Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Jun 15, 2024; 16(6): 2350-2361
Published online Jun 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i6.2350
Published online Jun 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i6.2350
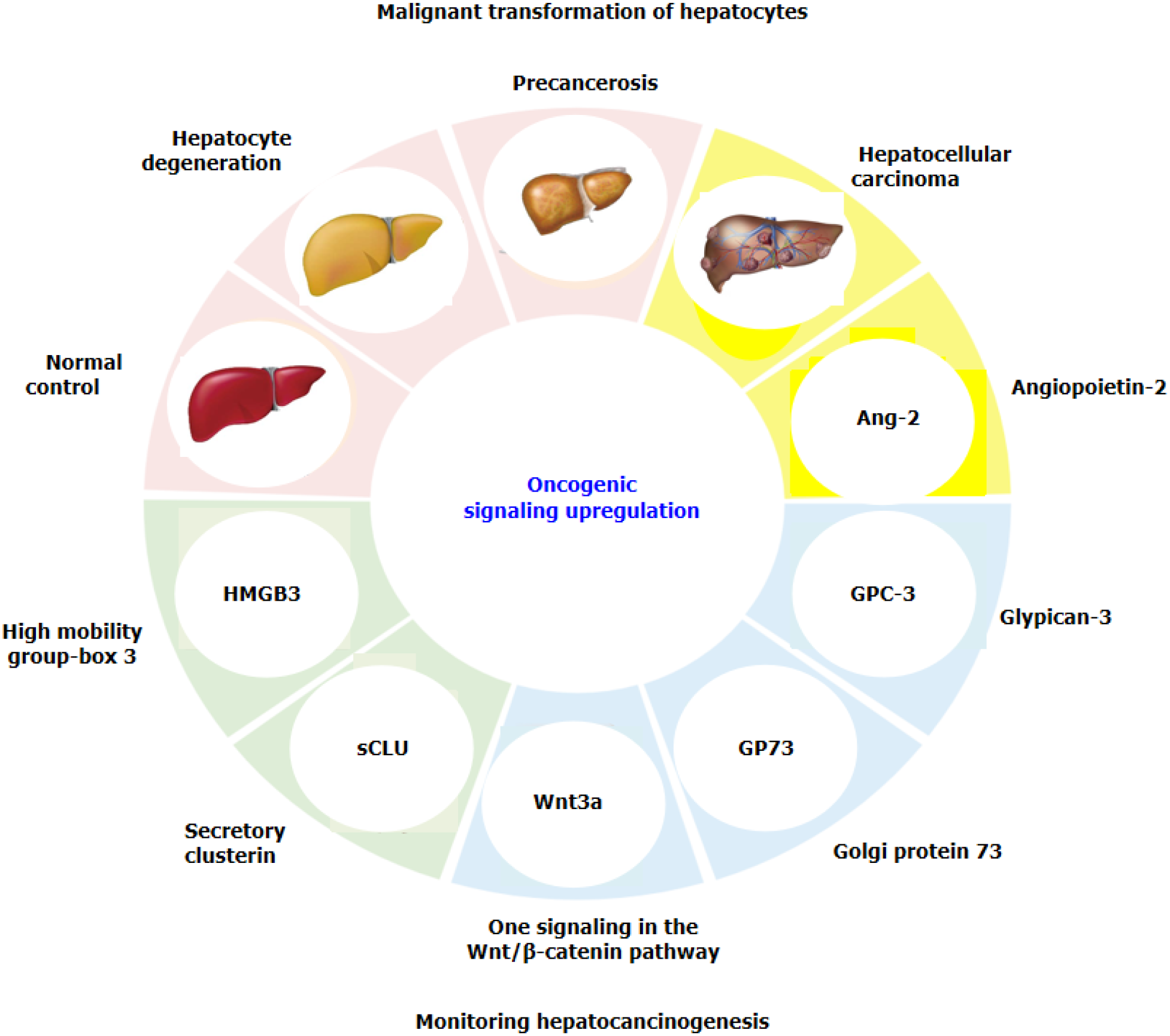
Figure 1 Novel signalling molecules involved in hepatocarcinogenesis[7,9,11,14].
Based on the data from animal models, the progressive alterations revealed by liver pathological examination ranged from normal liver to hepatocyte degeneration to precancerosis to hepatocellular carcinoma. Ang-2: Angiopoietin-2; GP73: Golgi protein 73; GPC-3: Glypican-3; HMGB3: High mobility group-Box 3; Sclu: Secretory clusterin; Wnt3a: A signalling molecule from the Wnt/β-catenin pathway.
