would like to acknowledge Xiaomo Su, the technician of gastroenterology laboratory, for the experimental assistance.
Provenance and peer review: Invited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Peer-review model: Single blind
Specialty type: Medicine, research & experimental
Country/Territory of origin: China
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): A
Grade B (Very good): 0
Grade C (Good): 0
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Ghiorzo P, Italy S-Editor: Chen YL L-Editor: A P-Editor: Zheng XM
| 1. | Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209-249. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 75126] [Cited by in RCA: 64442] [Article Influence: 16110.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (176)] |
| 2. | Blum Murphy MA, Elimova E, Ajani JA. Current concepts and future potential in neoadjuvant chemotherapy for esophageal cancer. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;10:383-392. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 10] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Ohashi S, Miyamoto S, Kikuchi O, Goto T, Amanuma Y, Muto M. Recent Advances From Basic and Clinical Studies of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2015;149:1700-1715. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 319] [Cited by in RCA: 413] [Article Influence: 41.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Bryant HE, Schultz N, Thomas HD, Parker KM, Flower D, Lopez E, Kyle S, Meuth M, Curtin NJ, Helleday T. Specific killing of BRCA2-deficient tumours with inhibitors of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. Nature. 2005;434:913-917. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3368] [Cited by in RCA: 3834] [Article Influence: 191.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Farmer H, McCabe N, Lord CJ, Tutt AN, Johnson DA, Richardson TB, Santarosa M, Dillon KJ, Hickson I, Knights C, Martin NM, Jackson SP, Smith GC, Ashworth A. Targeting the DNA repair defect in BRCA mutant cells as a therapeutic strategy. Nature. 2005;434:917-921. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 4316] [Cited by in RCA: 4878] [Article Influence: 243.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Roos WP, Thomas AD, Kaina B. DNA damage and the balance between survival and death in cancer biology. Nat Rev Cancer. 2016;16:20-33. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 711] [Cited by in RCA: 837] [Article Influence: 93.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Matt S, Hofmann TG. The DNA damage-induced cell death response: a roadmap to kill cancer cells. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016;73:2829-2850. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 206] [Cited by in RCA: 217] [Article Influence: 24.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Pilié PG, Tang C, Mills GB, Yap TA. State-of-the-art strategies for targeting the DNA damage response in cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2019;16:81-104. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 647] [Cited by in RCA: 804] [Article Influence: 134.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Ljungman M. Targeting the DNA damage response in cancer. Chem Rev. 2009;109:2929-2950. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 107] [Cited by in RCA: 103] [Article Influence: 6.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Hopkins JL, Lan L, Zou L. DNA repair defects in cancer and therapeutic opportunities. Genes Dev. 2022;36:278-293. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 79] [Cited by in RCA: 110] [Article Influence: 36.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Gao A, Guo M. Epigenetic based synthetic lethal strategies in human cancers. Biomark Res. 2020;8:44. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 10] [Cited by in RCA: 24] [Article Influence: 4.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | O'Neil NJ, Bailey ML, Hieter P. Synthetic lethality and cancer. Nat Rev Genet. 2017;18:613-623. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 323] [Cited by in RCA: 442] [Article Influence: 55.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Perkhofer L, Gout J, Roger E, Kude de Almeida F, Baptista Simões C, Wiesmüller L, Seufferlein T, Kleger A. DNA damage repair as a target in pancreatic cancer: state-of-the-art and future perspectives. Gut. 2021;70:606-617. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 104] [Cited by in RCA: 131] [Article Influence: 32.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Brown JS, O'Carrigan B, Jackson SP, Yap TA. Targeting DNA Repair in Cancer: Beyond PARP Inhibitors. Cancer Discov. 