Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Sep 15, 2024; 16(9): 3781-3797
Published online Sep 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i9.3781
Published online Sep 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i9.3781
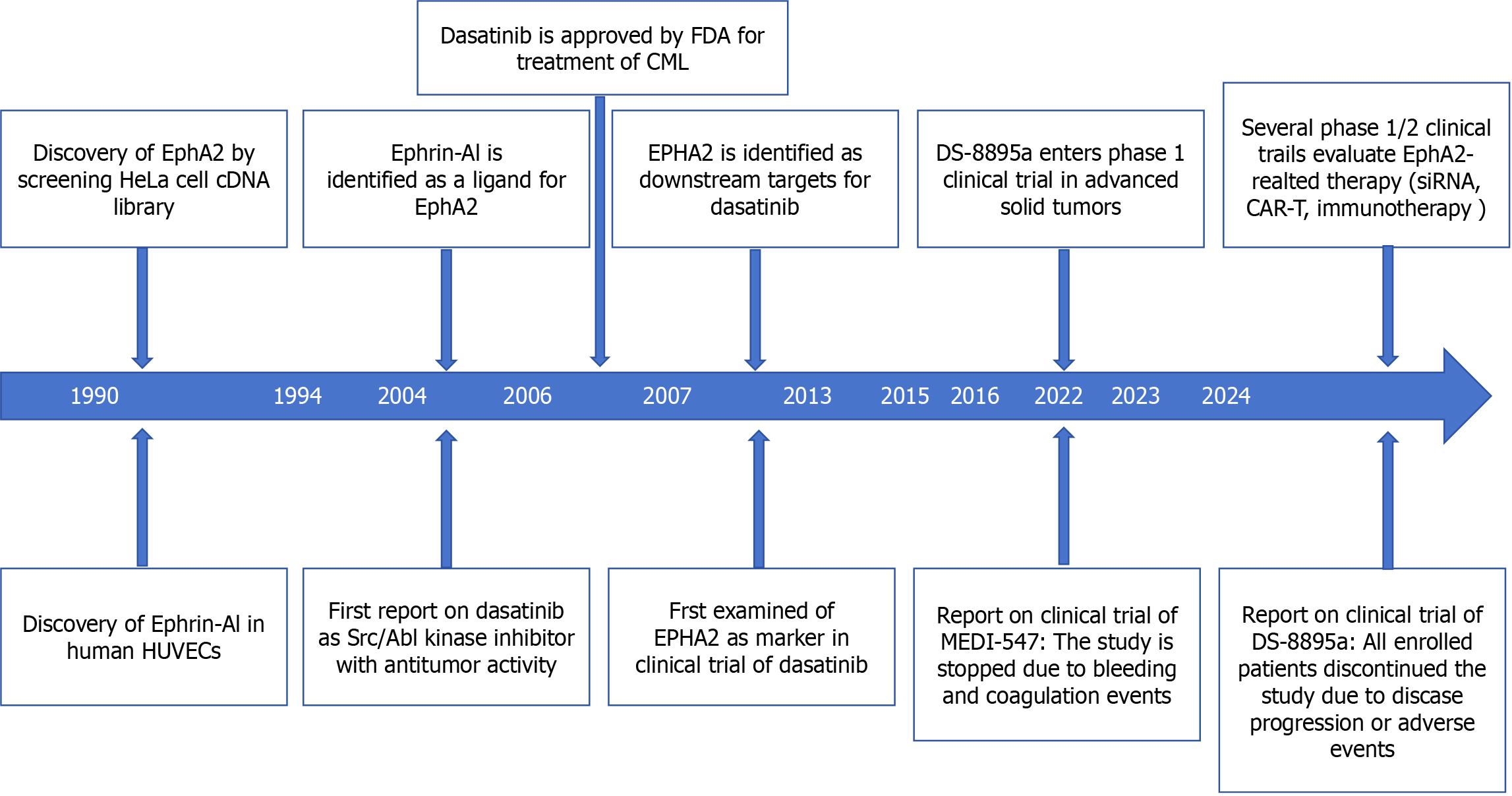
Figure 1 Timeline summary of erythropoietin-induced hepatocyte receptor A2-related research.
