Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Aug 15, 2024; 16(8): 3635-3650
Published online Aug 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i8.3635
Published online Aug 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i8.3635
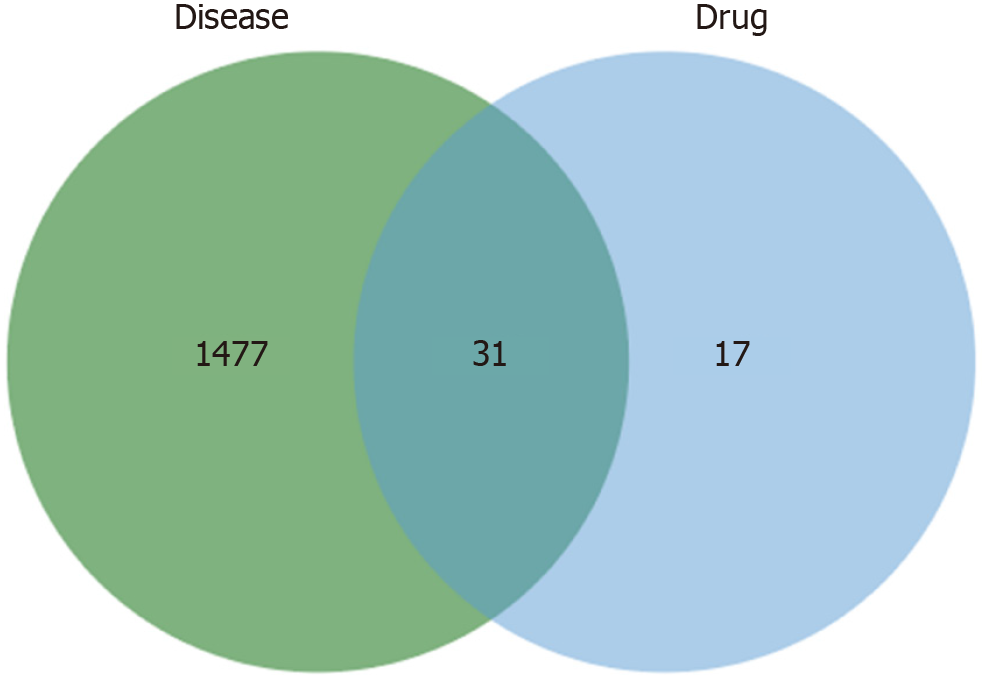
Figure 1 Curcumin–GC overlapping genes.
The green circle on the left represents the disease targets corresponding to gastric cancer, while the blue circle on the right represents the compound targets corresponding to curcumin. The dark blue area indicates the intersection targets between curcumin and gastric cancer.
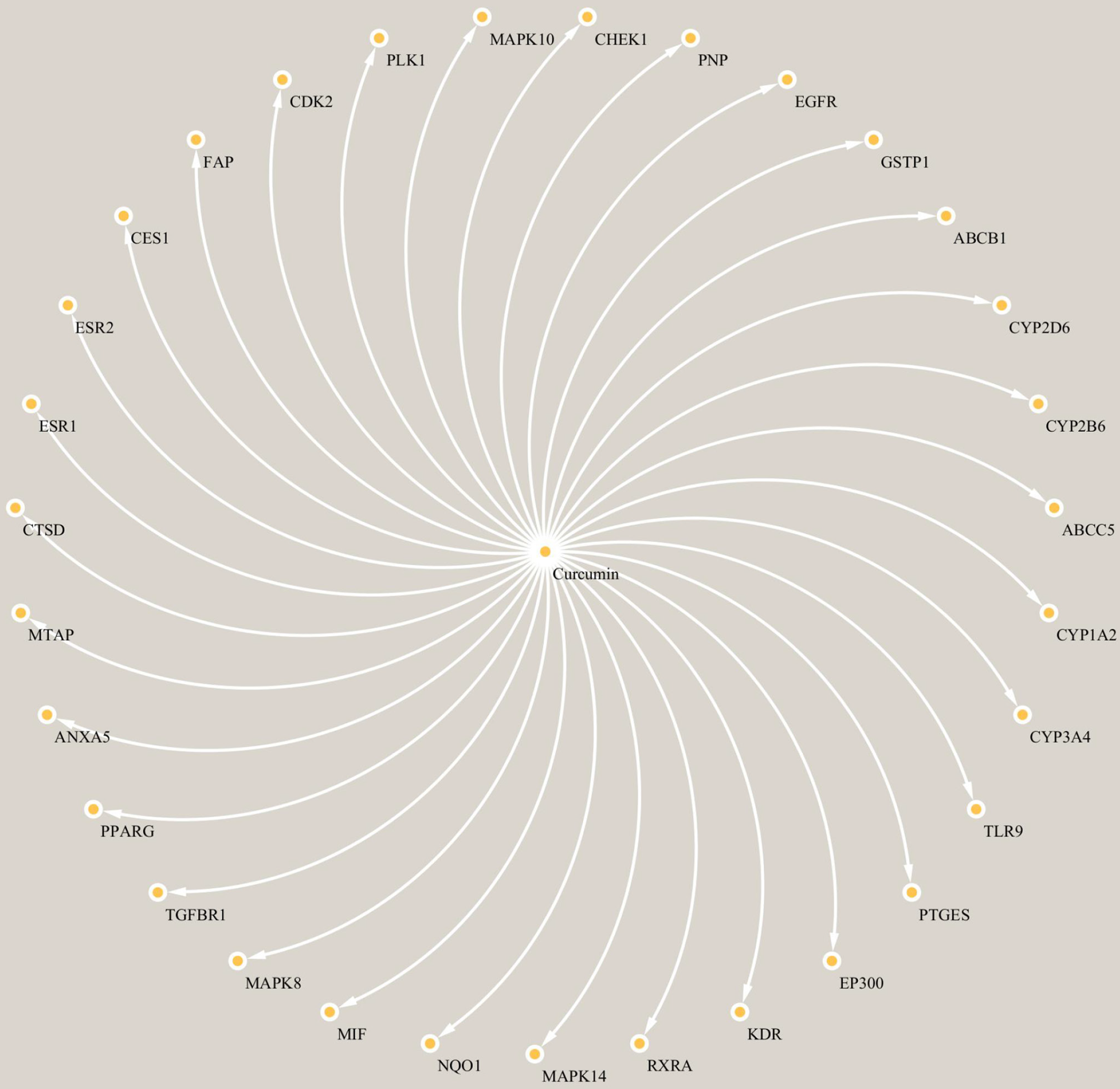
Figure 2 Compound–target network.
