Published online Dec 15, 2020. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v12.i12.1394
Peer-review started: August 31, 2020
First decision: September 12, 2020
Revised: September 20, 2020
Accepted: October 26, 2020
Article in press: October 26, 2020
Published online: December 15, 2020
Processing time: 100 Days and 20.9 Hours
Due to the special clinical features and biologic characteristics of adolescent and young adult (AYA) cancers, AYA cancers are different from cancers in children and elderly individuals. However, there are few reports on AYA hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
To investigate the overall survival (OS) of AYA (15-39 years) and elderly (40-74 years) patients with HCC.
The data of all the HCC cases were extracted from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database from 2004 to 2015 and were then divided into two groups based on age: AYA group (15-39 years) and older group (40-74 years). Kaplan-Meier curves and log-rank tests were used to compare the OS of the two groups. Propensity score matching (PSM) was employed to analyze the OS difference between the two groups. The Cox proportional hazards regression model was used to perform multivariate analysis to explore the risk factors for OS of HCC patients.
Compared to elderly cancer patients, AYA patients with HCC had a worse Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results stage, including the distant stage (22.1% vs 15.4%, P < 0.001), and a more advanced American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) stage, including AJCC III and IV (49.2% vs 38.3%, P < 0.001), and were more likely to receive surgery (64.5% vs 47.5%, P < 0.001). Before PSM, the AYA group had a longer survival in months (median: 20.00, interquartile range [IQR]: 5.00-62.50) than the older group (median: 15.00, IQR: 4.00-40.00) (P < 0.001). After PSM, the AYA group still had a longer survival in months (median: 21.00, IQR: 5.00-64.50) than the older group (median: 18.00, IQR: 6.00-53.00) (P < 0.001). The Cox proportional hazards regression model showed that advanced age (hazard ratio [HR] = 1.405, 95%CI: 1.218-1.621, P < 0.001) was a risk factor for OS of HCC patients. In the subgroup analysis, the Cox proportional hazards regression model showed that in AJCC I/II HCC patients, advanced age (HR = 1.749, 95%CI: 1.352-2.263, P < 0.001) was a risk factor for OS, while it was not a risk factor in AJCC III/IV HCC patients (HR = 1.186, 95%CI: 0.997-1.410, P = 0.054) before PSM. After PSM, advanced age (HR = 1.891, 95%CI: 1.356-2.637, P < 0.001) was still a risk factor for OS in AJCC I/II HCC patients, but was not a risk factor for OS in AJCC III/IV HCC patients (HR = 1.192, 95%CI: 0.934-1.521, P = 0.157) after PSM.
AYA patients with HCC have different clinical characteristics from older adults. In different AJCC stages, the two groups of patients have different OS: In AJCC I/II HCC patients, advanced age is a risk factor for OS, but it is not a risk factor for OS in the AJCC III/IV HCC patient group.
Core Tip: Adolescent and young adult (AYA) population refer to people aged 15-39 years old in the United States, and AYA has become a special age phase in oncology research in recent years. We aimed to investigate overall survival (OS) of AYA and older hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Our study confirmed that in different American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) stages, the two groups of patients had different OS: In the AJCC I/II group, advanced age was a risk factor for OS, but it was not a risk factor for OS in the AJCC III/IV group.
- Citation: Ren J, Tong YM, Cui RX, Wang Z, Li QL, Liu W, Qu K, Zhang JY, Liu C, Wan Y. Comparison of survival between adolescent and young adult vs older patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2020; 12(12): 1394-1406
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v12/i12/1394.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v12.i12.1394
Adolescent and young adult (AYA) population refer to people aged 15-39 years old in the United States[1,2]. With advancements in cancer diagnosis and treatment, people have increasingly realized that AYA cancer survivors have some unique challenges in the diagnosis and treatment process[3-5]. Due to specific socioeconomic factors, i.e., AYA cancer survivors experience graduations, new careers, and marriages[3,4], and in certain specific biologic characteristics[5], AYA cancers are different from those in children and older individuals. Therefore, AYA has become a special age phase in oncology research in recent years[2]. The number of AYA cancer survivors has been estimated to be 678420, accounting for approximately 5% of all cancer survivors, while there were 70000 new cancer cases in the United States by January 1, 2019[6-8]. From the time of cancer diagnosis, the 5-year survival rate rose from 71% in the mid-1970s to 86% during 2008-2014[9,10]. Between 2007 and 2016, the death rate declined by 0.8% annually[8], mainly due to the decrease in mortality of leukemia, non-Hodgkin' lymphoma, melanoma of the skin, and ovarian cancer, as these tumors account for a large proportion of AYA cancers[8].
Liver cancer is the sixth most common malignant cancer in the world and the fourth cancer-related cause of death. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common pathological type of liver cancer, accounting for approximately 90% of liver cancers[11-13]. Current research shows that advanced age is a risk factor for HCC[11-13]. Research performed by Yang et al[14] shows that the age at which HCC is likely to occur is different in different regions of the world. Although childhood liver cancer is rare, some studies have reported the clinical features and diagnosis of and treatment options for childhood liver cancer[15,16]. However, there are few reports on AYA HCC research.
Therefore, this study aimed to: Describe the clinical characteristics of AYA HCC, and compare OS between AYA (15-39 years) and older (40-74 years) HCC patients.
The Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database incorporates cancer information from the populations of 18 regions in the United States; these 18 regions comprise approximately 28% of the population of the United States. The general data, clinical data, pathological data, and follow-up data of all HCC patients in the SEER database were extracted from 2004 to 2015, including age, gender, race, marital status, histology, tumor stage, tumor grade, therapies, survival status, cause of death, survival months, sequence number, and International Classification of Diseases for Oncology, Third Edition (ICD-O-3) code.