Created by the BioRender. EphA2: Erythropoietin-induced hepatocyte receptor A; FDA: Food and Drug Administration; CML: Chronic myeloid leukemia; siRNA: Small interfering RNA; CAR-T: Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy; HUVECs: Human umbilical vein endothelial cells.
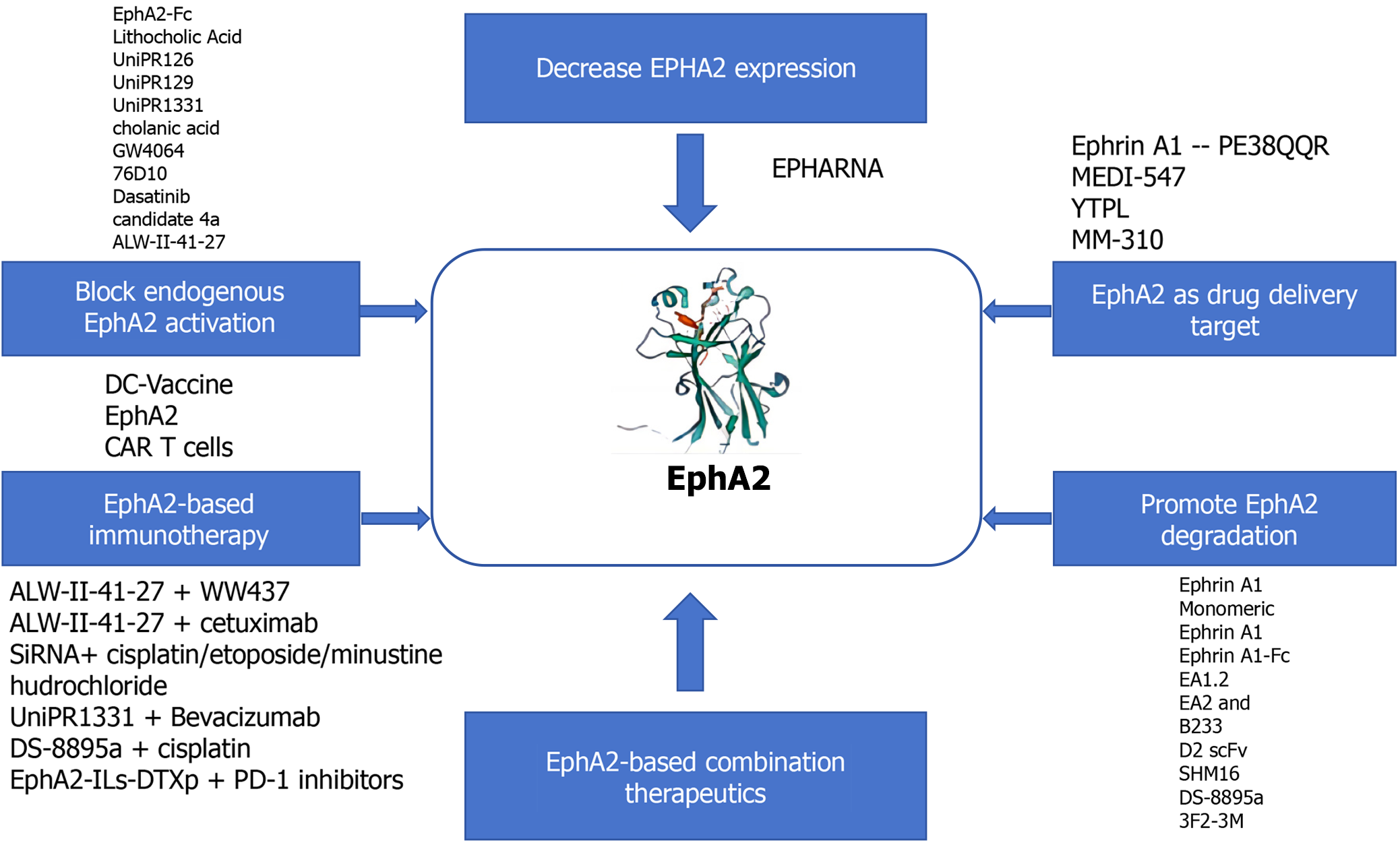
Figure 2 Overview of the signaling pathways affected by erythropoietin-induced hepatocyte receptor A2.
Created by the BioRender. EphA2: Erythropoietin-induced hepatocyte receptor A.
