Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Feb 15, 2025; 17(2): 98556
Published online Feb 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i2.98556
Published online Feb 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i2.98556
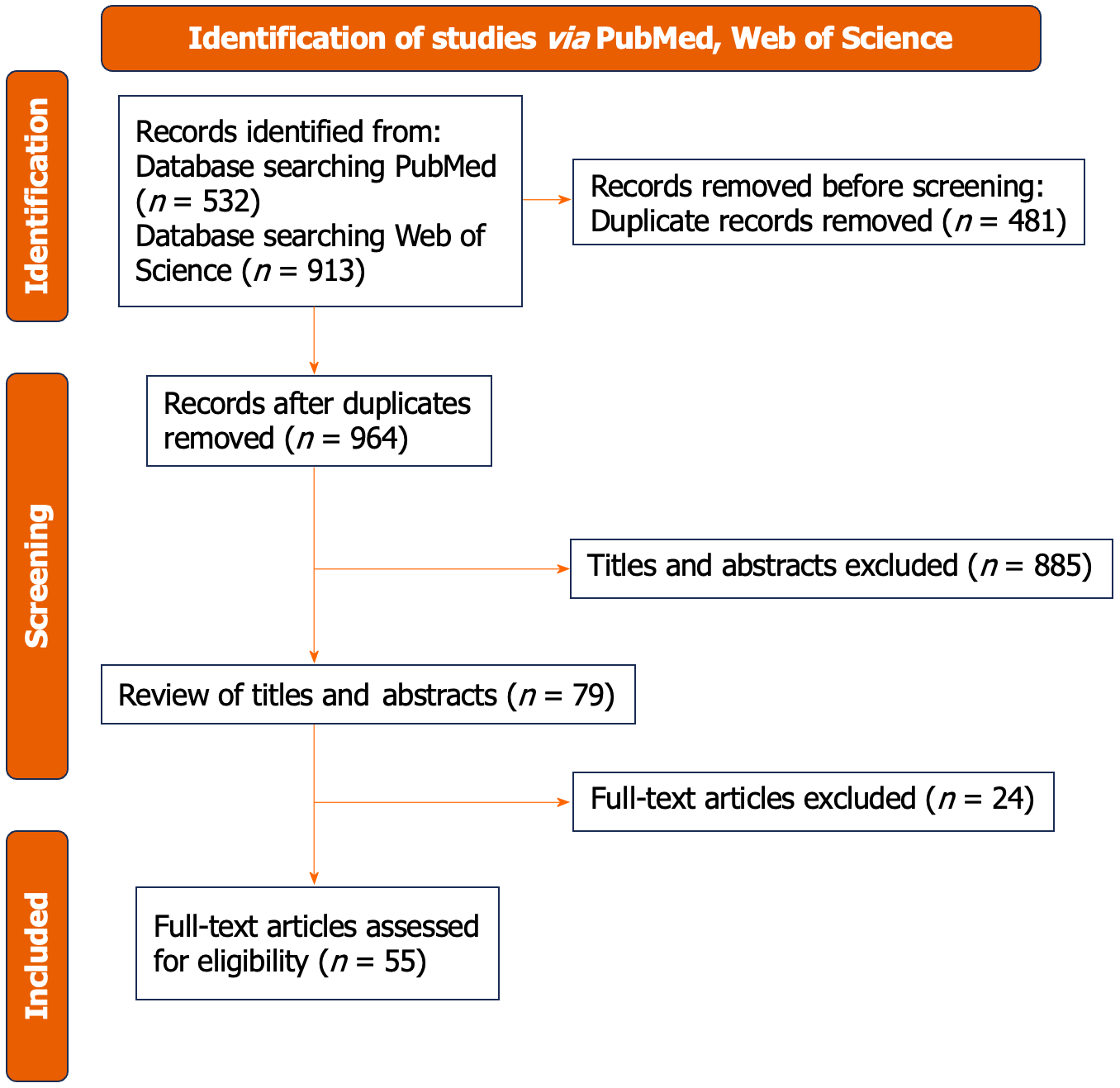
Figure 1 Selection process diagram.
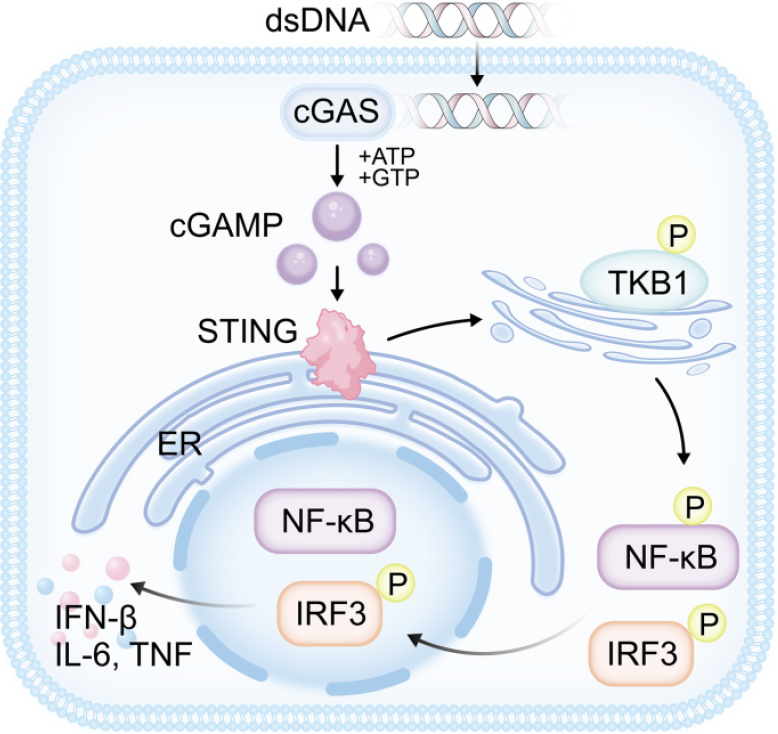
Figure 2 Molecular mechanism of cyclic guanosine monophosphate-adenosine monophosphate synthase-stimulator of interferon gene signalling.
