Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Aug 15, 2011; 3(8): 119-122
Published online Aug 15, 2011. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v3.i8.119
Published online Aug 15, 2011. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v3.i8.119
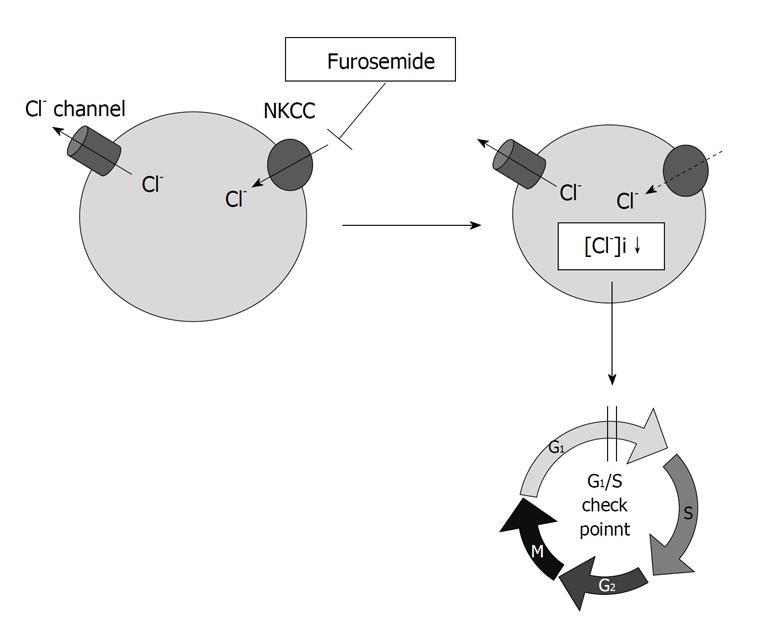
Figure 1 Na+/K+/2Cl- cotransporter controls the intracellular chloride concentration via uptake of Cl- into the intracellular space.
Furosemide, a blocker of Na+/K+/2Cl- cotransporter, delays the G1-S phase progression by decreasing the intracellular chloride concentration ([Cl-]i) in gastric cancer cells.
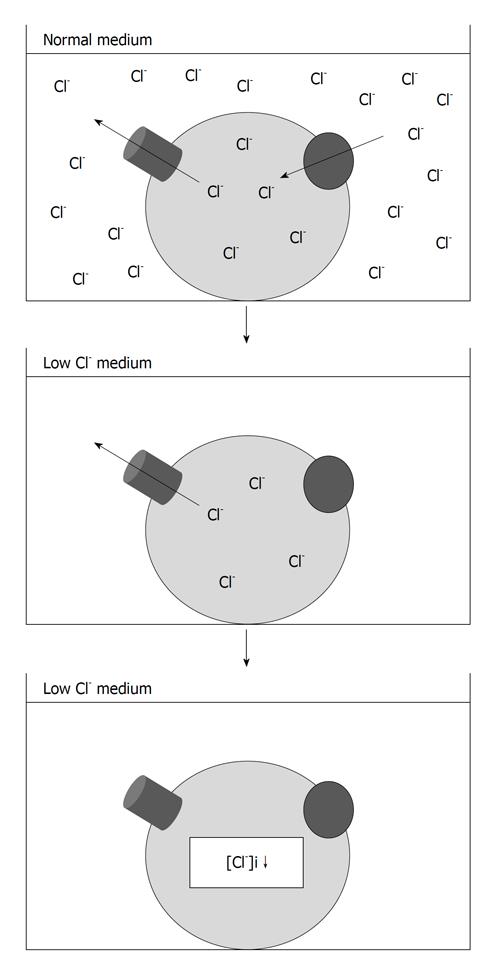
Figure 2 Experimental method for regulation of the intracellular chloride concentration of cultured cells.
The intracellular chloride concentration ([Cl-]i) of gastric cancer cells is decreased by the culture in the low Cl- medium, which were prepared by substituting, respectively, NaCl and KCl with NaNO3 and KNO3.