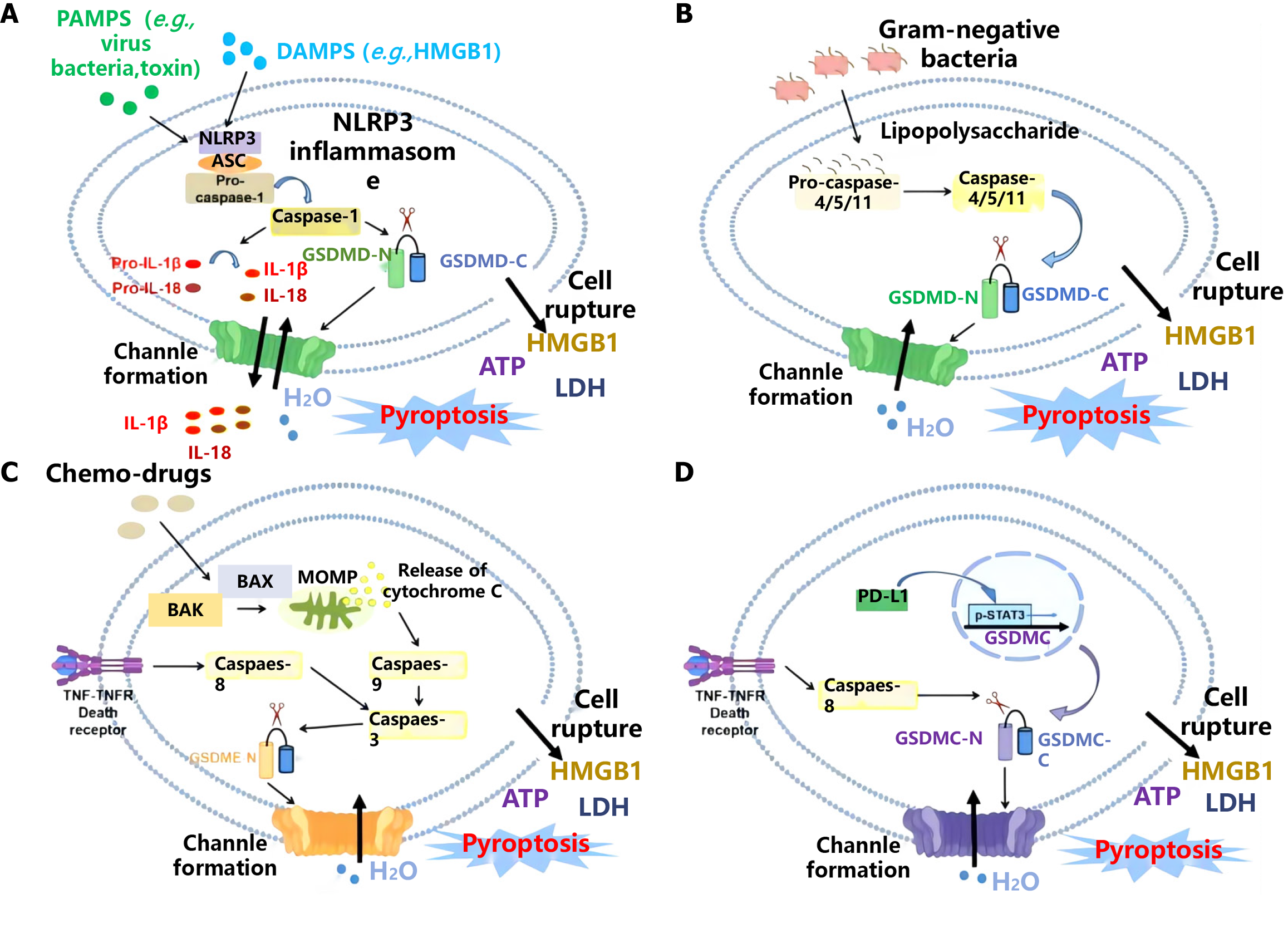
Figure 3 Analysis of signal transduction pathways related to erythropoietin-induced hepatocyte receptor A2 and pyroptosis.