The inclusion criteria were: (1) Patients older than 18 years of age; (2) “Positive histology” to ensure correct diagnosis; (3) Data with complete survival time for the survival month flag; and (4) “Active follow-up” to ensure the effectiveness of follow-up. The exclusion criteria were: (1) Cases obtained from autopsies and only death reports; and (2) Patients with multiple primary malignancies.
In the baseline data comparison between AYA and older HCC patients, the t test or Mann-Whitney U test was used for measurement data, the Chi-square test or Mann-Whitney U test was used for count data, and the Mann-Whitney U test was used for ranked data. Kaplan-Meier curves and the log-rank tests were used to compare the overall survival (OS) of AYA and older patients. OS was defined as the time interval from cancer diagnosis to death due to any cause. Variables with statistical significance in univariate analysis were subjected to multivariate analysis. The Cox proportional hazards regression model was used for multivariate analysis to identify the risk factors for OS of HCC patients. After 1:1 propensity score matching (PSM) of the baseline data, the OS difference between the two groups was analyzed again. Subsequently, a subgroup analysis was carried out. After the two groups of patients were stratified according to American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) stage, the Cox proportional hazards regression model was used to analyze the OS difference. SPSS 22.0 (IBM Corp, Armonk, NY, United States) was used for statistical analyses, the test was two-sided, and P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
A total of 12721 patients were included in the study, including 366 (2.9%) AYA HCC patients and 12355 (97.1%) patients in the older group. Compared to older patients, AYA HCC patients had a worse SEER stage, including the distant stage (22.1% vs 15.4%, P < 0.001); a more advanced AJCC stage, including AJCC stages III and IV (49.2% vs 38.3%, P < 0.001); and were more likely to receive surgery (64.5% vs 47.5%, P < 0.001) (Table 1).
| Characteristic | Total | AYA | Older | P value | |
| n = 12721 | n = 366 (2.9%) | n = 12355 (97.1%) | |||
| Sex | < 0.001 | ||||
| Male | 10075 | 249 (68.0%) | 9826 (79.5%) | ||
| Female | 2646 | 117 (32.0%) | 2529 (20.5%) | ||
| Race | < 0.001 | ||||
| White | 8323 | 190 (51.9%) | 8133 (65.8%) | ||
| Black | 1990 | 59 (16.1%) | 1931 (15.6%) | ||
| Other | 2408 | 117 (32.0%) | 2291 (18.5%) | ||
| Marital status | < 0.001 | ||||
| Not married | 2818 | 197 (53.8%) | 2621 (21.2%) | ||
| Married | 9903 | 169 (46.2%) | 9734 (78.0%) | ||
| SEER stage | < 0.001 | ||||
| Localized | 7264 | 178 (48.6%) | 7086 (57.4%) | ||
| Regional | 3476 | 107 (29.2%) | 3396 (27.3%) | ||
| Distant | 1981 | 81 (22.1%) | 1900 (15.4%) | ||
| AJCC stage | < 0.001 | ||||
| I | 5063 | 118 (32.2%) | 4945 (40.0%) | ||
| II | 2744 | 68 (18.6%) | 2676 (21.7%) | ||
| III | 3036 | 105 (28.7%) | 2931 (23.7%) | ||
| IV | 1878 | 75 (20.5%) | 1803 (14.6%) | ||
| Grade | 0.158 | ||||
| I | 3913 | 114 (31.3%) | 3799 (30.7%) | ||
| II | 5719 | 141 (38.5%) | 5578 (45.1%) | ||
| III | 2848 | 102 (27.9%) | 2746 (22.2%) | ||
