Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Jun 15, 2025; 17(6): 106080
Published online Jun 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i6.106080
Published online Jun 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i6.106080
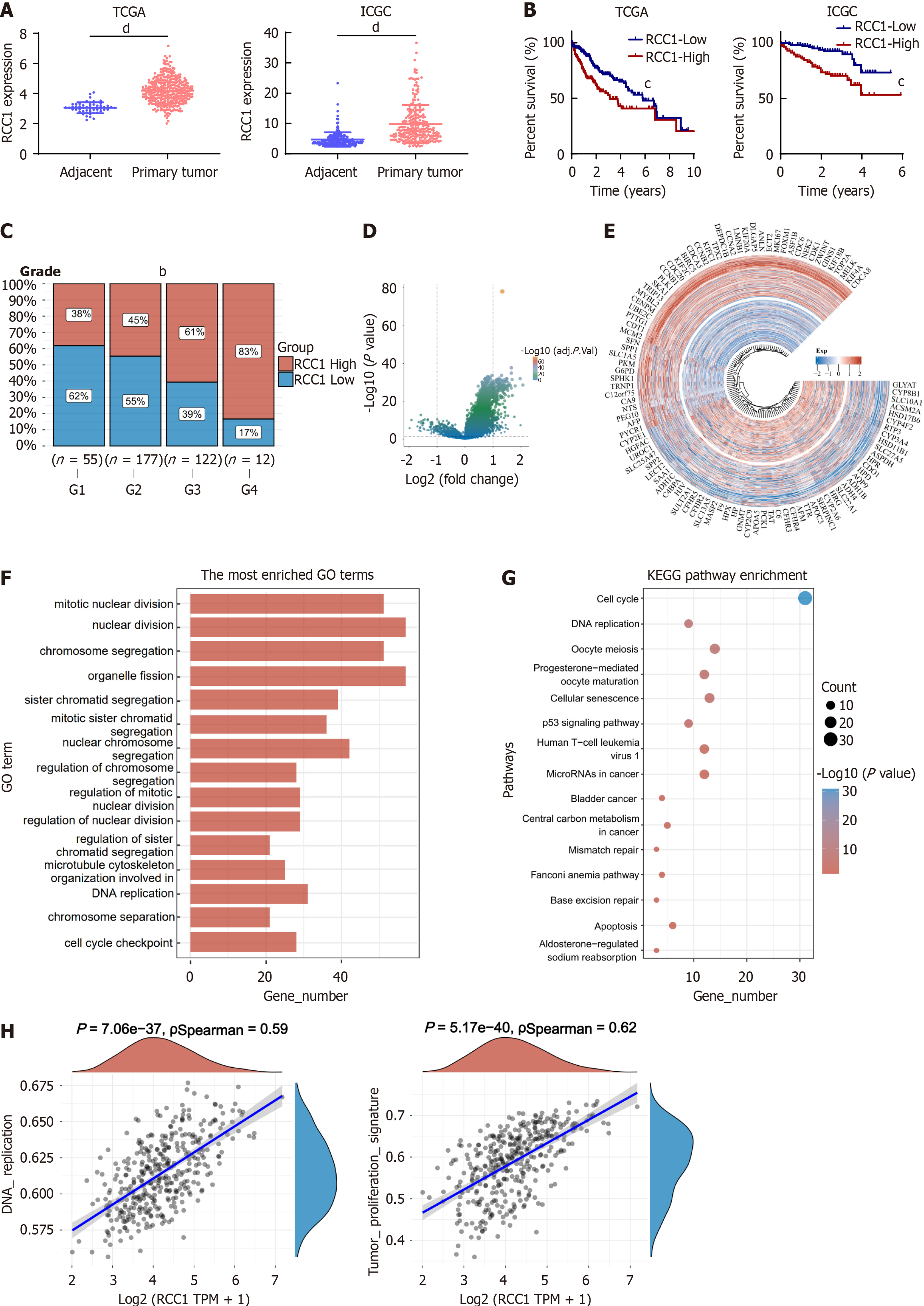
Figure 1 Bioinformatics analysis shows regulator of chromosome condensation 1 expression and its association with poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma patients.
bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001, dP < 0.0001. A: Regulator of chromosome condensation 1 (RCC1) expression levels in The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and International Cancer Genome Consortium databases; B: Prognostic analysis of high vs low RCC1 expression in TCGA and International Cancer Genome Consortium databases; C: Pathologic grade analysis of high vs low RCC1 expression in TCGA database; D: Volcano plot of differentially expressed genes between high and low RCC1 expression in TCGA database; E: Heatmap displaying top 50 upregulated genes and downregulated genes with greatest differential changes; F: Functional enrichment analysis: Gene Ontology term enrichment results of differentially upregulated genes; G: Functional enrichment analysis: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway enrichment of differentially upregulated genes; H: Spearman correlation analysis of gene expression and pathway scores. TCGA: The Cancer Genome Atlas; ICGC: International Cancer Genome Consortium; RCC1: Regulator of chromosome condensation 1; GO: Gene Ontology.
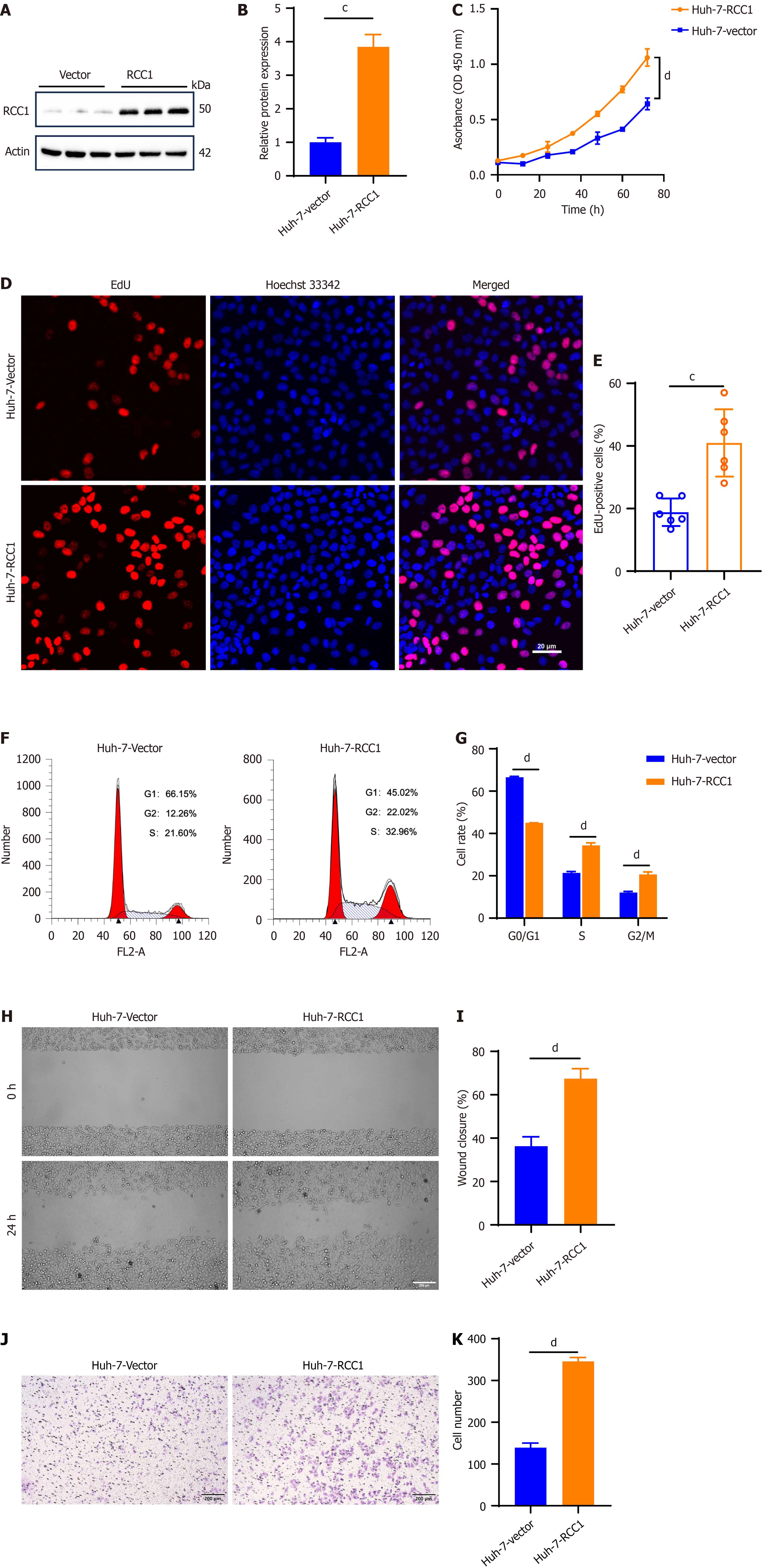