Created by the BioRender. A: Pathogen-associated molecular patterns and damage-associated molecular patterns; B: Gram-negative bacteria; C: Chemo-drugs; D: Channle formation. PAMPs: Pathogen-associated molecular patterns; DAMPs: Damage-associated molecular patterns; HMGB1: High mobility group box 1; NLRP: NOD-like receptor protein; ASC: Apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a caspase recruitment domain; IL: Interleukin; GSDMD: Gasdermin D; LDH: Lactate dehydrogenase; MOMP: Mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; PD-L1: Programmed death-ligand 1.
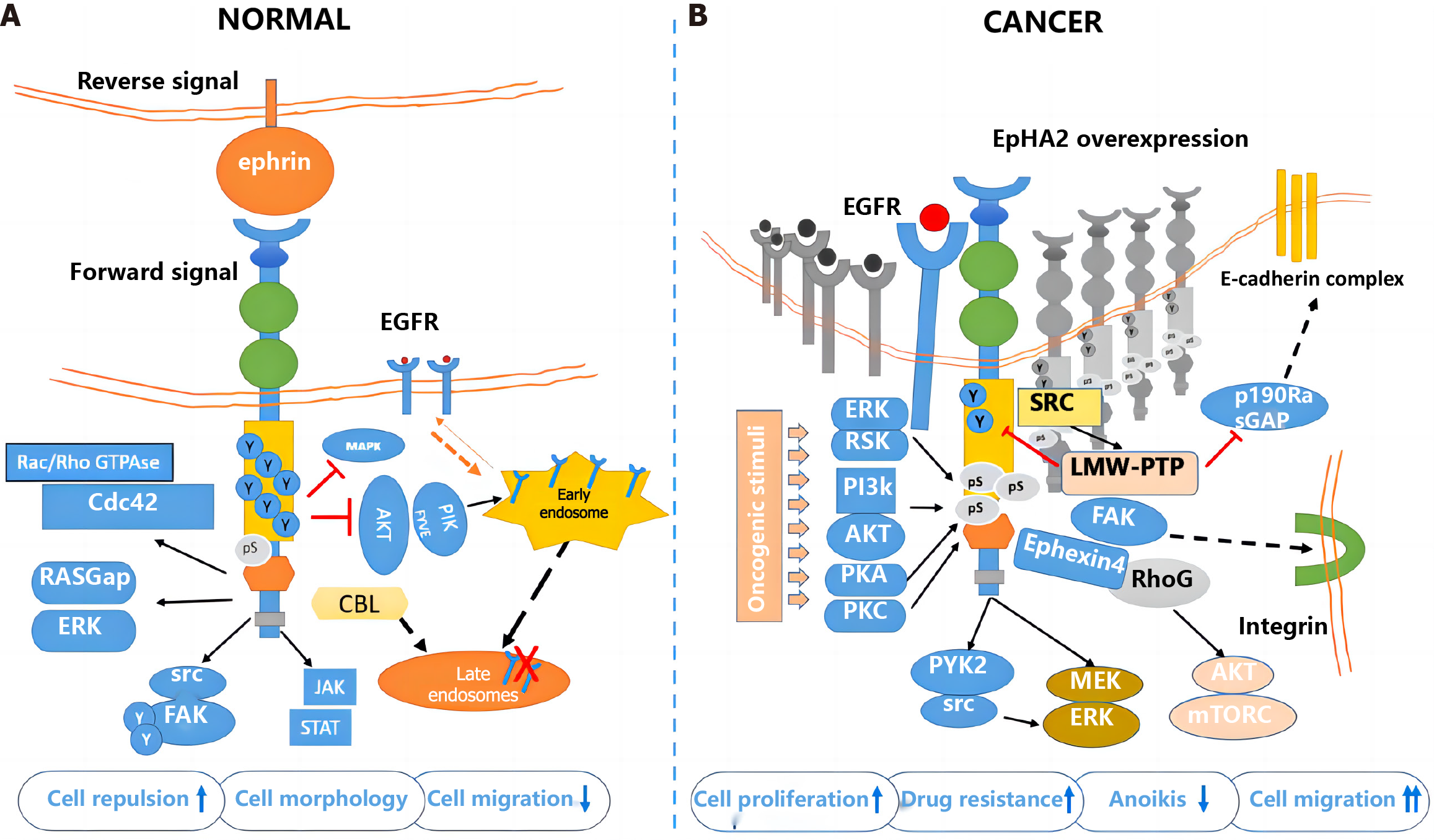
Figure 4 The role of erythropoietin-induced hepatocyte receptor A2 in the development of colorectal cancer.
