Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Feb 15, 2025; 17(2): 97858
Published online Feb 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i2.97858
Published online Feb 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i2.97858
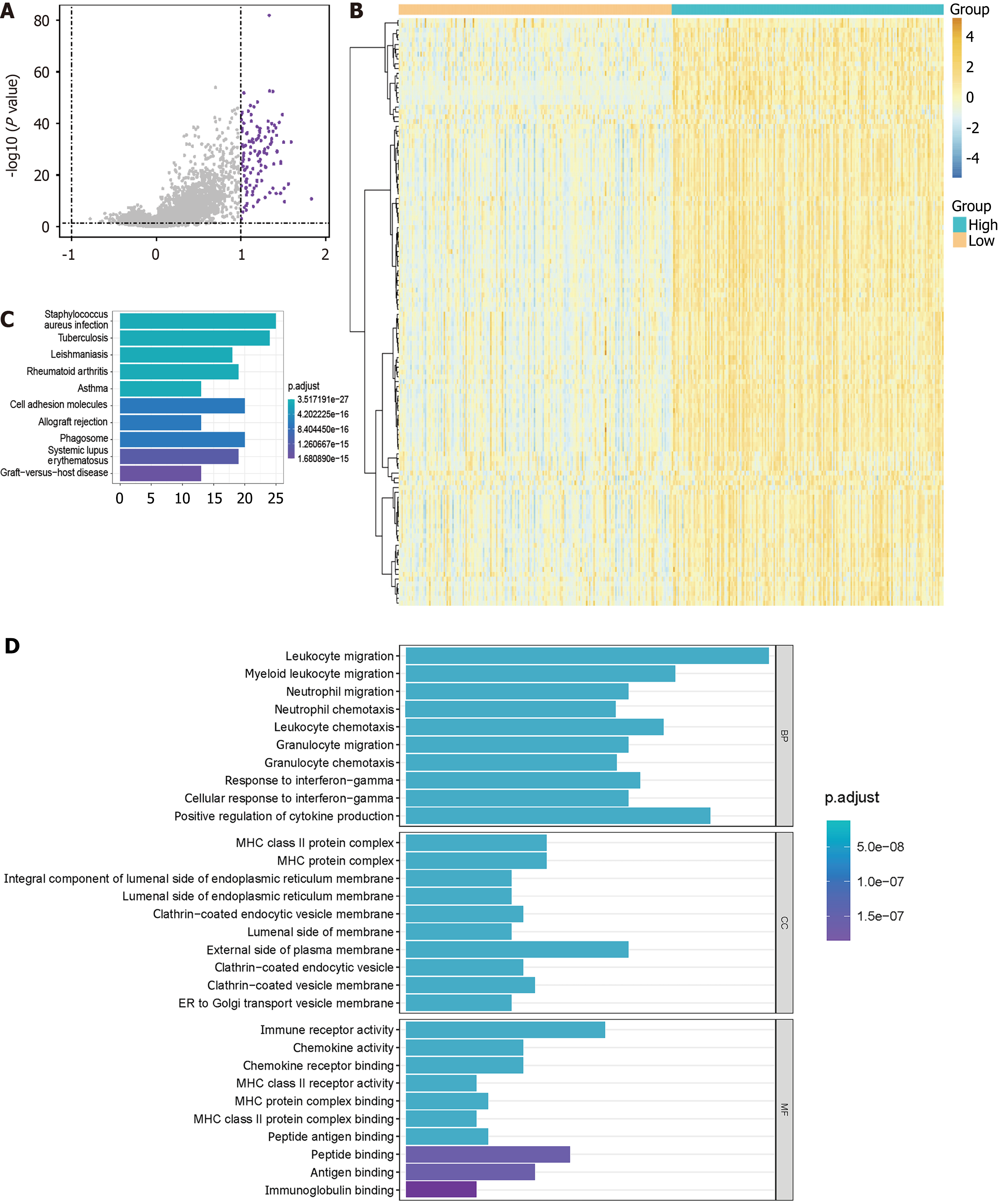
Figure 1 Analysis of differentially expressed genes between patients with high and low colony-stimulating factor 3 receptor expression.
A: Volcano plots of differentially expressed genes (DEGs); B: Heatmap of DEGs; C: Enrichment analysis of DEGs by Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes; D: Enrichment analysis of DEGs by Gene Ontology.
