Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Apr 15, 2025; 17(4): 103679
Published online Apr 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i4.103679
Published online Apr 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i4.103679
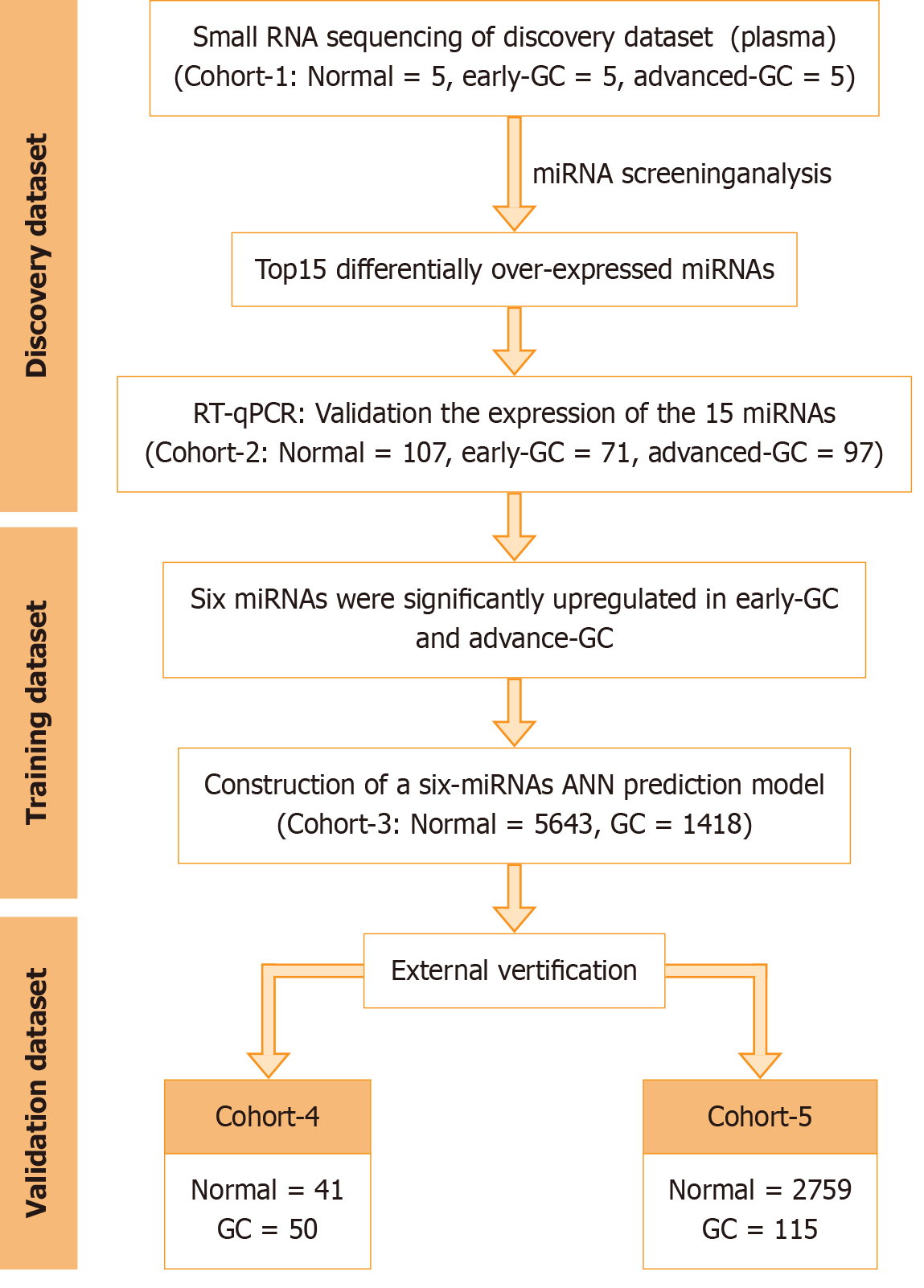
Figure 1 Workflow of the entire study.
GC: Gastric cancer.