Created by the BioRender. A: Normal group; B: Cancer group. EphA2: Erythropoietin-induced hepatocyte receptor A; EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor; ERK: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase; AKT: Protein kinase B; PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; CBL: Casitas B-lineage lymphoma; STAT: Signal transducer and activator of transcription; SRC: Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src; mTOR: Mechanistic target of rapamycin; GAP: GTPase-activating protein.
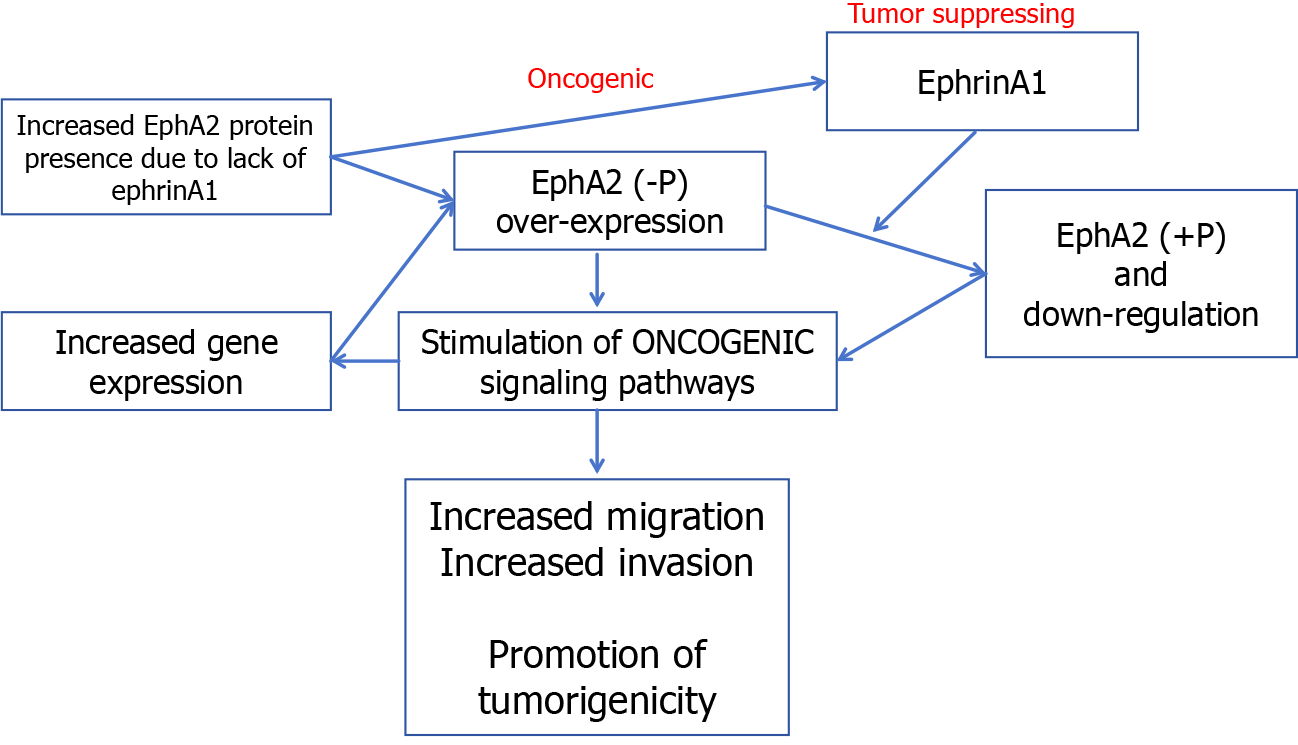
Figure 5 Erythropoietin-induced hepatocyte receptor A2 expression in colorectal cancer.
Created by the BioRender. EphA2: Erythropoietin-induced hepatocyte receptor A.
