Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Aug 15, 2021; 13(8): 799-821
Published online Aug 15, 2021. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v13.i8.799
Published online Aug 15, 2021. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v13.i8.799
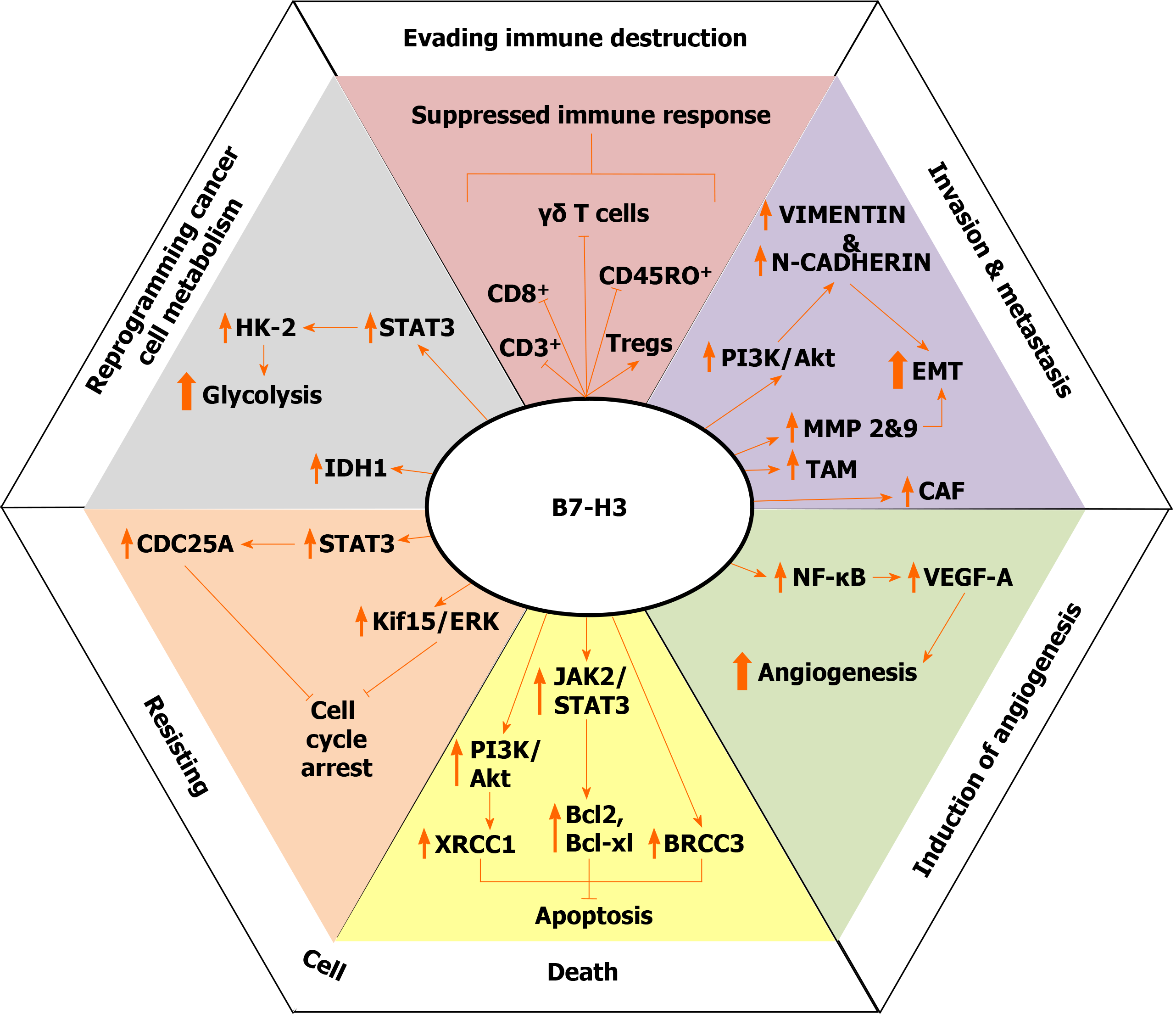
Figure 1 Potential roles of the B7 homologue 3 protein in gastrointestinal tumors described through the “hallmarks of cancer”.
In this schematic overview, we summarized the published findings of the B7 homologue 3 (B7-H3) effects on the biological behavior of gastrointestinal tract tumors. Some of these molecular mechanisms are presented as the result of B7-H3-related induction of several signaling pathways involved in the coordination of gene expression, reprogramming of cancer cell metabolism, resisting cell death, and promotion of angiogenesis, invasion, and metastasis. The arrow-headed lines represent induction, while the bar-headed lines denote inhibition. AKT: Protein kinase B; B7-H3: B7 homologue 3; Bcl-2: B cell lymphoma 2; Bcl-xl: B cell lymphoma-extra-large; BRCC3: BRCA1/BRCA2-containing complex 3; CAF: Cancer-associated fibroblasts; CDC25A: Cell division cycle 25A protein; EMT: Epithelial–mesenchymal transition; ERK: Extracellular-signal-regulated kinase; HK2: Hexokinase 2; IDH1: Isocitrate dehydrogenase 1; JAK2: Janus kinase 2; KIF15: Kinesin family member 15; MMP: Matrix metalloproteinase; NF-κB: Nuclear factor-kappa B; PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; STAT3: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; TAM: Tumor-associated macrophage; Tregs: Regulatory T cells; VEGFA: Vascular endothelial growth factor A; XRCC1: X-ray repair cross complementing group 1.
- Citation: Rasic P, Jovanovic-Tucovic M, Jeremic M, Djuricic SM, Vasiljevic ZV, Milickovic M, Savic D. B7 homologue 3 as a prognostic biomarker and potential therapeutic target in gastrointestinal tumors. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2021; 13(8): 799-821
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v13/i8/799.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v13.i8.799