Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Oct 15, 2024; 16(10): 4064-4079
Published online Oct 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i10.4064
Published online Oct 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i10.4064
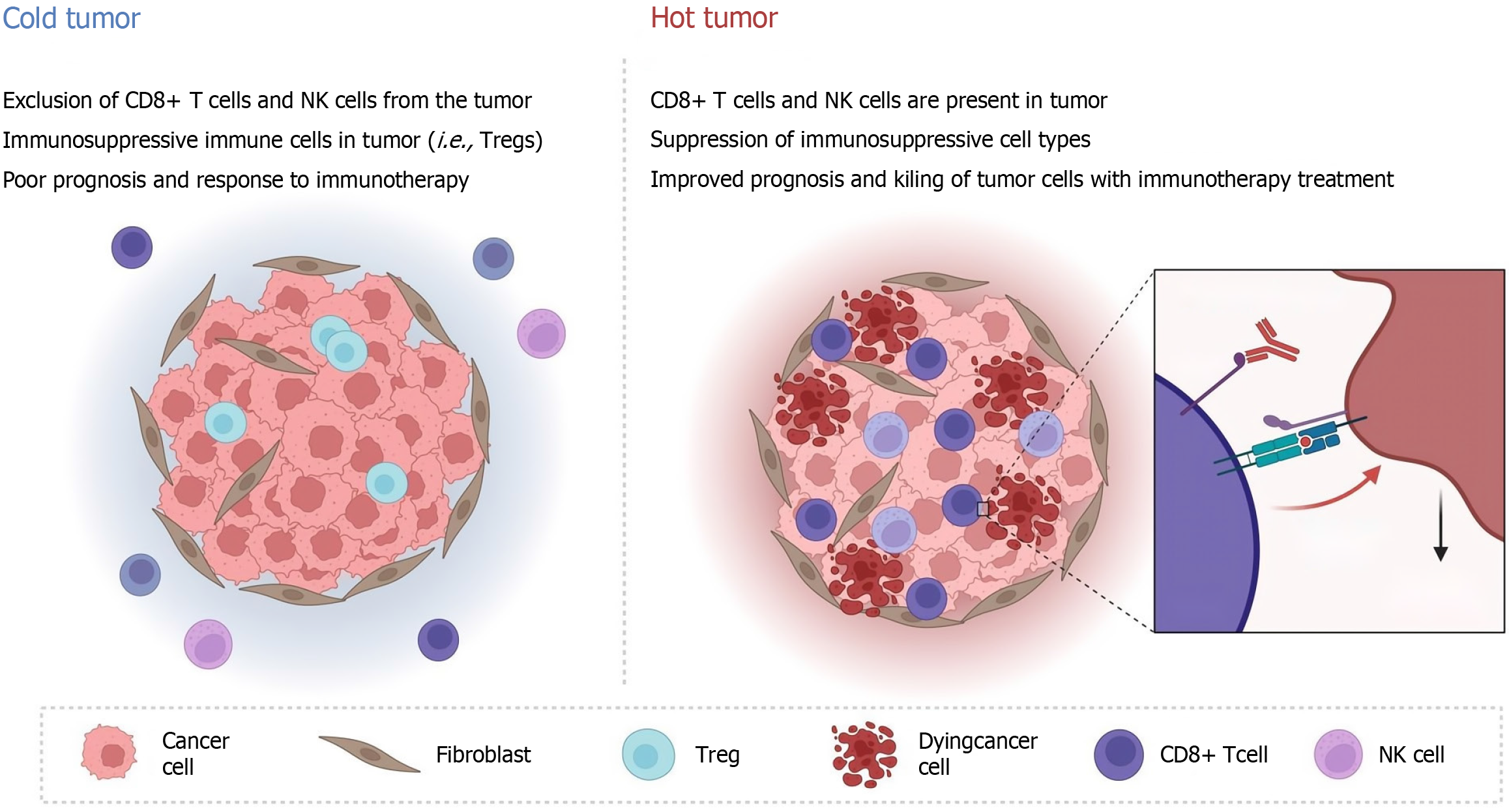
Figure 1 Immunogenicity and effects of immune microenvironment on cold and hot.
NK: Natural killer; Treg: Regulatory T cell.