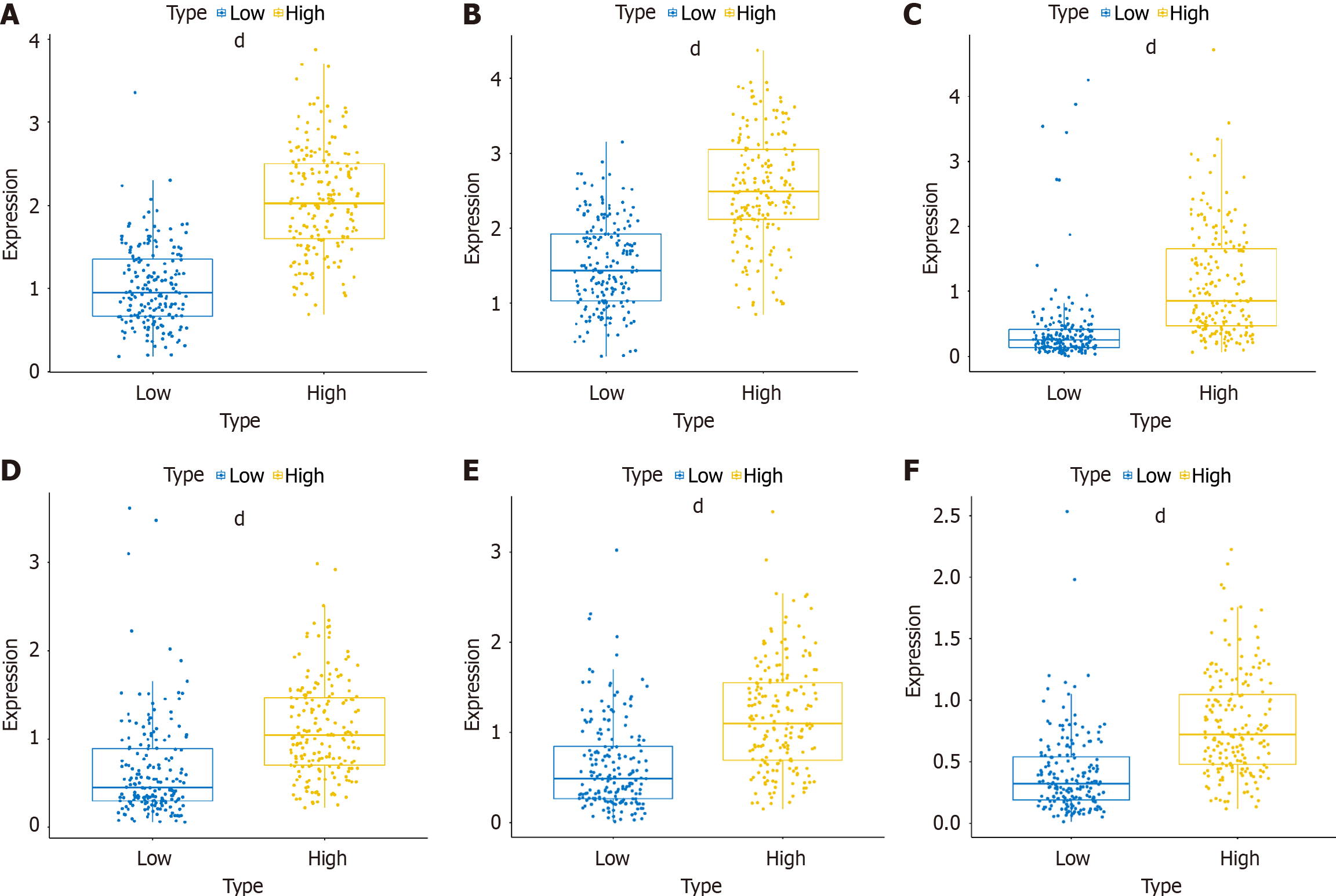
Figure 2 Immune checkpoints showing the most significant differences between high and low colony-stimulating factor 3 expression groups.
A: Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor B2; B: Hepatitis A virus cellular receptor 2; C: Chemokine receptor 2; D: CD80; E: Inducible T-cell costimulator; F: CD28. dP < 0.0001.
