Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Oct 15, 2015; 7(10): 184-203
Published online Oct 15, 2015. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v7.i10.184
Published online Oct 15, 2015. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v7.i10.184
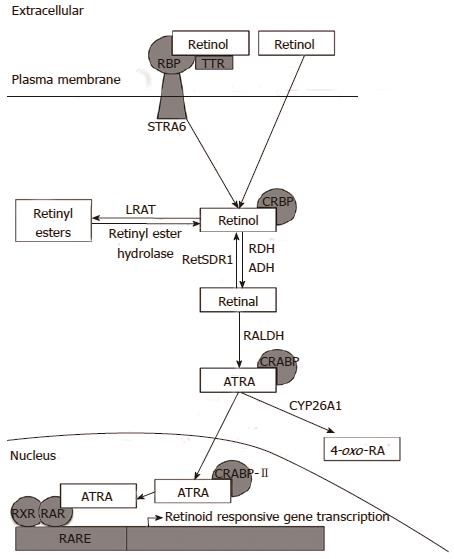
Figure 1 Retinoid metabolism.
Vitamin A circulates as retinol bound to RBP and TTR. Retinol can be absorbed into cells via STRA6 or diffusion through the cell membrane. Intracellularly, retinol can be stored as retinyl esters or converted to ATRA. ATRA travels to the nucleus where it binds RAR to induce the transcription of retinoid-responsive genes. RBP: Retinol binding protein; TTR: Transthyretin; STRA6: Stimulated by retinoic acid 6; CRBP: Cellular retinol binding protein; LRAT: Lecithin retinol acyltransferase; RALDH: Retinaldehyde dehydrogenase; CRABP: Cellular retinoic acid binding protein; CYP26A1: Cytochrome P450 26A1; 4-oxo-RA: 4-oxo-retinoic acid; ATRA: All-trans-retinoic acid; RXR: Retinoid X receptor; RAR: Retinoic acid receptor; RARE: Retinoic acid response element.
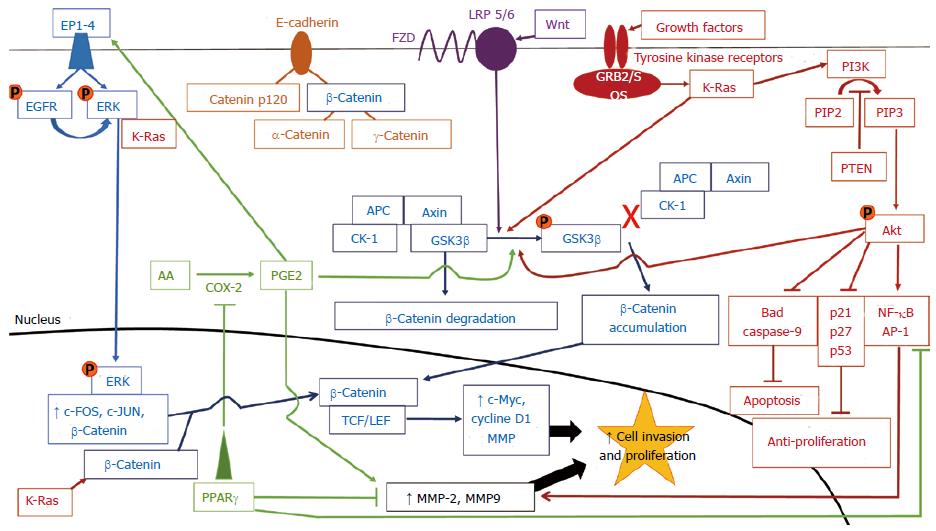
Figure 2 Crosstalk between signaling pathways that lead to colorectal cancer progression.
Each pathway is indicated by a specific color. Orange circles represent phosphate groups. β-Catenin is found at the cell membrane, complexed with E-cadherin, in the cytosol, and in the nucleus. Cytosolic β-catenin can be targeted for proteosomal degradation by GSK3β when GSK3β is not phosphorylated and is complexed with APC, Axin, and CK-1. Nuclear β-catenin induces gene transcription when complexed with TCF/LEF transcription factors. Ultimately, all pathways increase the transcription of genes favoring cellular proliferation (c-Myc, cyclin D1) and invasion (MMPs), most via increasing β-catenin-mediated gene transcription. CRC: Colorectal cancer; EP1-4: E-prostanoid receptor types 1-4; EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor; ERK: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase; K-Ras: Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog; FZD: Frizzled; LRP: Lipoprotein related receptor proteins 5/6; GRB2/SOS: Growth factor receptor-bound protein 2/son of sevenless; PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase; PIP2: Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate; PIP3: Phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-triphosphate; PTEN: Phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10; APC: Adenomatous polyposis coli; CK-1: Casein kinase 1; GSK3β: Glycogen synthase kinase 3β; PGE2: Prostaglandin E2; COX2: Cyclooxygenase 2; AA: Arachidonic acid; PPARγ: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ; TCF/LEF: T-cell factor/lymphoid enhancer factor; MMP: Matrix metalloproteinase; NF-κB: Nuclear factor-kappa B; AP-1: Activator protein 1.
- Citation: Applegate CC, Lane MA. Role of retinoids in the prevention and treatment of colorectal cancer. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2015; 7(10): 184-203
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v7/i10/184.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v7.i10.184