| IV | 241 | 9 (2.5%) | 232 (1.9%) | ||
| Surgery | < 0.001 | ||||
| No | 6622 | 130 (35.5%) | 6492 (52.5%) | ||
| Yes | 6099 | 236 (64.5%) | 5863 (47.5%) | ||
| Radiation | 0.319 | ||||
| No | 11862 | 346 (94.5%) | 11516 (93.2%) | ||
| Yes | 859 | 20 (5.5%) | 839 (6.8%) | ||
| Chemotherapy | 0.306 | ||||
| No | 8074 | 223 (60.9%) | 7851 (63.5%) | ||
| Yes | 4647 | 143 (39.1%) | 4504 (36.5%) |
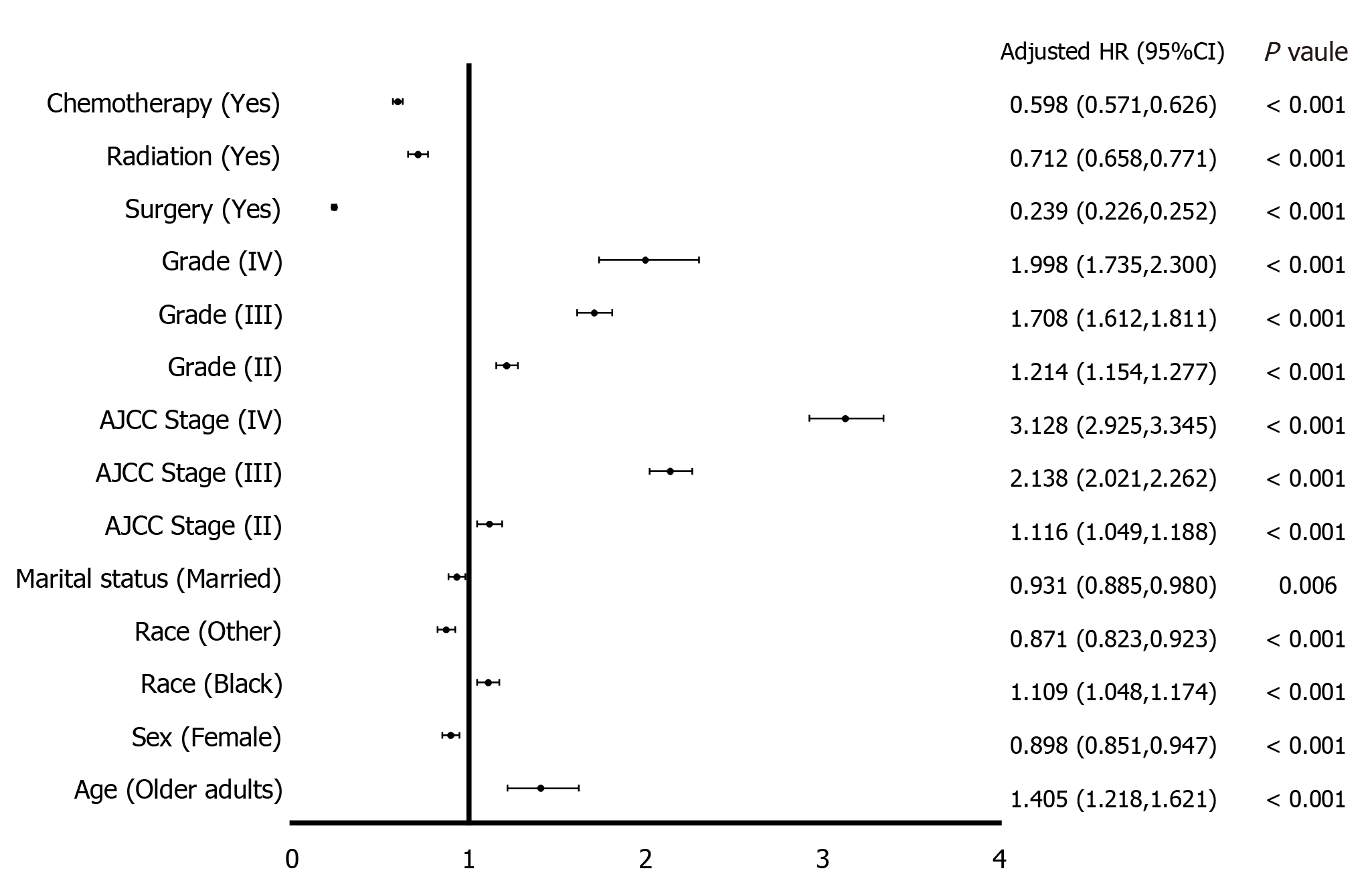
In the univariate analysis of OS of HCC patients, age, sex, race, marital status, AJCC stage, grade, surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy were all statistically significant (P < 0.05), although AJCC stage II was not (P = 0.376, taking AJCC stage I as the reference). In the multivariate analysis using the Cox proportional hazard regression model, advanced age, black ethnicity, advanced AJCC stage (II-IV), and advanced grade (II-IV) were risk factors for OS of HCC. Female gender, other races, being married, surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy were protective factors for OS of HCC patients (Table 2). Figure 1 shows the results of the multivariate analysis.
| Characteristic | Univariate analysis, HR (95%CI) | P value | Multivariate analysis, HR (95%CI) | P value | |
| Age | |||||
| AYA | Reference | Reference | |||
| Older | 1.504 (1.307-1.732) | < 0.001 | 1.405 (1.218-1.621) | < 0.001 | |
| Sex | |||||
| Male | Reference | Reference | |||
| Female | 0.817 (0.775-0.861) | < 0.001 | 0.898 (0.851-0.947) | < 0.001 | |
| Race | |||||
| White | Reference | Reference | |||
| Black | 1.293 (1.223-1.368) | < 0.001 | 1.109 (1.048-1.174) | < 0.001 | |
| Other | 0.812 (0.767-0.860) | < 0.001 | 0.871 (0.823-0.923) | < 0.001 | |
| Marital status | |||||
| Not married | Reference | Reference | |||
| Married | 0.805 (0.767-0.846) | < 0.001 | 0.931 (0.885-0.980) | 0.006 | |
| AJCC stage | |||||
| I | Reference | Reference | |||
| II | 1.028 (0.967-1.093) | 0.376 | 1.116 (1.049-1.188) | < 0.001 | |
| III | 2.810 (2.662-2.966) | < 0.001 | 2.138 (2.021-2.262) | < 0.001 | |
| IV | 5.629 (5.290-5.990) | < 0.001 | 3.128 (2.925-3.345) | < 0.001 | |
| Grade | |||||
| I | Reference | Reference | |||
| II | 1.068 (1.016-1.123) | 0.010 | 1.214 (1.154-1.277) | < 0.001 | |
| III | 1.856 (1.754-1.964) | < 0.001 | 1.708 (1.612-1.811) | < 0.001 | |
| IV | 2.270 (1.974-2.610) | < 0.001 | 1.998 (1.735-2.300) | < 0.001 | |
| Surgery | |||||
| No | Reference | Reference | |||
| Yes | 0.223 (0.213-0.234) | < 0.001 | 0.239 (0.226-0.252) | < 0.001 | |
| Radiation | |||||
| No | Reference | Reference | |||
| Yes | 1.428 (1.321-1.544) | < 0.001 | 0.712 (0.658-0.771) | < 0.001 | |
| Chemotherapy | |||||
| No | Reference | Reference | |||
| Yes | 1.053 (1.009-1.099) | 0.018 | 0.598 (0.571-0.626) | < 0.001 |
After PSM was performed on sex, race, marital status, AJCC stage, grade, surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy, the differences were balanced in the AYA and the older groups: Sex (P = 0.934), race (P = 0.985), marital status (P = 1.000), AJCC stage (P = 0.974), grade (P = 0.887), surgery (P = 1.000), radiation (P = 1.000), and chemotherapy (P = 0.937) (Table 3).
