Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Aug 15, 2013; 5(8): 181-185
Published online Aug 15, 2013. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v5.i8.181
Published online Aug 15, 2013. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v5.i8.181
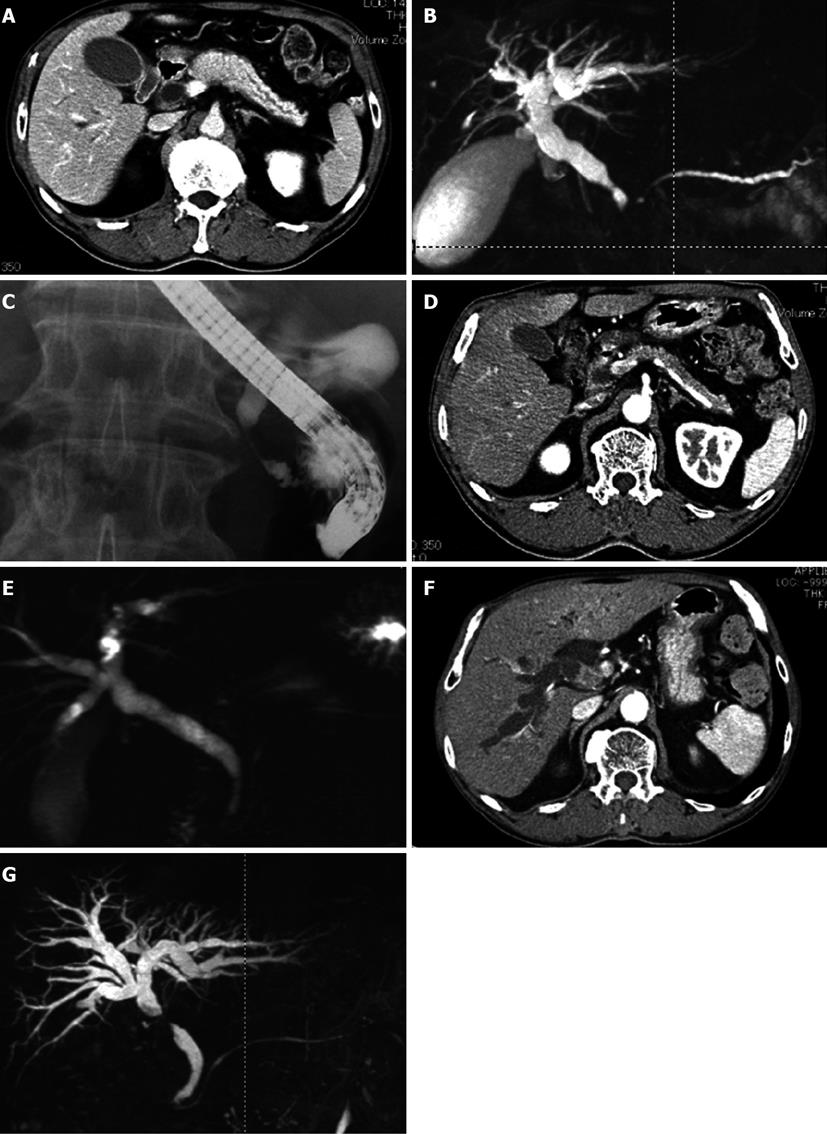
Figure 1 Radiologic findings.
A: Enhanced computed tomography showing diffuse enlargement of the pancreas with capsule-like rim and segmental wall thickening and enlargement of the lower common bile duct (CBD); B: Magnetic resonance imaging revealing narrowed main pancreatic duct and narrowed lower CBD; C: Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography showing narrowed lower CBD; D: Enhanced computed tomography (CT) showing that swelling and capsule-like rim of pancreas disappeared after corticosteroid treatment; E: Magnetic resonance imaging showing that stenosis of bile duct disappeared after corticosteroid treatment; F: CT scan showing segmental wall thickening with enhancement of the middle CBD; G: MRI revealing stenosis of the middle CBD.
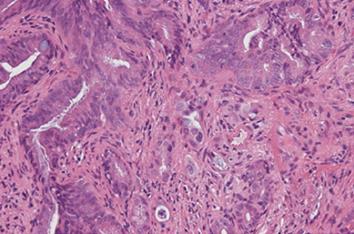
Figure 2 Histologic findings of the biopsy specimens.
The biopsy specimens obtained via the percutaneous transhepatic tract showing abnormal glandular formation, suggesting moderate, well-differentiated adenocarcinoma.
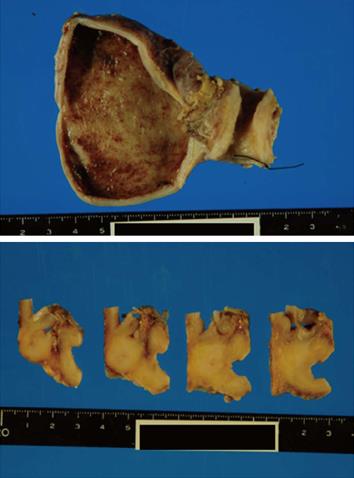
Figure 3 Gross findings of the pancreaticoduodenectomy specimen.
The wall of the middle common bile duct was markedly thickened without cancer invasion to serosa.
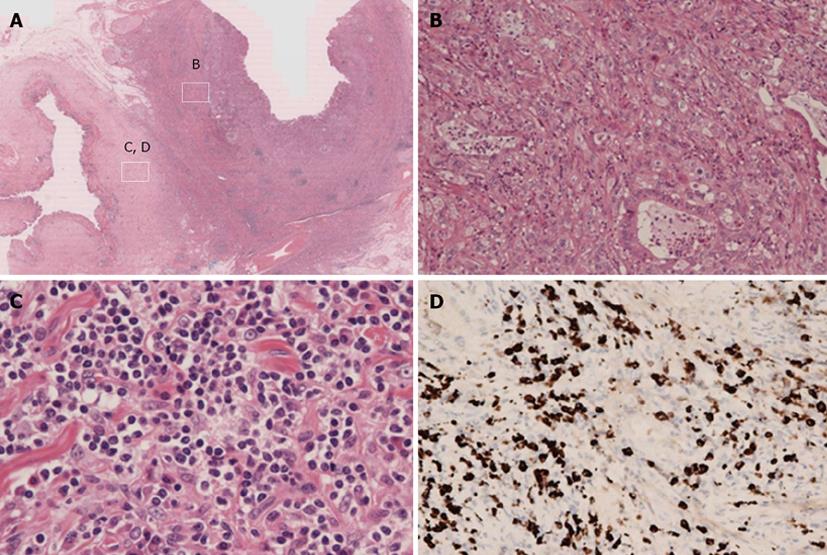
Figure 4 Histologic findings of the pancreaticoduodenectomy specimen.
A: Microscopic examination of the specimen; B: There was abnormal glandular formation, suggesting moderate, welldifferencated adenocarcinoma from mucosa to subserosa (HE × 40); C: Lymphoplasmacellular infiltrate with lymph follicles and obliterative phlebitis were present around the common bile duct (CBD) cancer (HE × 400); D: Immunohistochemistry was performed to identify IgG4-positive plasma cells. More than 10 IgG4-positive plasma cells/high power field were detected in the CBD (IgG4 × 400).
- Citation: Douhara A, Mitoro A, Otani E, Furukawa M, Kaji K, Uejima M, Sawai M, Yoshida M, Yoshiji H, Yamao J, Fukui H. Cholangiocarcinoma developed in a patient with IgG4-related disease. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2013; 5(8): 181-185
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v5/i8/181.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v5.i8.181