The mutual network between curcumin (central orange node) and its intersection targets (peripheral orange nodes) included 32 nodes and 31 edges. ESR1: Estrogen receptor 1; EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor; CYP3A4: Cytochrome P450 family 3 subfamily A member 4; MAPK14: Mitogen-activated protein kinase 14; CYP1A2: Cytochrome P450 family 1 subfamily A member 2; CYP2B6: Cytochrome P450 family 2 subfamily B member 6.
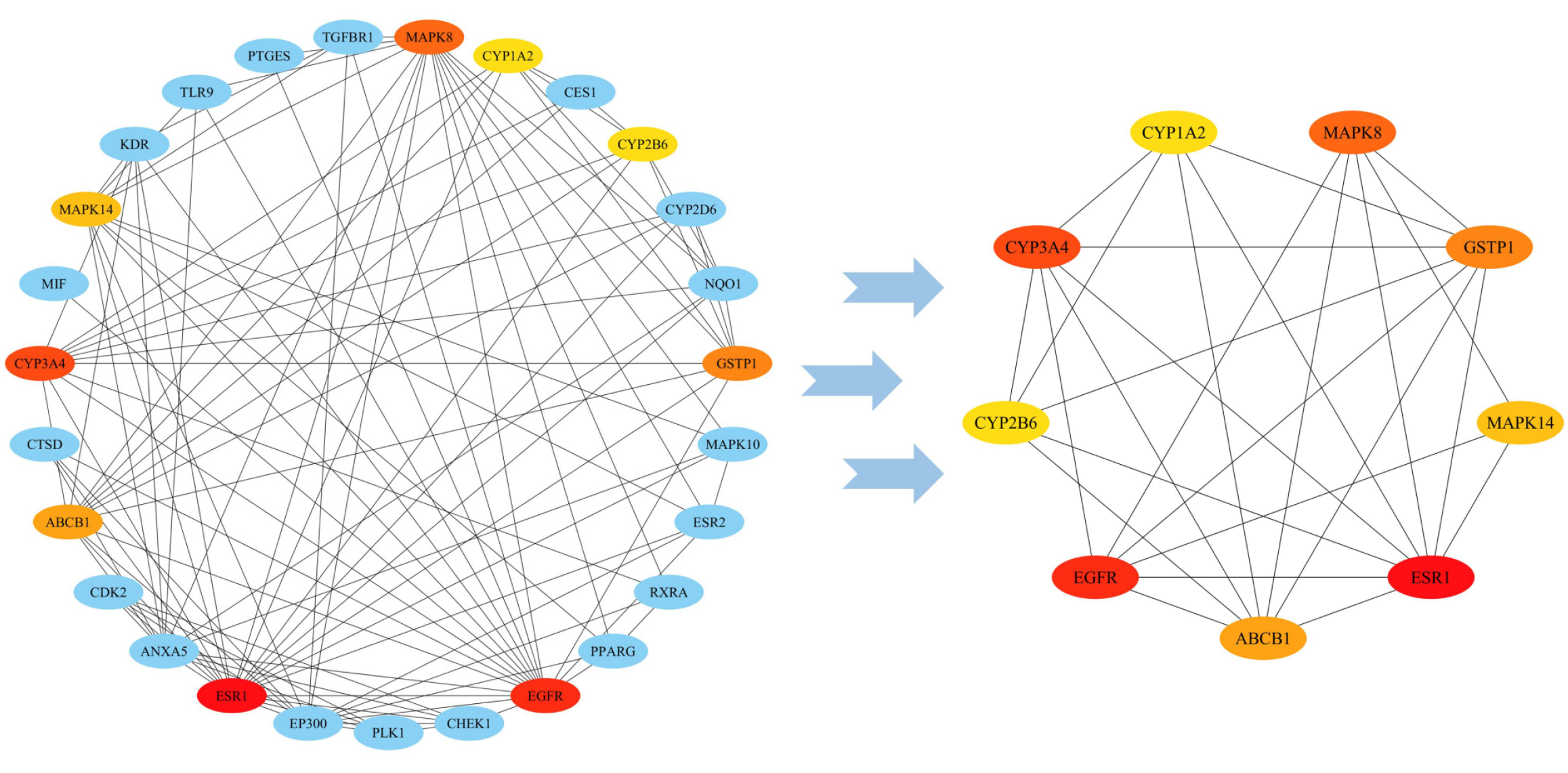
Figure 3 Protein-protein interaction network.
The network on the left represents the topological analysis of the network for curcumin–gastric cancer intersection targets, with the color becoming increasingly red as the degree value increases. The network on the right represents the topological graph of the target gene network with the top 8 degree values. ESR1: Estrogen receptor 1; EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor; CYP3A4: Cytochrome P450 family 3 subfamily A member 4; MAPK14: Mitogen-activated protein kinase 14; CYP1A2: Cytochrome P450 family 1 subfamily A member 2; CYP2B6: Cytochrome P450 family 2 subfamily B member 6.
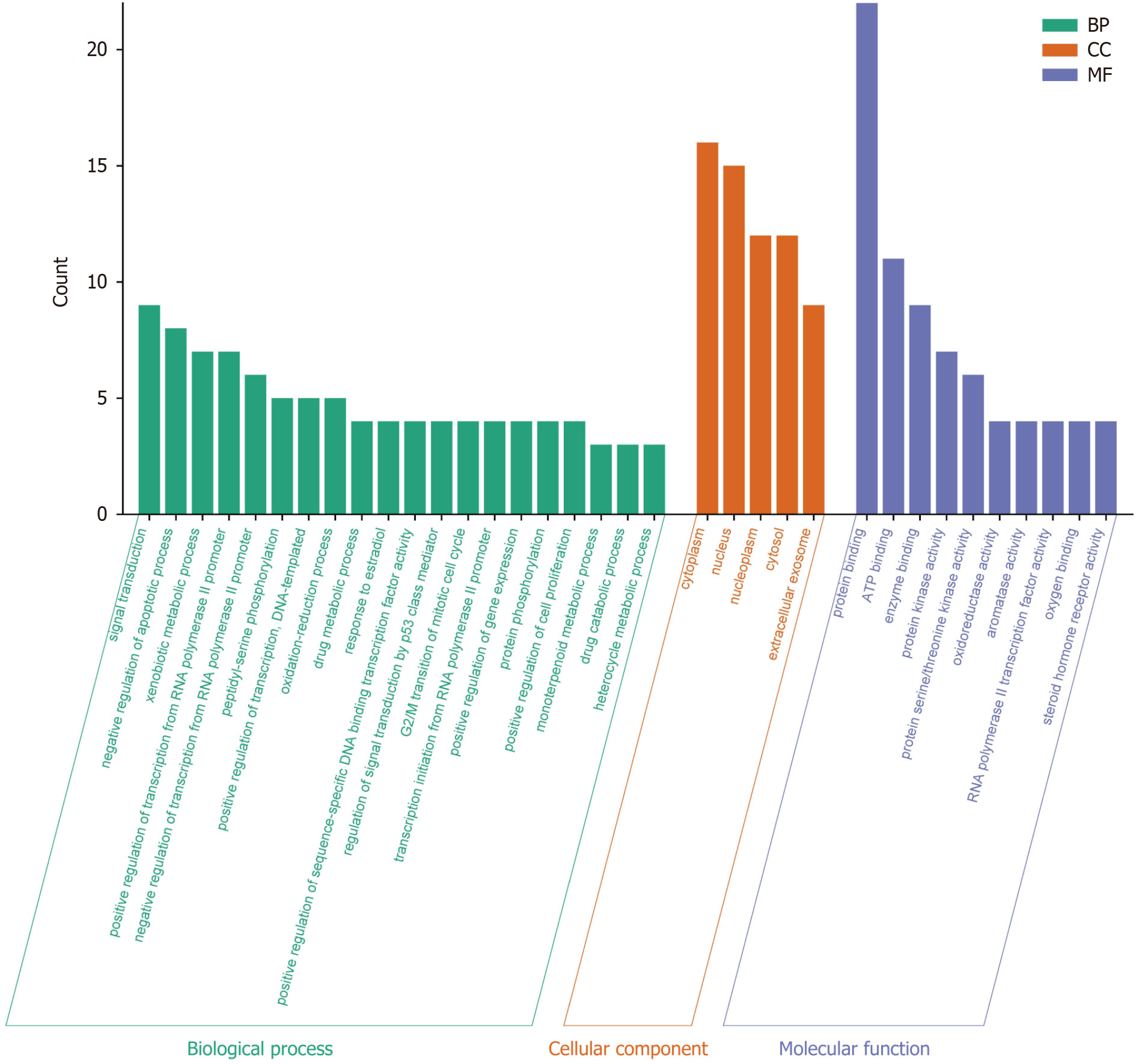
Figure 4 GO analysis of target genes.
BP: Biological process; CC: Cellular component; MF: Molecular function.
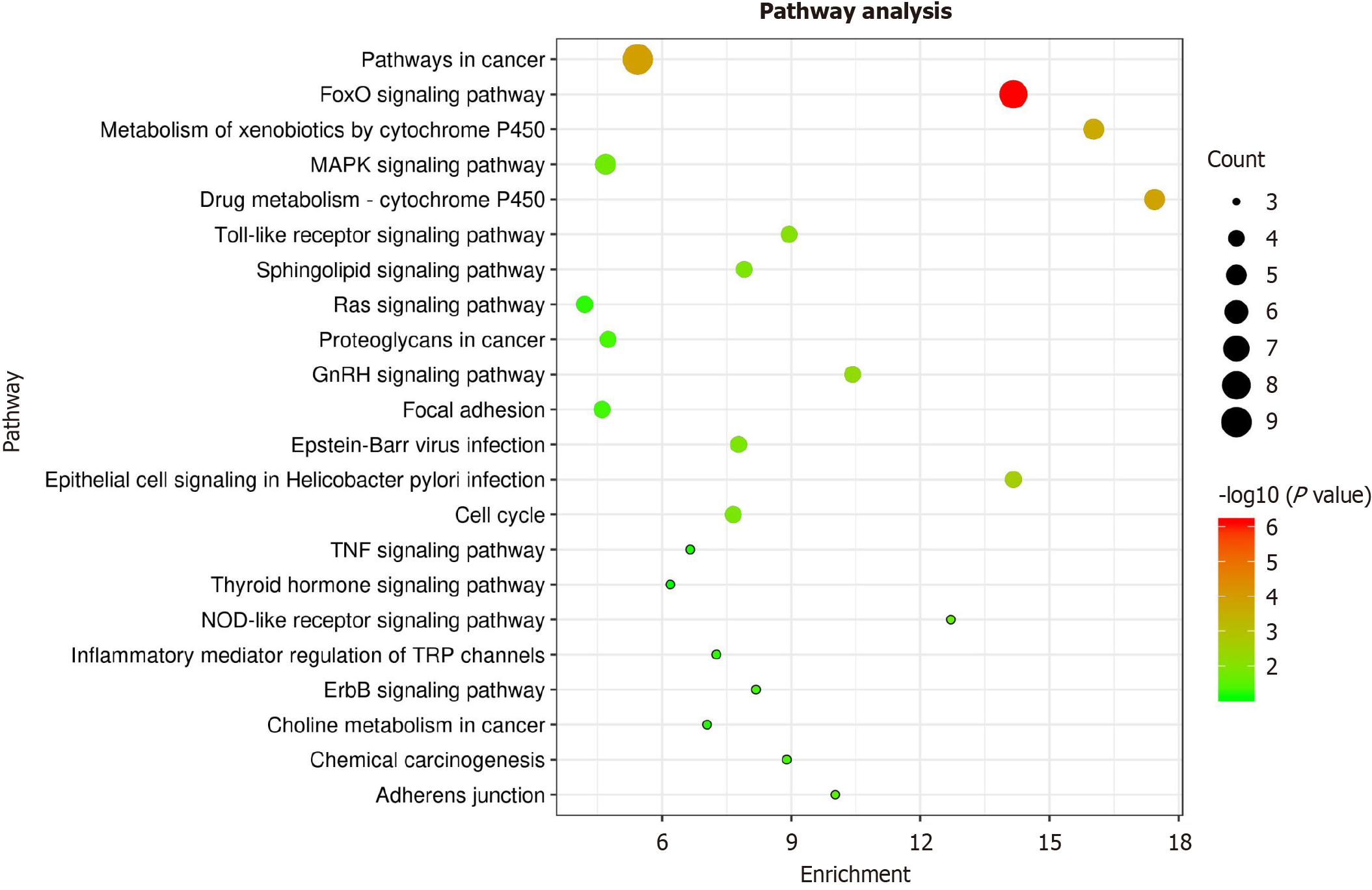
Figure 5 KEGG analysis of target genes.
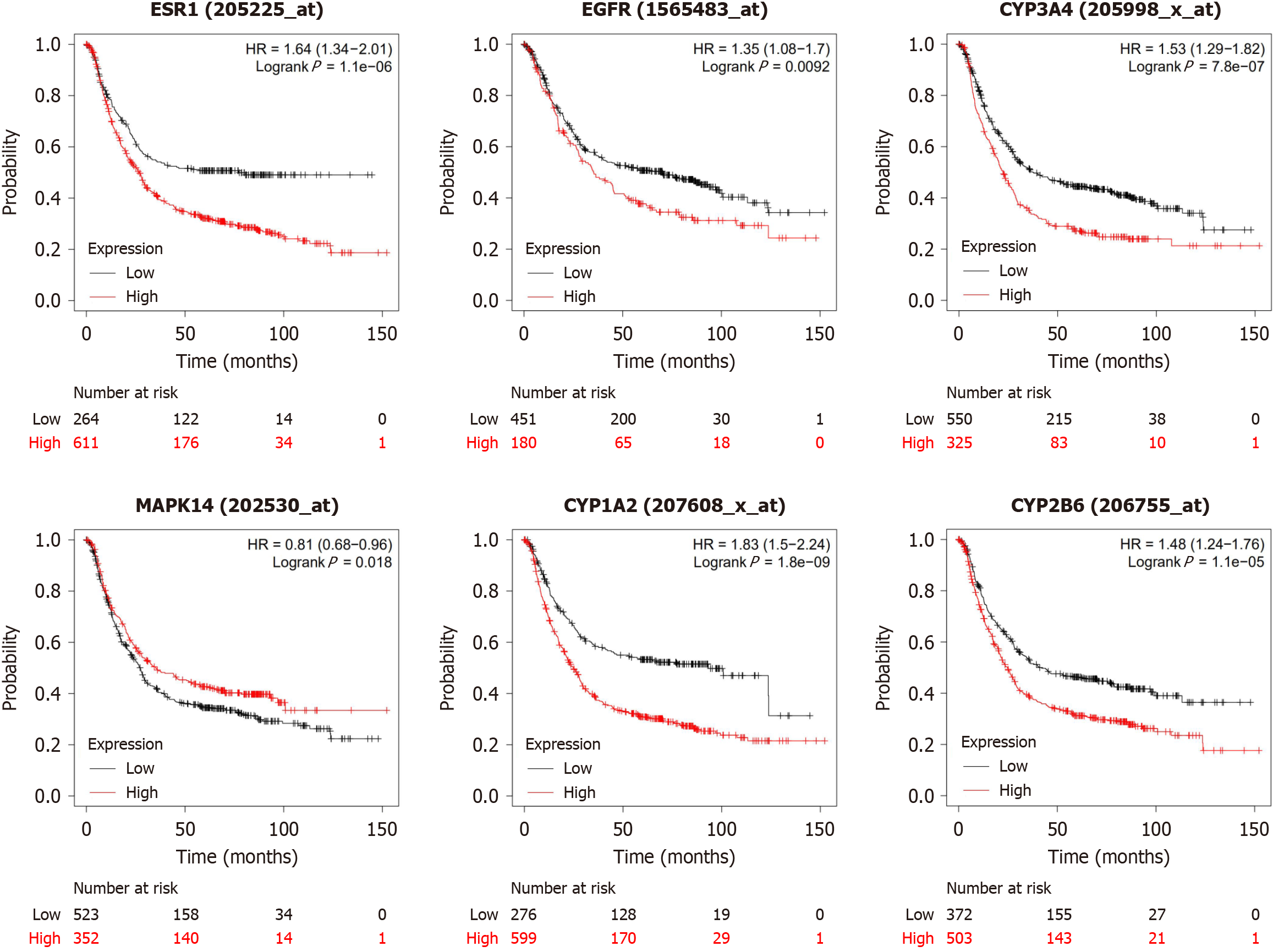
Figure 6 Prognostic value evaluation of the expression of the six hub targets.
Survival data were analyzed by the Kaplan-Meier plotter database (P < 0.05); red lines represent patients above the median, and black lines represent patients below the median. HR: Hazard ratio; ESR1: Estrogen receptor 1; EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor; CYP3A4: Cytochrome P450 family 3 subfamily A member 4; MAPK14: Mitogen-activated protein kinase 14; CYP1A2: Cytochrome P450 family 1 subfamily A member 2; CYP2B6: Cytochrome P450 family 2 subfamily B member 6.
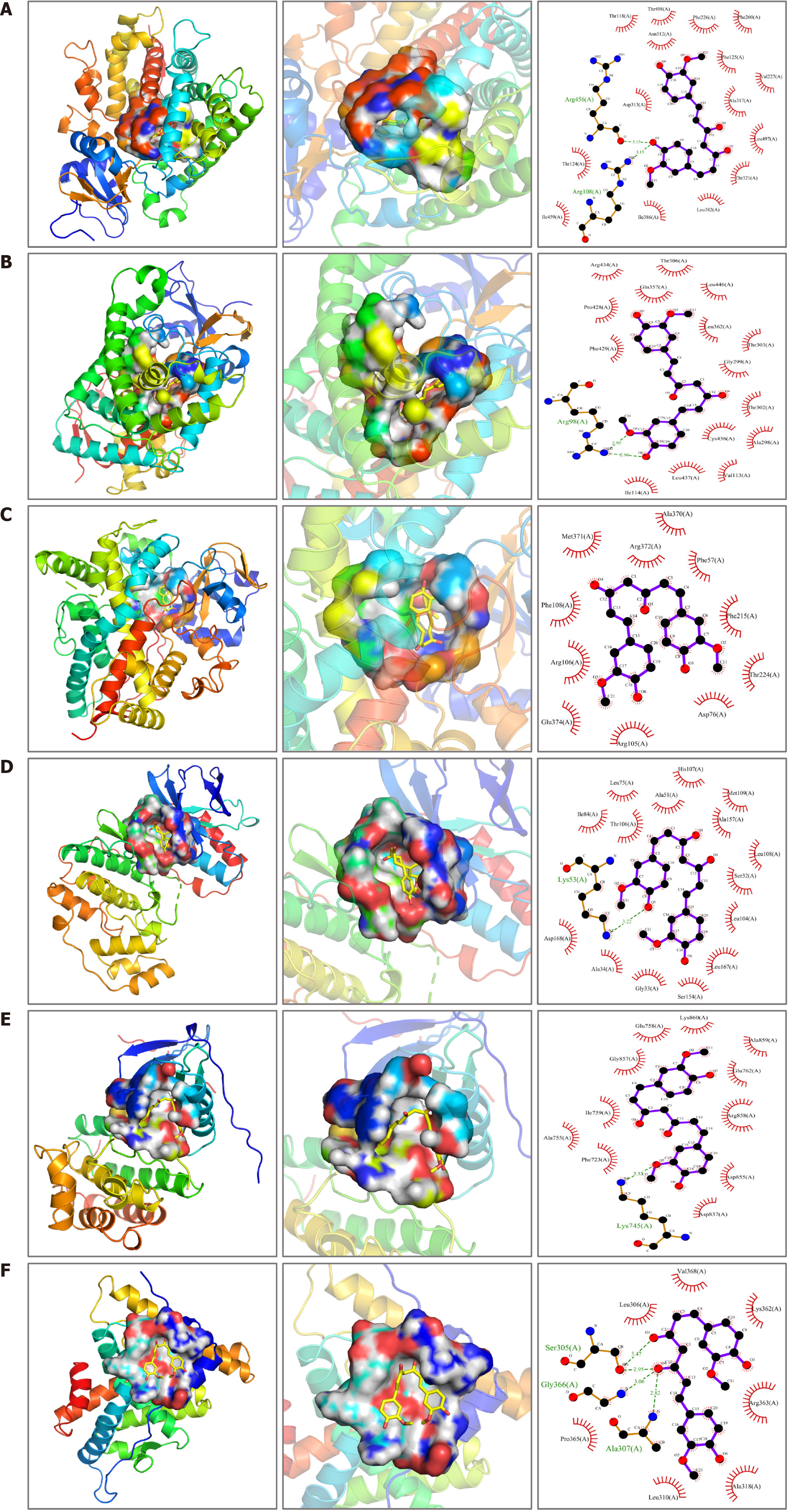
Figure 7 Docking results of curcumin and the six hub targets.
A: Cytochrome P450 family 1 subfamily A member 2; B: Cytochrome P450 family 2 subfamily B member 6; C: Cytochrome P450 family 3 subfamily A member 4; D: Mitogen-activated protein kinase 14; E: Epidermal growth factor receptor; F: Estrogen receptor 1.
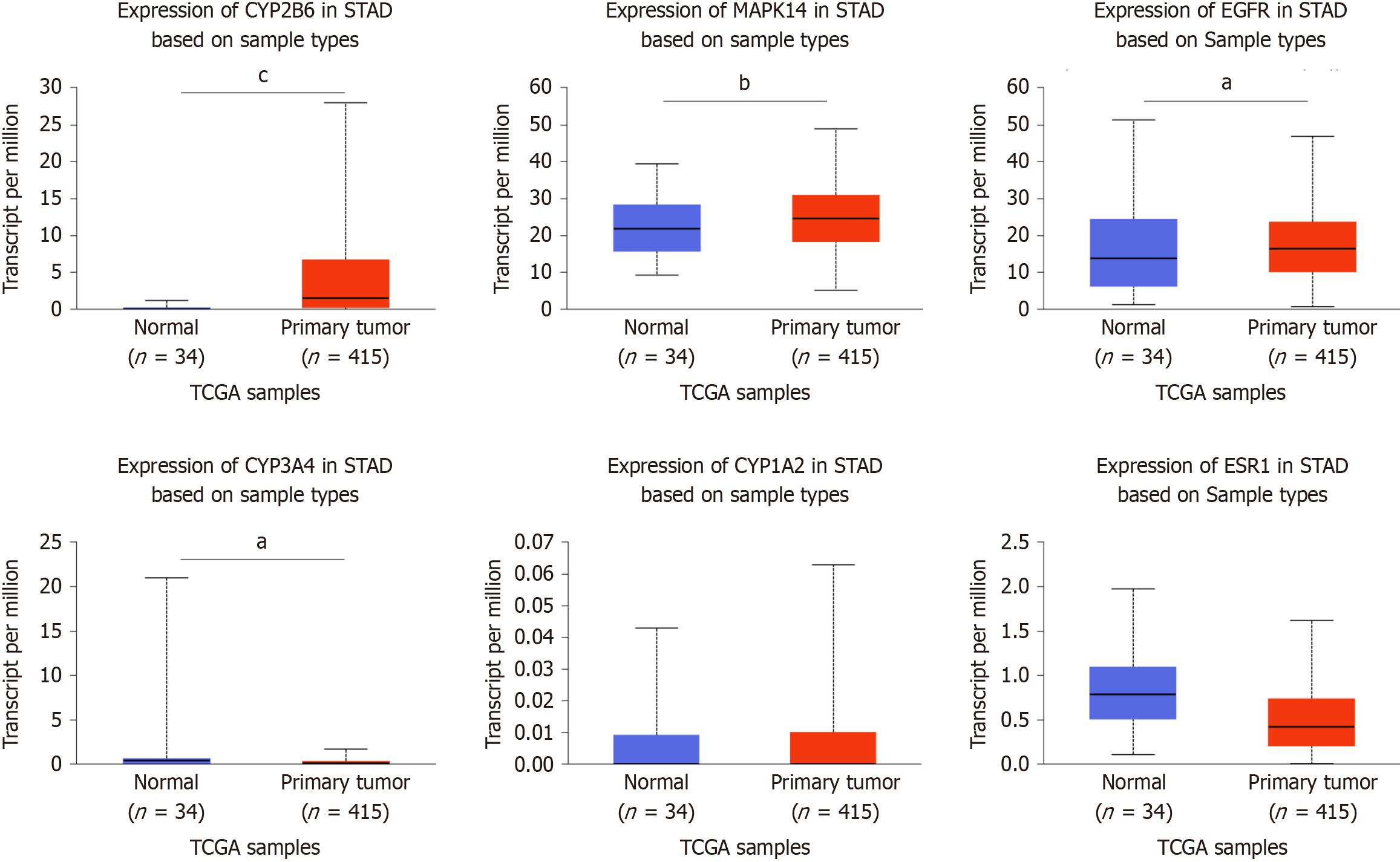
Figure 8 Expression of the estrogen receptor 1, epidermal growth factor receptor, cytochrome P450 family 3 subfamily A member 4, mitogen-activated protein kinase 14, cytochrome P450 family 1 subfamily A member 2, and cytochrome p450 family 2 subfamily B member 6 genes in gastric cancer tissue and normal gastric tissue.
aP < 0.05 vs normal group; bP < 0.01; vs normal group; cP < 0.001 vs normal group. ESR1: Estrogen receptor 1; EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor; CYP3A4: Cytochrome P450 family 3 subfamily A member 4; MAPK14: Mitogen-activated protein kinase 14; CYP1A2: Cytochrome P450 family 1 subfamily A member 2; CYP2B6: Cytochrome P450 family 2 subfamily B member 6.
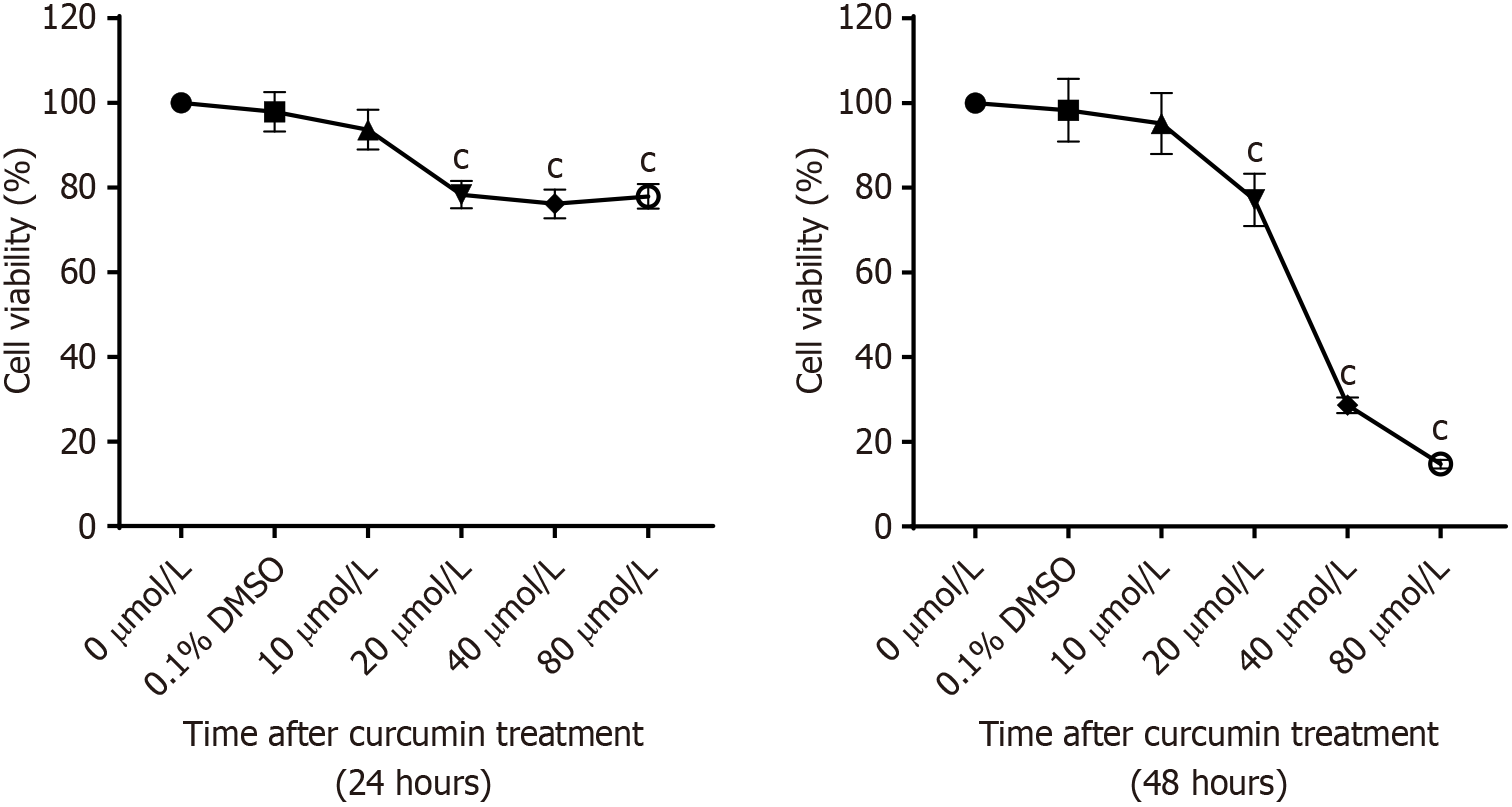
Figure 9 Inhibitory effect of different concentrations of curcumin on the proliferation of BGC-823 cells.
cP < 0.001 vs 0 μmol/L.
