Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. May 15, 2024; 16(5): 1890-1907
Published online May 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i5.1890
Published online May 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i5.1890
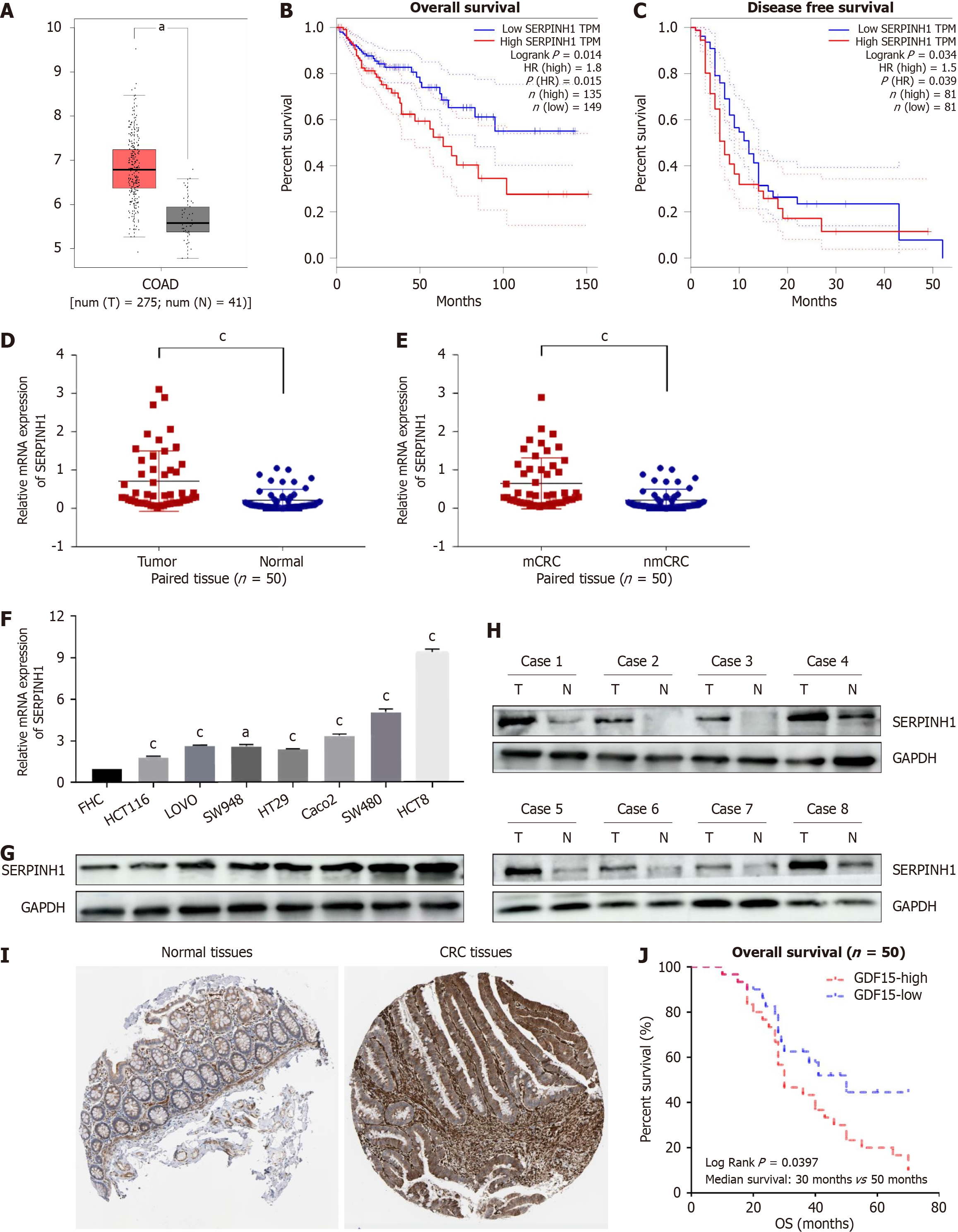
Figure 1 Identification and characterization of serpin peptidase inhibitor clade H member 1 in colorectal cancer cells and tissues.
A: Upregulated serpin peptidase inhibitor clade H member 1 (SERPINH1) mRNA expression in colorectal cancer (CRC) compared with normal colorectal tissue in The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database; B and C: Expression mRNA level; D and E: Kaplan-Meier analysis of overall survival and relapse-free survival of colorectal adenocarcinoma (COAD) patients with low vs high SERPINH1 expression from TCGA datasets; F and G: The relative expression of SERPINH1 protein and mRNA in normal human colon epithelial cells and seven CRC cell lines by western blotting and quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. mean ± SD (n = 3); H: Protein level of SERPINH1 in COAD (matched tissues and unmatched tissues); I: Protein expression level of SERPINH1 in normal tissues and CRC tissues from HPA; J: Kaplan-Meier survival analysis of the association between SERPINH1 expression and overall survival in 50 CRC patients. All the data are presented as the mean ± SEM. aP < 0.05, cP < 0.001. SERPINH1: Serpin peptidase inhibitor clade H member 1; CRC: Colorectal cancer; COAD: Colorectal adenocarcinoma.
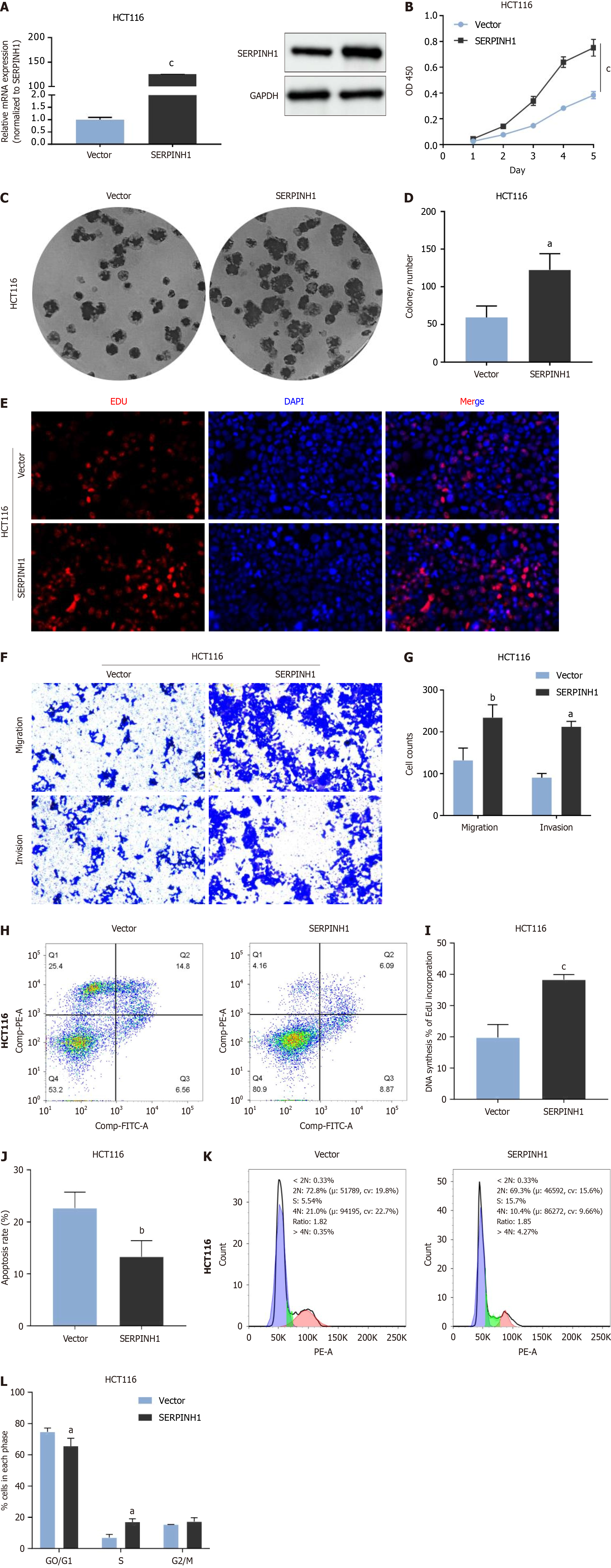
Figure 2 Overexpression of serpin peptidase inhibitor clade H member 1 significantly promoted proliferation, migration and invasion in colorectal cancer.
