Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Feb 15, 2025; 17(2): 100724
Published online Feb 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i2.100724
Published online Feb 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i2.100724
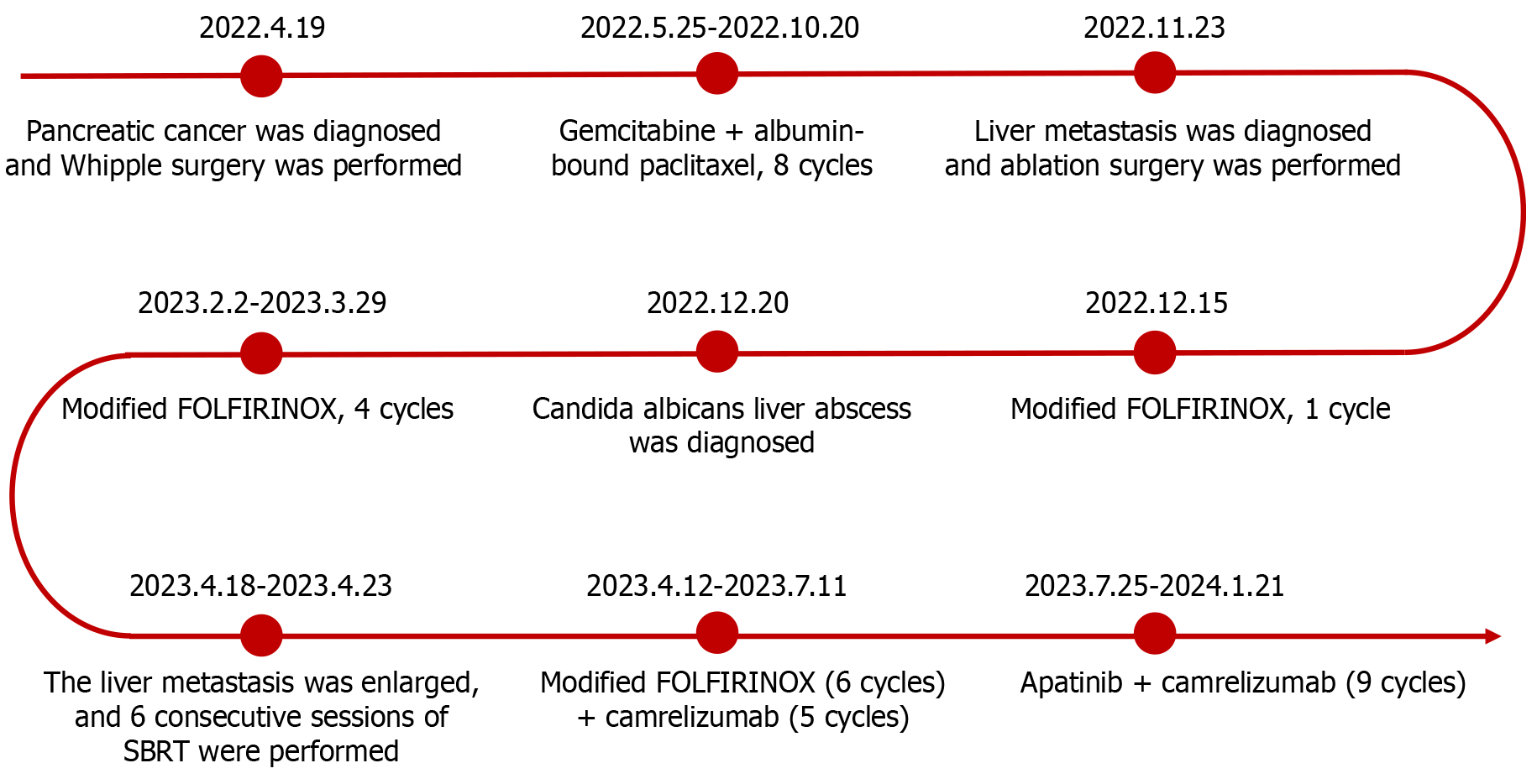
Figure 1
Anticancer regimens and courses of treatment for the patient at different stages of the disease.