Figure 2 Regulator of chromosome condensation 1 overexpression promotes the cell growth and motility of hepatocellular carcinoma cells.
cP < 0.001, dP < 0.0001. A: Immunoblotting analysis of regulator of chromosome condensation 1 (RCC1) in vector and RCC1-overexpressing Huh-7 cells, with actin as the loading control; B: Quantification of RCC1 expression normalized to actin according to Figure 2A; C and D: Cell counting kit-8 assay and 5-ethynyl-2’-deoxyuridine (EdU) incorporation assay detected the proliferation in vector and RCC1-overexpressing Huh-7 cells; E: Statistical results of 5-ethynyl-2’-deoxyuridine-positive cell percentage from Figure 2D; F and G: Cell cycle analysis and the statistical results between Huh-7-vector and Huh-7-RCC1 cells; H: Wound healing assay detected the migration in vector and RCC1-overexpressing Huh-7 cells; I: Statistical results of wound closure percentage from Figure 2H; J: Transwell invasion assay detected the invasion in Huh-7-vector and Huh-7-RCC1; K: Statistical results of cell numbers from Figure 2J. RCC1: Regulator of chromosome condensation 1.
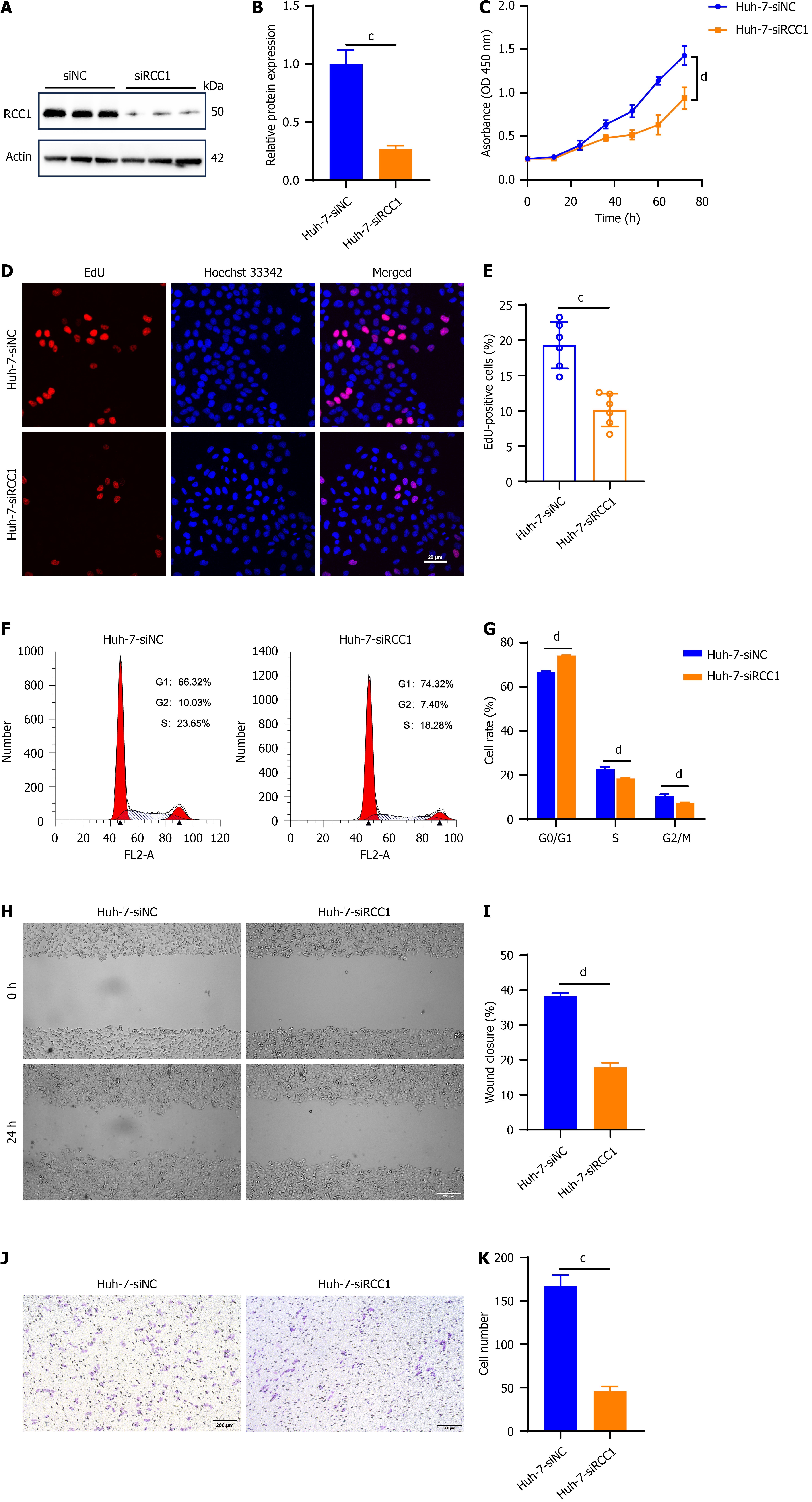
Figure 3 Knockdown of regulator of chromosome condensation 1 inhibits the proliferation and motility of hepatocellular carcinoma cells.
cP < 0.001, dP < 0.0001. A: Immunoblotting analysis of regulator of chromosome condensation 1 (RCC1) in small interfering RNA negative control (siNC) and RCC1-knockdown Huh-7 cells. Actin was used as the loading control; B: Quantification of RCC1 expression normalized to actin according to Figure 3A; C and D: Cell counting kit-8 assay and 5-ethynyl-2’-deoxyuridine (EdU) incorporation assay detected proliferation in siNC and RCC1-knockdown Huh-7 cells; E: Statistical results of 5-ethynyl-2’-deoxyuridine-positive cell percentage from Figure 3D; F and G: Cell cycle analysis and the statistical results between Huh-7-siNC and Huh-7-siRCC1; H: Wound healing assay detected the migration in siNC and RCC1-knockdown Huh-7 cells; I: Statistical results of wound closure percentage from Figure 3H; J: Transwell invasion assay detected the invasion in Huh-7-siNC and Huh-7-siRCC1; K: Statistical results of cell numbers from Figure 3J. siNC: Small interfering RNA negative control; RCC1: Regulator of chromosome condensation 1.