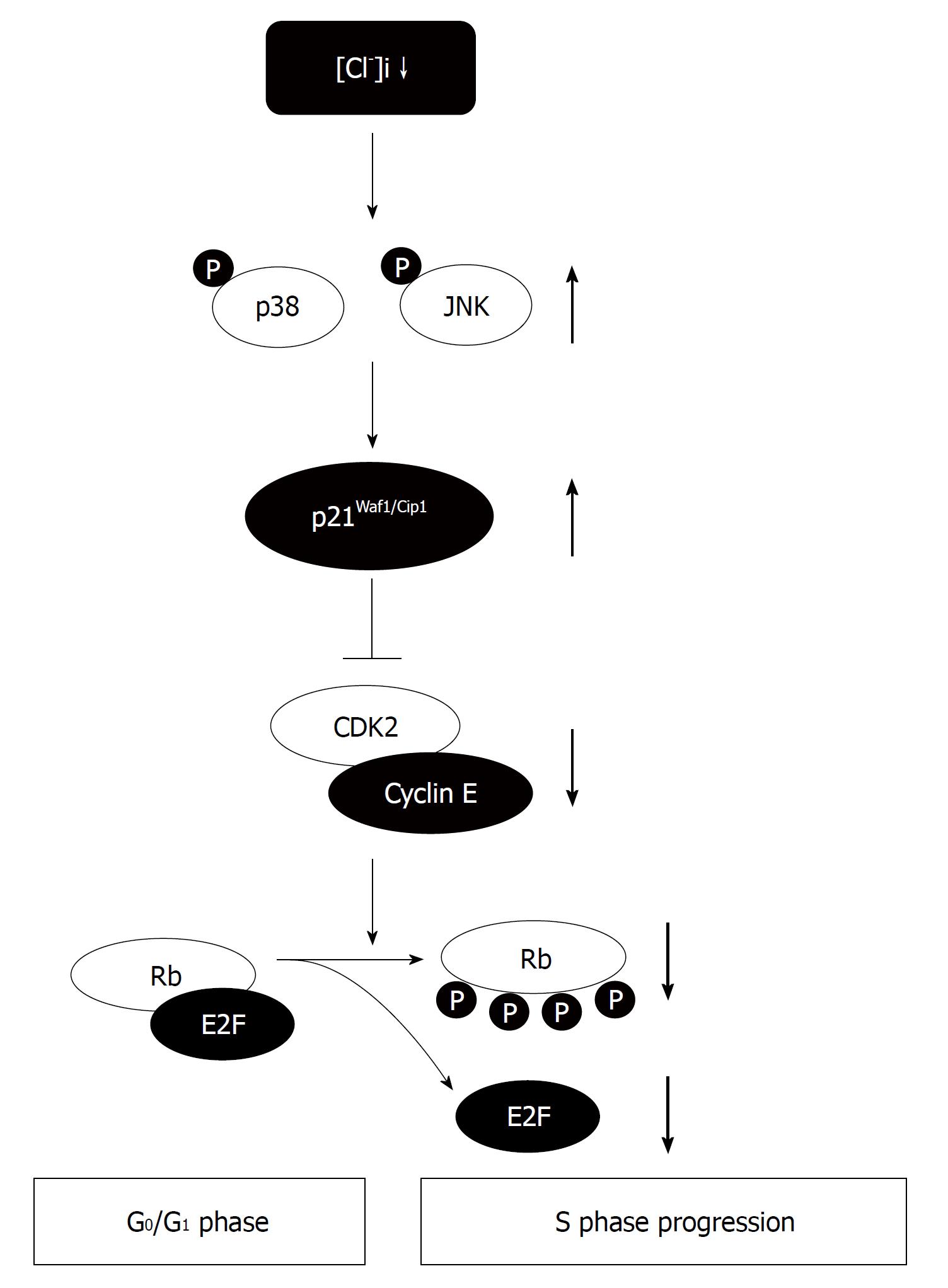
Figure 3 Roles of the intracellular chloride concentration in cell cycle progression of gastric cancer cells.
The intracellular chloride concentration ([Cl-]i) affects the cell proliferation via activation of p38 and/or JNK cascades through upregulation of the p21. The decrease of the [Cl-]i causes the G0/G1 phase arrest by diminishing expression of CDK2 and phosphorylated Rb due to an increase in expression of p21.
- Citation: Shiozaki A, Otsuji E, Marunaka Y. Intracellular chloride regulates the G1/S cell cycle progression in gastric cancer cells. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2011; 3(8): 119-122
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v3/i8/119.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v3.i8.119