A: Overexpression of serpin peptidase inhibitor clade H member 1 (SERPINH1) was confirmed at the protein and mRNA level in HCT116 cells by western blotting and quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. mean ± SD (n = 3); B-L: Cell counting kit 8, colony and 5-ethynyl-2’-deoxyuridine assays suggest that overexpression of SERPINH1 promoted the proliferation of colorectal cancer (CRC) cells (B, C, D, E, I). Overexpression of SERPINH1 promoted the migration and invasion of CRC cells (F, G). Overexpression of SERPINH1 inhibited the apoptosis of CRC cells (H, J); K and L: Overexpression of SERPINH1 promoted the G0/G1 ratio of CRC cells. All the data are presented as the mean ± SEM. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. SERPINH1: Serpin peptidase inhibitor clade H member 1.
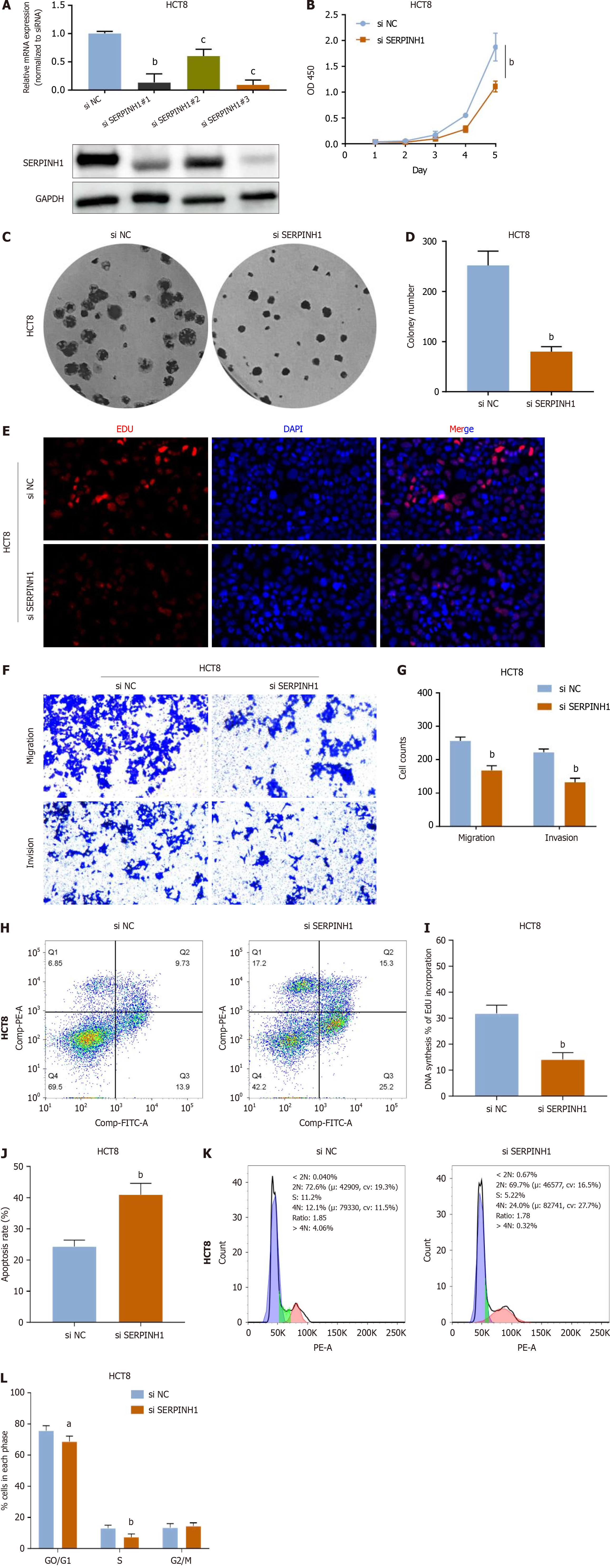
Figure 3 Knockdown of serpin peptidase inhibitor clade H member 1 significantly inhibited proliferation, migration and invasion in colorectal cancer.
A: Knockdown of serpin peptidase inhibitor clade H member 1 (SERPINH1) was confirmed at the protein and mRNA level in HCT8 cells by western blotting and quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. mean ± SD (n = 3); B-L: Cell counting kit 8, colony and 5-ethynyl-2’-deoxyuridine assays suggest that knockdown of SERPINH1 inhibited the proliferation of colorectal cancer (CRC) cells (B, C, D, E, I). Knockdown of SERPINH1 inhibited the migration and invasion of CRC cells (F, G). Knockdown of SERPINH1 promoted the apoptosis of CRC cells (H, J); K and L: Knockdown of SERPINH1 inhibited the G0/G1 ratio of CRC cells. All the data are presented as the mean ± SEM. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. SERPINH1: Serpin peptidase inhibitor clade H member 1.
