Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Jul 15, 2025; 17(7): 107380
Published online Jul 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i7.107380
Published online Jul 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i7.107380
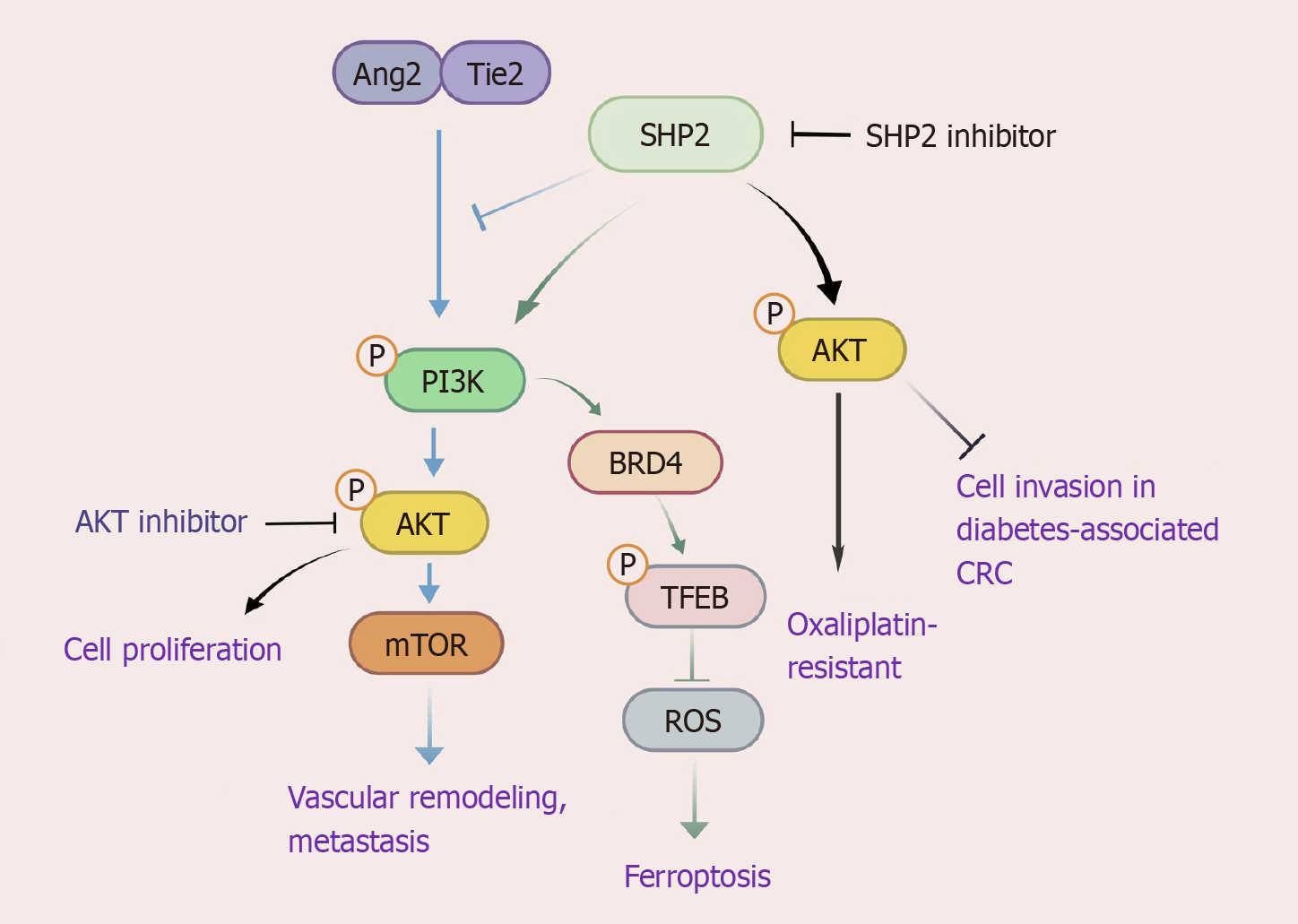
Figure 1 SHP2 plays a dual regulatory role in the PI3K/AKT pathway.
SHP2 activates the PI3K/AKT pathway, contributing to chemoresistance. SHP2 decreases ROS production and inhibits ferroptosis via the PI3K/BRD4/TFEB axis. SHP2 stimulates the Tie2-PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling cascade to mediate vascular remodeling and colorectal cancer (CRC) metastasis. In diabetes-associated CRC, SHP2 knockdown suppresses PI3K-AKT phosphorylation, enhances invasiveness. Monotherapy targeting SHP2 triggers feedback activation of AKT, necessitating its combination with AKT inhibitors for effective blockade. SHP2 inhibitors suppress the PI3K/AKT pathway and cell proliferation. CRC: Colorectal cancer. Created with biogdp.com (Supplementary material).