Cyclic guanosine monophosphate-adenosine monophosphate synthase (cGAS) is an integral protein responsible for detecting a diverse array of cytosolic double-stranded DNA (dsDNA). Upon binding to dsDNA, cGAS utilizes adenosine triphosphate and guanosine triphosphate as substrates to catalyze the synthesis of cyclic guanosine monophosphate-adenosine monophosphate, serving as a crucial second messenger that activates stimulator of interferon gene (STING). Subsequently, STING undergoes translocation from the endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi compartments, where it orchestrates the recruitment of kinases such as TANK-binding kinase 1 (TBK1) and IκB kinase. These kinases, in turn, catalyze the phosphorylation of interferon regulatory factor 3 (IRF3) and the nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) inhibitor, IκBα. Phosphorylated IRF3 transits to the nucleus, prompting the transcription of type I interferon genes. Concurrently, phosphorylated IκBα engages NF-κB, initiating the transcription of genes that encode proinflammatory cytokines. dsDNA: Double-stranded DNA; cGAS: Cyclic guanosine monophosphate-adenosine monophosphate synthase; cGAMP: Cyclic guanosine monophosphate-adenosine monophosphate; ATP: Adenosine triphosphate; GTP: Guanosine triphosphate; STING: Stimulator of interferon gene; NF-κB: Nuclear factor-κB; TKB1: TANK binding kinase 1; IRF3: I nterferon regulatory factor 3; ER: Endoplasmic reticulum; IFN: Interferon; IL: Interleukin; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor.
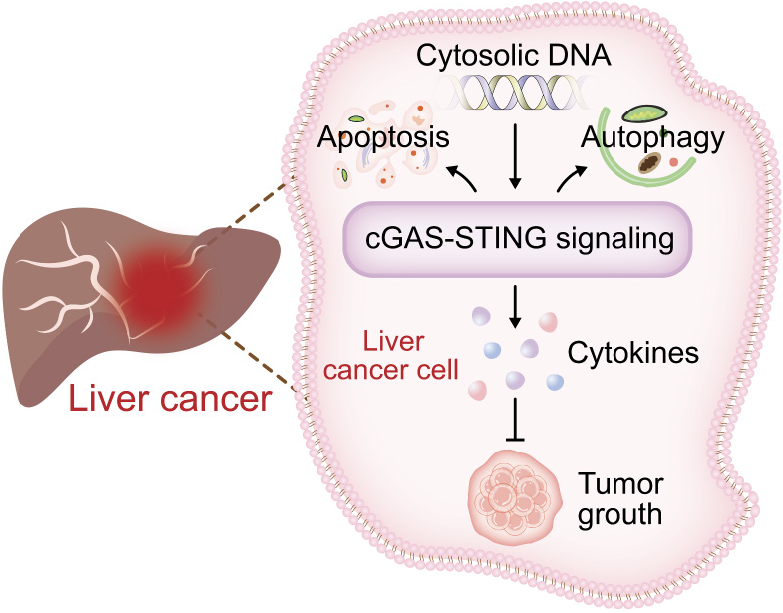
Figure 3 The role of the cyclic guanosine monophosphate-adenosine monophosphate synthase-stimulator of interferon gene signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma.
The pivotal role of the cyclic guanosine monophosphate-adenosine monophosphate synthase-stimulator of interferon gene (cGAS-STING) signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is profound. When DNA damage occurs within HCC cells, it triggers the formation of double-stranded DNA. This, in turn, stimulates and activates the cGAS-STING signaling cascade, ultimately inducing autophagy and activating the apoptotic process. Furthermore, this pathway facilitates the release of cytokines, which subsequently elicits a robust systemic antitumor immune response. This immune response is instrumental in controlling both local and distant metastasis, thereby mitigating the progression of tumor growth.
- Citation: Nie AY, Xiao ZH, Deng JL, Li N, Hao LY, Li SH, Hu XY. Bidirectional regulation of the cyclic guanosine monophosphate-adenosine monophosphate synthase-stimulator of interferon gene pathway and its impact on hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2025; 17(2): 98556
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v17/i2/98556.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v17.i2.98556