| Characteristic | Total, n = 690 | AYA, n = 345 (50%) | Older, n = 345 (50%) | P value | |
| Sex | 0.934 | ||||
| Male | 475 | 238 (69.0%) | 237 (68.7%) | ||
| Female | 215 | 107 (31.0%) | 108 (31.3%) | ||
| Race | 0.985 | ||||
| White | 371 | 185 (53.6%) | 186 (53.9%) | ||
| Black | 117 | 58 (16.8%) | 59 (17.1%) | ||
| Other | 202 | 102 (29.6%) | 100 (29.0%) | ||
| Marital status | 1.000 | ||||
| No married | 356 | 178 (51.6%) | 178 (51.6%) | ||
| Married | 334 | 167 (48.4%) | 167 (48.4%) | ||
| AJCC stage | 0.974 | ||||
| I | 230 | 115 (33.3%) | 115 (33.3%) | ||
| II | 127 | 64 (18.6%) | 63 (18.3%) | ||
| III | 197 | 98 (28.4%) | 99 (28.7%) | ||
| IV | 136 | 68 (19.7%) | 68 (19.7%) | ||
| Grade | 0.887 | ||||
| I | 217 | 109 (31.6%) | 108 (31.3%) | ||
| II | 271 | 136 (39.4%) | 135 (39.1%) | ||
| III | 188 | 93 (27.0%) | 95 (27.5%) | ||
| IV | 14 | 7 (2.0%) | 7 (2.0%) | ||
| Surgery | 1.000 | ||||
| No | 250 | 125 (36.2%) | 125 (36.2%) | ||
| Yes | 440 | 220 (63.8%) | 220 (63.8%) | ||
| Radiation | 1.000 | ||||
| No | 666 | 333 (96.5%) | 333 (96.5%) | ||
| Yes | 24 | 12 (3.5%) | 12 (3.5%) | ||
| Chemotherapy | 0.937 | ||||
| No | 437 | 219 (63.5%) | 218 (63.2%) | ||
| Yes | 253 | 126 (36.5%) | 127 (36.8%) |
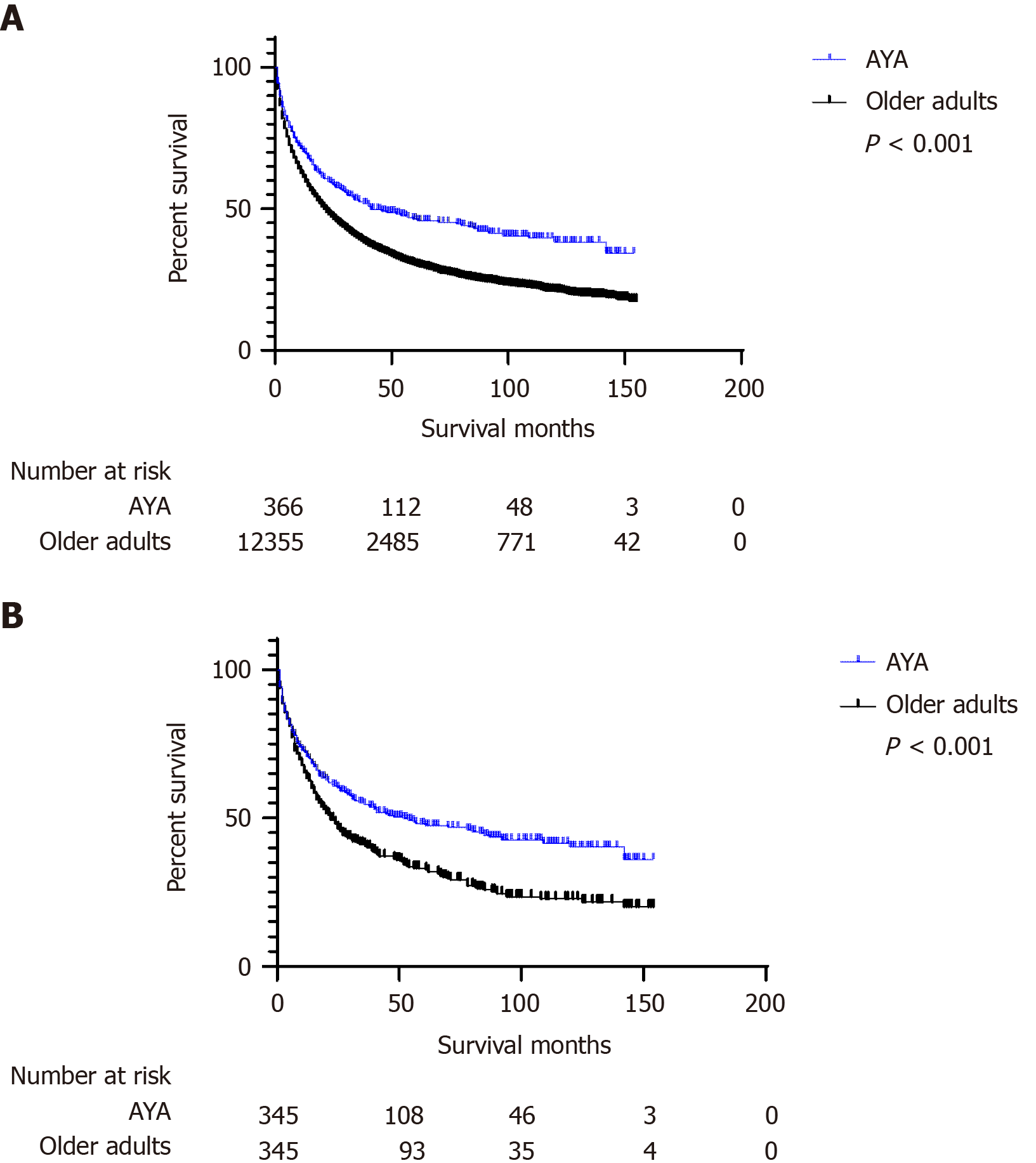
Kaplan-Meier curves were used to compare OS of AYA and older patients. Before PSM, the AYA group had a longer survival in months (median: 20.00, IQR: 5.00-62.50) than the older group (median: 15.00, IQR: 4.00-40.00) (P < 0.001). After PSM, the AYA group still had a longer survival in months (median: 21.00, IQR: 5.00-64.50) than the older group (median: 18.00, IQR: 6.00-53.00) (P < 0.001) (Table 4). Figure 2 shows the difference in OS between the two groups.