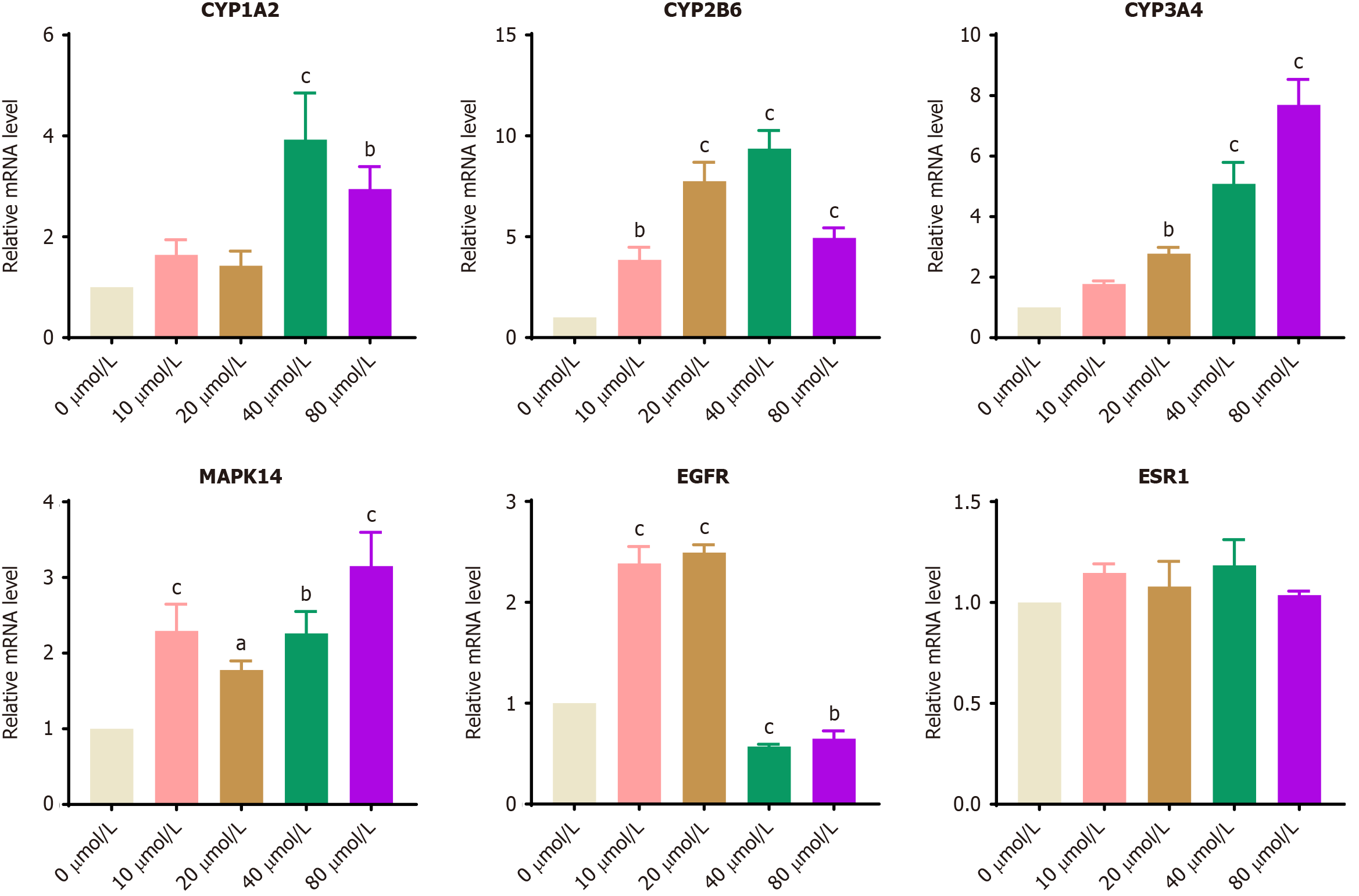
Figure 10 The mRNA expression levels of estrogen receptor 1, epidermal growth factor receptor, cytochrome P450 family 3 subfamily A member 4, mitogen-activated protein kinase 14, cytochrome P450 family 1 subfamily A member 2, and cytochrome p450 family 2 subfamily B member 6.
aP < 0.05 vs 0 μmol/L; bP < 0.01 vs 0 μmol/L; cP < 0.001 vs 0 μmol/L. ESR1: Estrogen receptor 1; EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor; CYP3A4: Cytochrome P450 family 3 subfamily A member 4; MAPK14: Mitogen-activated protein kinase 14; CYP1A2: Cytochrome P450 family 1 subfamily A member 2; CYP2B6: Cytochrome P450 family 2 subfamily B member 6.
- Citation: Yang PH, Wei YN, Xiao BJ, Li SY, Li XL, Yang LJ, Pan HF, Chen GX. Curcumin for gastric cancer: Mechanism prediction via network pharmacology, docking, and in vitro experiments. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2024; 16(8): 3635-3650
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v16/i8/3635.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v16.i8.3635