2017;7:20-37. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 449] [Cited by in RCA: 466] [Article Influence: 58.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Cheng B, Pan W, Xing Y, Xiao Y, Chen J, Xu Z. Recent advances in DDR (DNA damage response) inhibitors for cancer therapy. Eur J Med Chem. 2022;230:114109. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 13] [Cited by in RCA: 76] [Article Influence: 25.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Gao D, Herman JG, Guo M. The clinical value of aberrant epigenetic changes of DNA damage repair genes in human cancer. Oncotarget. 2016;7:37331-37346. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 58] [Cited by in RCA: 67] [Article Influence: 9.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Guo M, Peng Y, Gao A, Du C, Herman JG. Epigenetic heterogeneity in cancer. Biomark Res. 2019;7:23. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 90] [Cited by in RCA: 149] [Article Influence: 24.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Schwarz DA, Katayama CD, Hedrick SM. Schlafen, a new family of growth regulatory genes that affect thymocyte development. Immunity. 1998;9:657-668. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 163] [Cited by in RCA: 182] [Article Influence: 6.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Neumann B, Zhao L, Murphy K, Gonda TJ. Subcellular localization of the Schlafen protein family. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;370:62-66. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 50] [Cited by in RCA: 63] [Article Influence: 3.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Bustos O, Naik S, Ayers G, Casola C, Perez-Lamigueiro MA, Chippindale PT, Pritham EJ, de la Casa-Esperón E. Evolution of the Schlafen genes, a gene family associated with embryonic lethality, meiotic drive, immune processes and orthopoxvirus virulence. Gene. 2009;447:1-11. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 69] [Cited by in RCA: 91] [Article Influence: 5.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Jo U, Pommier Y. Structural, molecular, and functional insights into Schlafen proteins. Exp Mol Med. 2022;54:730-738. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in RCA: 29] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 22. | Zoppoli G, Regairaz M, Leo E, Reinhold WC, Varma S, Ballestrero A, Doroshow JH, Pommier Y. Putative DNA/RNA helicase Schlafen-11 (SLFN11) sensitizes cancer cells to DNA-damaging agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109:15030-15035. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 195] [Cited by in RCA: 263] [Article Influence: 20.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 23. | Mu Y, Lou J, Srivastava M, Zhao B, Feng XH, Liu T, Chen J, Huang J. SLFN11 inhibits checkpoint maintenance and homologous recombination repair. EMBO Rep. 2016;17:94-109. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 85] [Cited by in RCA: 118] [Article Influence: 11.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 24. | Murai J, Tang SW, Leo E, Baechler SA, Redon CE, Zhang H, Al Abo M, Rajapakse VN, Nakamura E, Jenkins LMM, Aladjem MI, Pommier Y. SLFN11 Blocks Stressed Replication Forks Independently of ATR. Mol Cell. 2018;69:371-384.e6. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 125] [Cited by in RCA: 191] [Article Influence: 31.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 25. | Lok BH, Gardner EE, Schneeberger VE, Ni A, Desmeules P, Rekhtman N, de Stanchina E, Teicher BA, Riaz N, Powell SN, Poirier JT, Rudin CM. PARP Inhibitor Activity Correlates with SLFN11 Expression and Demonstrates Synergy with Temozolomide in Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2017;23:523-535. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 187] [Cited by in RCA: 286] [Article Influence: 31.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 26. | Murai J, Feng Y, Yu GK, Ru Y, Tang SW, Shen Y, Pommier Y. Resistance to PARP inhibitors by SLFN11 inactivation can be overcome by ATR inhibition. Oncotarget. 2016;7:76534-76550. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 170] [Cited by in RCA: 232] [Article Influence: 33.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 27. | Allison Stewart C, Tong P, Cardnell RJ, Sen T, Li L, Gay CM, Masrorpour F, Fan Y, Bara RO, Feng Y, Ru Y, Fujimoto J, Kundu ST, Post LE, Yu K, Shen Y, Glisson BS, Wistuba I, Heymach JV, Gibbons DL, Wang J, Byers LA. Dynamic variations in epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), ATM, and SLFN11 govern response to PARP inhibitors and cisplatin in small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget. 2017;8:28575-28587. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 114] [Cited by in RCA: 177] [Article Influence: 25.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 28. | He T, Zhang M, Zheng R, Zheng S, Linghu E, Herman JG, Guo M. Methylation of SLFN11 is a marker of poor prognosis and cisplatin resistance in colorectal cancer. Epigenomics. 2017;9:849-862. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 47] [Cited by in RCA: 44] [Article Influence: 5.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 29. | Zhang B, Ramkumar K, Cardnell RJ, Gay CM, Stewart CA, Wang WL, Fujimoto J, Wistuba II, Byers LA. A wake-up call for cancer DNA damage: the role of Schlafen 11 (SLFN11) across multiple cancers. Br J Cancer. 2021;125:1333-1340. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 13] [Cited by in RCA: 37] [Article Influence: 9.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 30. | Coleman N, Zhang B, Byers LA, Yap TA. The role of Schlafen 11 (SLFN11) as a predictive biomarker for targeting the DNA damage response. Br J Cancer. 2021;124:857-859. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 15] [Cited by in RCA: 41] [Article Influence: 8.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 31. | Pietanza MC, Waqar SN, Krug LM, Dowlati A, Hann CL, Chiappori A, Owonikoko TK, Woo KM, Cardnell RJ, Fujimoto J, Long L, Diao L, Wang J, Bensman Y, Hurtado B, de Groot P, Sulman EP, Wistuba II, Chen A, Fleisher M, Heymach JV, Kris MG, Rudin CM, Byers LA. Randomized, Double-Blind, Phase II Study of Temozolomide in Combination With Either Veliparib or Placebo in Patients With Relapsed-Sensitive or Refractory Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36:2386-2394. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 279] [Cited by in RCA: 323] [Article Influence: 46.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 32. | van Erp AEM, van Houdt L, Hillebrandt-Roeffen MHS, van Bree NFHN, Flucke UE, Mentzel T, Shipley J, Desar IME, Fleuren EDG, Versleijen-Jonkers YMH, van der Graaf WTA. Olaparib and temozolomide in desmoplastic small round cell tumors: a promising combination in vitro and in vivo. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2020;146:1659-1670. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 8] [Cited by in RCA: 23] [Article Influence: 4.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 33. | Winkler C, Armenia J, Jones GN, Tobalina L, Sale MJ, Petreus T, Baird T, Serra V, Wang AT, Lau A, Garnett MJ, Jaaks P, Coker EA, Pierce AJ, O'Connor MJ, Leo E. SLFN11 informs on standard of care and novel treatments in a wide range of cancer models. Br J Cancer. 2021;124:951-962. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 38] [Cited by in RCA: 50] [Article Influence: 12.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 34. | Luan J, Gao X, Hu F, Zhang Y, Gou X. SLFN11 is a general target for enhancing the sensitivity of cancer to chemotherapy (DNA-damaging agents). J Drug Target. 2020;28:33-40. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 10] [Cited by in RCA: 16] [Article Influence: 2.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 35. | Li M, Kao E, Malone D, Gao X, Wang JYJ, David M. DNA damage-induced cell death relies on SLFN11-dependent cleavage of distinct type II tRNAs. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2018;25:1047-1058. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 53] [Cited by in RCA: 92] [Article Influence: 13.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 36. | Okamoto Y, Abe M, Mu A, Tempaku Y, Rogers CB, Mochizuki AL, Katsuki Y, Kanemaki MT, Takaori-Kondo A, Sobeck A, Bielinsky AK, Takata M. SLFN11 promotes stalled fork degradation that underlies the phenotype in Fanconi anemia cells. Blood. 2021;137:336-348. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 10] [Cited by in RCA: 24] [Article Influence: 6.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 37. | Davalos V, Esteller M. Cancer epigenetics in clinical practice. CA Cancer J Clin. 2023;73:376-424. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 123] [Article Influence: 41.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 38. | Yan W, Herman JG, Guo M. Epigenome-based personalized medicine in human cancer. Epigenomics. 2016;8:119-133. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 56] [Cited by in RCA: 65] [Article Influence: 6.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 39. | Bates SE. Epigenetic Therapies for Cancer. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:650-663. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 198] [Cited by in RCA: 310] [Article Influence: 62.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |