Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Jul 15, 2025; 17(7): 108274
Published online Jul 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i7.108274
Published online Jul 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i7.108274
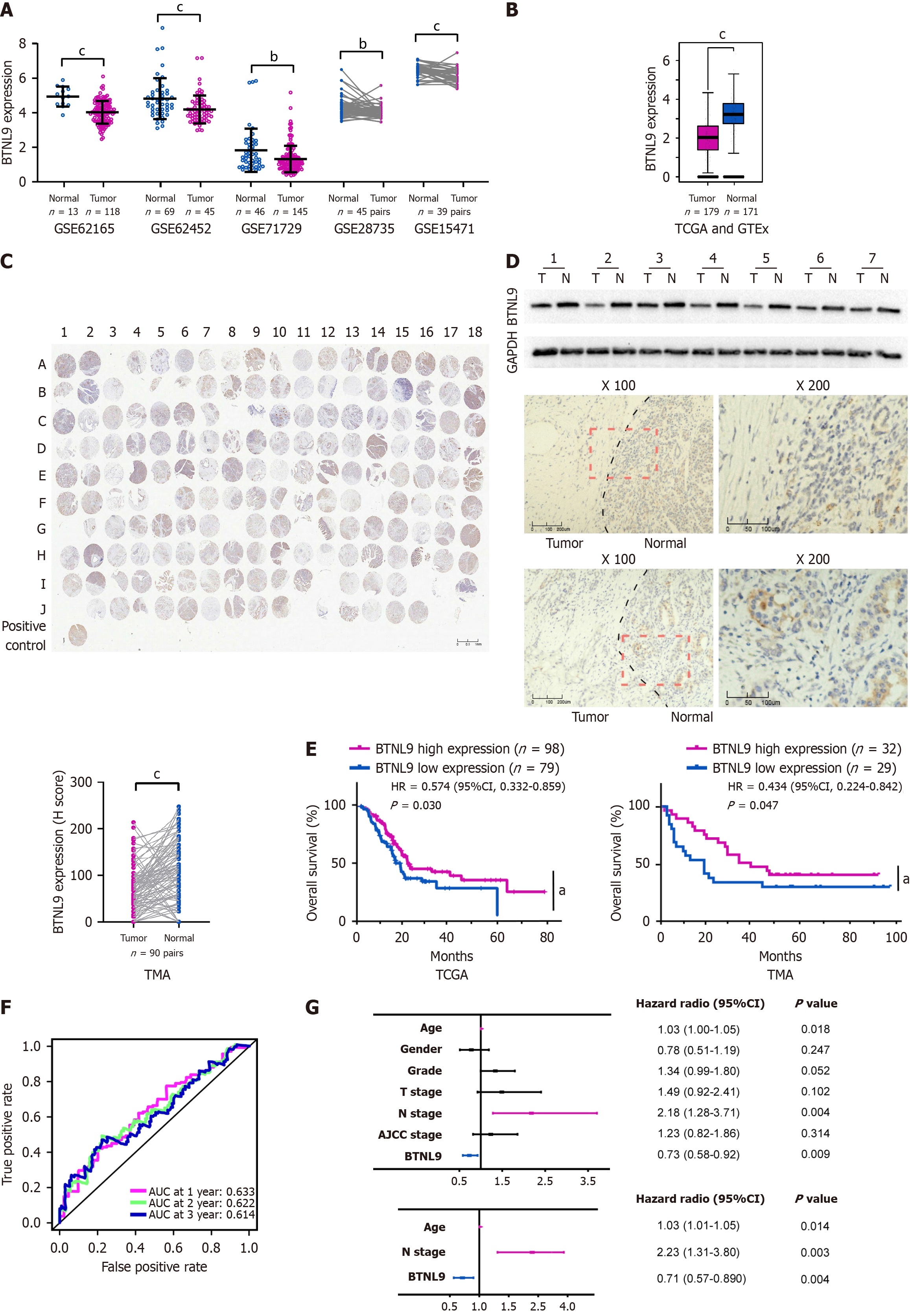
Figure 1 The expression level of BTNL9 in pancreatic cancer and its relationship with prognosis.