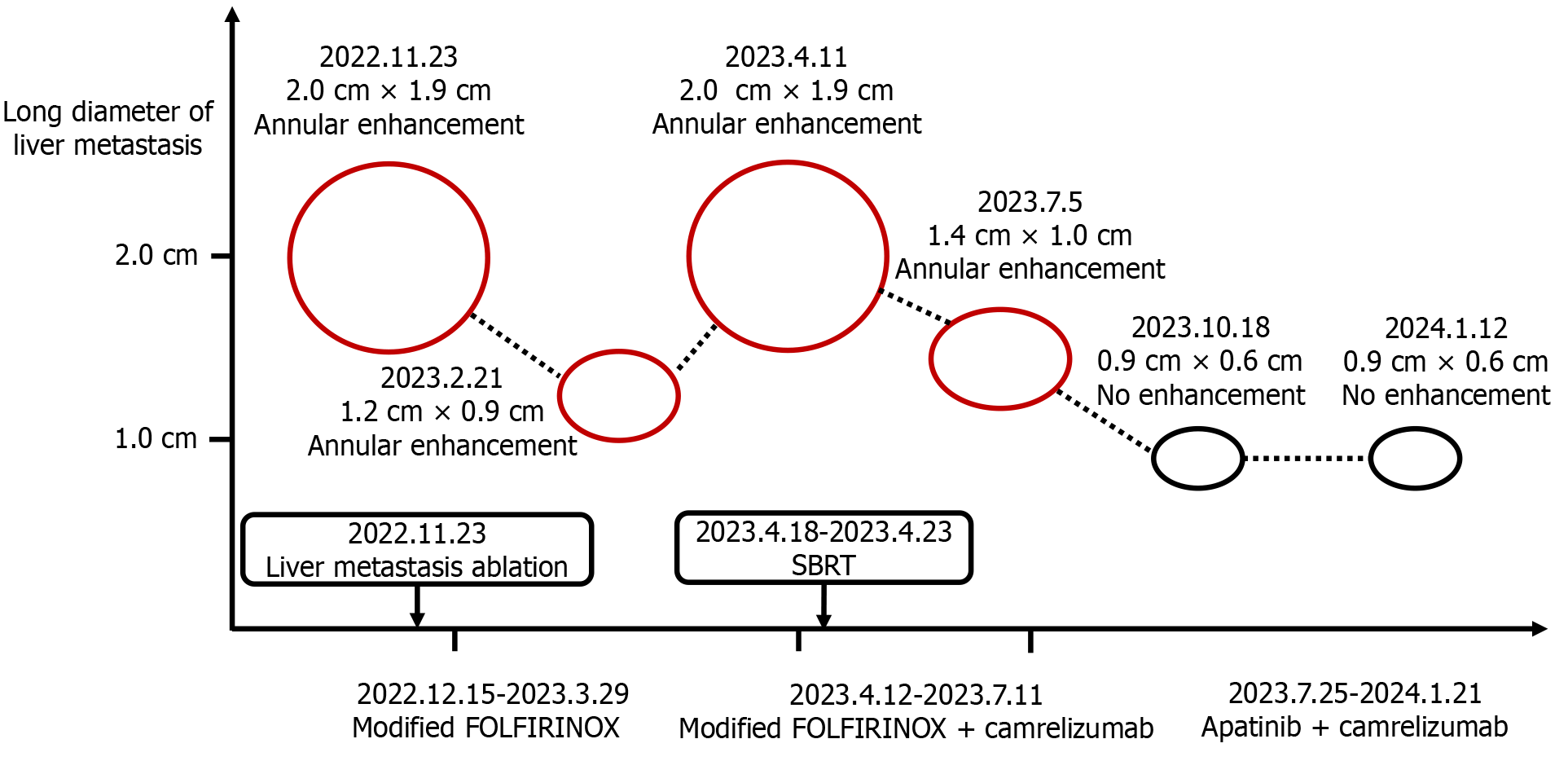
Figure 2 Imaging changes in liver metastasis in the patient receiving different anticancer regimens.
Following treatment with camrelizumab in combination with apatinib, enhanced abdominal magnetic resonance imaging revealed no increase in size or enhancement of the liver metastasis.