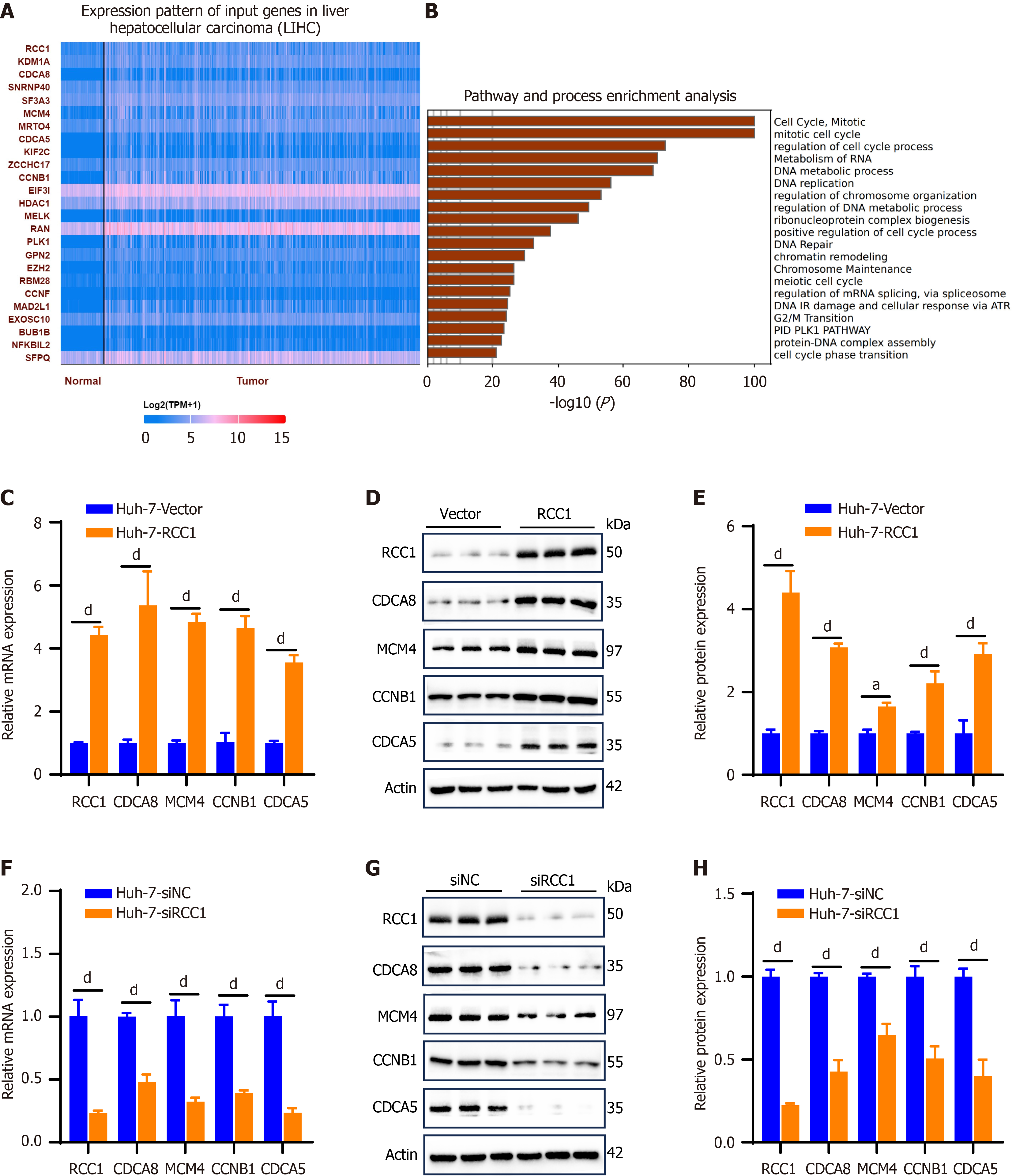
Figure 4 Regulator of chromosome condensation 1 modulates the expression of cell cycle-associated genes in hepatocellular carcinoma.