A: Differential expression of BTNL9 in pancreatic cancer (PC) and adjacent non-cancerous tissues across five data sets from the Gene Expression Omnibus; B: The expression of BTNL9 in cancer and normal pancreas was different analyzed in Gene Expression Profiling Interactive Analysis; C: The expression level of BTNL9 in the tissue microarray detected by immunohistochemistry (the odd-numbered columns are tumor tissues, and the even-numbered columns are adjacent normal tissues); D: Expression level of BTNL9 in 7 cases with PC in our hospital; E: Based on The Cancer Genome Atlas and tumor microarray data, the prognostic differences of different BTNL9 expression levels; F: The predictive efficacy of BTNL9 expression for overall survival; G: The expression of BTNL9 was an independent factor affecting overall survival in patients with PC. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. TCGA: The Cancer Genome Atlas; GTEx: Genotype-Tissue Expression Project; TMA: Tissue microarray; AUC: Aera under the curve; HR: Hazard ratio; CI: Confidence interval; AJCC: American Joint Committee on Cancer.
Figure 2 Effects of BTNL9 expression on proliferation and metastasis of pancreatic cancer cells.
A: Expression of BTNL9 in common pancreatic cancer (PC) cell lines; B: Establishment of stable PC cell model of BTNL9 overexpression; C: The effect of BTNL9 expression on cell proliferation assessed by CCK8 assay; D: The clone formation assays analyzed the effect of BTNL9 expression on cell clonogenesis; E: The EdU experiment showed a decrease in the proportion of EDU-positive cells by overexpressing BTNL9; F: Transwell experiment showed the migration and infiltration ability decreased when BTNL9 was overexpressed. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001.
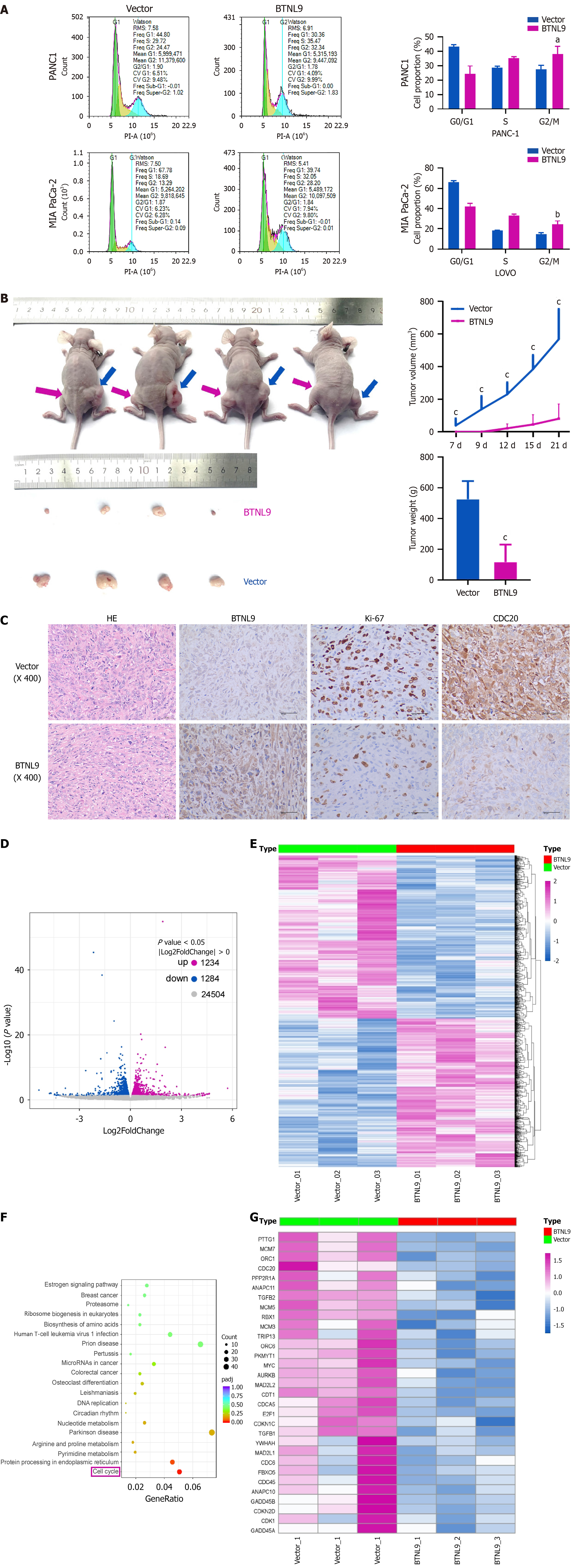
Figure 3 Effect of BTNL9 expression on pancreatic cancer cell cycle.
A: Flow cytometry detected BTNL9 overexpressed cells arrested at G2/M phase; B: Xenograft tumor models showed decreased tumorigenic ability of BTNL9-overexpressing cells; C: Immunohistochemistry results of xenograft tumor tissue; D and E: Differentially expressed genes detected by RNA sequencing; F: BTNL9 overexpression showed significant enrichment of cell cycle signaling pathway; G: Expression of cell cycle related genes in two groups of cells. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. HE: Hematoxylin and eosin.