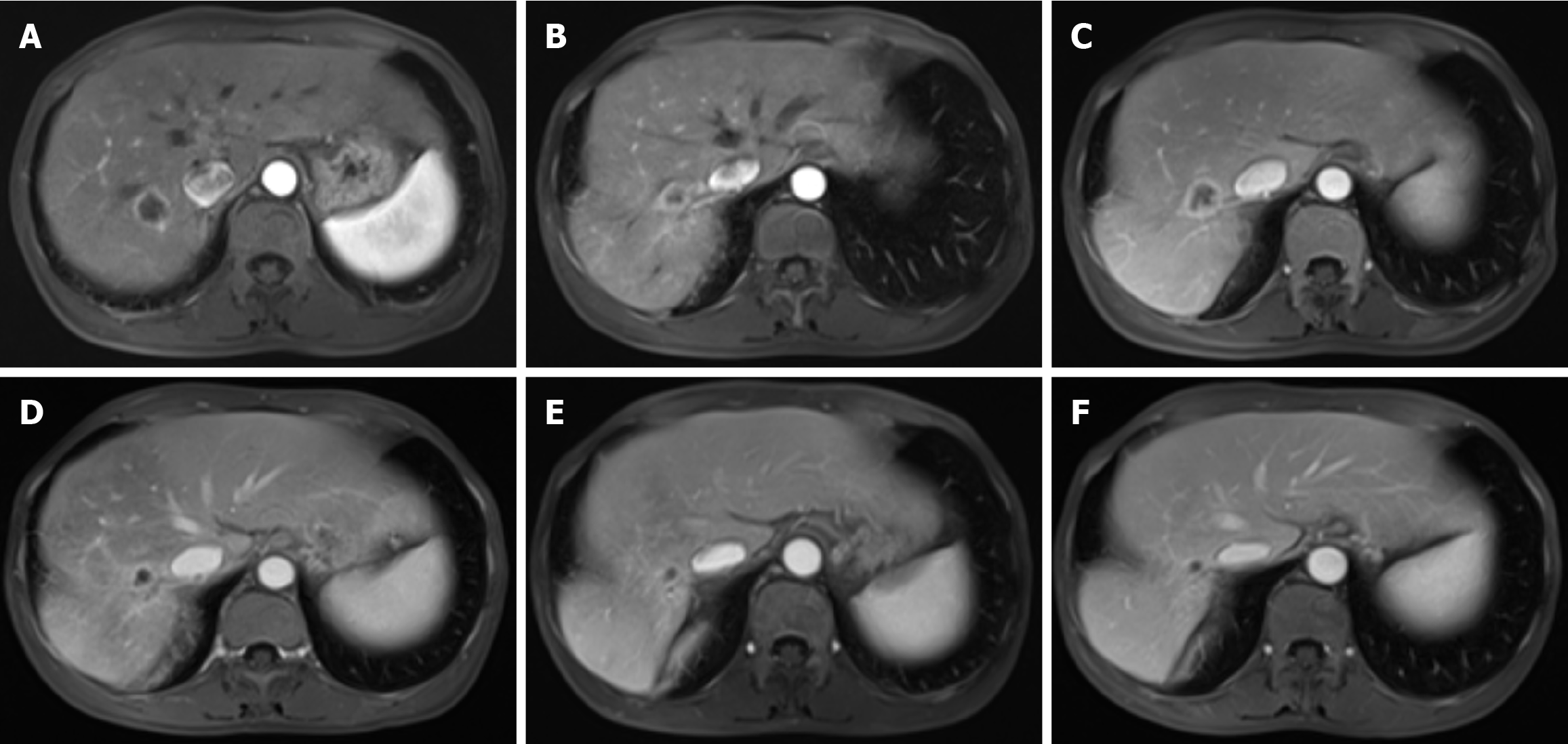
Figure 3 Magnetic resonance imaging of liver metastasis during different anticancer treatment regimens.
A: On November 23, 2022, an enhanced abdominal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) revealed a nodular lesion in the right posterior lobe of the liver, with a maximum cross-section of 2.0 cm × 1.9 cm. The lesion exhibited annular enhancement, indicative of a metastatic lesion; B: On February 21, 2023, follow-up MRI revealed a decrease in the size of the nodular lesion to 1.2 cm × 0.9 cm, with persistent annular enhancement; C: On April 11, 2023, MRI revealed an increase in the size of the lesion to 2.0 cm × 1.9 cm, maintaining annular enhancement; D: On July 5, 2023, the lesion was observed to have decreased in size again, measuring 1.4 cm × 1.0 cm, with annular enhancement still present; E: On October 18, 2023, the MRI showed a further reduction in lesion size to 0.9 cm × 0.6 cm, and no enhancement was noted; F: On January 12, 2024, the final MRI revealed no change in lesion size, remaining at 0.9 cm × 0.6 cm, and no enhancement was observed.
- Citation: Luo YH, He T, Lin L, Wang RQ, Cai HX, Hu W. Advanced pancreatic cancer treated with camrelizumab combined with apatinib: A case report. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2025; 17(2): 100724
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v17/i2/100724.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v17.i2.100724