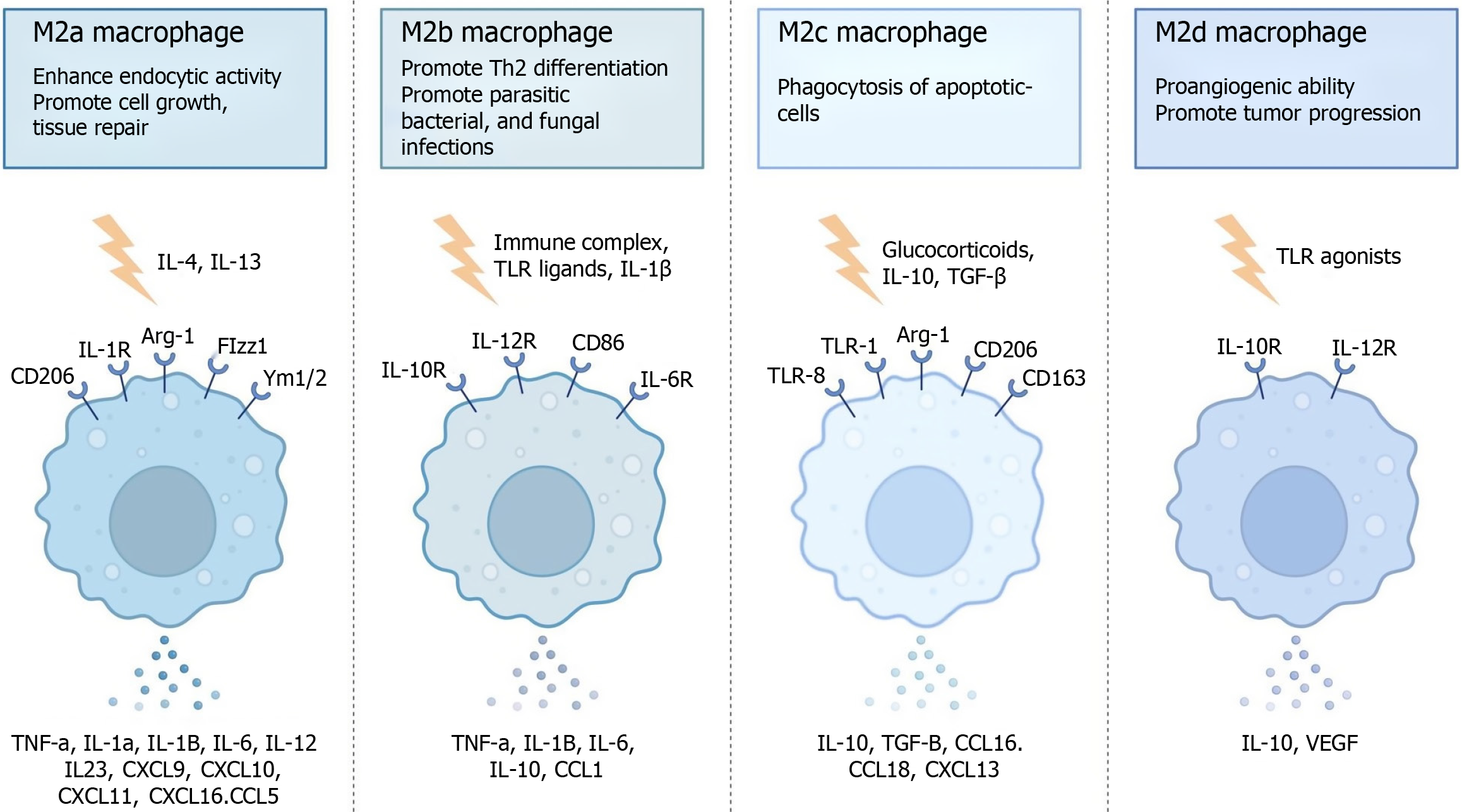
Figure 2 M2 macrophage subtypes.
IL: Interleukin; TLR: Toll-like receptor; TGF: Transforming growth factor; CXCL: C-X-C motif chemokine ligand; CCL: C-C motif chemokine ligand; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; Arg-1: Arginase-1.