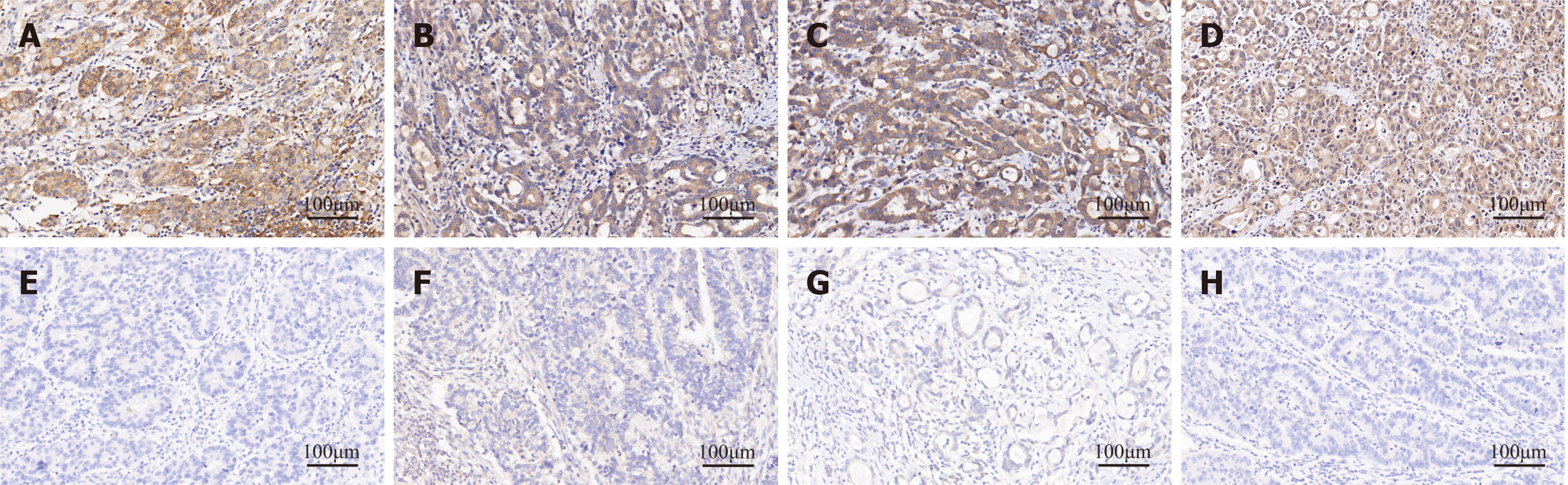
Figure 3 Immunohistochemical staining of gastric cancer tissues (200 ×).
A: Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor B2 (high expression); B: Angiopoietin-like protein 2 (high expression); C: Human leukocyte antigen-G (high expression); D: Colony-stimulating factor 3 receptor (high expression); E: Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor B2 (low expression); F: Angiopoietin-like protein 2 (low expression); G: Human leukocyte antigen-G (low expression); H: Colony-stimulating factor 3 receptor (low expression).
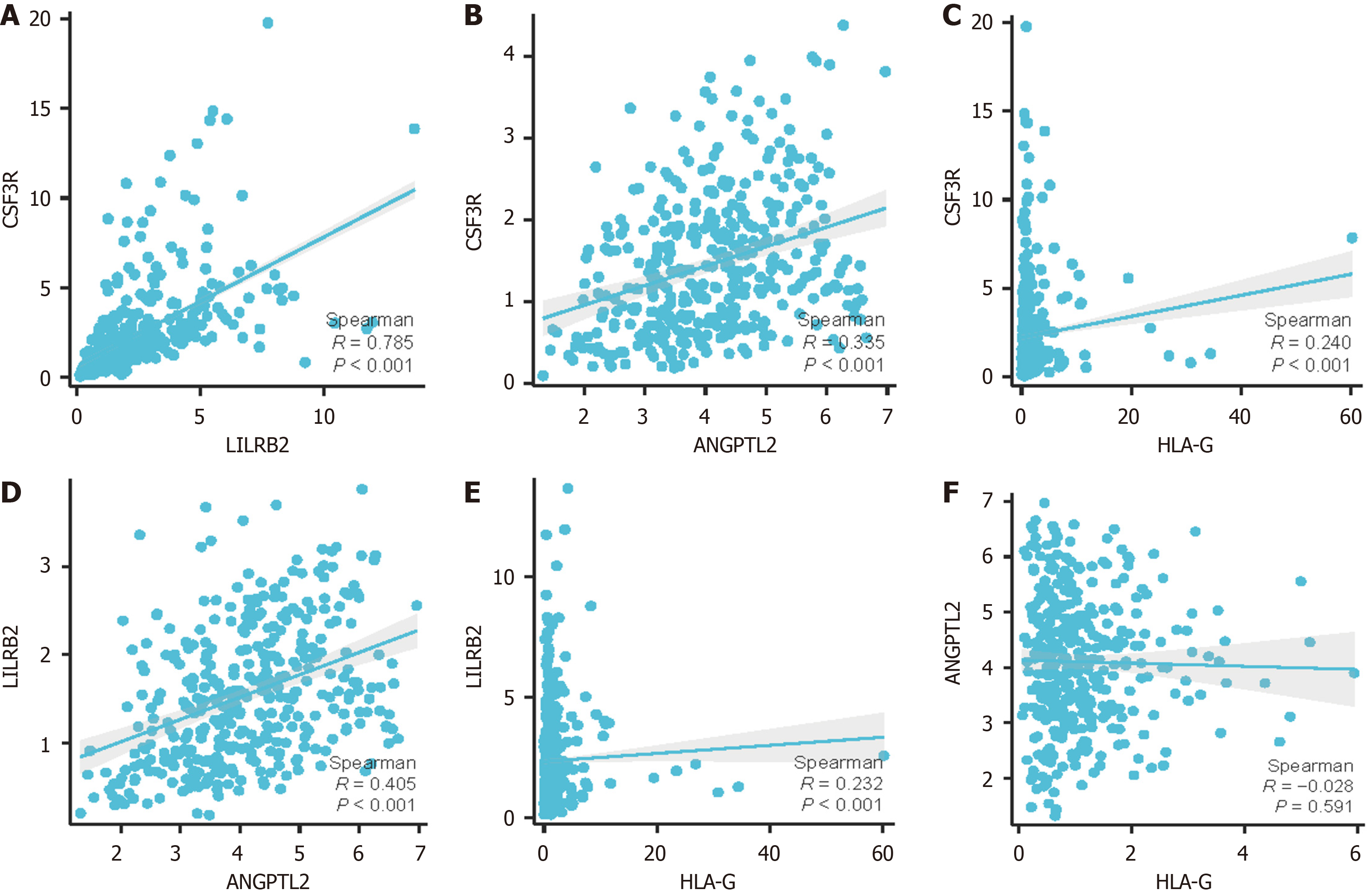
Figure 4 Correlation of mRNA expression.
A-F: Correlation of mRNA expression levels between colony-stimulating factor 3 receptor, leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor B2, angiopoietin-like protein 2, and human leukocyte antigen-G. CSF3R: Colony-stimulating factor 3 receptor; LILRB2: Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor B2; ANGPTL2: Angiopoietin-like protein 2; HLA-G: Human leukocyte antigen-G.
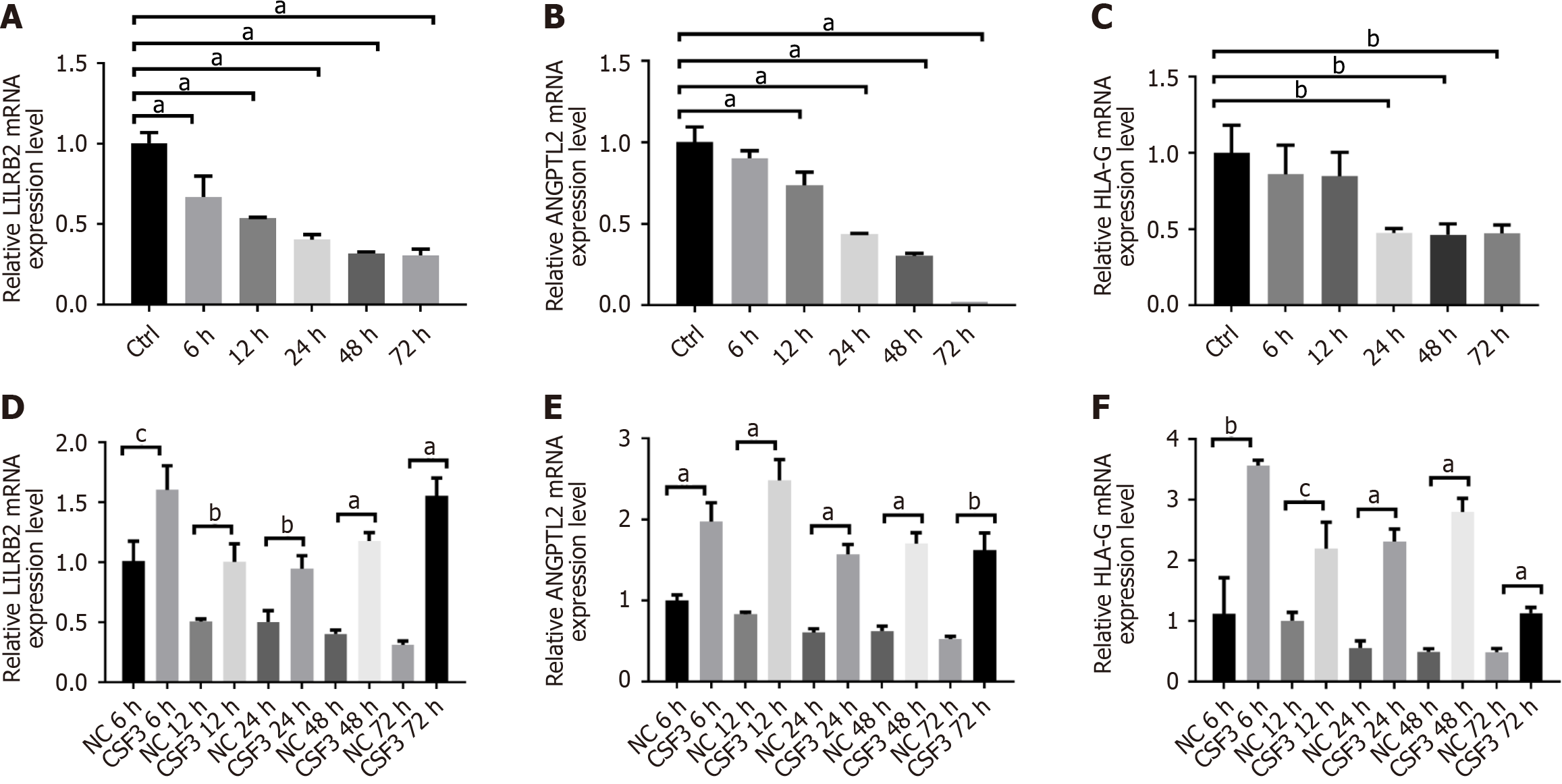
Figure 5 The mRNA expression of leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor B2, angiopoietin-like protein 2, and human leukocyte antigen-G.
A-C: The mRNA expression levels at different time points; D-F: The mRNA expression levels at different time points after administration of colony-stimulating factor 3 compared with control groups. aP < 0.001; bP < 0.01; cP < 0.05. LILRB2: Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor B2; ANGPTL2: Angiopoietin-like protein 2; HLA-G: Human leukocyte antigen-G; CSF3: Colony-stimulating factor 3; NC: Negative control.
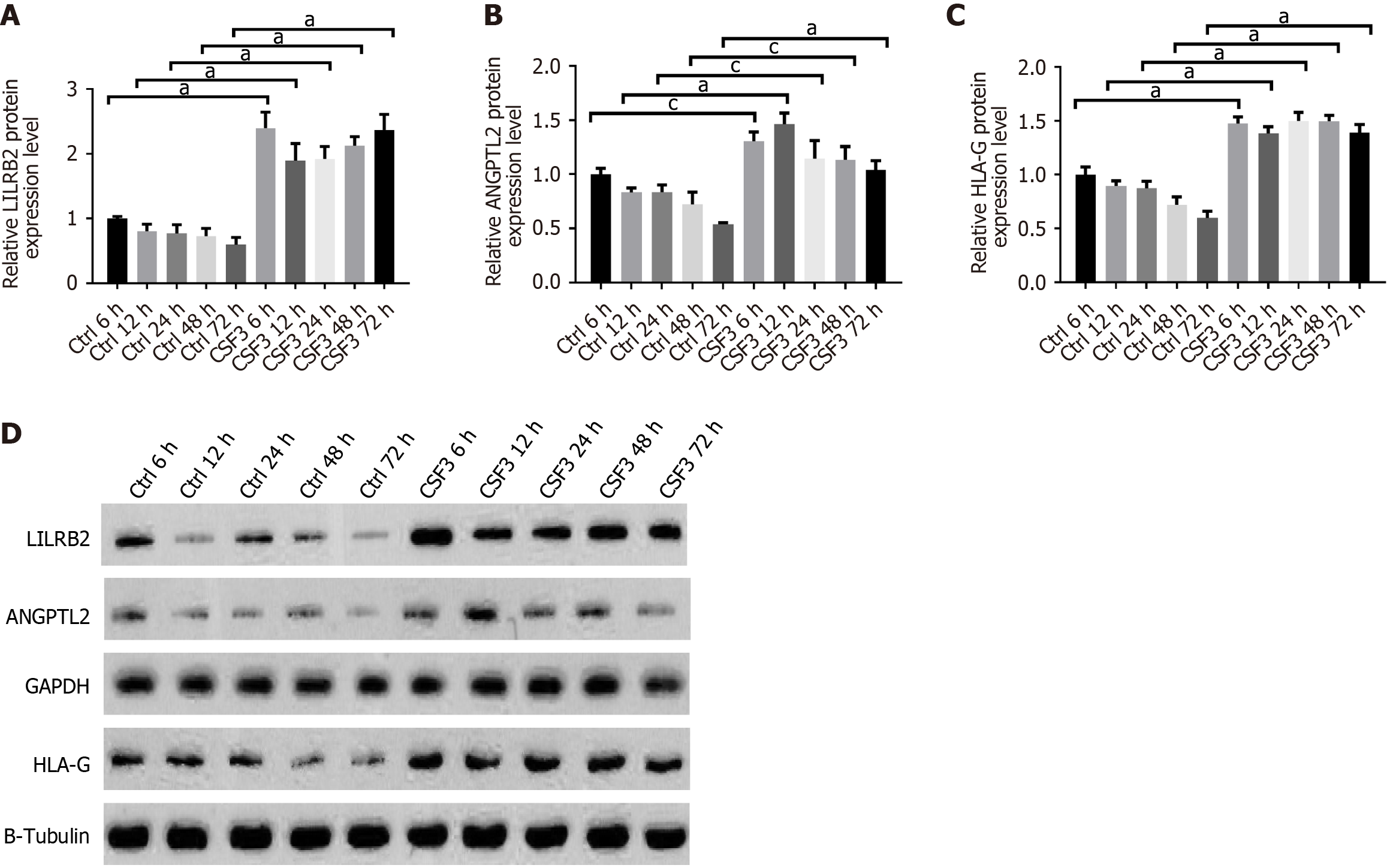
Figure 6 Protein expression of leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor B2, angiopoietin-like protein 2, and human leukocyte antigen-G at different time points after administration of colony-stimulating factor 3 compared with control groups.
A-C: Protein expression levels at different time points. D: Protein expression at different time points. aP < 0.001; cP < 0.05. LILRB2: Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor B2; ANGPTL2: Angiopoietin-like protein 2; HLA-G: Human leukocyte antigen-G; CSF3: Colony-stimulating factor 3.
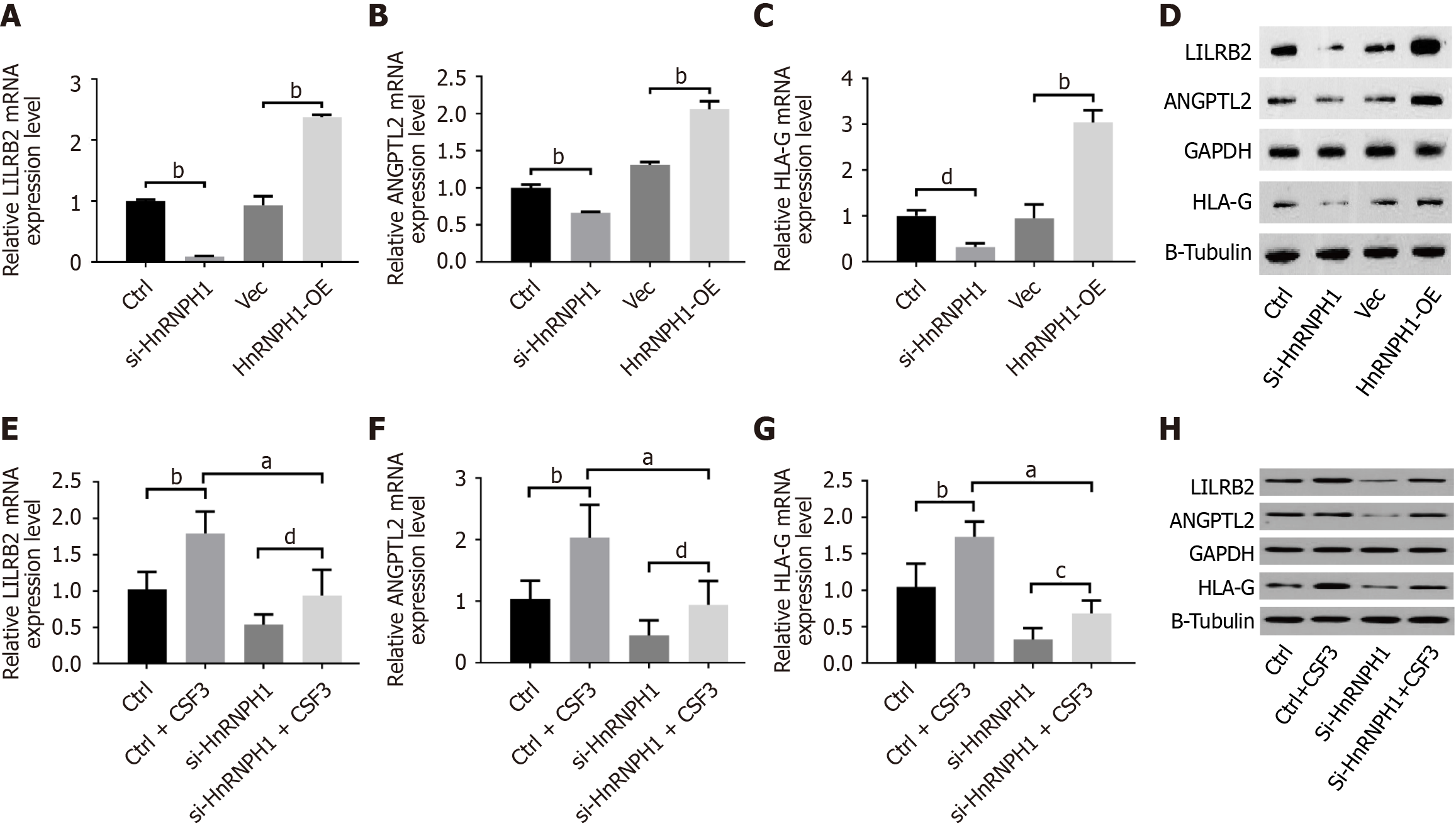
Figure 7 Colony-stimulating factor/colony-stimulating factor 3 receptor regulates the expression of leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor B2, angiopoietin-like protein 2, and human leukocyte antigen-G through heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein H1.
A-C: The mRNA expression levels when heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein H1 (hnRNPH1) expression is downregulated or upregulated; D: Protein expression levels when hnRNPH1 expression is downregulated or upregulated; E-G: The mRNA expression levels when hnRNPH1 expression is downregulated with or without colony-stimulating factor 3 stimulation; H: Protein expression levels when hnRNPH1 expression is downregulated with or without colony-stimulating factor 3 stimulation. aP < 0.0001; bP < 0.001; cP < 0.01; dP < 0.05. LILRB2: Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor B2; ANGPTL2: Angiopoietin-like protein 2; HLA-G: Human leukocyte antigen-G; hnRNPH1: heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein H1; CSF3R: Colony-stimulating factor 3 receptor.
- Citation: Wang L, Wu Q, Zhang ZW, Zhang H, Jin H, Zhou XL, Liu JY, Li D, Liu Y, Fan ZS. Colony-stimulating factor 3 and its receptor promote leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor B2 expression and ligands in gastric cancer. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2025; 17(2): 97858
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v17/i2/97858.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v17.i2.97858