Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Aug 15, 2014; 6(8): 275-288
Published online Aug 15, 2014. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v6.i8.275
Published online Aug 15, 2014. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v6.i8.275
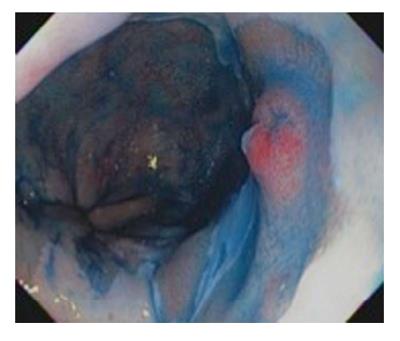
Figure 1 Chromoendoscopy with indigo carmine showing dysplastic nodule in a background of Barrett’s mucosa.
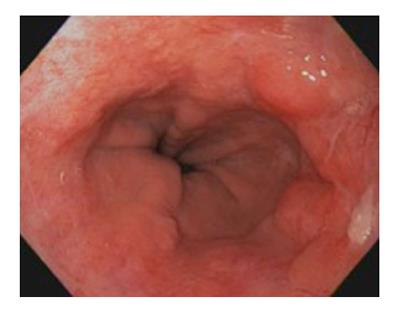
Figure 2 Barrett's esophagus with nodularity concerning for dysplasia or malignancy between 1 and 5 o'clock.
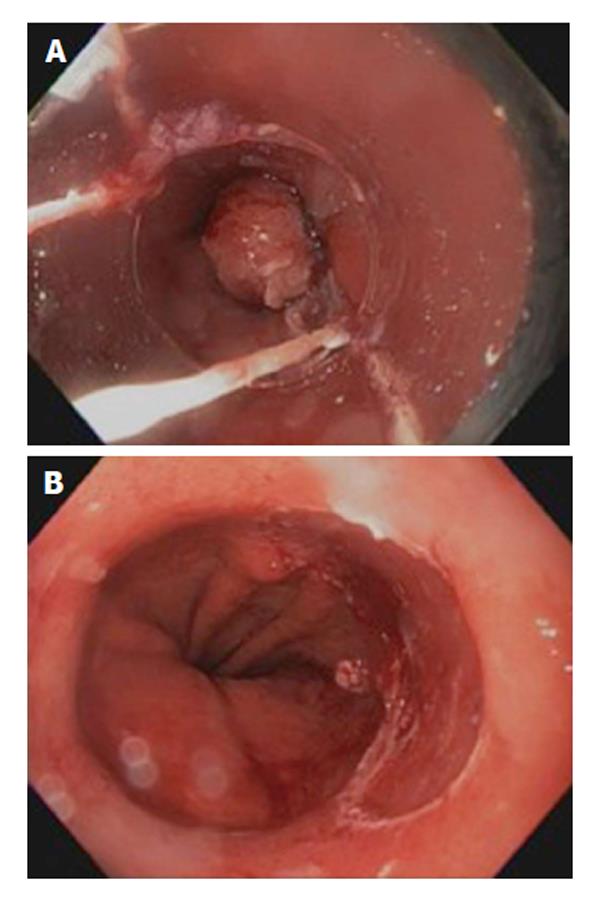
Figure 3 Endoscopic mucosal resection.
A: Using Band ligation of Barrette's esophagus nodule; B: Defect after endoscopic mucosal resection using band ligation and resection of Barrett's esophagus nodules.
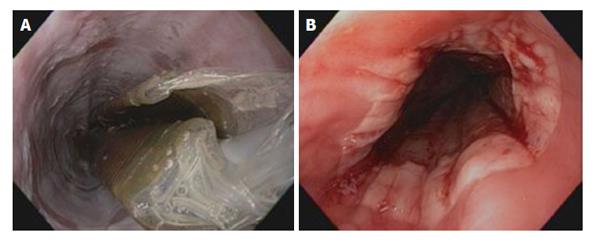
Figure 4 Barrett's esophagus.
A: Ablation of Barrett's esophagus using the circumferential balloon catheter; B: Barrett's esophagus after the first round of ablation using the circumferential balloon ablation catheter.
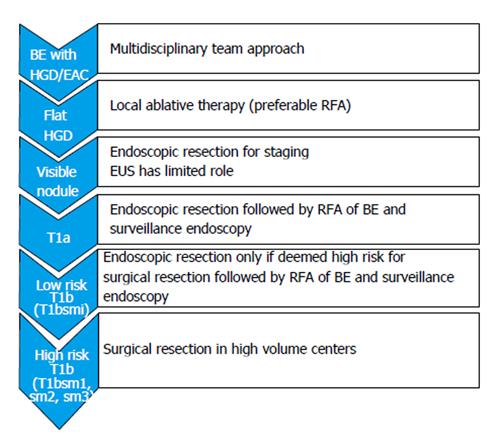
Figure 5 The current practical approach for patients with early esophageal neoplasia.
BE: Barrett’s esophagus; HGD: High grade dysplasia; EAC: Esophageal adenocarcinoma; EUS: Endoscopic ultrasound.
- Citation: Hammoud GM, Hammad H, Ibdah JA. Endoscopic assessment and management of early esophageal adenocarcinoma. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2014; 6(8): 275-288
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v6/i8/275.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v6.i8.275