aP < 0.05, dP < 0.0001. A: Heatmap displaying the genes correlated with regulator of chromosome condensation 1 (RCC1) in hepatocellular carcinoma samples from The Cancer Genome Atlas database; B: Enrichment analysis of genes with correlation coefficients exceeding 05; C-E: The mRNA and protein expression analysis of cell division cycle-associated (CDCA) 8, minichromosome maintenance complex component, cyclin B1 and CDCA5 in vector and RCC1-overexpressing Huh-7 cells; F-H: Quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction and immunoblotting analysis of CDCA8, minichromosome maintenance complex component 4, cyclin B1 and CDCA5 in small interfering RNA negative control and RCC1-knockdown Huh-7 cells. RCC1: Regulator of chromosome condensation 1; CDCA: Cell division cycle-associated; MCM4: Minichromosome maintenance complex component 4; CCNB1: Cyclin B1; siNC: Small interfering RNA negative control.
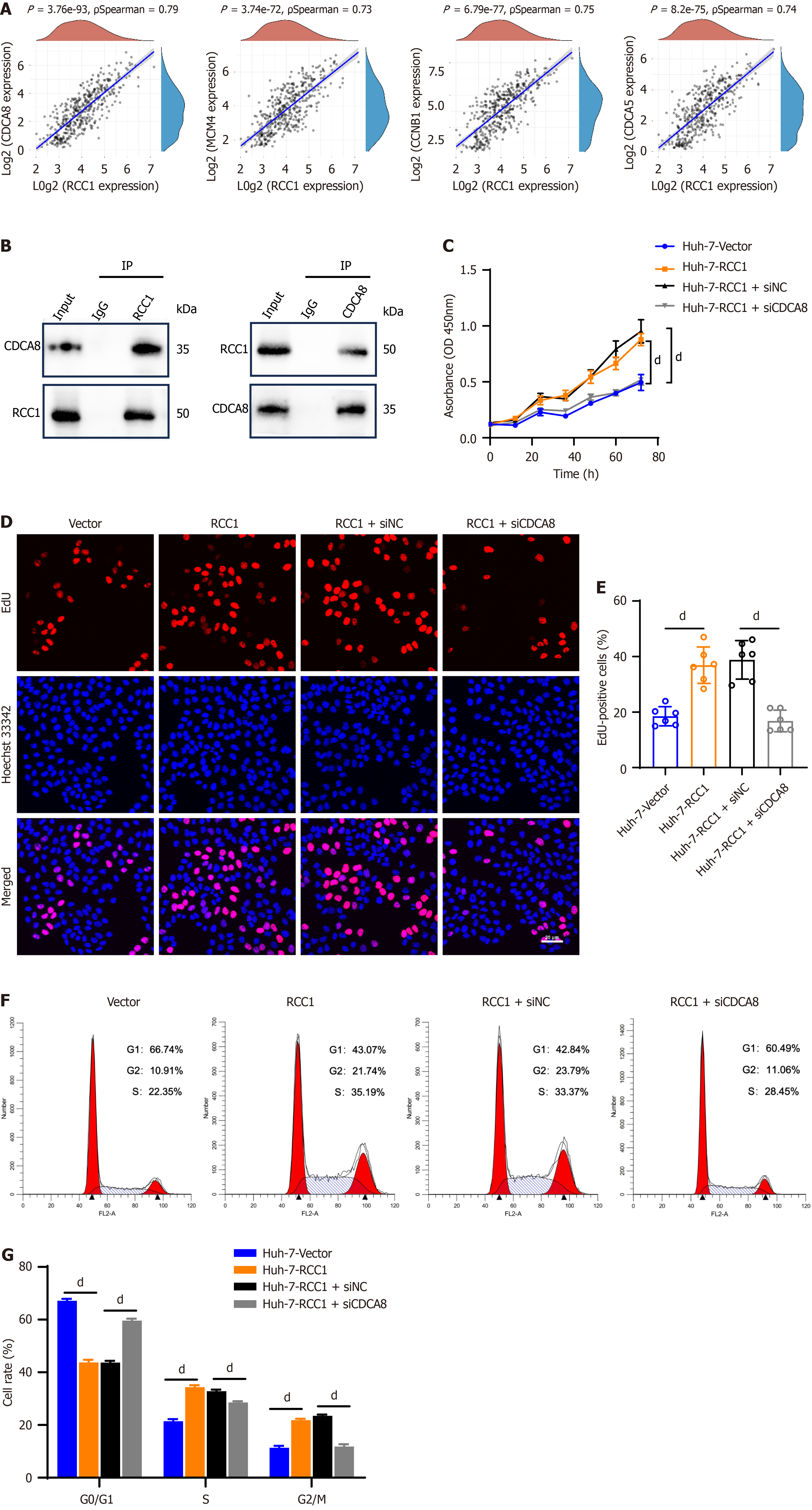
Figure 5 Silencing cell division cycle-associated 8 attenuates the proliferative enhancement induced by regulator of chromosome condensation 1 overexpression in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.
