Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Oct 15, 2024; 16(10): 4194-4208
Published online Oct 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i10.4194
Published online Oct 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i10.4194
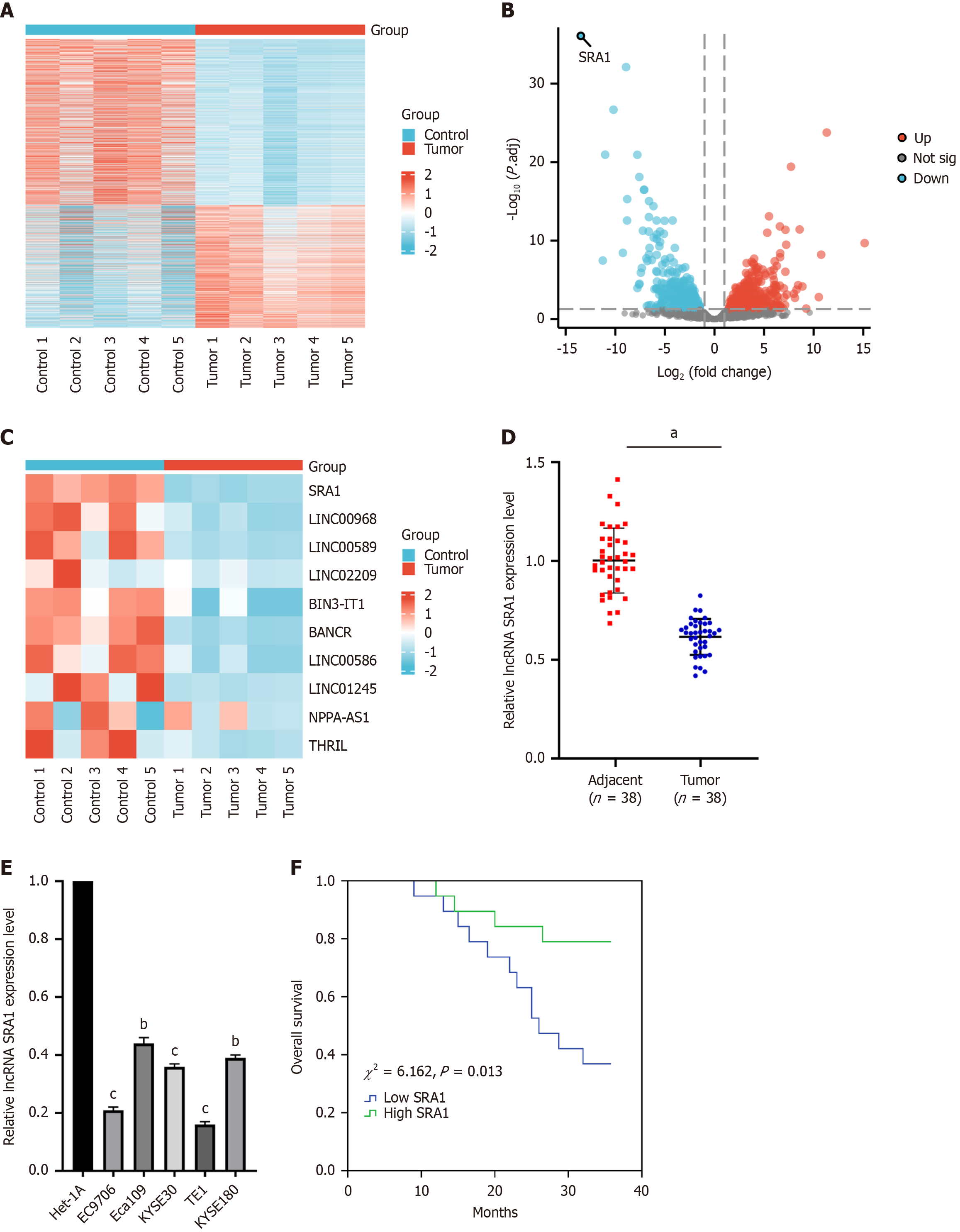
Figure 1 Steroid receptor RNA activator 1 expression level was decreased in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma tissues and cell lines.