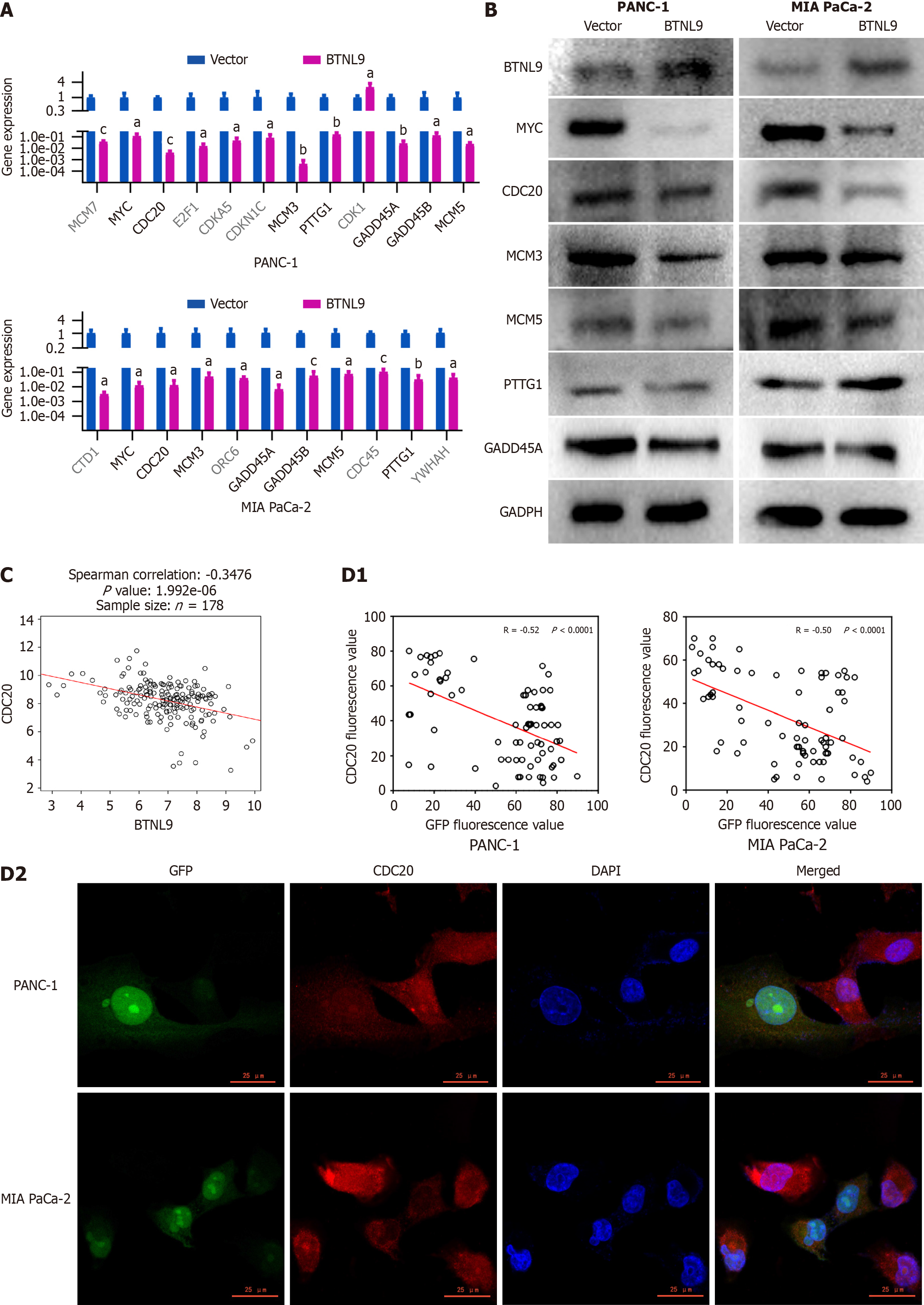
Figure 4 Regulation of BTNL9 expression on downstream molecules.
A: Reverse transcription quantitative PCR results of cell cycle related genes; B: The protein expression levels of genes with significant differences in reverse transcription quantitative PCR validation were detected by Western blot; C: Correlation analysis of CDC20 and BNTL9 expression in The Cancer Genome Atlas RNA sequencing data of pancreatic cancer; D: The expression of BTNL9 and CDC20 in pancreatic cancer cells with BTNL9 overexpression detected by immunofluorescence (green = green fluorescence protein; red= CDC20). aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. GFP: Green fluorescence protein.