dP < 0.0001. A: Spearman correlation analysis of regulator of chromosome condensation 1 with cell division cycle-associated (CDCA) 8, minichromosome maintenance complex component 4, cyclin B1 and CDCA5 expression; B: Immunoblotting analysis of the interaction between regulator of chromosome condensation 1 and CDCA8 in Huh-7 cell line; C and D: Cell counting kit-8 assay and 5-ethynyl-2’-deoxyuridine incorporation assay detected proliferation in Huh-7 cells under different treatments; E: Statistical results of ethynyl-2’-deoxyuridine-positive cells percentage from Figure 5D; F and G: Cell cycle analysis and the statistical results in different treatment Huh-7 cells. RCC1: Regulator of chromosome condensation 1; CDCA: Cell division cycle-associated; IP: Immunoprecipitation; siNC: Small interfering RNA negative control; IgG: Immunoglobulin G.
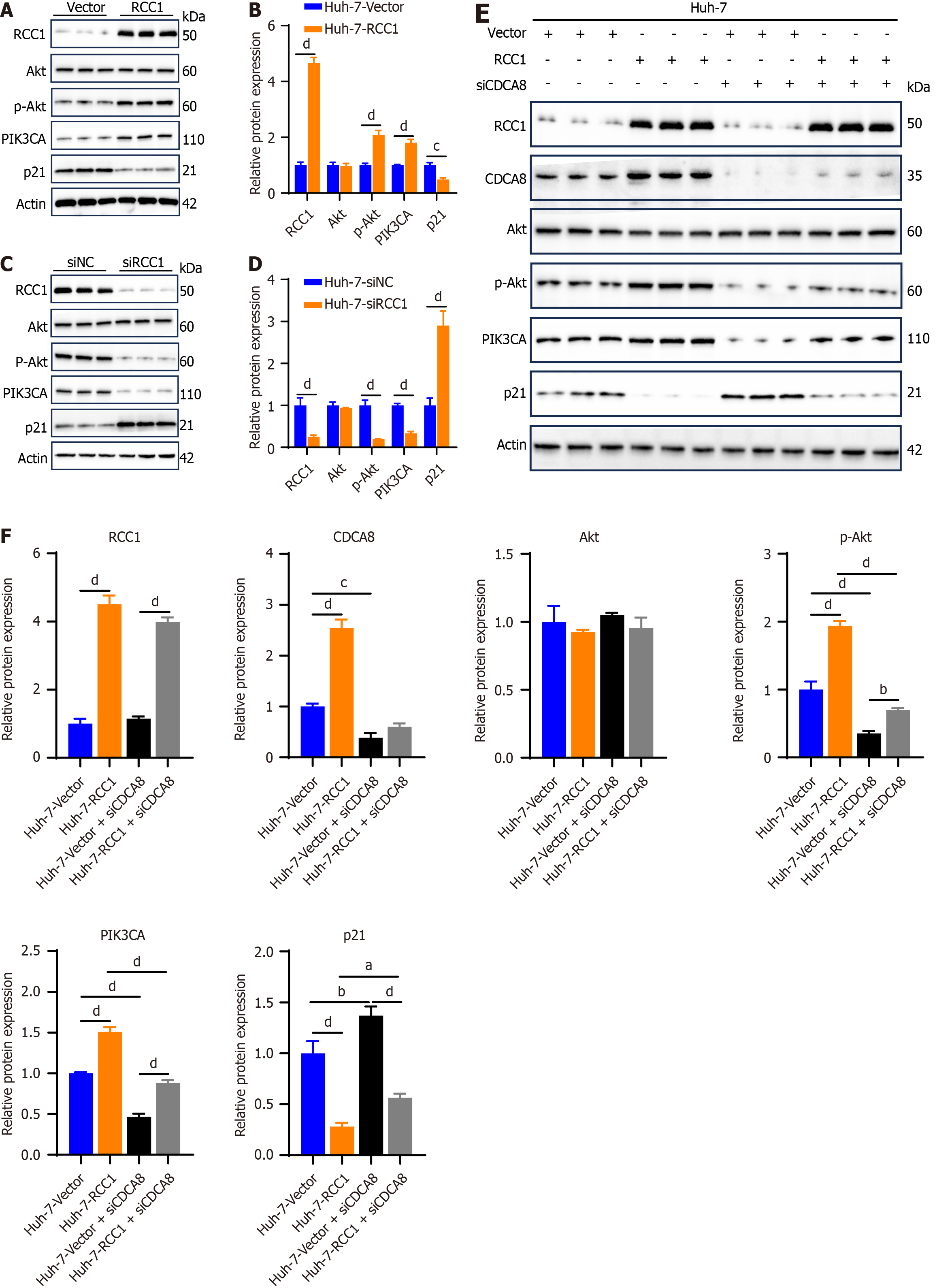
Figure 6 Regulator of chromosome condensation 1 regulates phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B/cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1a pathway through cell division cycle-associated 8 in hepatocellular carcinoma.
aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001, dP< 0.0001. A: Immunoblotting analysis of phosphatidylinositol - 4,5 - bisphosphate 3 - kinase catalytic subunit alpha (PIK3CA), protein kinase B (Akt), p-Akt and cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1a (p21) in vector and regulator of chromosome condensation 1-overexpressing Huh-7 cells. Actin was used as the loading control; B: Quantification of PIK3CA, Akt, p-Akt and p21 expression normalized to actin; C: Immunoblotting analysis of PIK3CA, Akt, p-Akt and p21 in small interfering RNA negative control and regulator of chromosome condensation 1-knockdown Huh-7 cells. Actin was used as the loading control; D: Quantification of PIK3CA, Akt, p-Akt and p21 expression normalized to actin; E: Immunoblotting analysis of PIK3CA, Akt, p-Akt and p21 in different treatment Huh-7 cells. Actin was used as the loading control; F: The quantification of PIK3CA, Akt, p-Akt and p21 expression normalized to actin. RCC1: Regulator of chromosome condensation 1; siNC: Small interfering RNA negative control; CDCA: Cell division cycle-associated; PIK3CA: Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit alpha; Akt: Protein kinase B.
- Citation: Wang YT, Yong YL, Liu ZK, Shen YX, Yang XM, Chen ZN. Regulator of chromosome condensation 1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation via cell-division-cycle-associated-8 dependent phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B signaling. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2025; 17(6): 106080
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v17/i6/106080.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v17.i6.106080