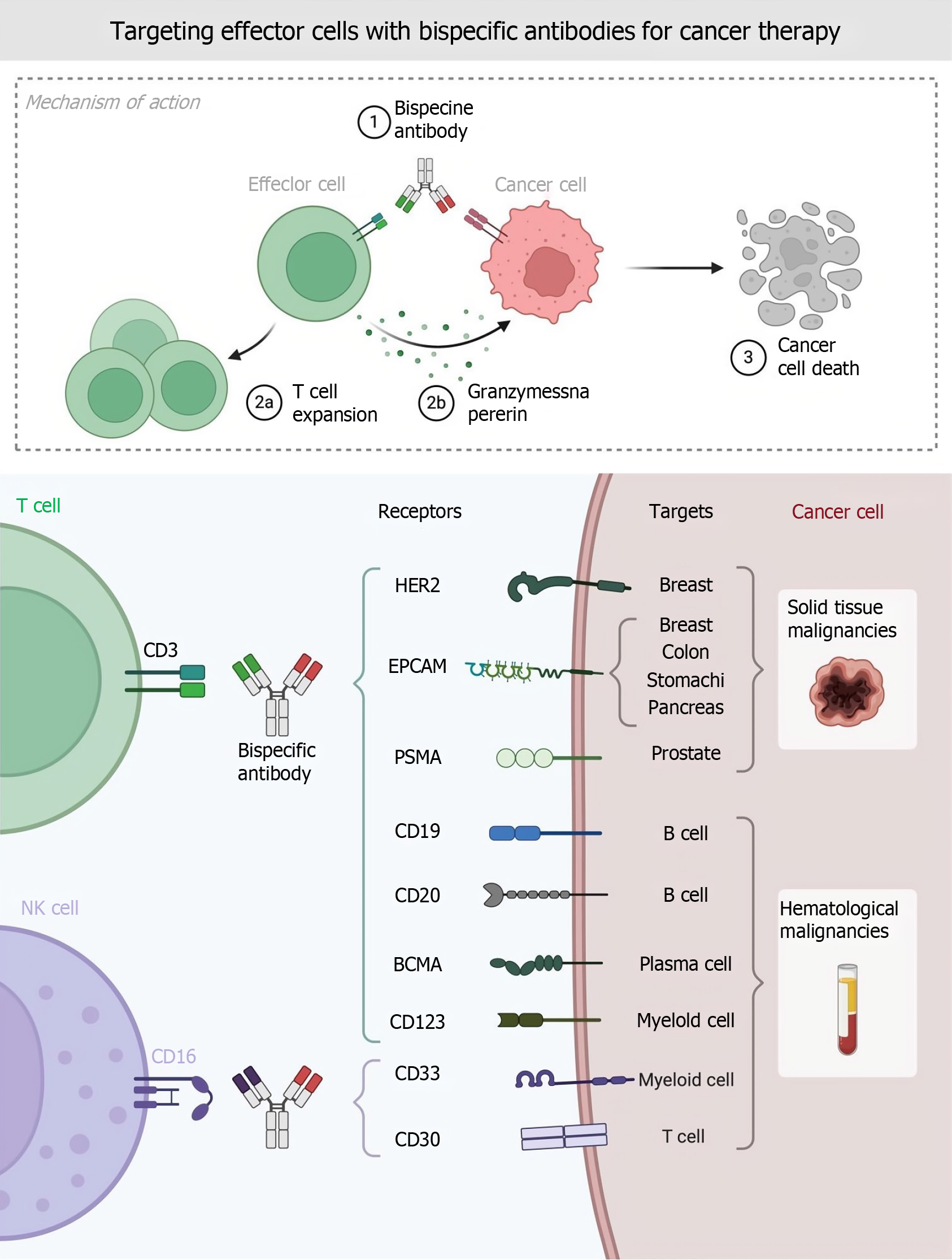
Figure 3 Targeting effector cells with bispecific antibodies for cancer therapy.
NK: Natural killer; EPCAM: Epithelial cell adhesion molecule; PSMA: Prostate-specific membrane antigen; BCMA: Bulbospinal muscular atrophy.