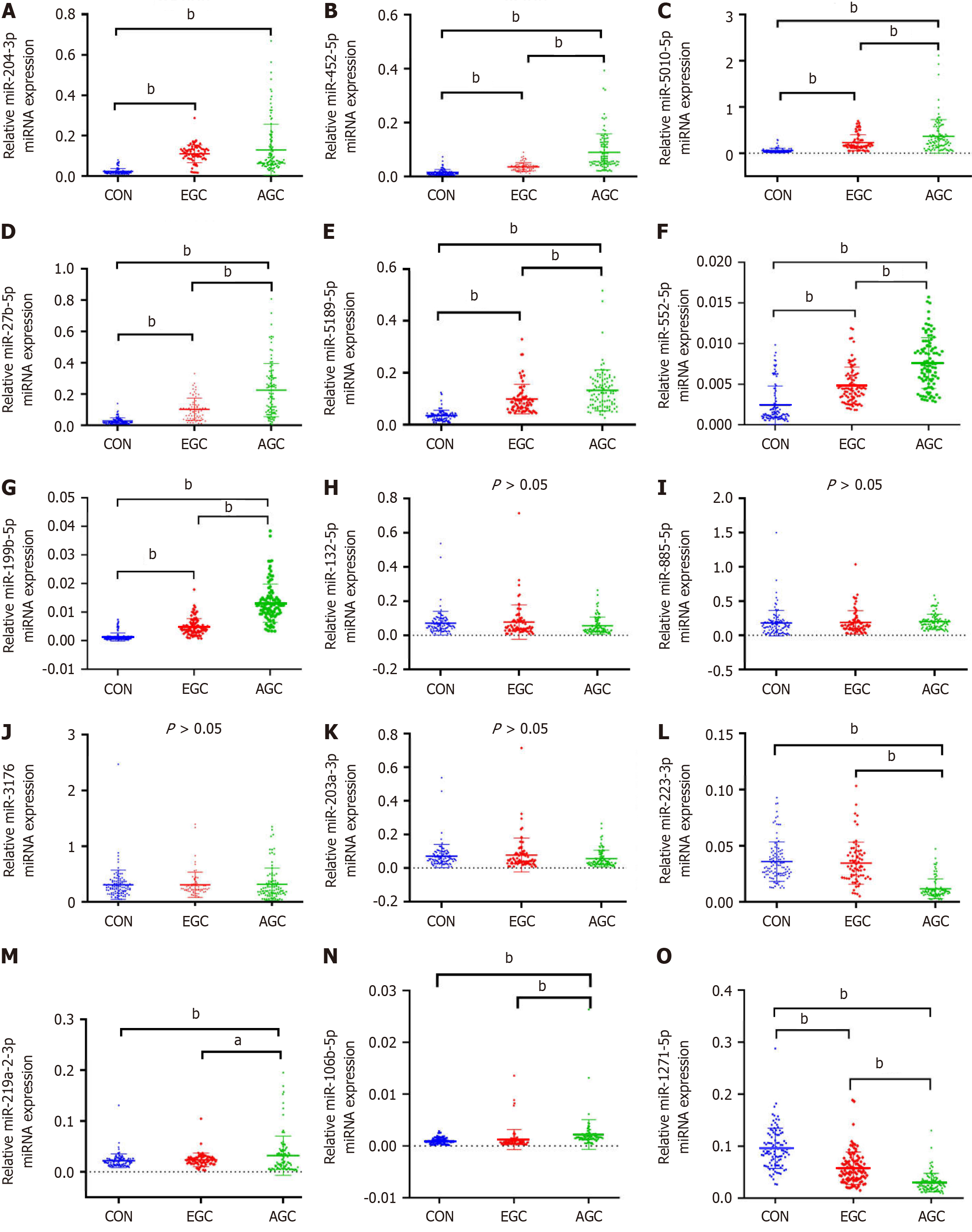
Figure 2 Expression of miRNAs in the three groups.
A: miR-204-3p; B: miR-452-5p; C: miR-5010-5p; D: miR-27b-5p; E: miR-5189-5p; F: miR-552-5p; G: miR-199b-5p; H: miR-132-5p; I: miR-885-5p; J: miR-3176; K: miR-203a-3p; L: miR-223-3p; M: miR-219a-2-3p; N: miR-106b-5p; O: miR-1271-5p. aP < 0.05. bP < 0.01. CON: A group including 107 control samples; EGC: A group including 71 early gastric cancer samples; AGC: A group including 97 advanced gastric cancer samples.
