Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Oct 15, 2024; 16(10): 4166-4176
Published online Oct 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i10.4166
Published online Oct 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i10.4166
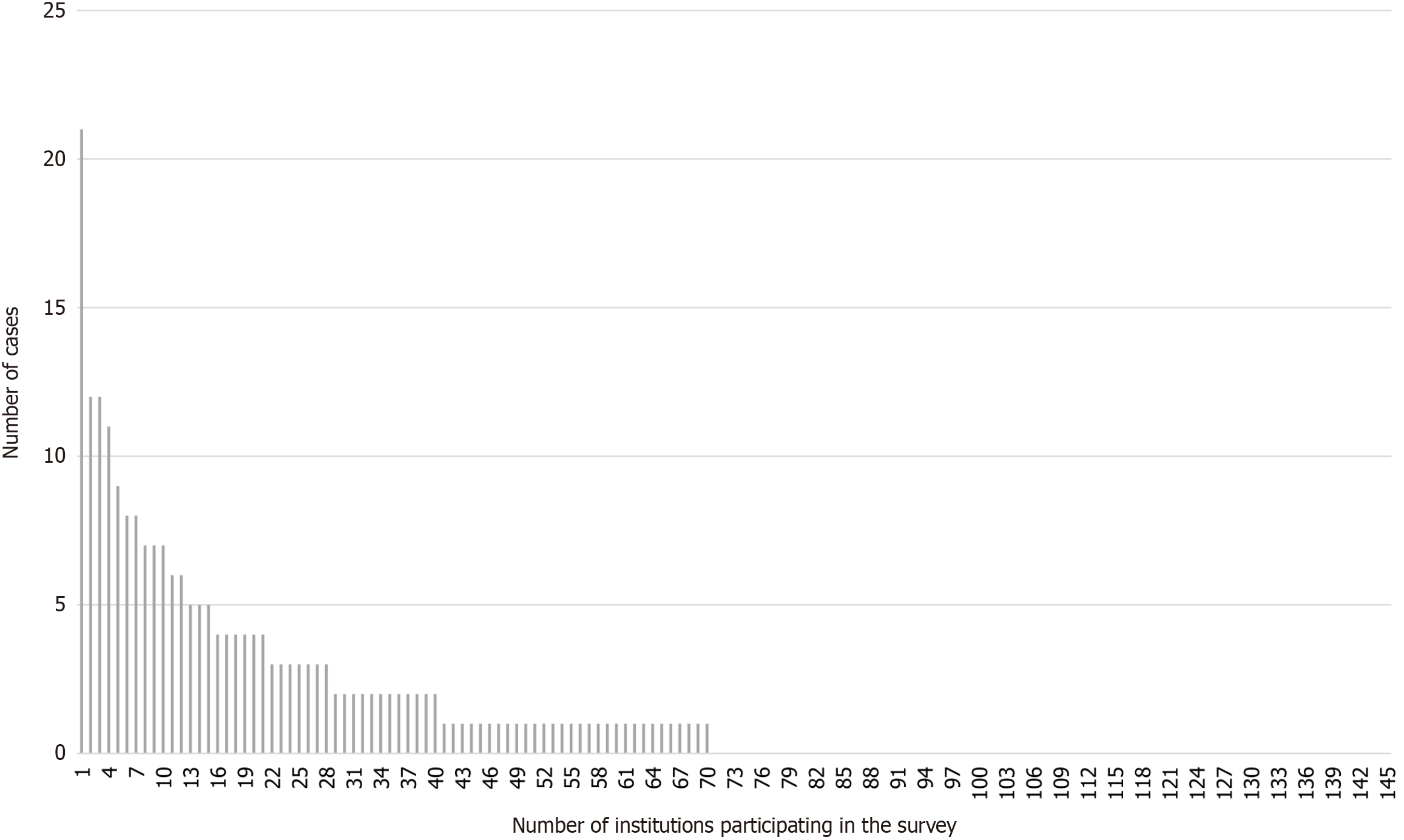
Figure 1 Distribution of cases per institution.