| Characteristics | Survival months (Median, IQR) | P value | |
| Before PSM | AYA | 20.00 (5.00-62.50) | < 0.001 |
| Older adults | 15.00 (4.00-40.00) | ||
| After PSM | AYA | 21.00 (5.00-64.50) | < 0.001 |
| Older adults | 18.00 (6.00-53.00) |
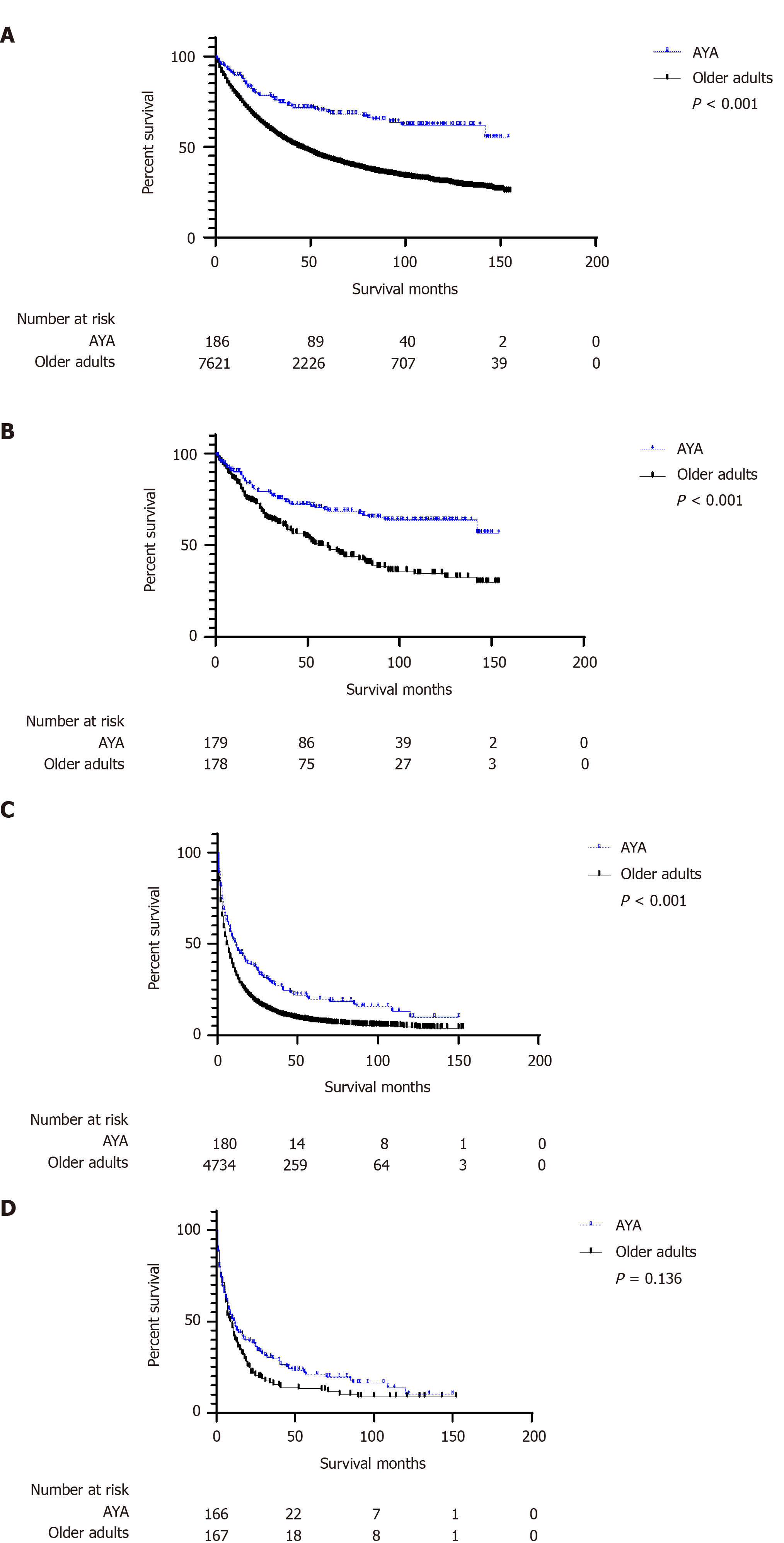
To compare the survival difference between AYA and older patients in different AJCC stages, we divided the AJCC stage into two levels. Figure 3 shows the difference in OS between the two groups of patients in different AJCC stages before and after PSM using Kaplan-Meier curves and the log-rank tests. AYA patients had a better OS (P < 0.001) in the stage AJCC I/II and AJCC stage III/IV groups before PSM; after PSM, AYA patients had a better OS than older patients (P < 0.001) in the AJCC stage I/II group, while in the AJCC stage III/IV group, the difference in OS between AYA and older patients was not statistically significant (P = 0.136). Then, we performed multivariate analysis of different AJCC stages to compare the survival difference between the two groups of patients. After joint adjustment of age, sex, race, marital status, AJCC stage, grade, surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy, we found that before PSM, advanced age was a risk factor for OS in the AJCC stage I/II group, but in the AJCC stage III/IV group, it was not observed that advanced age was a risk factor. After PSM, in the AJCC stage I/II group, advanced age was a risk factor for OS. In the AJCC stage III/IV group, advanced age was not a risk factor for OS (Table 5).