A: The five pairs of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) and adjacent normal tissues were carried out long non-coding RNA (LncRNA) microarray analysis, and the lncRNA expression patterns were performed through hierarchical clustering; B: Changes in the lncRNA level were displayed in the volcano plot; C: LncRNA SRA1 had the highest fold of differential expression; D: Steroid receptor RNA activator 1 (SRA1) expression was apparently downregulated in ESCC tissues; E: SRA1 expression was apparently downregulated in ESCC cell line; F: ESCC patients with low SRA1 expression had shorter overall survival than patients with high SRA1 expression. aP < 0.01; bP < 0.05 vs Het-1A; cP < 0.01 vs Het-1A; LncRNA: Long non-coding RNA; SRA1: Steroid receptor RNA activator 1.
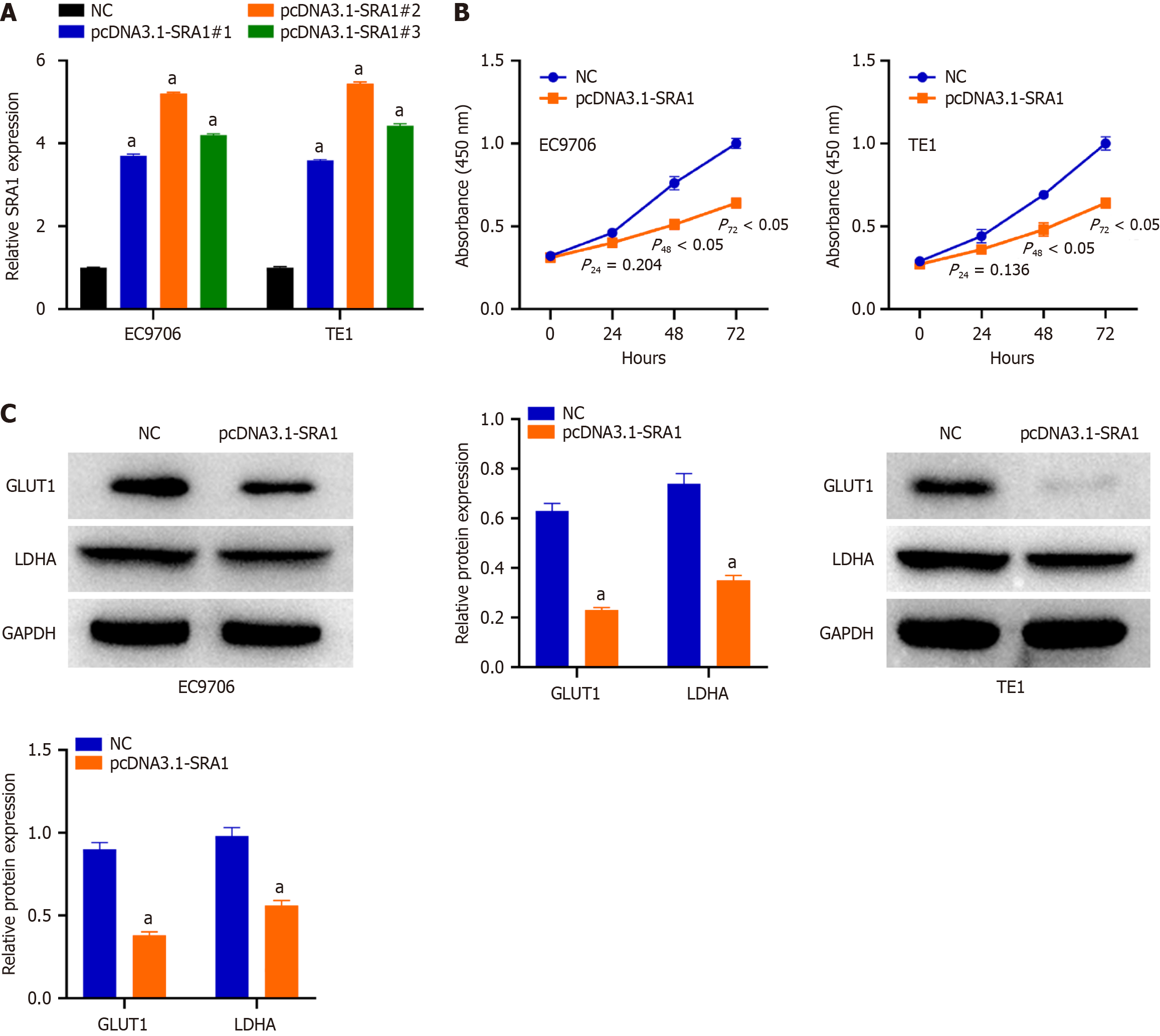
Figure 2 Overexpression of steroid receptor RNA activator 1 suppresses esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cell proliferation and glycolysis in vitro.