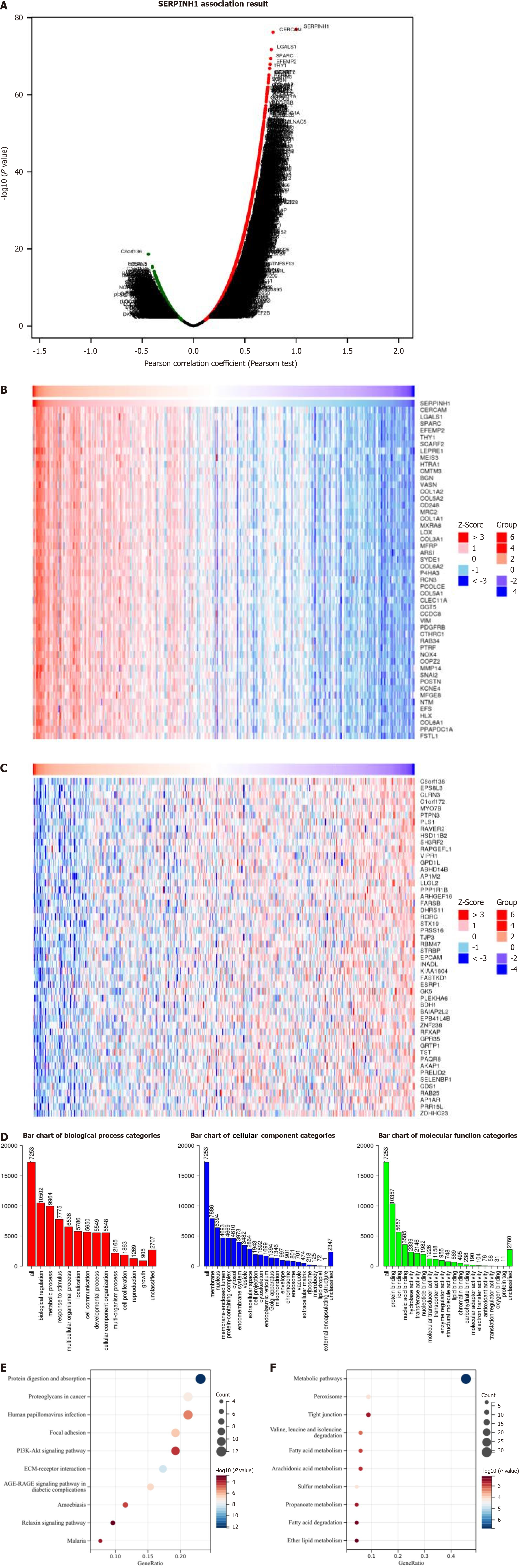
Figure 4 The enrichment analysis of serpin peptidase inhibitor clade H member 1 co-expression genes in colorectal adenocarcinoma.
A: The serpin peptidase inhibitor clade H member 1 (SERPINH1) co-expression genes in colorectal adenocarcinoma (COAD); B and C: The top 50 genes positively and negatively correlated to SERPINH1; D: The Gene Ontology analysis of SERPINH1 co-expression genes in the COAD cohort; E and F: The Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes analysis of SERPINH1 co-expression genes in the COAD cohort. SERPINH1: Serpin peptidase inhibitor clade H member 1.