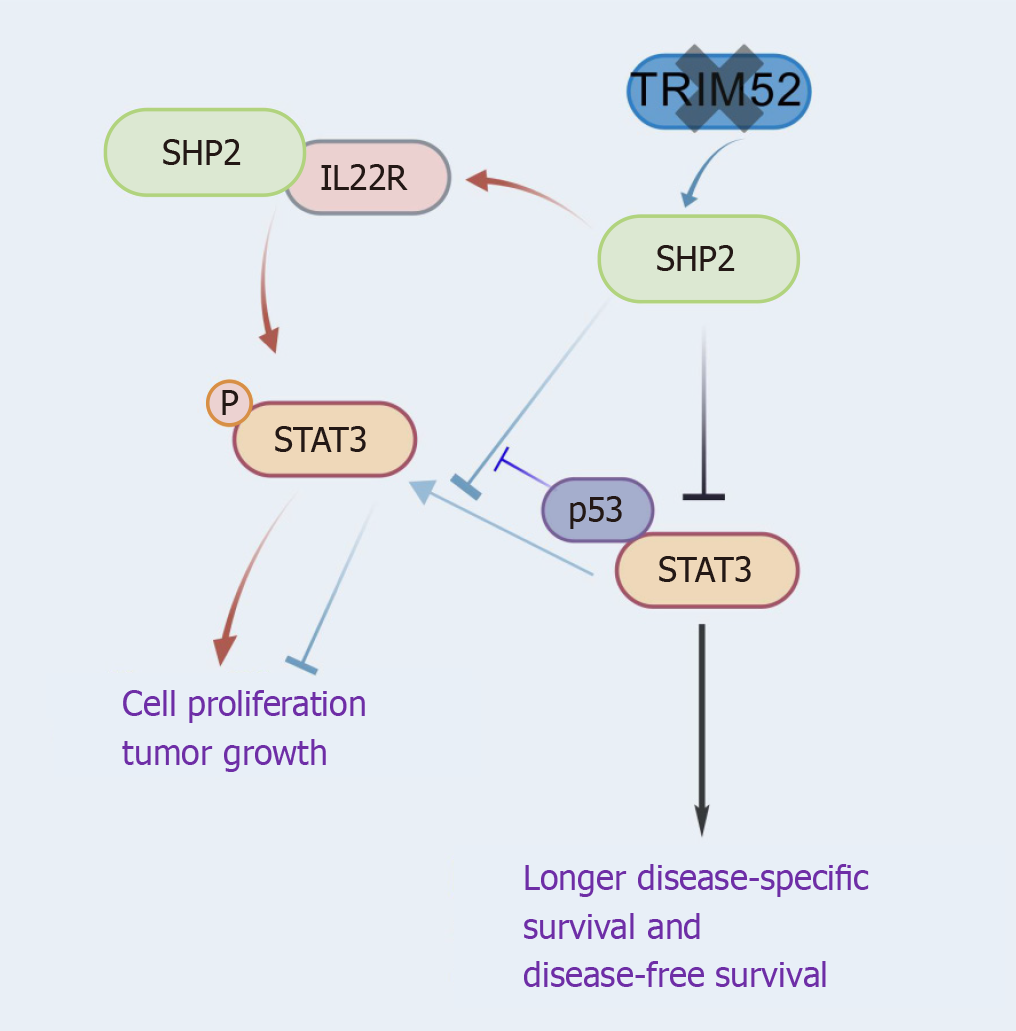
Figure 2 SHP2 regulates the STAT3 pathway.
SHP2 negatively regulates STAT3 in colorectal cancer, correlating with improved disease-specific survival and disease-free survival. TRIM52 deletion suppresses STAT3 phosphorylation via SHP2 upregulation, inhibiting tumor growth. SHP2 dephosphorylates STAT3 to block proliferation, while mutant p53 competitively binds to STAT3 to reverse this suppression. Paradoxically, the SHP2-IL22R1 interaction activates STAT3-mediated JAK/STAT signaling, driving proliferation. Created with biogdp.com (Supplementary material).