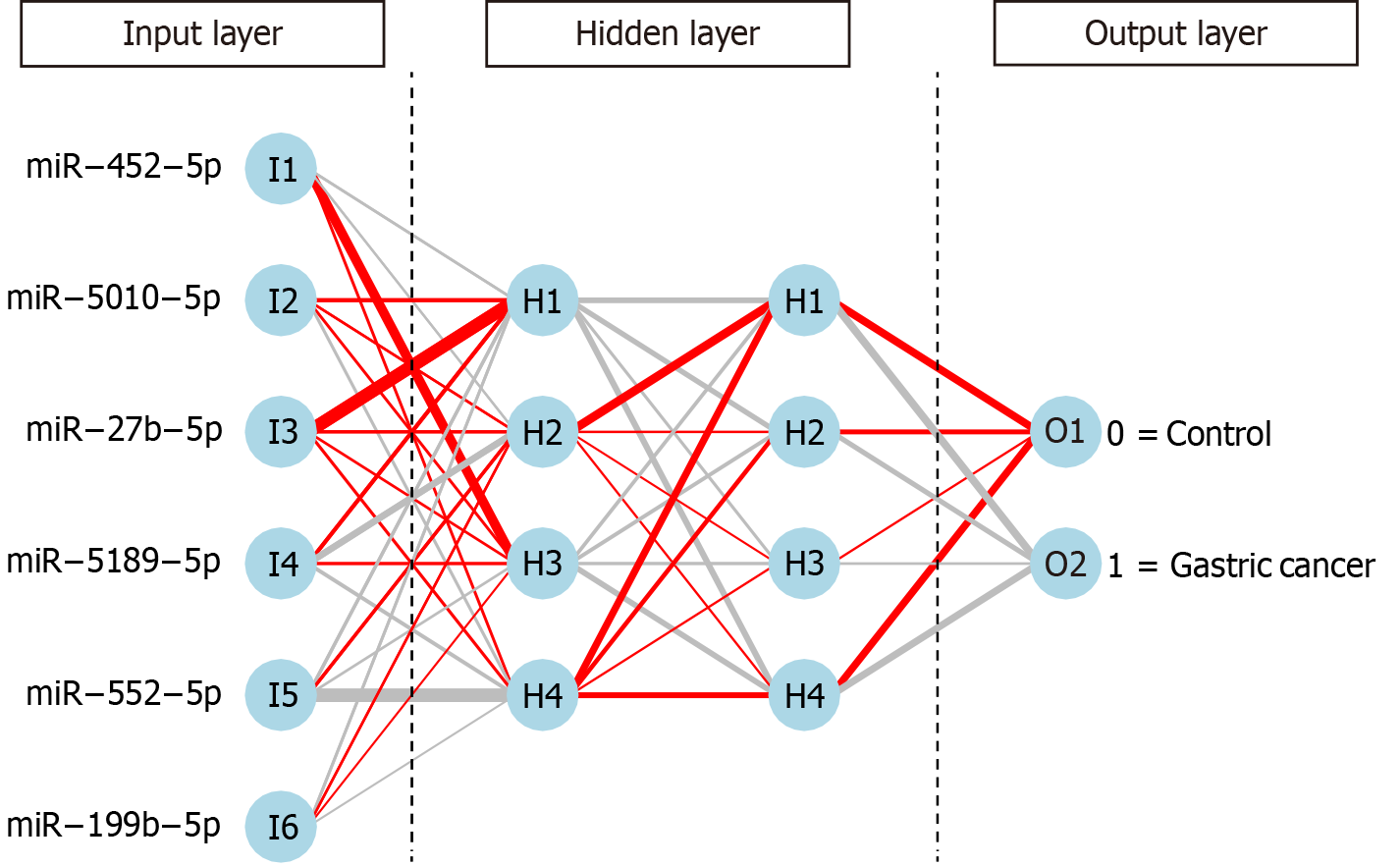
Figure 3
Six-miRNA artificial neural network model.