| Characteristics (AYA vs Older adults) | Multivariate analysis HR (95%CI) | P value | |
| Before PSM | AJCC stage I/II | 1.749 (1.352-2.263) | < 0.001 |
| AJCC stage III/IV | 1.186 (0.997-1.410) | 0.054 | |
| After PSM | AJCC stage I/II | 1.891 (1.356-2.637) | < 0.001 |
| AJCC stage III/IV | 1.192 (0.934-1.521) | 0.157 |
AYA cancer survivors have an inferior 5-year OS compared with the general population, while the long-term survival of AYA cancer survivors has improved[17]. However, the improvements of the survival rate and mortality of AYA cancer patients are not as good as those of younger or older patients, mainly because past oncologists and researchers did not pay attention to AYA cancer patients and there are few clinical studies on them[18,19]. With the emphasis on AYA cancer, recent studies have analyzed the reasons for the low participation rate of AYA cancer survivors in clinical trials, which may be related to the low availability of medical insurance for patients of this age group and to tumor type and stage[20,21]. A previous study tried to explore methods to improve the participation rate and accuracy of clinical trials for AYA cancer survivors[22]. Therefore, it is particularly significant to explore the clinical characteristics and prognosis of AYA HCC patients.
After comparing the baseline data, we found that compared to older patients, AYA HCC patients had a worse SEER stage and more advanced AJCC stage and were more likely to receive surgery. These findings were consistent with the finding of a previous study that cancer in AYA patients was often in advanced stages and showed more aggressiveness[23]. The research by Bleyer et al[23] showed that young women with breast cancer were more likely to develop larger, higher-grade tumors that were less sensitive to hormones than older women, and most Burkitt lymphomas were at stage III/IV according to another study[24]. Research involving acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL) showed that compared with children, AYA patients with ALL were more likely to have unfavorable biological characteristics[25], which may be related to the poor prognosis of AYA cancer patients.
The hospitalization rate of AYA cancer survivors increased by 56% compared with noncancer patients of the same age, and they had a longer hospital stay[26,27]. Zhi et al showed that an appropriate and active exercise intervention had a positive effect in improving the quality of life of AYA cancer survivors[28]. However, Rabin et al[29] found that more than half of AYA cancer survivors remained sedentary and did not undergo scientific exercise interventions. AYA cancer survivors were more likely to have negative life narratives and more disease-related future thoughts than noncancer patients of the same age, which greatly increased their risk of mental illness[30]. In the field of psycho-oncology, age-appropriate interventions are also needed for AYA cancer survivors[31]. In terms of comorbidities, studies have shown that AYA cancer survivors have an increased risk of comorbidities compared with the general population. Different cancer treatments and exposures can cause different complications[32]. The study by Kaul et al[33] showed that AYA cancer survivors had a higher percentage of smoking than noncancer patients of the same age after 5 years of receiving a cancer diagnosis; had more comorbidities, such as asthma and diabetes; and had worse health conditions. Insufficient exercise, mental illness, bad living habits, and comorbidities may not be conducive to the OS of AYA cancer patients[28-33].
After using Kaplan-Meier curves to compare the OS of the two groups of patients, we found that before and after PSM, advanced age was a risk factor for OS in AYA patients with HCC. This result was consistent with the results of the multivariate analysis and seemed to indicate that AYA patients with HCC had a better prognosis than older patients. In a further subgroup analysis, we found that in the AJCC stage I/II group, advanced age was a risk factor; combined with previous research, this may be because compared with older patients, AYA patients with HCC had worse biological characteristics and were more likely to receive surgery, which was a strong protective factor for OS. Therefore, AYA patients with HCC had a better OS than older patients. In the AJCC stage III/IV group, advanced age was not a risk factor because for this stage of HCC, even if surgery was performed, it did not help improve the prognosis.
This study has some limitations. First, the data in this study came from a database, and variable inclusion was limited to that database. Thus, information such as laboratory examinations, combined diseases, and economic status could not be obtained. Second, this study was a retrospective case-control study, which may have an inherent bias. Finally, more samples were needed to verify our findings.
AYA HCC patients have different clinical characteristics from older adults. In different AJCC stages, the two groups of patients have different OS: In the AJCC stage I/II group, advanced age is a risk factor for OS, while advanced age is not a risk factor in the AJCC stage III/IV group. More basic studies are needed to explore this mechanism.
Adolescent and young adult (AYA) population refer to people aged 15-39 years old. AYA cancers are different from those in children and elderly individuals due to their special clinical features and biologic characteristics. Liver cancer is the sixth most common malignant cancer in the world and the fourth cancer-related cause of death. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common pathological type of liver cancer. Age-related studies of HCC are needed to guide the diagnosis and treatment of this malignancy.
There have been studies on liver cancer among children and elderly individuals. However, there are few studies on AYA HCC.
First, this study aimed to describe the clinical characteristics of AYA HCC. Second, this study intended to compare overall survival (OS) between AYA (15-39 years) and older (40-74 years) HCC patients.
A total of 12721 patients were included in the study, including 366 (2.9%) AYA HCC patients and 12355 (97.1%) patients in the older group. Kaplan-Meier curves and the log-rank tests were used to compare OS of the AYA and older patients. The Cox proportional hazards regression model was used for multivariate analysis to identify the risk factors for OS of HCC patients. After a 1:1 PSM of the baseline data, the OS difference between the two groups was analyzed again. Subsequently, a subgroup multivariate analysis was carried out, and patients were stratified according to American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) stage.