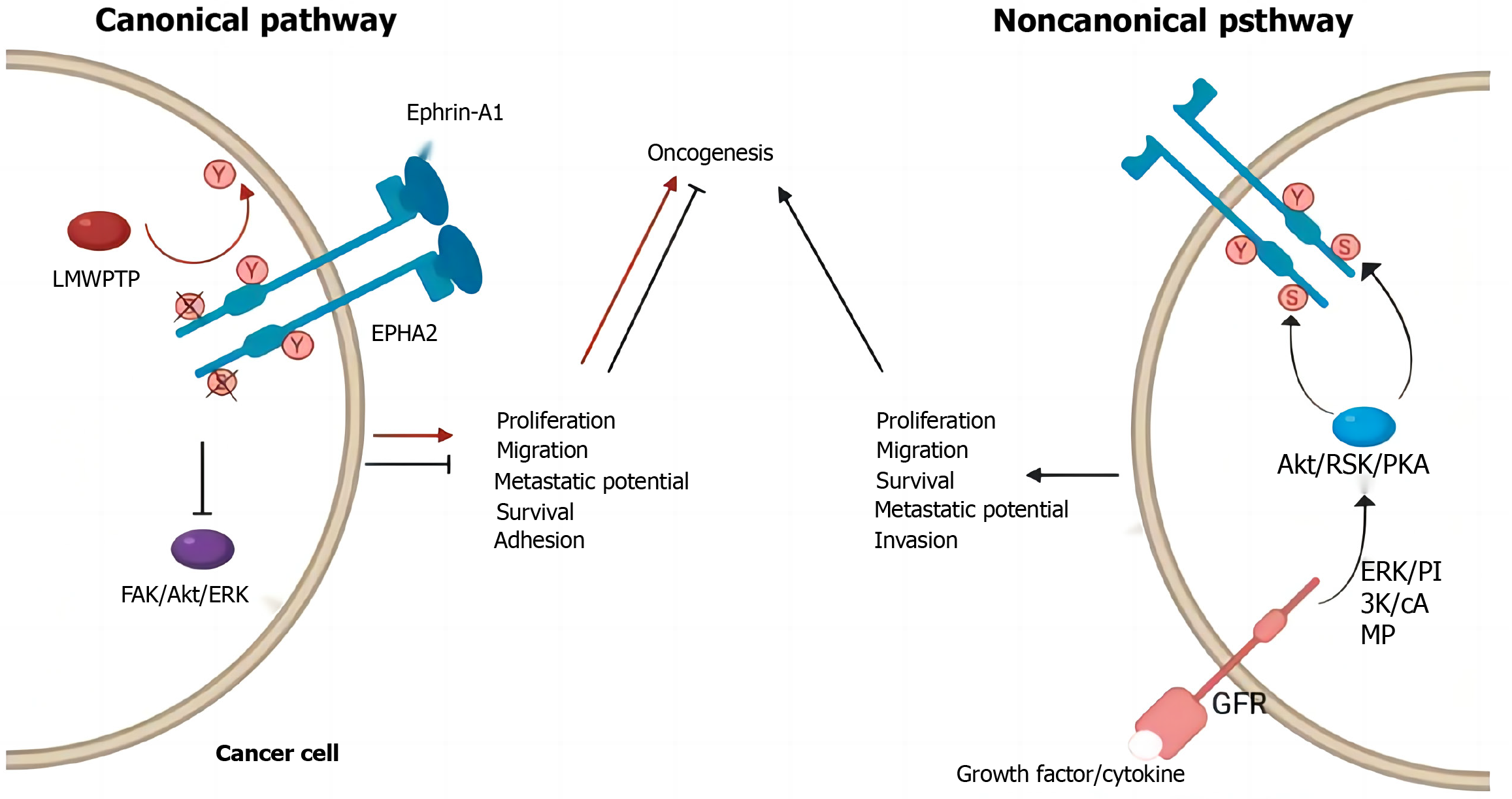
Figure 6 Canonical and noncanonical erythropoietin-induced hepatocyte receptor A2 pathway components in cancer cells.
Created by the BioRender. EphA2: Erythropoietin-induced hepatocyte receptor A2; ERK: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase; PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; AKT: Protein kinase B; GFR: Glomerular filtration rate.