A: Steroid receptor RNA activator 1 (SRA1) overexpression was verified by quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction; B: Overexpression of SRA1 caused an obvious decrease in proliferation rate in EC9706 and TE1 cells; C: Upregulation of SRA1 triggered a decrease of GLUT1 and LDHA in EC9706 and TE1 cells. aP < 0.01 vs negative control; NC: Negative control; SRA1: Steroid receptor RNA activator 1.
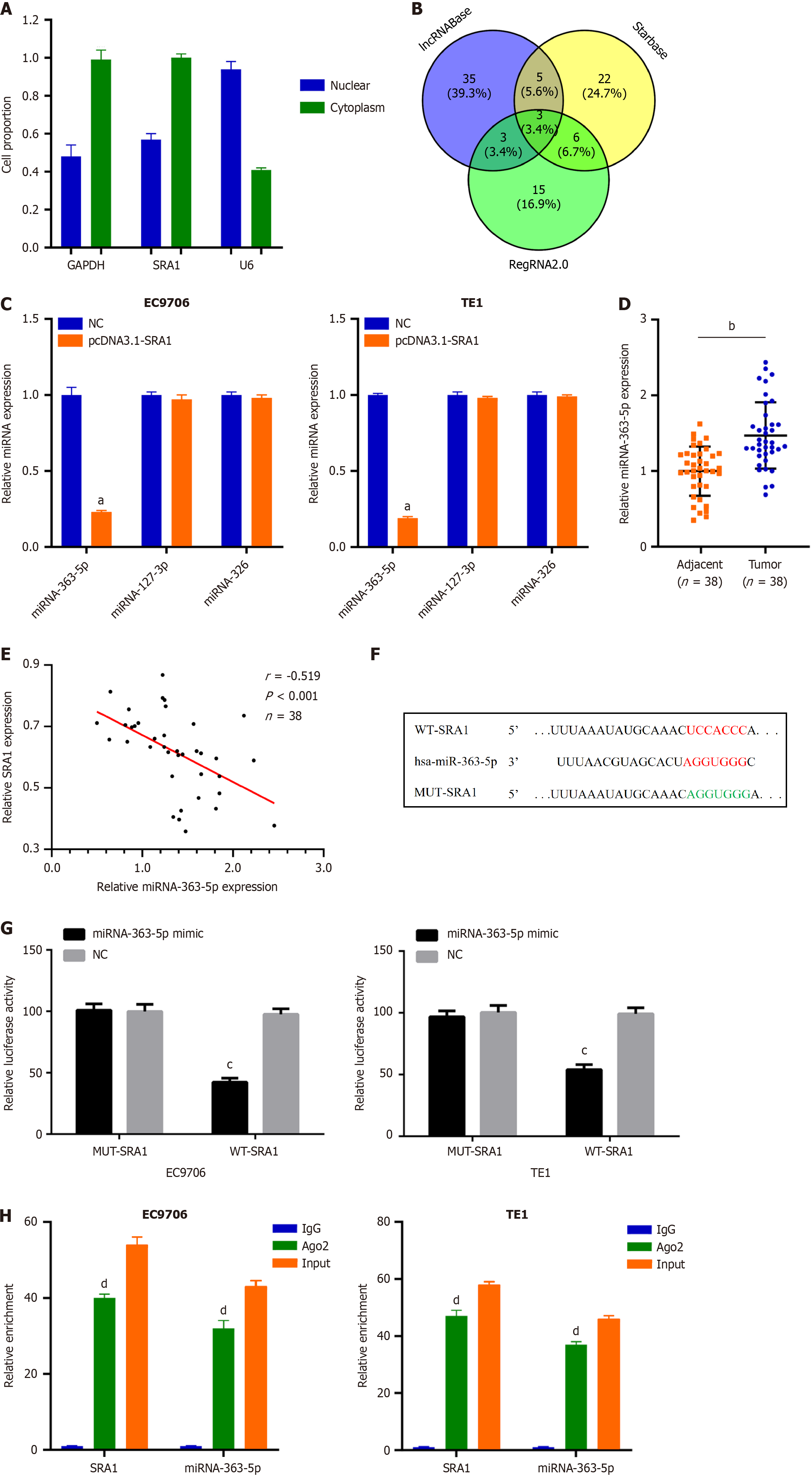
Figure 3 MiRNA-363-5p is sponged by steroid receptor RNA activator 1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
A: Steroid receptor RNA activator 1 (SRA1) was observed to be enriched in the cytoplasm of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) cells; B: Using lncRNABase, starBase, and RegRNA2.0, a total of 3 miRNAs were predicted to contain putative binding sites within SRA1; C: MiRNA-363-5p expression was inhibited in EC9706 and TE1 cells transfected with pcDNA3.1-SRA1; D: Upregulated miRNA-363-5p was found in ESCC tissues; E: MiRNA-363-5p is negatively correlated with SRA1; F and G: Luciferase activity of WT-SRA1 instead of MUT-SRA1 was evidently decreased by miRNA-363-5p upregulation in EC9706 and TE1 cells; H: RIP assay defined that both SRA1 and miRNA-363-5p could be remarkably enriched by anti-Ago2 in EC9706 and TE1 cells. aP < 0.01 vs negative control (NC); bP < 0.01 vs Adjacent; cP < 0.05 vs NC; dP < 0.01 vs IgG; NC: Negative control; LncRNA: Long non-coding RNA; SRA1: Steroid receptor RNA activator 1.
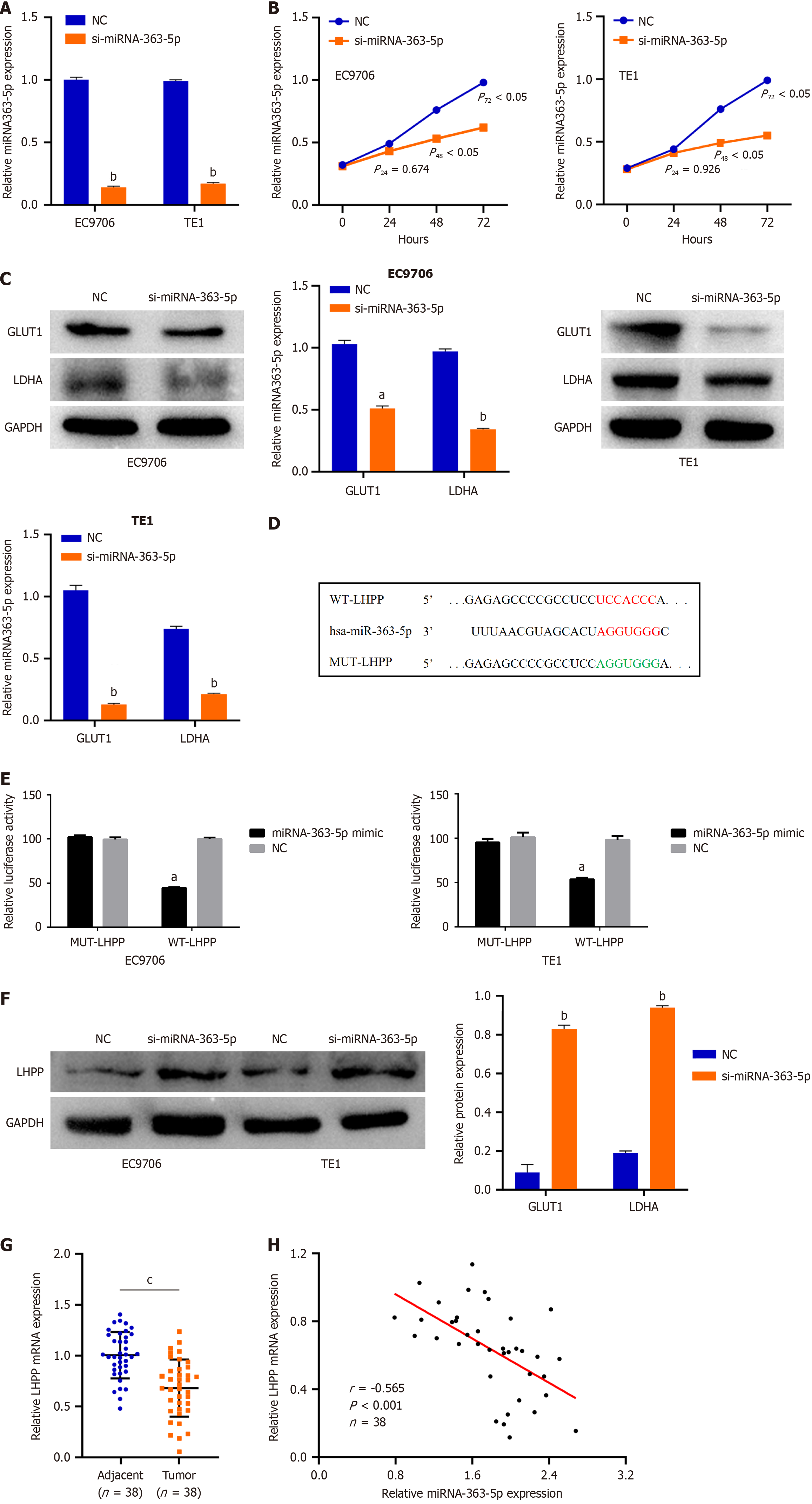
Figure 4 MiRNA-363-5p directly targets phospholysine phosphohistidine inorganic pyrophosphate phosphatase in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells.
A: Quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction analysis indicated that miRNA-363-5p expression remarkably decreased after si-miRNA-363-5p transfection; B: Inhibition of miRNA-363-5p