Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Oct 15, 2017; 9(10): 423-430
Published online Oct 15, 2017. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v9.i10.423
Published online Oct 15, 2017. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v9.i10.423
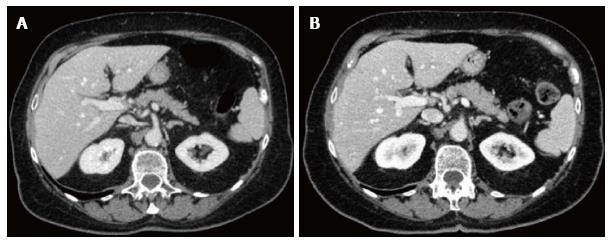
Figure 1 Axial contrast-enhanced computed tomography images at the level of upper abdomen obtained in a 81 years old female patient with lung cancer (height 160 cm, weight 61 kg).
A: Standard dose protocol (120 kV, 300 mAs, DLP 1317.4 mGy*cm, CDTI 21.1 mGy); B: Lower dose protocol (120 kV, 142-222 mAs, DLP 846.0 mGy*cm, CDTI 13.6 mGy): Lower dose image shows increased sharpness and enhancement in comparison with standard dose image in spite of mild increase of noise, and similar diagnostic quality with a 35.8% Dose-Length-Product reduction.
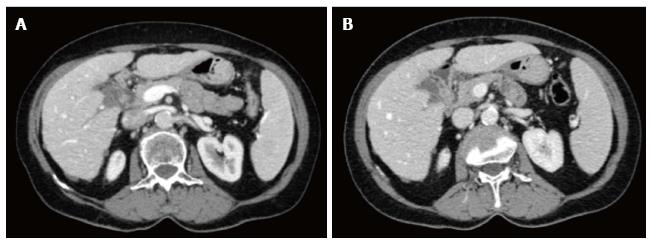
Figure 2 Axial contrast-enhanced computed tomography images at the level of upper abdomen obtained in a 70 years old female patient with ovarian cancer and some small hypoattenuating hepatic subcapsular implants with well-defined margins (height 160 cm, weight 68 kg).
A: Standard dose protocol (120 kV, 300 mAs, Dose-Length-Product 1304.6 mGy*cm, CDTI 21.0 mGy); B: Lower dose protocol (120 kV, 123-231 mAs, Dose-Length-Product 840.9 mGy*cm, CDTI 13.1 mGy).
- Citation: Ippolito D, Casiraghi AS, Franzesi CT, Fior D, Meloni F, Sironi S. Low-dose computed tomography with 4th-generation iterative reconstruction algorithm in assessment of oncologic patients. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2017; 9(10): 423-430
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v9/i10/423.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v9.i10.423