Copyright
©2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Oct 15, 2010; 2(10): 369-379
Published online Oct 15, 2010. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v2.i10.369
Published online Oct 15, 2010. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v2.i10.369
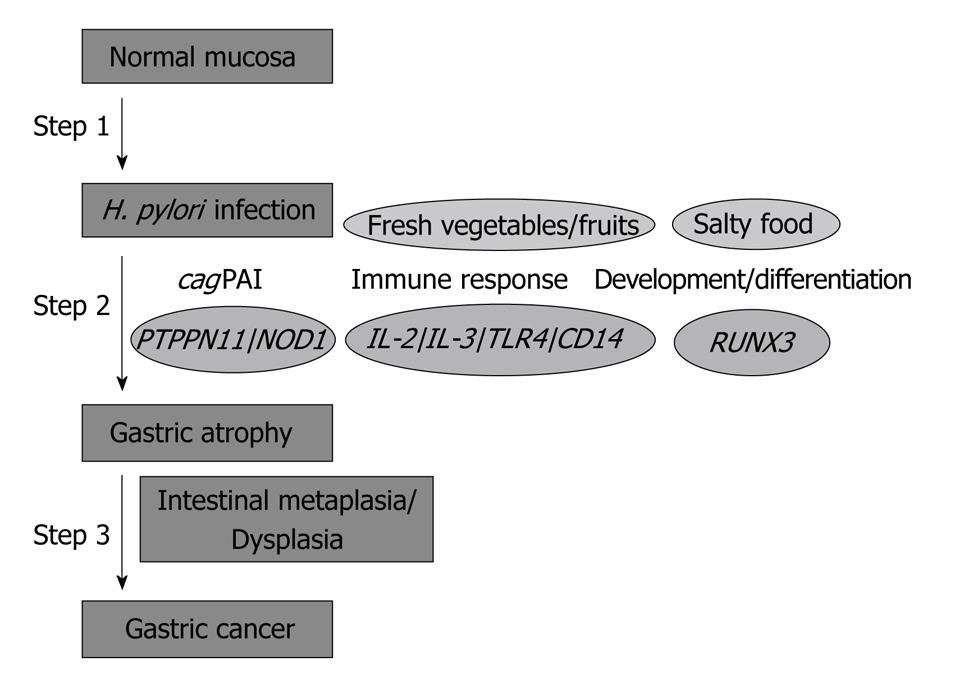
Figure 1 Steps in Helicobacter pylori-related gastric cancer.
H. pylori: Helicobacter pylori; NOD1: Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain protein 1; PTPN11: Protein-tyrosine phosphatase non receptor-type 11; RUNX3: Runt-related gene 3; cagPAI: cag pathogenicity island.
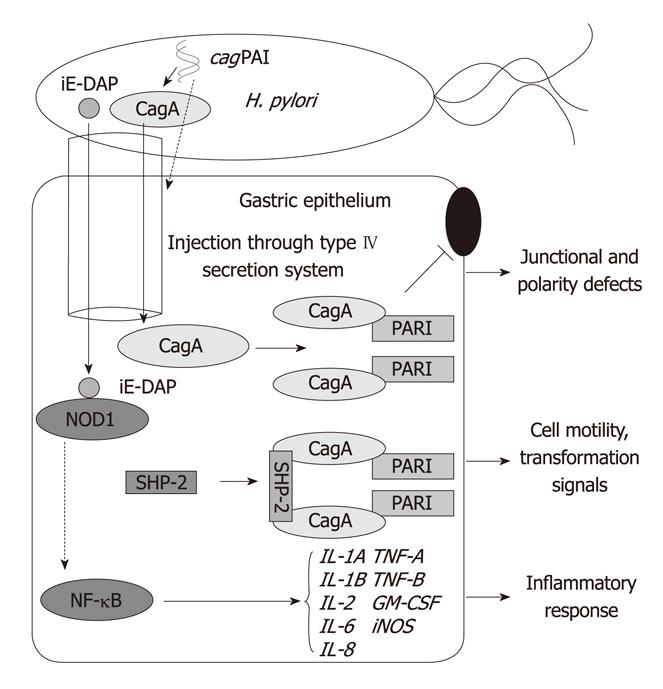
Figure 2 Changes in the gastric epithelial cells due to the activation of Helicobacter pylori cag pathogenicity island-related molecules.
H. pylori: Helicobacter pylori; iE-DAP: γ-D-glutamyl-meso-diaminopimelic acid; iNOS: Inducible nitric oxide synthase; NF-κB, Nuclear factor κB; NOD1: Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain protein 1; PAR1: Partitioning-defective-1; SHP-2: Src homology 2 domain-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase-2; cagPAI: cag pathogenicity island.
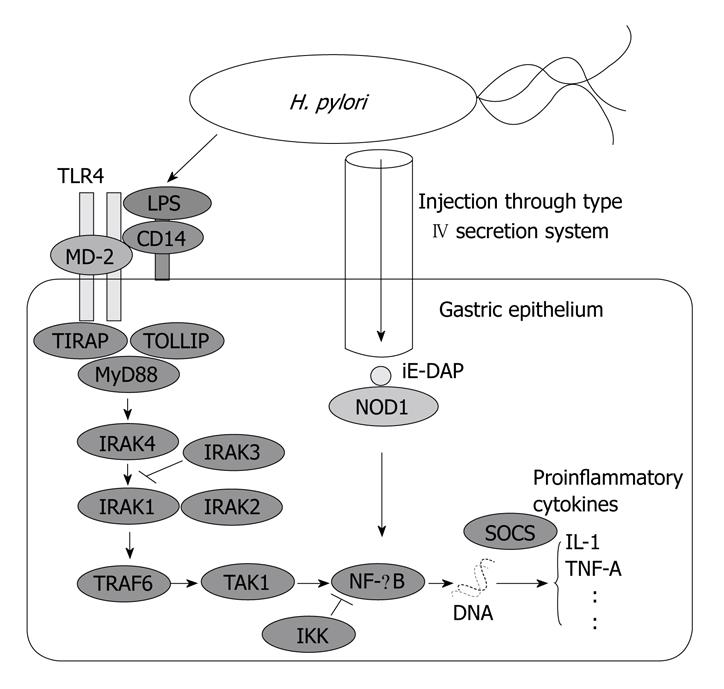
Figure 3 Signal pathways from Helicobacter pylori to cytokine gene expression through innate immunity.
H. pylori: Helicobacter pylori; IKK: Inhibitory κB kinase; iE-DAP: γ-D-glutamyl-meso-diaminopimelic acid; IRAK: Interleukin 1 receptor-associated kinase; MyD88: Myeloid differentiation factor 88; NF-κB, Nuclear factor κB; NOD1: Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain protein 1; SOCS: Suppressor of cytokine signaling; TOLLIP: Toll-interacting protein; TIRAP: TIR domain-containing adaptor protein.
- Citation: Hishida A, Matsuo K, Goto Y, Hamajima N. Genetic predisposition to Helicobacter pylori-induced gastric precancerous conditions. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2010; 2(10): 369-379
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v2/i10/369.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v2.i10.369