Compared to older patients, AYA HCC patients had a worse SEER stage, including distant stage (22.1% vs 15.4%, P < 0.001); a more advanced AJCC stage, including AJCC stages III and IV (49.2% vs 38.3%, P < 0.001); and were more likely to receive surgery (64.5% vs 47.5%, P < 0.001). Before PSM, the AYA group had a longer survival in months (median: 20.00, IQR: 5.00-62.50) than the older group (median: 15.00, IQR: 4.00-40.00) (P < 0.001). After PSM, the AYA group still had a longer survival in months (median: 21.00, IQR: 5.00-64.50) than the older group (median: 18.00, IQR: 6.00-53.00) (P < 0.001). The Cox proportional hazards regression model showed that advanced age (HR = 1.405, 95%CI: 1.218-1.621, P < 0.001) was a risk factor for OS of HCC. In the subgroup analysis, the Cox proportional hazards regression model showed that in AJCC stage I/II patients, advanced age (HR = 1.749, 95%CI: 1.352-2.263, P < 0.001) was a risk factor for OS, while advanced age (HR = 1.186, 95%CI: 0.997-1.410, P = 0.054) was not a risk factor in AJCC stage III/IV patients before PSM. Advanced age (HR = 1.891, 95%CI: 1.356-2.637, P < 0.001) was a risk factor for OS in AJCC stage I/II patients, while it (HR = 1.192, 95%CI: 0.934-1.521, P = 0.157) was not a risk factor for OS in AJCC stage III/IV patients after PSM.
AYA HCC patients have different clinical characteristics from older adults. In different AJCC stages, the two groups of patients have different OS: In the AJCC stage I/II group, advanced age was a risk factor for OS, while it was not a risk factor for OS in the AJCC stage III/IV group.
The data in this study came from a database; thus, variable inclusion was limited to the database, and information such as laboratory examinations, combined diseases, and economic status could not be obtained. More samples are needed to verify our research results, and more basic studies are needed to explore the molecular mechanism of this research result.
We are indebted to all individuals who participated in or helped with this research project.
Manuscript source: Unsolicited manuscript
Specialty type: Oncology
Country/Territory of origin: China
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): 0
Grade C (Good): C, C
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: MD SW S-Editor: Zhang L L-Editor: Wang TQ P-Editor: Li JH
| 1. | Coccia PF, Pappo AS, Beaupin L, Borges VF, Borinstein SC, Chugh R, Dinner S, Folbrecht J, Frazier AL, Goldsby R, Gubin A, Hayashi R, Huang MS, Link MP, Livingston JA, Matloub Y, Millard F, Oeffinger KC, Puccetti D, Reed D, Robinson S, Rosenberg AR, Sanft T, Spraker-Perlman HL, von Mehren M, Wechsler DS, Whelan KF, Yeager N, Gurski LA, Shead DA. Adolescent and Young Adult Oncology, Version 2.2018, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2018;16:66-97. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 131] [Cited by in RCA: 224] [Article Influence: 37.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Sender L, Zabokrtsky KB. Adolescent and young adult patients with cancer: a milieu of unique features. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2015;12:465-480. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 72] [Cited by in RCA: 96] [Article Influence: 9.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Overholser L, Kilbourn K, Liu A. Survivorship Issues in Adolescent and Young Adult Oncology. Med Clin North Am. 2017;101:1075-1084. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 15] [Cited by in RCA: 21] [Article Influence: 2.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Thomas DM, Albritton KH, Ferrari A. Adolescent and young adult oncology: an emerging field. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:4781-4782. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 85] [Cited by in RCA: 102] [Article Influence: 6.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Tricoli JV, Bleyer A. Adolescent and Young Adult Cancer Biology. Cancer J. 2018;24:267-274. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 28] [Cited by in RCA: 41] [Article Influence: 6.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020;70:7-30. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 12667] [Cited by in RCA: 15314] [Article Influence: 3062.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (4)] |
| 7. | Miller KD, Nogueira L, Mariotto AB, Rowland JH, Yabroff KR, Alfano CM, Jemal A, Kramer JL, Siegel RL. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 2019;69:363-385. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2417] [Cited by in RCA: 3074] [Article Influence: 512.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Close AG, Dreyzin A, Miller KD, Seynnaeve BKN, Rapkin LB. Adolescent and young adult oncology-past, present, and future. CA Cancer J Clin. 2019;69:485-496. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 97] [Cited by in RCA: 158] [Article Influence: 26.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Liu L, Moke DJ, Tsai KY, Hwang A, Freyer DR, Hamilton AS, Zhang J, Cockburn M, Deapen D. A Reappraisal of Sex-Specific Cancer Survival Trends among Adolescents and Young Adults in the United States. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2019;111:509-518. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 37] [Cited by in RCA: 50] [Article Influence: 10.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Keegan TH, Ries LA, Barr RD, Geiger AM, Dahlke DV, Pollock BH, Bleyer WA; National Cancer Institute Next Steps for Adolescent and Young Adult Oncology Epidemiology Working Group. Comparison of cancer survival trends in the United States of adolescents and young adults with those in children and older adults. Cancer. 2016;122:1009-1016. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 219] [Cited by in RCA: 277] [Article Influence: 30.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Villanueva A. Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2019;380:1450-1462. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2066] [Cited by in RCA: 3173] [Article Influence: 528.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (37)] |
| 12. | Kulik L, El-Serag HB. Epidemiology and Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2019; 156: 477-491. e1. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 754] [Cited by in RCA: 1216] [Article Influence: 202.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 13. | Fujiwara N, Friedman SL, Goossens N, Hoshida Y. Risk factors and prevention of hepatocellular carcinoma in the era of precision medicine. J Hepatol. 2018;68:526-549. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 423] [Cited by in RCA: 524] [Article Influence: 74.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Yang JD, Hainaut P, Gores GJ, Amadou A, Plymoth A, Roberts LR. A global view of hepatocellular carcinoma: trends, risk, prevention and management. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;16:589-604. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2184] [Cited by in RCA: 2905] [Article Influence: 484.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (17)] |