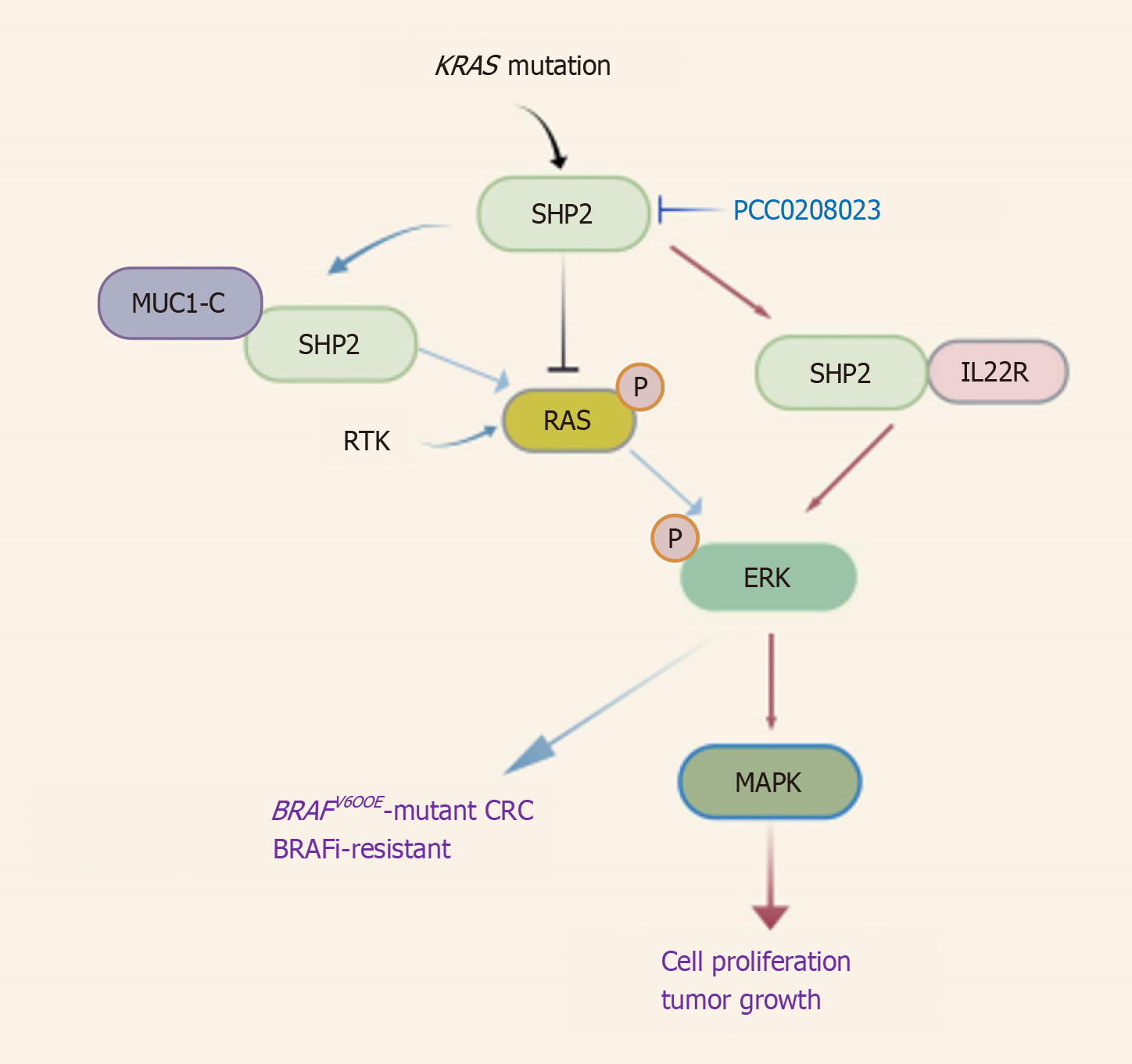
Figure 3 SHP2 modulates the RAS/ERK pathway.
SHP2 binding to IL-22R1 activates ERK signaling, thereby facilitating MAPK signaling and promoting cell proliferation. MUC1-C interacts with SHP2, enhancing RTK-RAS/ERK signaling, thus making it a promising therapeutic target for BRAFV600E-mutant CRC. SHP2 deficiency diminishes RAF/MEK/ERK phosphorylation in KRAS-mutant CRC cells. The SHP2 inhibitor PCC0208023 suppresses cell proliferation by inhibiting the RAS/MAPK pathway and exhibits tumor volume reduction in preclinical models. CRC: Colorectal cancer. Created with biogdp.com (Supplementary material).
