Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Dec 15, 2017; 9(12): 492-496
Published online Dec 15, 2017. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v9.i12.492
Published online Dec 15, 2017. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v9.i12.492
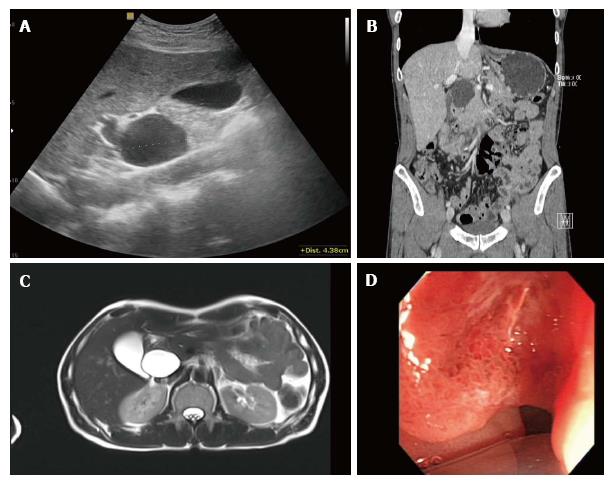
Figure 1 Evaluation of clinical findings.
A: Ultrasonography of upper abdomen shows a 4.5 cm sized anechoic cystic mass adjacent to the head of the pancreas and common bile duct; B: Coronal multiplanar reformatted image of contrast-enhanced abdominal computed tomograph shows a homogeneous low-density cystic mass with thin, smooth walls abutting the common bile duct, with possible communication between the two structures; C: Axial T2-weighted magnetic resonance image demonstrates the cystic mass as a homogeneously high signal intensity lesion with thin walls, and there was no evidence of mural nodularity in the cystic mass; D: Endoscopic image of the duodenum shows irregular mucosal thickening with hyperemic change in the second portion of the duodenum.
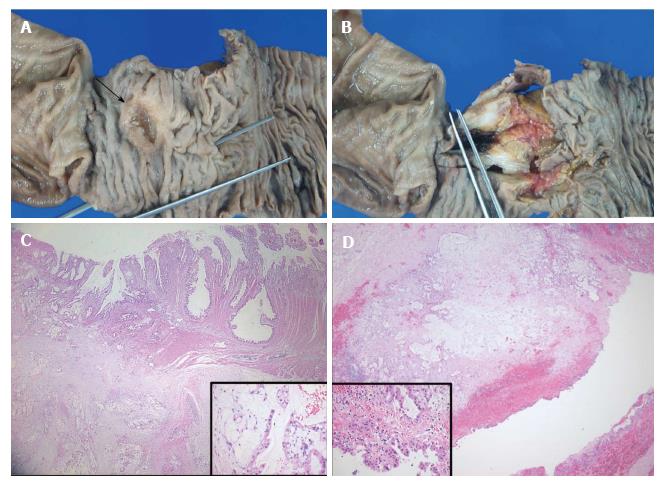
Figure 2 Gross specimen and pathological findings.
A: The ulcerofungating mass measuring 2.4 cm × 2.0 cm (arrow), 2.5 cm distant from the ampulla of vater, is observed in the duodenum; B: The cut surface reveals a grey-white mass that abuts the head of the pancreas; C: Histologically, the duodenal mass proved to be an infiltrative adenocarcinoma with subserosal invasion, note the abundant extracellular mucin with floating neoplastic epithelium (Inset); D: Photomicrograph of the cystic mass shows invasive tumor cells in the lining of the cyst and the surrounding soft tissue which is a definite malignant feature (Inset).
- Citation: Kim YN, Song JS. Cystic metastasis from a mucinous adenocarcinoma of duodenum mimicking type II choledochal cyst: A case report. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2017; 9(12): 492-496
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v9/i12/492.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v9.i12.492