Over the 22-year period, 75 of 145 institutions (51.7%) reported zero cases, 55 institutions (37.9%) reported 1-4 cases, and 11 institutions (7.6%) reported 5-9 cases. Four institutions (2.8%) managed > 10 cases, with only one of these institutions reporting > 20 cases. The number of cases experienced varies greatly from facility to facility.
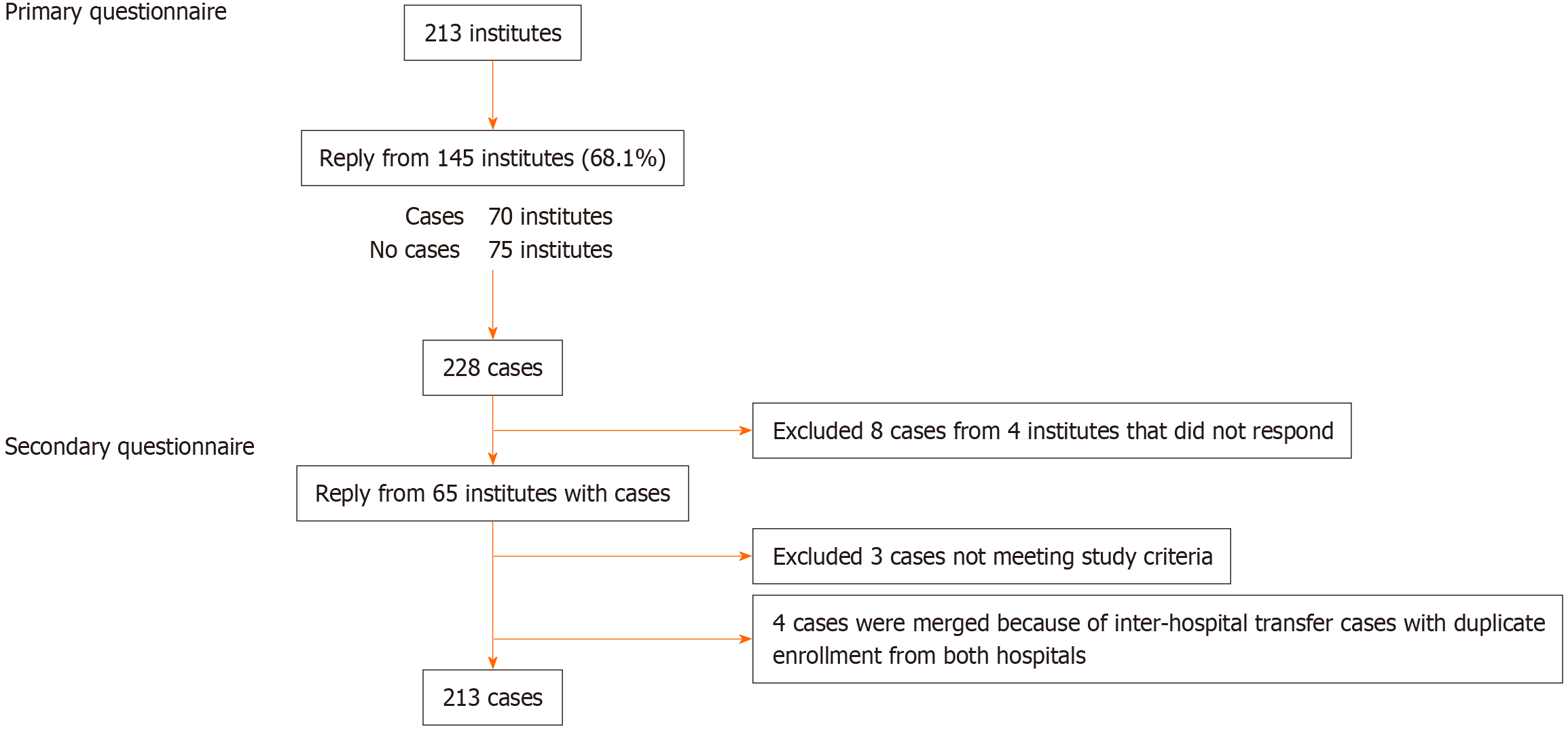
Figure 2 Questionnaire results.