expression significantly attenuated proliferation in EC9706 and TE1 cells; C: Inhibition of miRNA-363-5p expression significantly attenuated glycolysis in EC9706 and TE1 cells; D: Phospholysine phosphohistidine inorganic pyrophosphate phosphatase (LHPP) was predicted to have binding sequences for miRNA-363-5p; E: Luciferase reporter turned out that miRNA-363-5p mimic clearly weakened the luciferase activity of WT-LHPP; F: Downregulating miRNA-363-5p enhanced the LHPP protein levels in EC9706 and TE1 cells; G: LHPP expression was low in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma tissues compared to adjacent normal tissues; H: MiRNA-363-5p is negatively correlated with LHPP. aP < 0.05 vs NC; bP < 0.01 vs NC; cP < 0.01 vs Adjacent. NC: Negative control; LHPP: Phospholysine phosphohistidine inorganic pyrophosphate phosphatase.
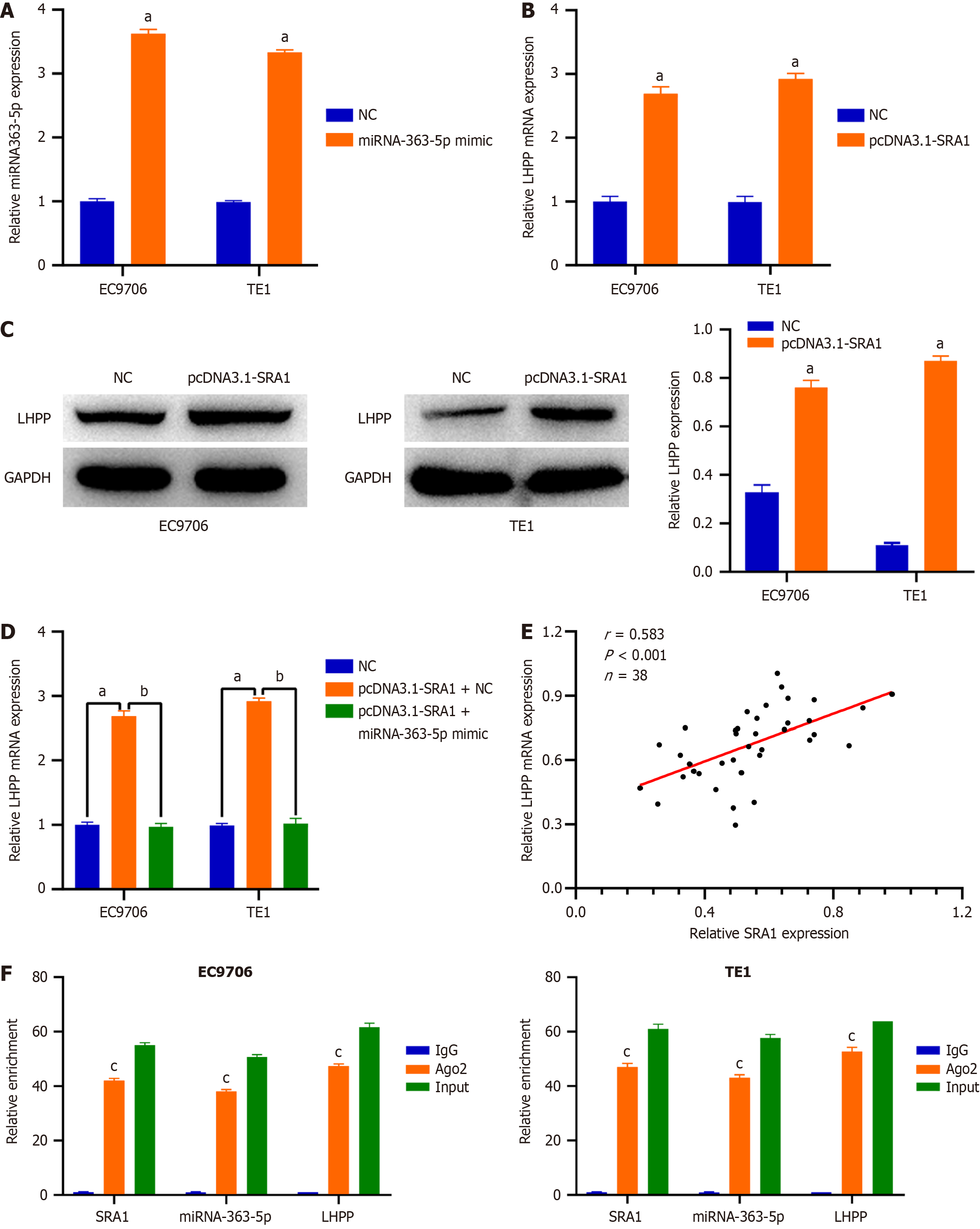
Figure 5 Steroid receptor RNA activator 1 overexpression promotes phospholysine phosphohistidine inorganic pyrophosphate phosphatase expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells by sponging miRNA-363-5p.
A: The delivery of miRNA-363-5p mimic caused a prominent miRNA-363-5p upregulation in EC9706 and TE1 cells; B-D: Steroid receptor RNA activator 1 (SRA1) upregulation triggered an obvious overexpressed effect on the endogenous phospholysine phosphohistidine inorganic pyrophosphate phosphatase (LHPP) mRNA and protein levels in EC9706 and TE1 cells, whereas the delivery of miRNA-363-5p mimic counteracted such effect; E: LHPP expression was positively correlated with SRA1 expression in ESCC tissues; F: SRA1, miRNA-363-5p, and LHPP were preferentially concentrated in the anti-Ago2 precipitate. aP < 0.01 vs NC; bP < 0.01 vs pcDNA3.1-SRA1 + miRNA-363-5p mimic; cP < 0.01 vs IgG; NC: Negative control; SRA1: Steroid receptor RNA activator 1; LHPP: Phospholysine phosphohistidine inorganic pyrophosphate phosphatase.