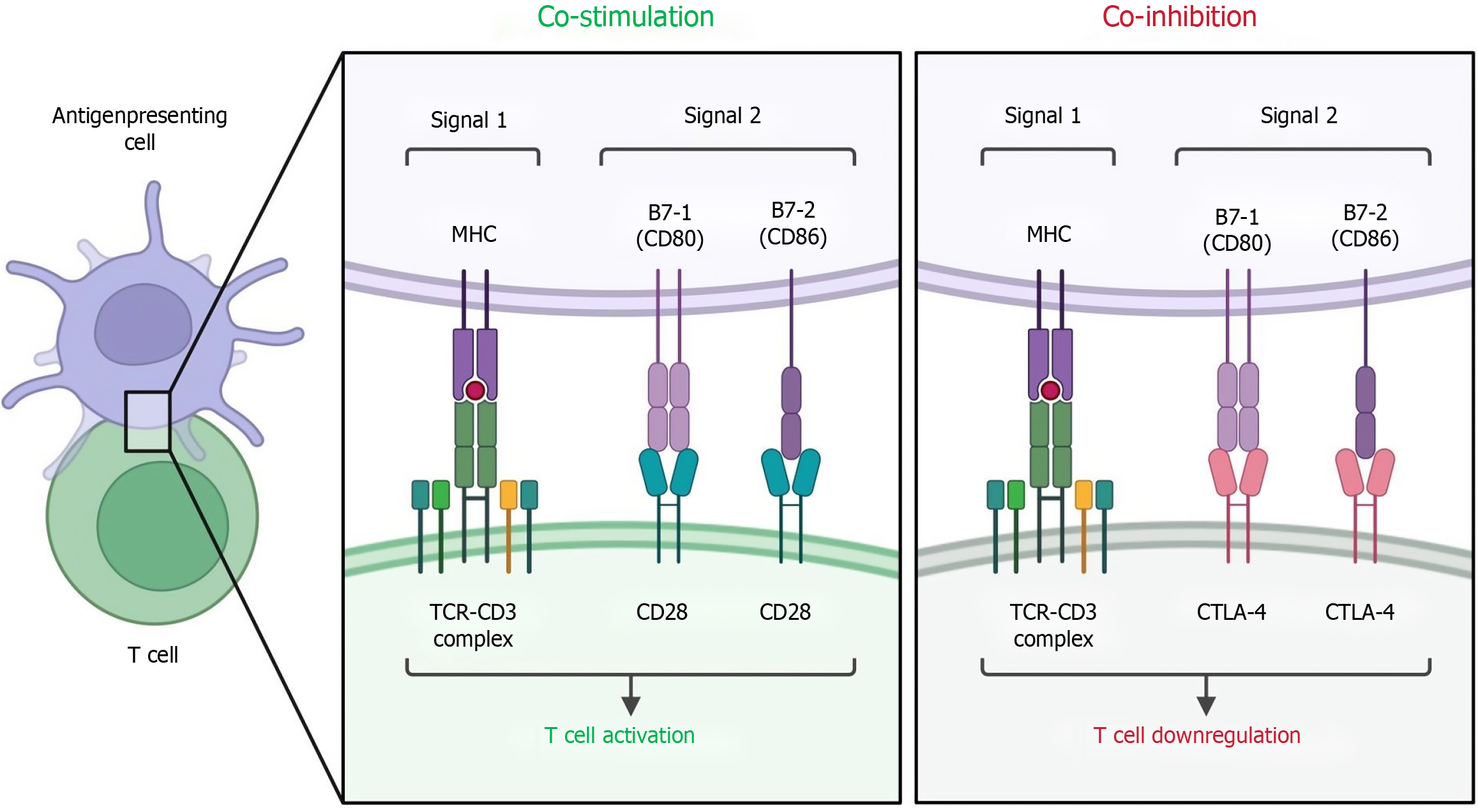
Figure 4 T cell co-stimulation and co-inhibition.
TCR: T cell receptor; MHC: Major histocompatibility complex; CTLA: Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein.