In the primary survey, 228 cases were enrolled, and 213 cases were finally enrolled in the secondary survey.
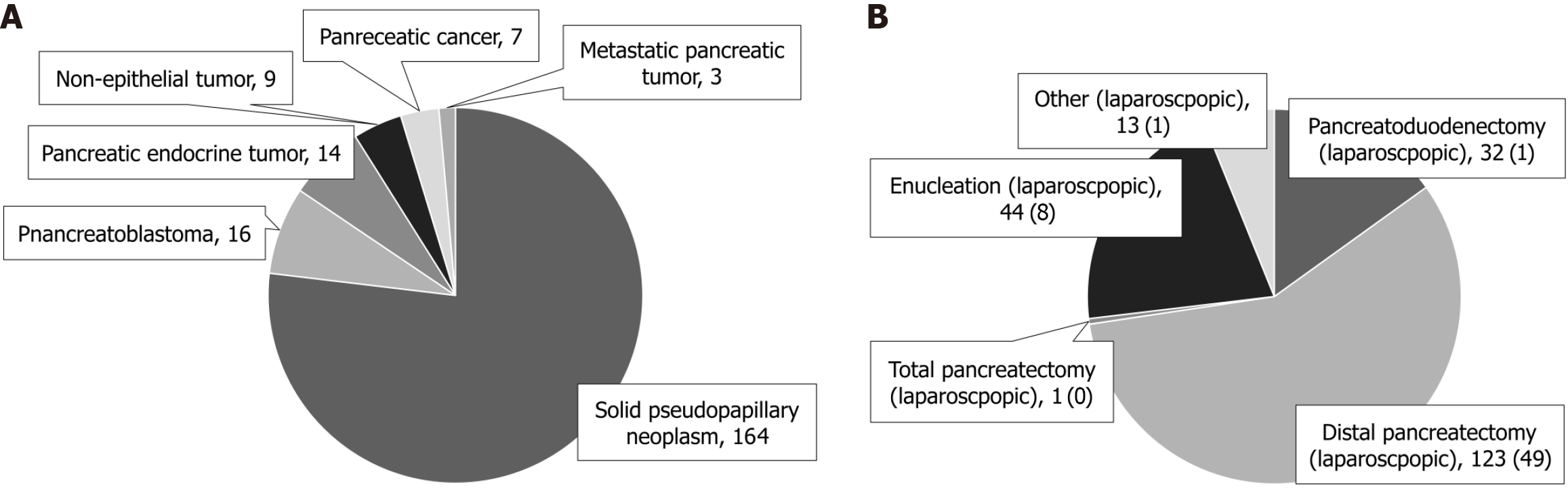
Figure 3 Diagnoses and procedures performed in the 213 cases.
A: Diagnoses of the 213 cases. The most common type of pancreatic tumor was SPN [n = 164 (77.0%)] , followed by pancreatoblastoma [n = 16 (7.5%)], pancreatic endocrine tumor [n = 14 (6.6%)], non-epithelial tumor [n = 9 (4.2%)], pancreatic cancer [n = 7 (3.3%)] , and metastatic pancreatic tumor [n = 3 (1.4%)]; B: Procedures performed in the 213 cases. In total, 123 (57.7%) patients underwent distal pancreatectomy, of whom 49 underwent laparoscopic surgery. Furthermore, 44 (20.7%) patients underwent enucleation, of whom eight underwent laparoscopic surgery. In total, 32 (15.0%) patients underwent pancreaticoduodenectomy, of whom one underwent laparoscopic surgery. Moreover, one patient underwent total pancreatectomy, and the remaining 13 patients underwent other procedures. Of them, one patient had laparoscopic surgery.
- Citation: Makita S, Uchida H, Kano M, Kawakubo N, Miyake H, Yoneda A, Tajiri T, Fukumoto K. Nationwide questionnaire survey on pediatric pancreatic tumors in Japan. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2024; 16(10): 4166-4176
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v16/i10/4166.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v16.i10.4166