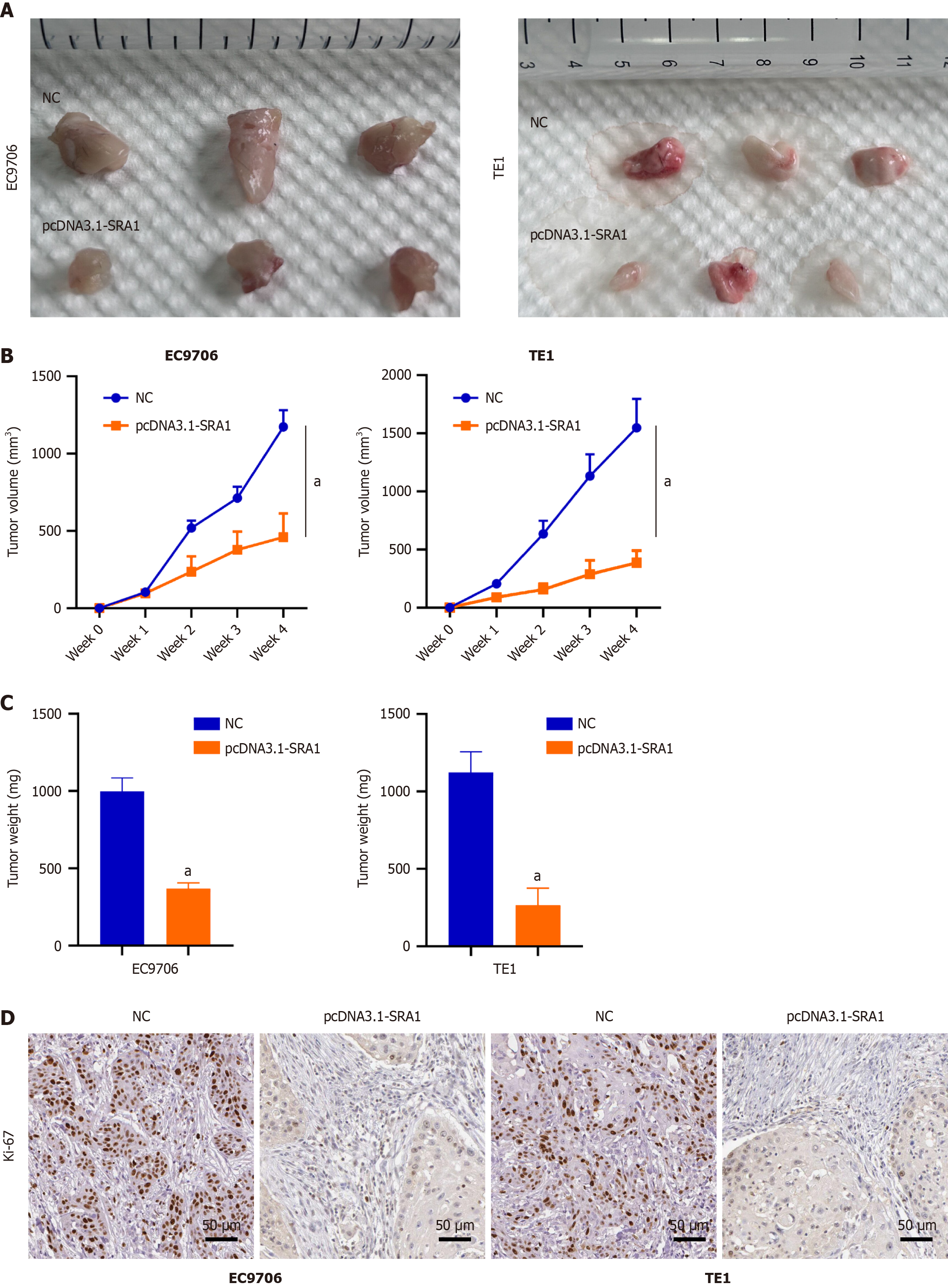
Figure 6 Steroid receptor RNA activator 1 overexpression inhibits esophageal squamous cell carcinoma tumor growth in vivo.
A-C: Overexpressing steroid receptor RNA activator 1 (SRA1) exhibited weaker tumorigenic ability; D: Immunohistochemical staining confirmed the relatively low level of proliferation marker Ki-67 in the tumors with overexpressing SRA1. Scale bar = 50μm. aP < 0.01 vs negative control; NC: Negative control.