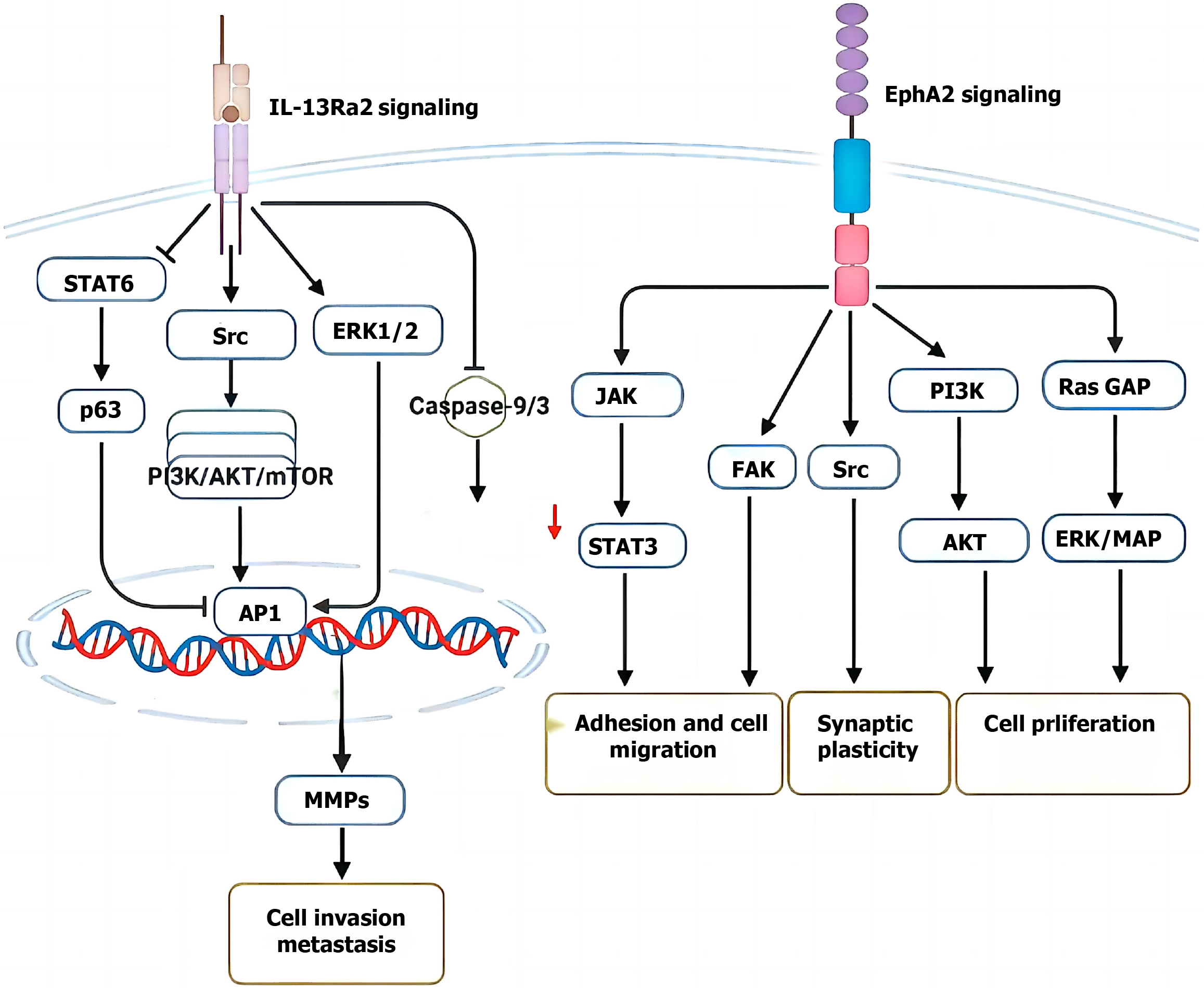
Figure 7 Erythropoietin-induced hepatocyte receptor A2 signaling in colorectal cancer cell invasion and metastasis.
Created by the BioRender. EphA2: Erythropoietin-induced hepatocyte receptor A2; IL: Interleukin; STAT6: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 6; ERK1/2: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2; PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; AKT: Protein kinase B; mTOR: Mechanistic target of rapamycin; AP1: Activator protein 1; MMPs: Matrix metalloproteinases; JAK: Janus kinase; GAP: GTPase-activating protein.
- Citation: Zhang YK, Shi R, Meng RY, Lin SL, Zheng M. Erythropoietin-induced hepatocyte receptor A2 regulates effect of pyroptosis on gastrointestinal colorectal cancer occurrence and metastasis resistance. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2024; 16(9): 3781-3797
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v16/i9/3781.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v16.i9.3781