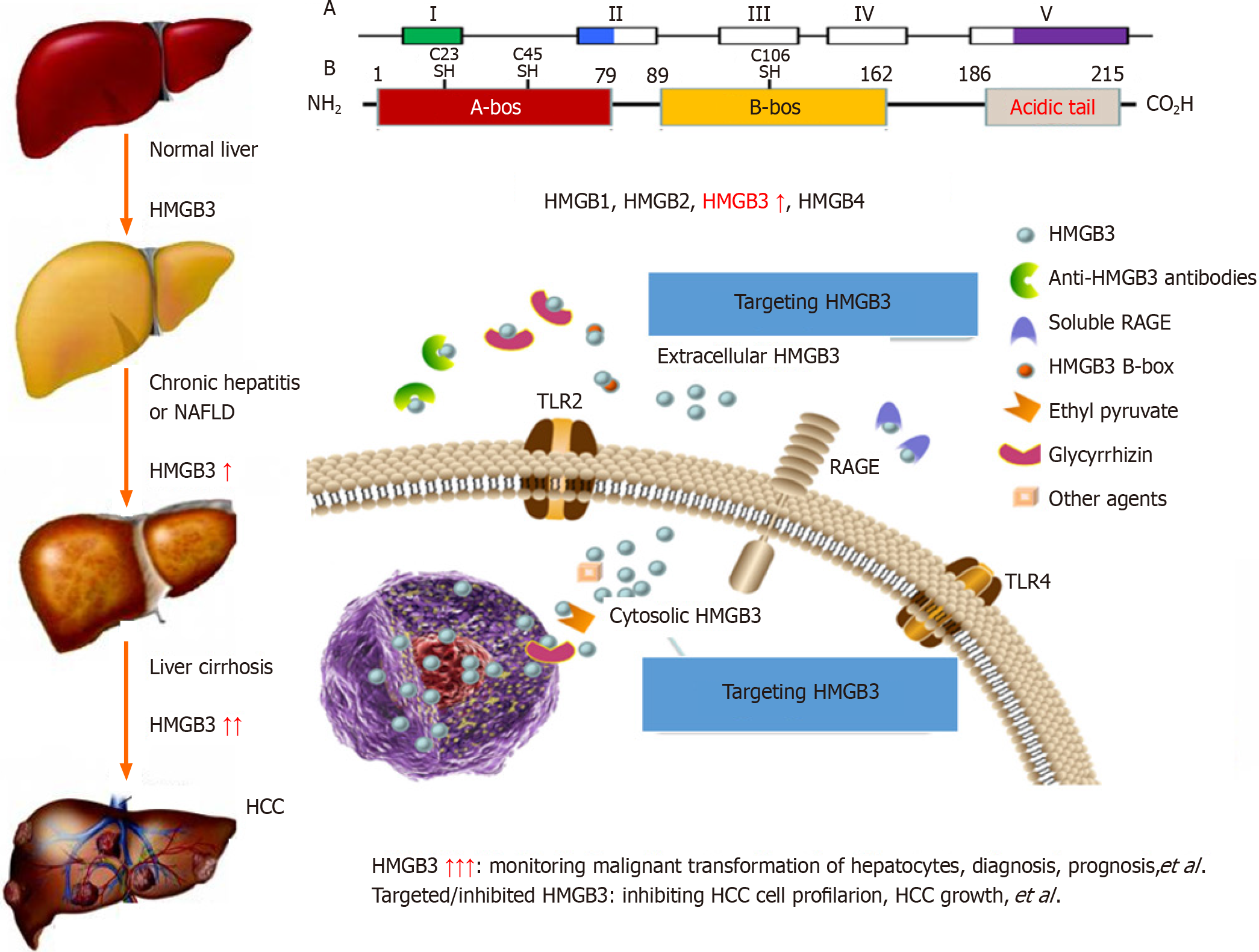
Figure 2 High mobility group-Box 3 during hepatocellular carcinoma progression[21,31-33,35].
Based on the data of basic or clinical studies, the progressive upregulation of high mobility group-Box 3 (HMGB3) at the mRNA or protein level occurred from the normal liver to chronic hepatitis to liver cirrhosis to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). An abnormal level of HMGB3 is helpful for monitoring hepatocyte malignant transformation and diagnosing or determining the prognosis of patients with HCC. In addition, interfering with HMGB3 transcription inhibited HCC cell proliferation in vitro or HCC xenograft growth in vivo. RAGE: Receptor for advanced glycation end products; TLR: Toll-like receptor; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; HMGB3: High mobility group-Box 3.