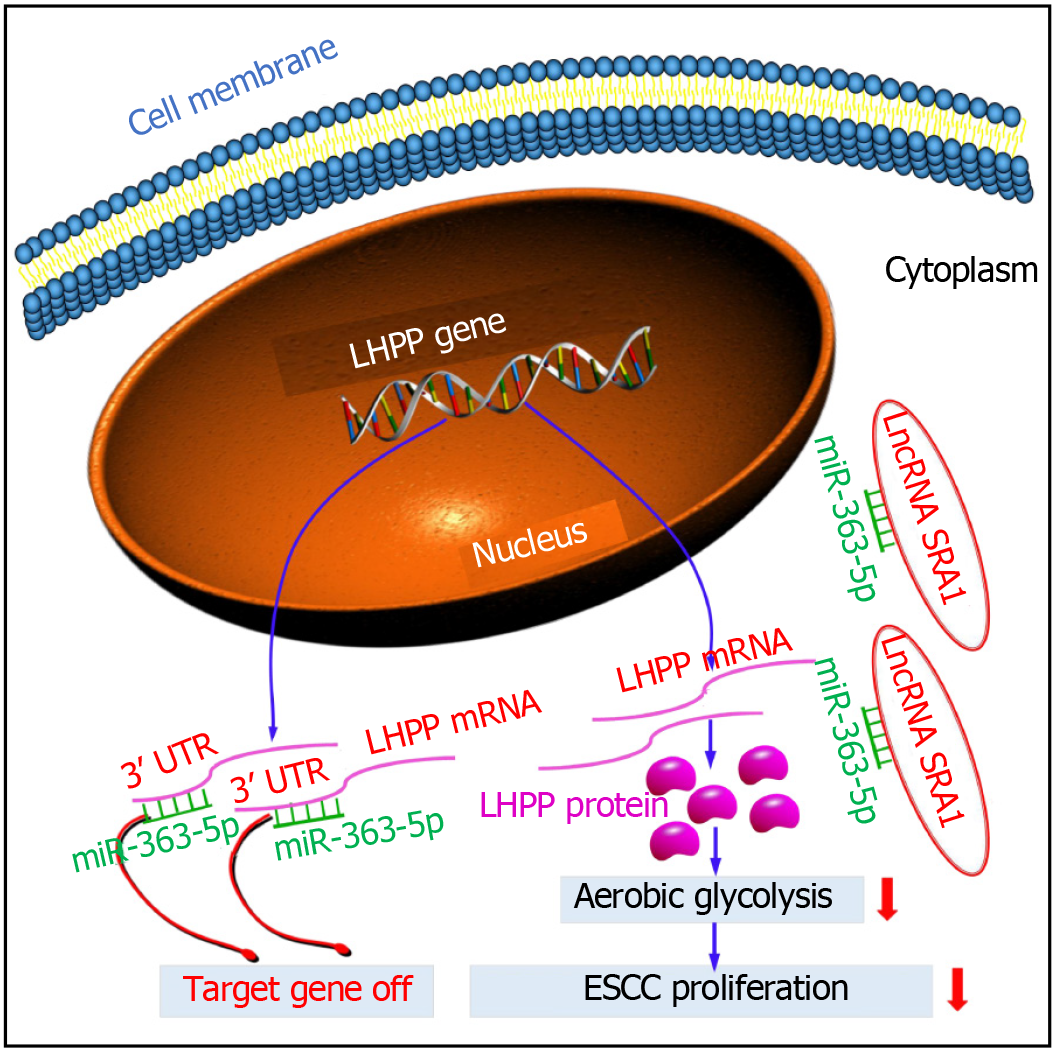
Figure 7 Schematic diagram showing the regulatory mechanism of steroid receptor RNA activator 1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
LncRNA: Long non-coding RNA; SRA1: Steroid receptor RNA activator 1; ESCC: Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; LHPP: Phospholysine phosphohistidine inorganic pyrophosphate phosphatase.
- Citation: He M, Qi Y, Zheng ZM, Sha M, Zhao X, Chen YR, Chen ZH, Qian RY, Yao J, Yang ZD. Long noncoding RNA steroid receptor RNA activator 1 inhibits proliferation and glycolysis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2024; 16(10): 4194-4208
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v16/i10/4194.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v16.i10.4194