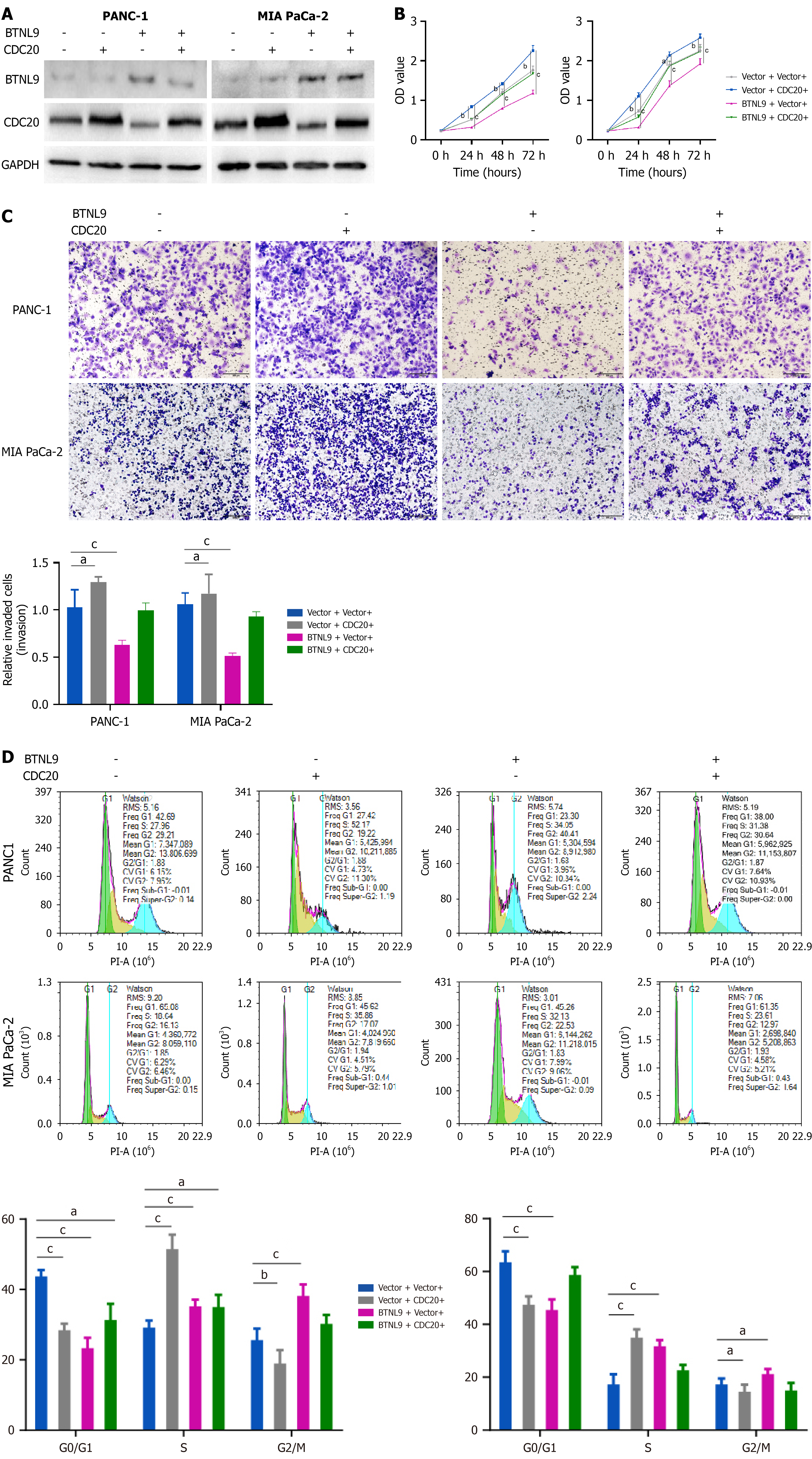
Figure 5 Effects of BTNL9/CDC20 on proliferation, migration, and cell cycle of pancreatic cancer cells.
A: Pancreatic cancer cells were transfected with BTNL9 and CDC20; B: The proliferative ability of four types of cells in the CCK8 assay; C: Transwell assay was used to analyze the migration capacity in four types of cells; D: The cell cycle distribution of cells was measured by flow cytometry. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001.
- Citation: Xiao M, Luo ZY, Yu AR, Xu K, Zhou W. BTNL9 exerts anti-cancer effects by inhibiting CDC20 to induce G2/M arrest in pancreatic cancer. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2025; 17(7): 108274
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v17/i7/108274.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v17.i7.108274