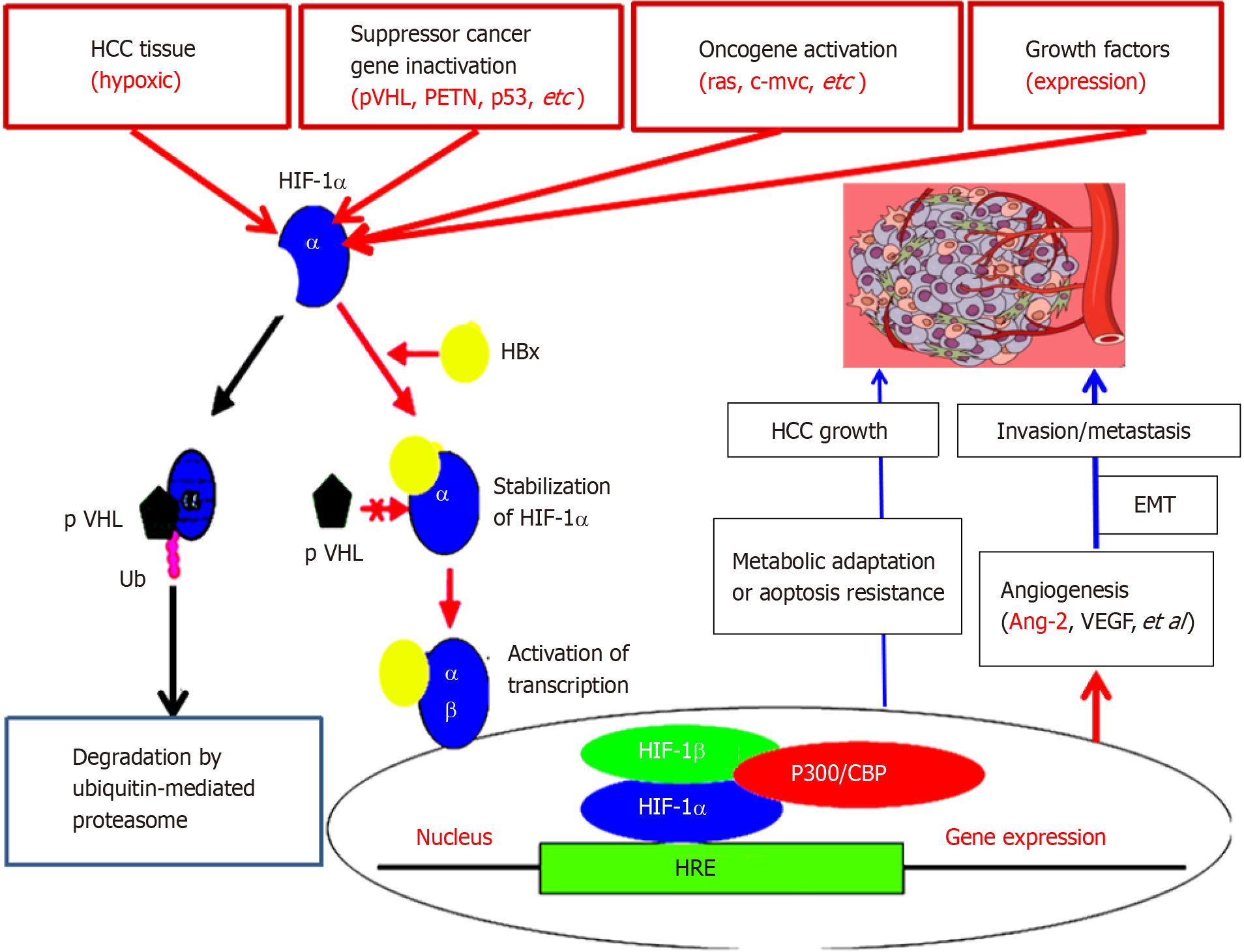
Figure 3 Abnormal angiopoietin-2 expression during hepatocarcinogenesis[37-39,43].
Neovascularization is a fundamental process involved in a variety of pathological processes that sustain the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. angiopoietin-2 (Ang-2) is a key driver of tumour angiogenesis, and abnormal Ang-2 during hepatocarcinogenesis in rats is closely related to hepatic hypoxia. Ang-2 could be used as an early index to monitor the malignant transformation of hepatocytes. EMT: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition; HRE: Hypoxia-responsive element; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma.