| 15. | Kelly D, Sharif K, Brown RM, Morland B. Hepatocellular carcinoma in children. Clin Liver Dis. 2015;19:433-447. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 56] [Cited by in RCA: 57] [Article Influence: 5.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Reuben A. Hepatocellular carcinoma in adults and children. Clin Liver Dis. 2015;19:xiii-xxvi. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 2] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Berkman AM, Livingston JA, Merriman K, Hildebrandt M, Wang J, Dibaj S, McQuade J, You N, Ying A, Barcenas C, Bodurka D, DePombo A, Lee HJ, de Groot J, Roth M. Long-term survival among 5-year survivors of adolescent and young adult cancer. Cancer. 2020;126:3708-3718. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 34] [Cited by in RCA: 39] [Article Influence: 7.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Tai E, Beaupin L, Bleyer A. Clinical trial enrollment among adolescents with cancer: supplement overview. Pediatrics. 2014;133 Suppl 3:S85-S90. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 19] [Cited by in RCA: 22] [Article Influence: 2.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Bleyer A, Budd T, Montello M. Adolescents and young adults with cancer: the scope of the problem and criticality of clinical trials. Cancer. 2006;107:1645-1655. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 250] [Cited by in RCA: 262] [Article Influence: 14.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Parsons HM, Harlan LC, Seibel NL, Stevens JL, Keegan TH. Clinical trial participation and time to treatment among adolescents and young adults with cancer: does age at diagnosis or insurance make a difference? J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:4045-4053. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 145] [Cited by in RCA: 149] [Article Influence: 10.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Kirchhoff AC, Lyles CR, Fluchel M, Wright J, Leisenring W. Limitations in health care access and utilization among long-term survivors of adolescent and young adult cancer. Cancer. 2012;118:5964-5972. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 104] [Cited by in RCA: 122] [Article Influence: 9.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 22. | Fern LA, Bleyer A. Dynamics and Challenges of Clinical Trials in Adolescents and Young Adults with Cancer. Cancer J. 2018;24:307-314. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 8] [Cited by in RCA: 13] [Article Influence: 2.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 23. | Bleyer A, Barr R, Hayes-Lattin B, Thomas D, Ellis C, Anderson B; Biology and Clinical Trials Subgroups of the US National Cancer Institute Progress Review Group in Adolescent and Young Adult Oncology. The distinctive biology of cancer in adolescents and young adults. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8:288-298. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 438] [Cited by in RCA: 487] [Article Influence: 28.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 24. | Hochberg J, El-Mallawany NK, Abla O. Adolescent and young adult non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Br J Haematol. 2016;173:637-650. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 21] [Cited by in RCA: 31] [Article Influence: 3.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 25. | Möricke A, Zimmermann M, Reiter A, Gadner H, Odenwald E, Harbott J, Ludwig WD, Riehm H, Schrappe M. Prognostic impact of age in children and adolescents with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: data from the trials ALL-BFM 86, 90, and 95. Klin Padiatr. 2005;217:310-320. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 71] [Cited by in RCA: 73] [Article Influence: 3.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 26. | Printz C. Adolescent and young adult cancer survivors appear to have higher hospitalization risk. Cancer. 2020;126:2509. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 27. | Anderson C, Kaddas HK, Ou JY, Ramsay JM, Trogdon JG, Kirchhoff AC, Nichols HB. Hospitalization after Adolescent and Young Adult (AYA) Cancer: A Population-Based Study in Utah. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2020;29:336-342. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 1.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 28. | Zhi X, Xie M, Zeng Y, Liu JE, Cheng ASK. Effects of Exercise Intervention on Quality of Life in Adolescent and Young Adult Cancer Patients and Survivors: A Meta-Analysis. Integr Cancer Ther. 2019;18:1534735419895590. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 11] [Cited by in RCA: 25] [Article Influence: 5.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 29. | Rabin C, Pinto B, Fava J. Randomized Trial of a Physical Activity and Meditation Intervention for Young Adult Cancer Survivors. J Adolesc Young Adult Oncol. 2016;5:41-47. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 28] [Cited by in RCA: 45] [Article Influence: 4.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 30. | Sansom-Daly UM, Wakefield CE, Robertson EG, McGill BC, Wilson HL, Bryant RA. Adolescent and young adult cancer survivors' memory and future thinking processes place them at risk for poor mental health. Psychooncology. 2018;27:2709-2716. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 17] [Cited by in RCA: 26] [Article Influence: 3.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 31. | Richter D, Koehler M, Friedrich M, Hilgendorf I, Mehnert A, Weißflog G. Psychosocial interventions for adolescents and young adult cancer patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2015;95:370-386. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 78] [Cited by in RCA: 104] [Article Influence: 10.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 32. | Chao C, Bhatia S, Xu L, Cannavale KL, Wong FL, Huang PS, Cooper R, Armenian SH. Chronic Comorbidities Among Survivors of Adolescent and Young Adult Cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2020;38:3161-3174. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 36] [Cited by in RCA: 121] [Article Influence: 24.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 33. | Kaul S, Veeranki SP, Rodriguez AM, Kuo YF. Cigarette smoking, comorbidity, and general health among survivors of adolescent and young adult cancer. Cancer. 2016;122:2895-2905. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 37] [Cited by in RCA: 49] [Article Influence: 5.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |