Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Feb 15, 2025; 17(2): 100954
Published online Feb 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i2.100954
Published online Feb 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i2.100954
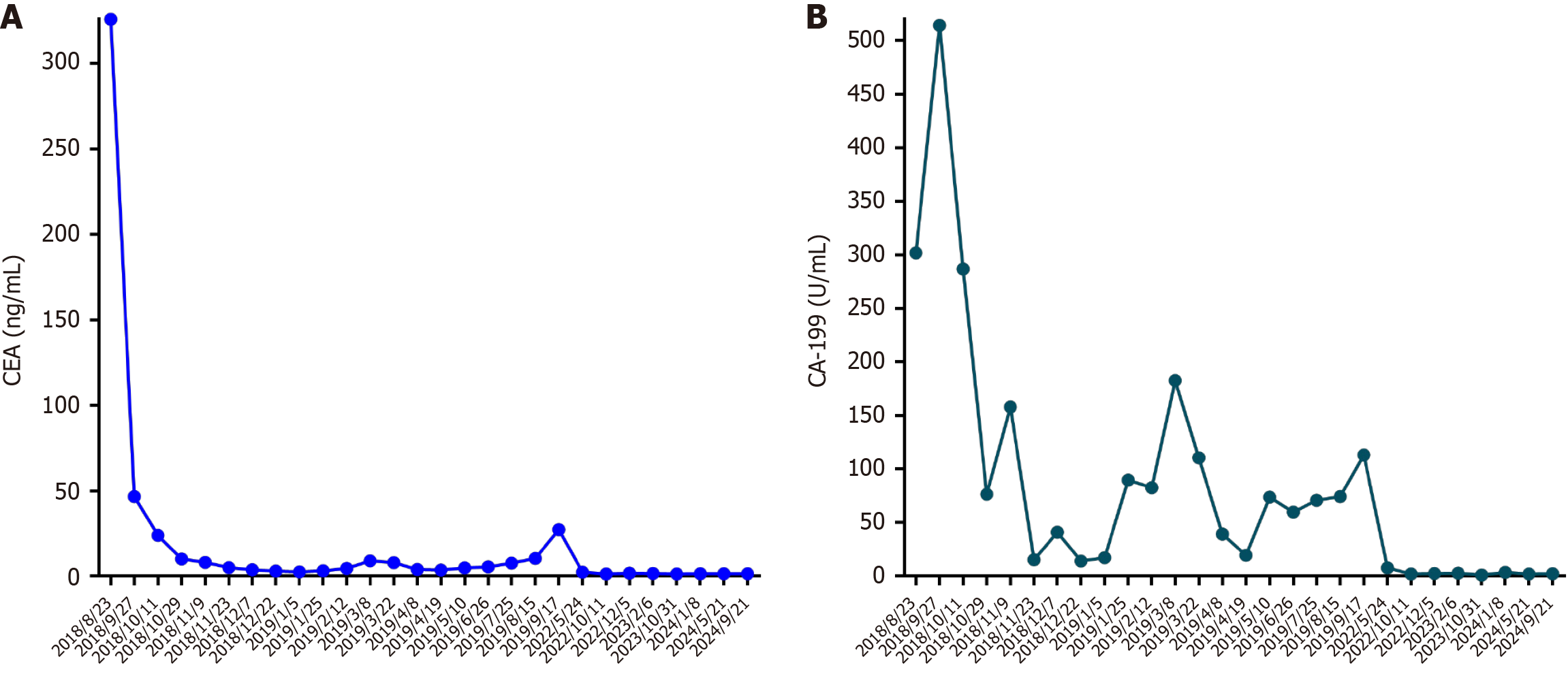
Figure 1 Tumor markers.
A: Carcinoembryonic antigen; B: Carbohydrate antigen 199. CEA: Carcinoembryonic antigen; CA-199: Carbohydrate antigen 199.
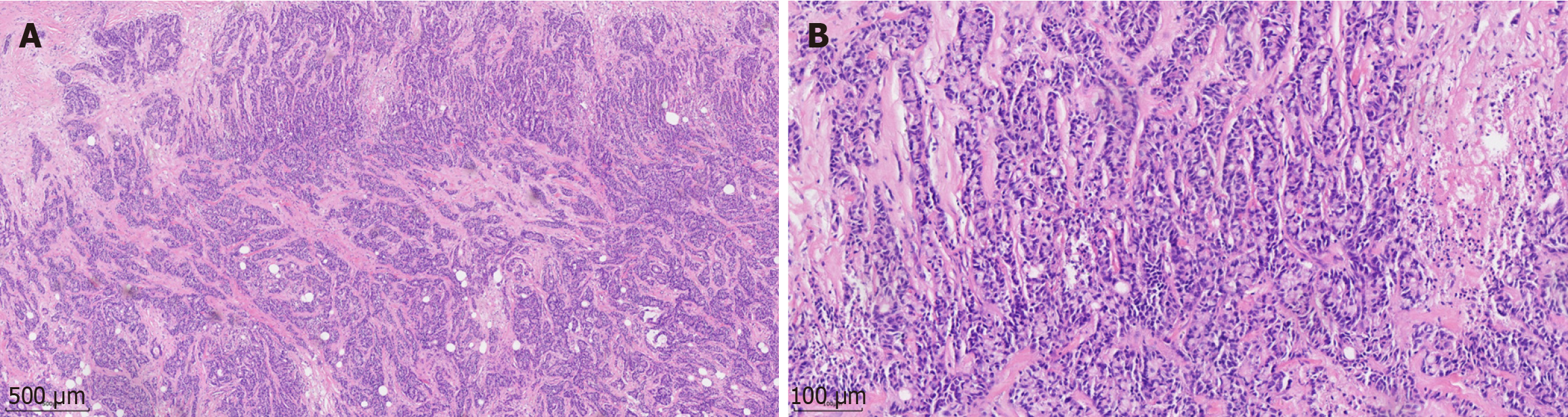
Figure 2 Pathological examination of the ileocecal region of the resected right colon mass specimen (hematoxylin and eosin staining).
A: Original magnification, × 10; B: Original magnification, × 40.
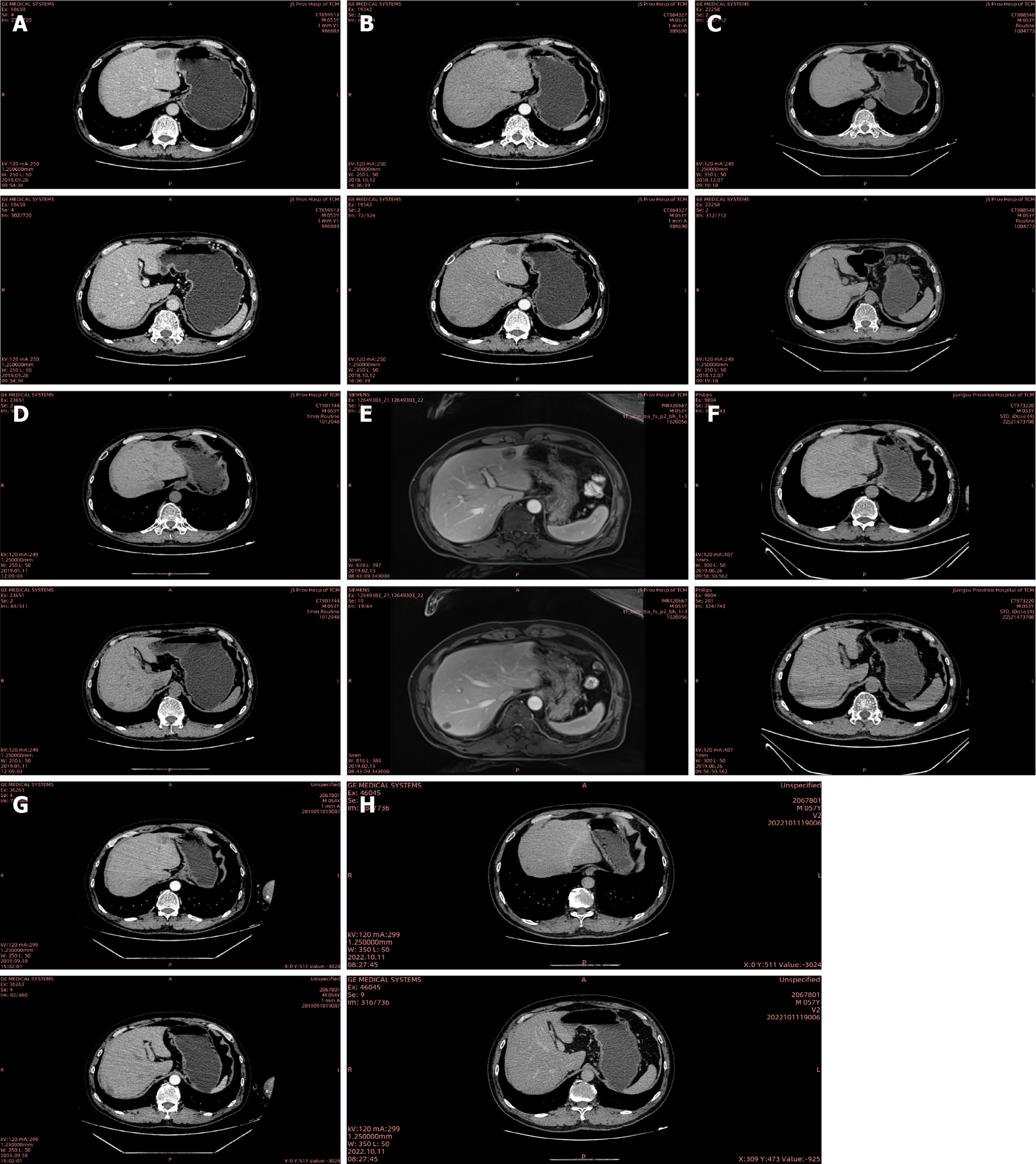
Figure 3 Radiologic images of computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging.
A: September 28, 2018 computed tomography (CT) imaging [colorectal liver metastasis (CRLM) 27 mm]; B: October 12, 2018 CT imaging (CRLM 23 mm × 13 mm); C: December 7, 2018 CT imaging (CRLM 20 mm × 12 mm); D: January 11, 2019 CT imaging (CRLM 23 mm × 16 mm); E: February 13, 2019 magnetic resonance imaging (CRLM 25 mm); F: June 26, 2019 CT imaging (CRLM 24 mm × 27 mm); G: September 18, 2019 CT imaging (CRLM 25 mm × 30 mm); H: October 11, 2022 CT imaging (CRLM not observed). R: Right; L: Left; A: Anterior; P: Posterior; S: Superjacent; I: Inferior.
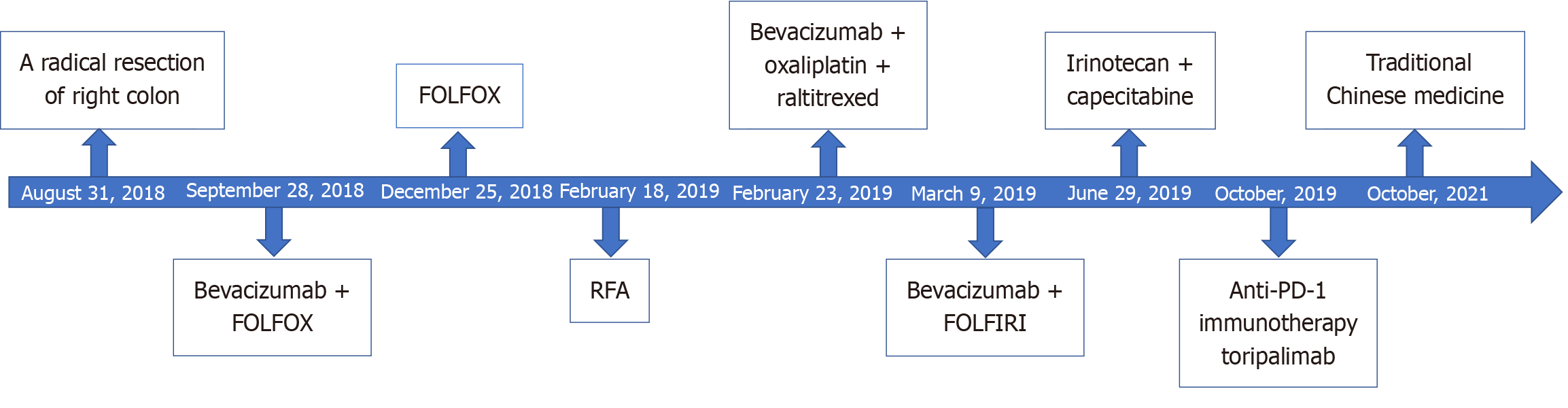
Figure 4 The entire treatment process in this patient.
RFA: Radiofrequency ablation; PD-1: Programmed death-1.
- Citation: Guo TH, Hong SW, Zhu WJ, Hui YF, Qiu WL, Wu Y, Li X, Ke F, Li L, Cheng HB. Anti-programmed death-1 immunotherapy-promising treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer: A case report. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2025; 17(2): 100954
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v17/i2/100954.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v17.i2.100954