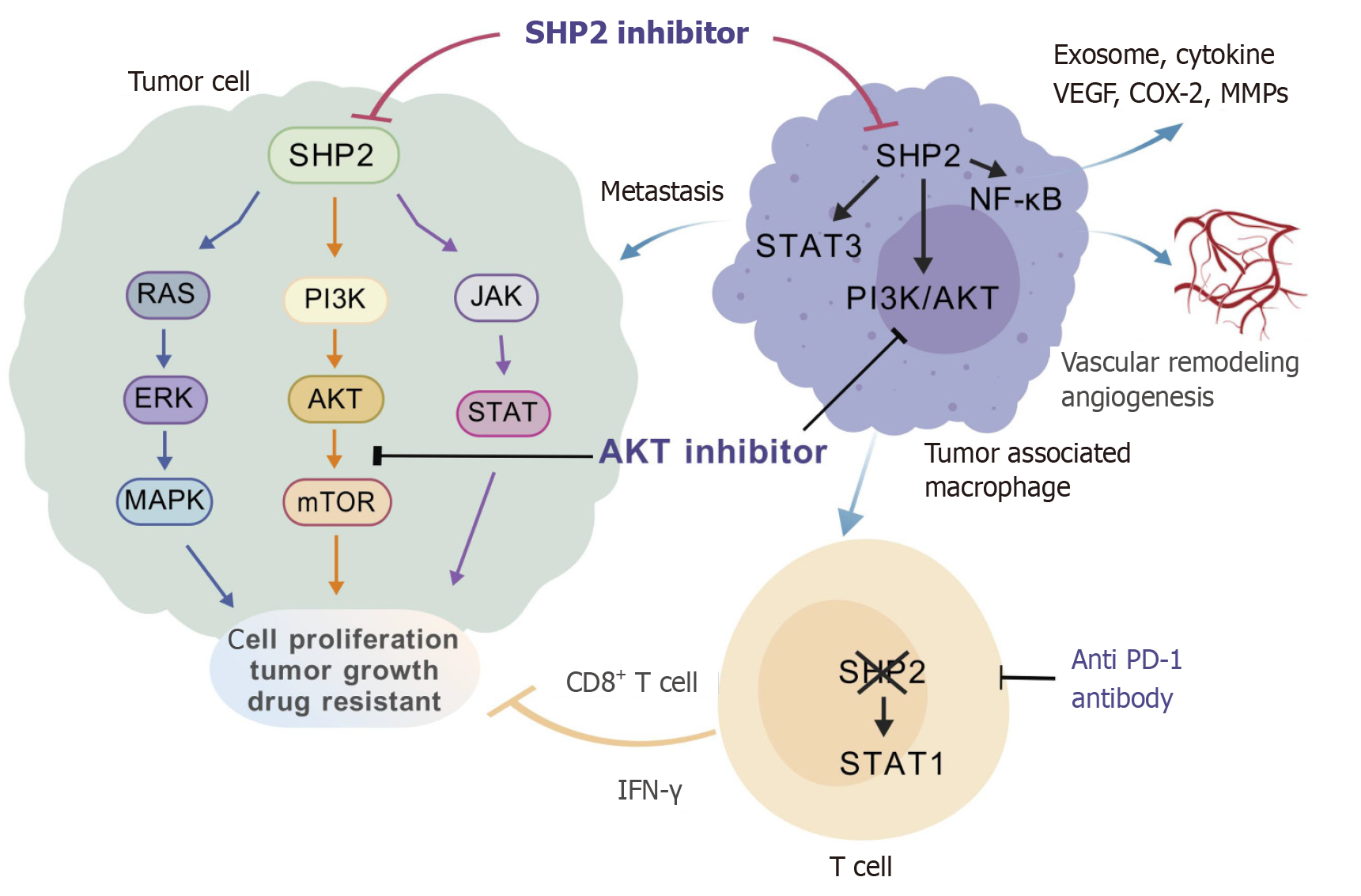
Figure 4 SHP2 regulates the colorectal cancer tumor microenvironment.
SHP2 regulates the PI3K/AKT, JAK/STAT, and RAS/ERK pathways to mediate tumor cell proliferation, drug resistance, and tumor growth. In tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs), SHP2 mediates cytokine release, angiogenesis, and tumor microenvironment remodeling through PI3K/AKT, NF-κB, and STAT3 signaling pathways, leading to colorectal cancer metastasis. In T cells, SHP2 primarily participates in tumor microenvironment remodeling and mediates tumor suppression through the STAT1 and IFN-γ pathways. VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; MMP: Matrix metalloproteinase. Created with biogdp.com (Supplementary material).
- Citation: Liu P, Chen J. Targeting SHP2: Dual breakthroughs in colorectal cancer therapy–from signaling pathway modulation to immune microenvironment remodeling. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2025; 17(7): 107380
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v17/i7/107380.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v17.i7.107380