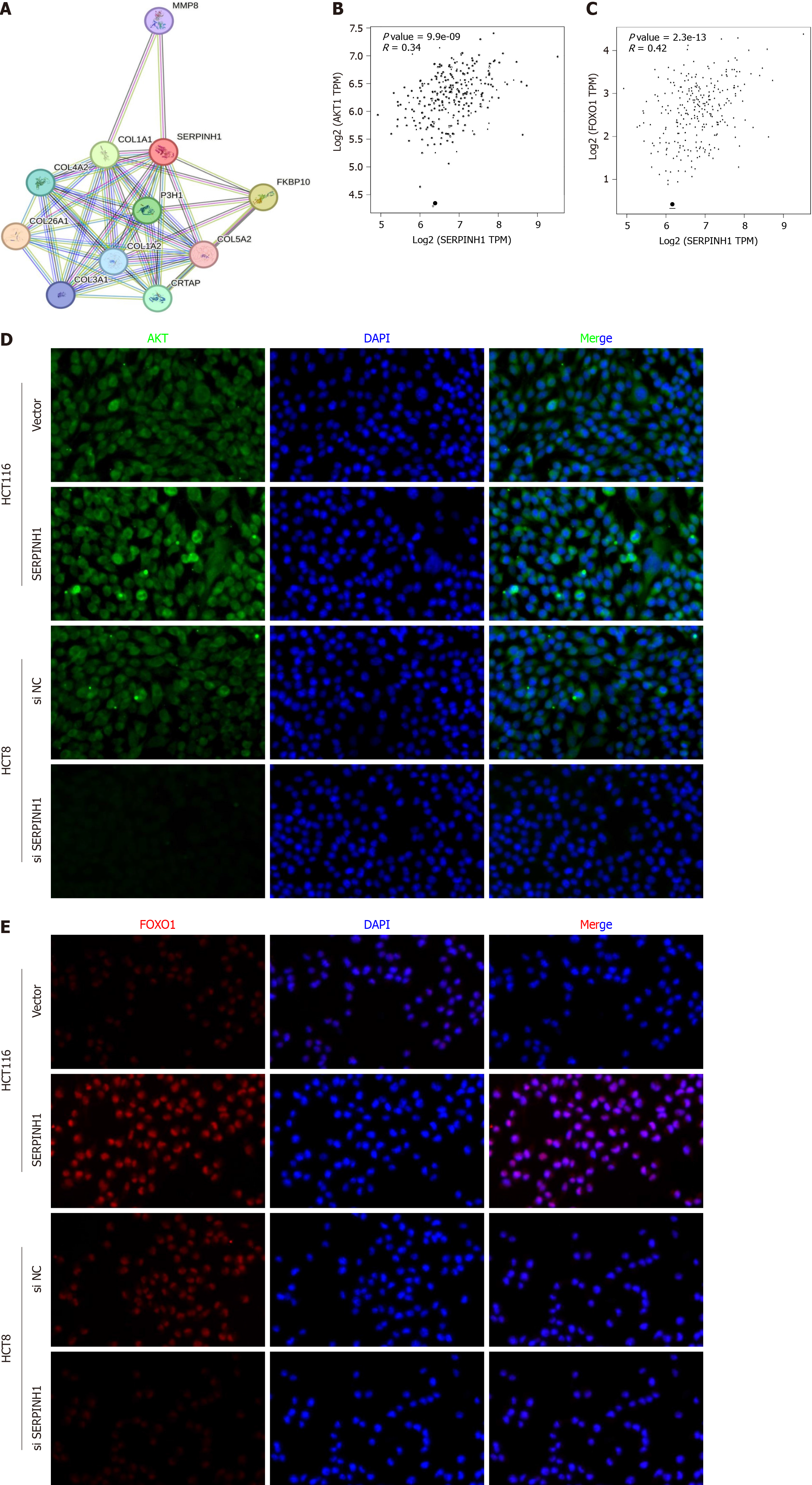
Figure 5 The effect of serpin peptidase inhibitor clade H member 1 on phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT/mechanistic target of rapamycin and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT/FOXO1 signaling pathways.
A: The protein-protein interaction network of serpin peptidase inhibitor clade H member 1 (SERPINH1); B and C: The expression of SERPINH1 is positively correlated to the AKT/FOXO1 of colorectal adenocarcinoma; D and E: Immunofluorescent staining of AKT and FOXO1 in HCT116 cells. SERPINH1: Serpin peptidase inhibitor clade H member 1.