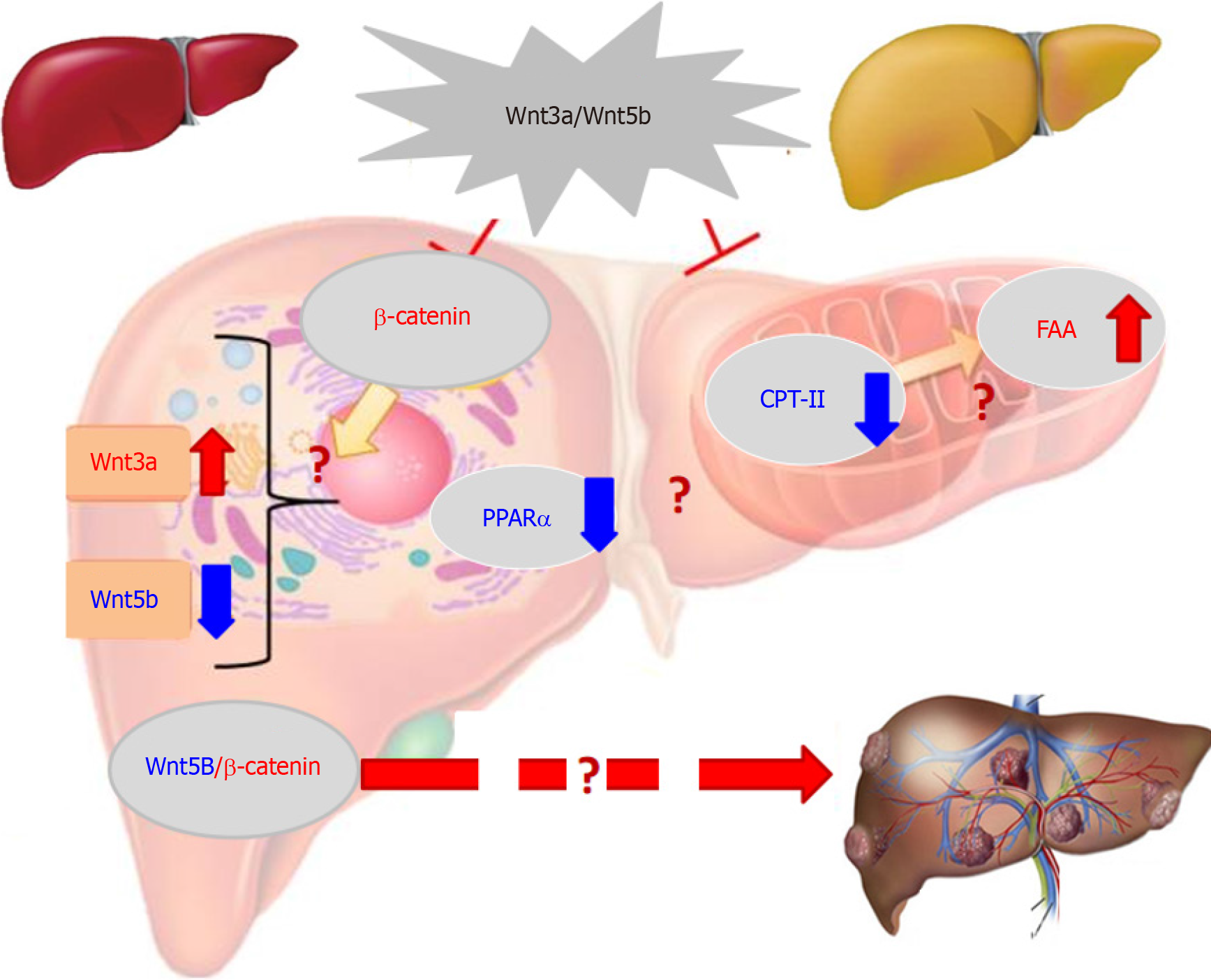
Figure 4 Abnormal activation of Wnt3a in hepatocarcinogenesis[49,53,56,57,61].
The Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway contains 19 mammalian Wnt proteins. Wnt3a gene located on chromosome 17q21 is regarded as an activator of the canonical Wnt pathway, which induces β-catenin accumulation. An increase in Wnt3a is closely related to hepatocyte malignant transformation and could be a marker for monitoring hepatocarcinogenesis. FA: Fatty acid; PPARα: Peroxisome proliferation activated receptor α.
- Citation: Yao M, Fang RF, Xie Q, Xu M, Sai WL, Yao DF. Early monitoring values of oncogenic signalling molecules for hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2024; 16(6): 2350-2361
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v16/i6/2350.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v16.i6.2350