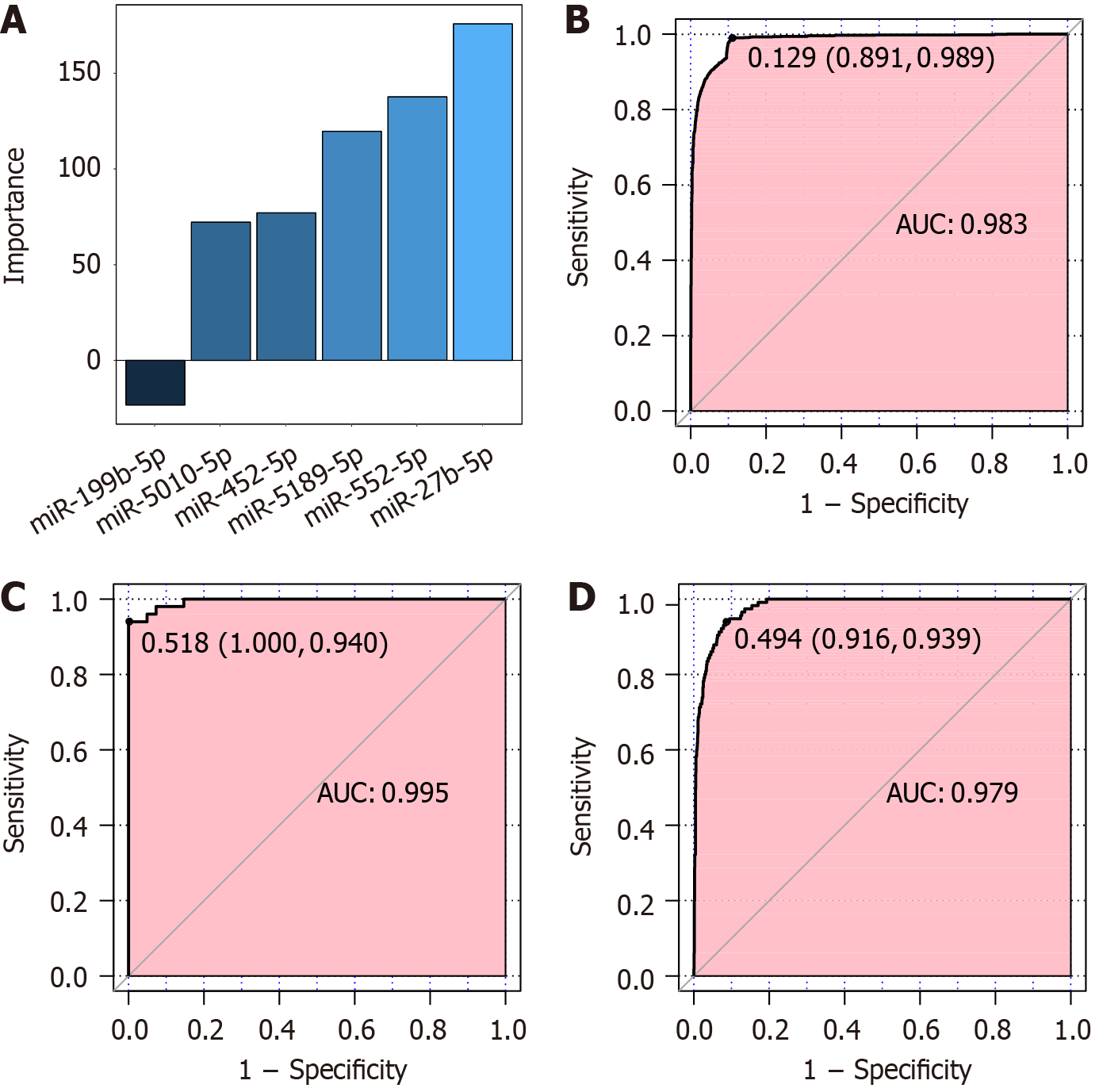
Figure 4 Important variables and receiver operating characteristic analysis of the six-microRNA artificial neural network model.
A: Importance analysis of six risk-related miRNAs; B: Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve of cohort-3; C: ROC curve of cohort-4; D: ROC curve of cohort-5. AUC: Area under the curve.
- Citation: Ma FC, Zhang GL, Chi BT, Tang YL, Peng W, Liu AQ, Chen G, Gao JB, Wei DM, Ge LY. Blood-based machine learning classifiers for early diagnosis of gastric cancer via multiple miRNAs. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2025; 17(4): 103679
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v17/i4/103679.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v17.i4.103679