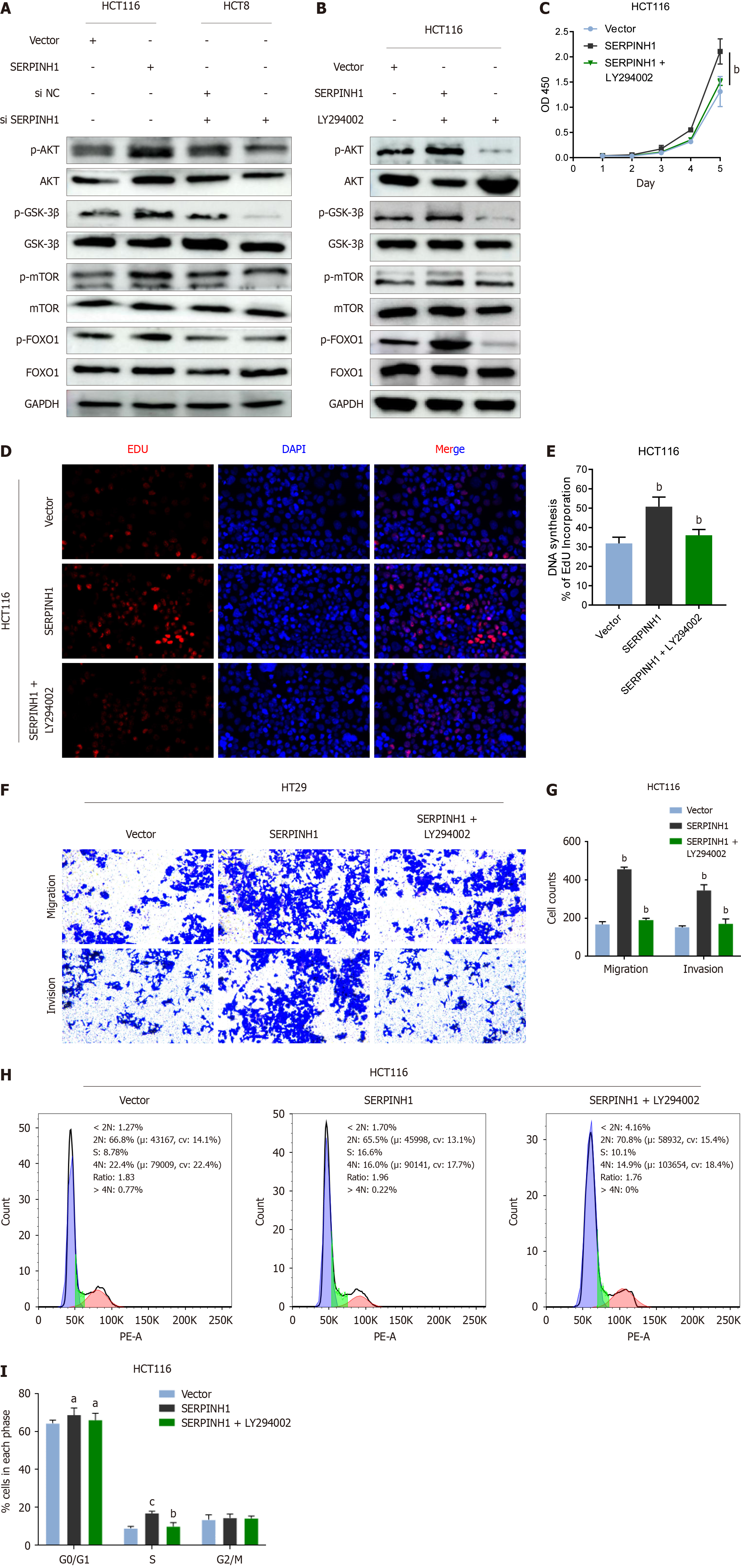
Figure 6 Serpin peptidase inhibitor clade H member 1 promoted colorectal cancer progression through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT/mechanistic target of rapamycin and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT/FOXO1 signaling pathways.
A: Western blotting analysis of p-AKT, total AKT, p-glycogen synthase kinase (GSK)-3β, total GSK-3β, p-mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR), total mTOR, p-FOXO1, and total FOXO1 in serpin peptidase inhibitor clade H member 1 (SERPINH1)-overexpressed cells or SERPINH1 siRNA-infected cells; B: HCT116/SERPINH1 cells were treated with the AKT inhibitor LY294002 (20IM) and DMSO for 24 h, then harvested to examine the expression levels of the indicated proteins by western blotting; C-E: The proliferation ability of HCT116/SERPINH1 cells were determined by cell counting kit 8 assay and 5-ethynyl-2’-deoxyuridine assay; F and G: The invasive and migratory abilities of HCT116/SERPINH1 cells were determined by transwell assays after treatment with rapamycin and DMSO; H and I: The G0/G1 ratio of HCT116/SERPINH1 cells were determined by flow assays after treatment with rapamycin and DMSO. All the data are presented as the mean ± SEM. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. SERPINH1: Serpin peptidase inhibitor clade H member 1.
- Citation: Jin XS, Chen LX, Ji TT, Li RZ. SERPINH1 promoted the proliferation and metastasis of colorectal cancer by activating PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2024; 16(5): 1890-1907
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v16/i5/1890.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v16.i5.1890