Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Nov 15, 2011; 3(11): 153-164
Published online Nov 15, 2011. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v3.i11.153
Published online Nov 15, 2011. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v3.i11.153
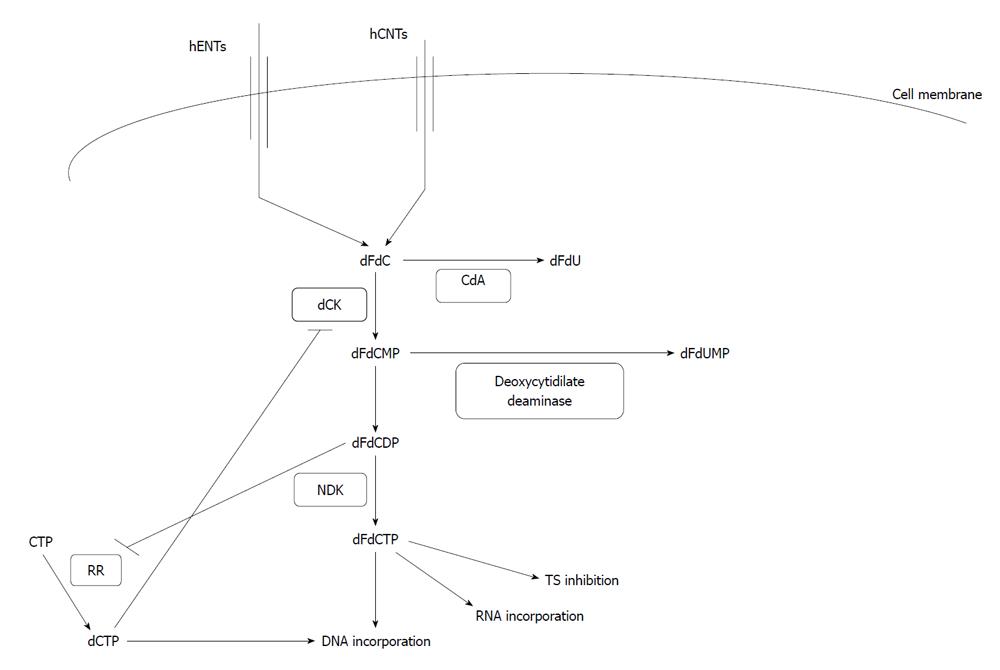
Figure 1 Intracellular transport and metabolism of gemcitabine.
For abbreviations see text. Enzymatic transformations are represented by arrows and inhibitions by т type joining.
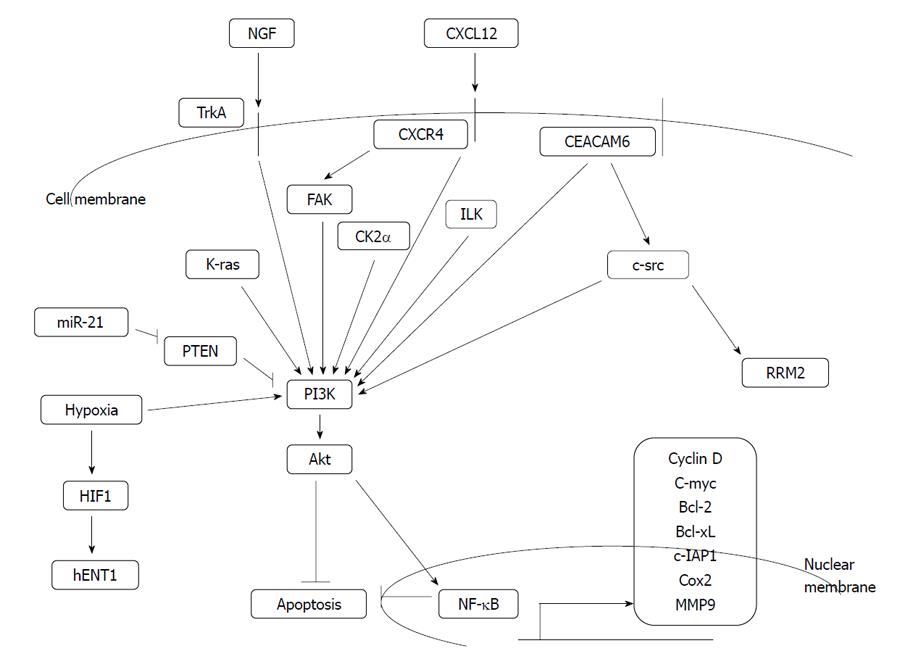
Figure 2 Phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase/akt/nuclear factor-κB-related pathways involved in gemcitabine resistance.
Arrows denote up-regulation or activation and т type joinings denote down-regulation or inhibition. NGF: Nerve growth factor; ILK: Integrin-linked kinase; CEACAM6: Carcinoembryonic antigen cell adhesion molecule 6; FAK: Focal adhesion kinase; PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase; NF-κB: Nuclear factor-κB.
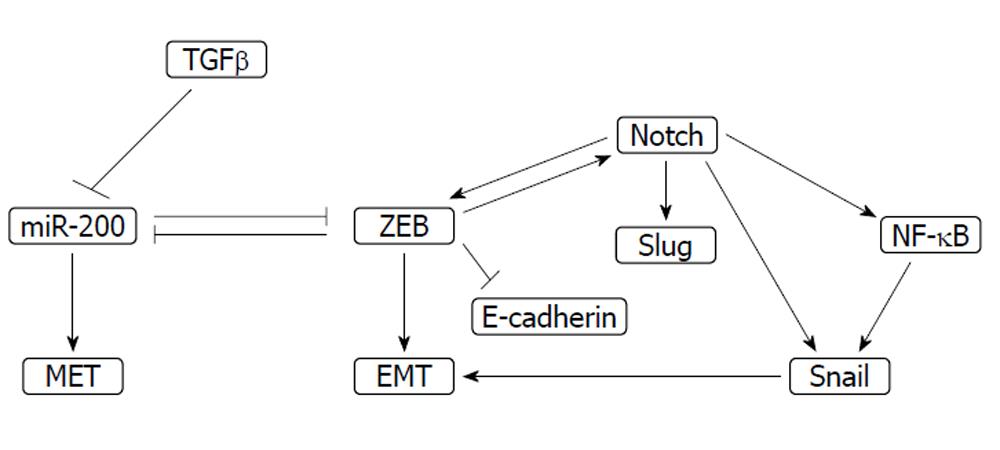
Figure 3 Simplified representation of the web that regulates epithelial to mesenchymal transition or the reverse process mesenchymal to epithelial transition.
Epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) promotion is associated with gemcitabine resistance. Arrows denote up-regulation or activation and т type joinings denote down-regulation or inhibition. MET: Mesenchymal to epithelial transition; ZEB: Zinc finger E-box binding; TGFβ: Transforming growth factor β; NF-κB: Nuclear factor-κB.
- Citation: Voutsadakis IA. Molecular predictors of gemcitabine response in pancreatic cancer. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2011; 3(11): 153-164
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v3/i11/153.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v3.i11.153