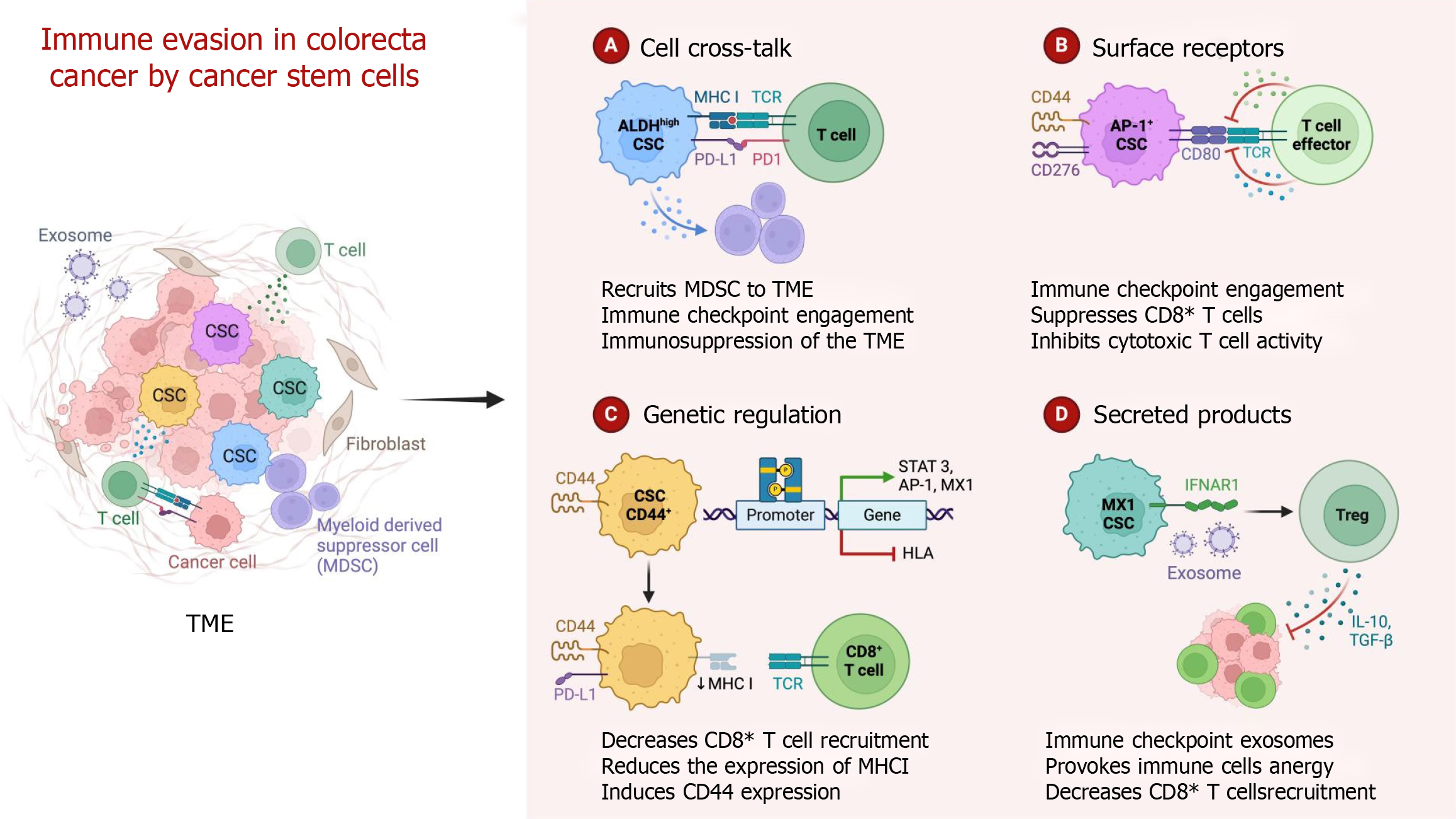
Figure 5 Mechanisms of immune evasion in colorectal cancer by cancer stem cells.
CSC: Cancer stem cell; TME: Tumor microenvironment; TCR: T cell receptor; MHC: Major histocompatibility complex; MDSC: Myeloid-derived suppressor cell; PD-L1: Programmed cell death ligand 1; PD-1: Programmed cell death protein 1; STAT 3: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; AP-1: Activating protein-1; HLA: Human leukocyte antigen; IFNAR1: Interferon alpha/beta receptor 1; Treg: Regulatory T cell; IL: Interleukin; TGF: Transforming growth factor.
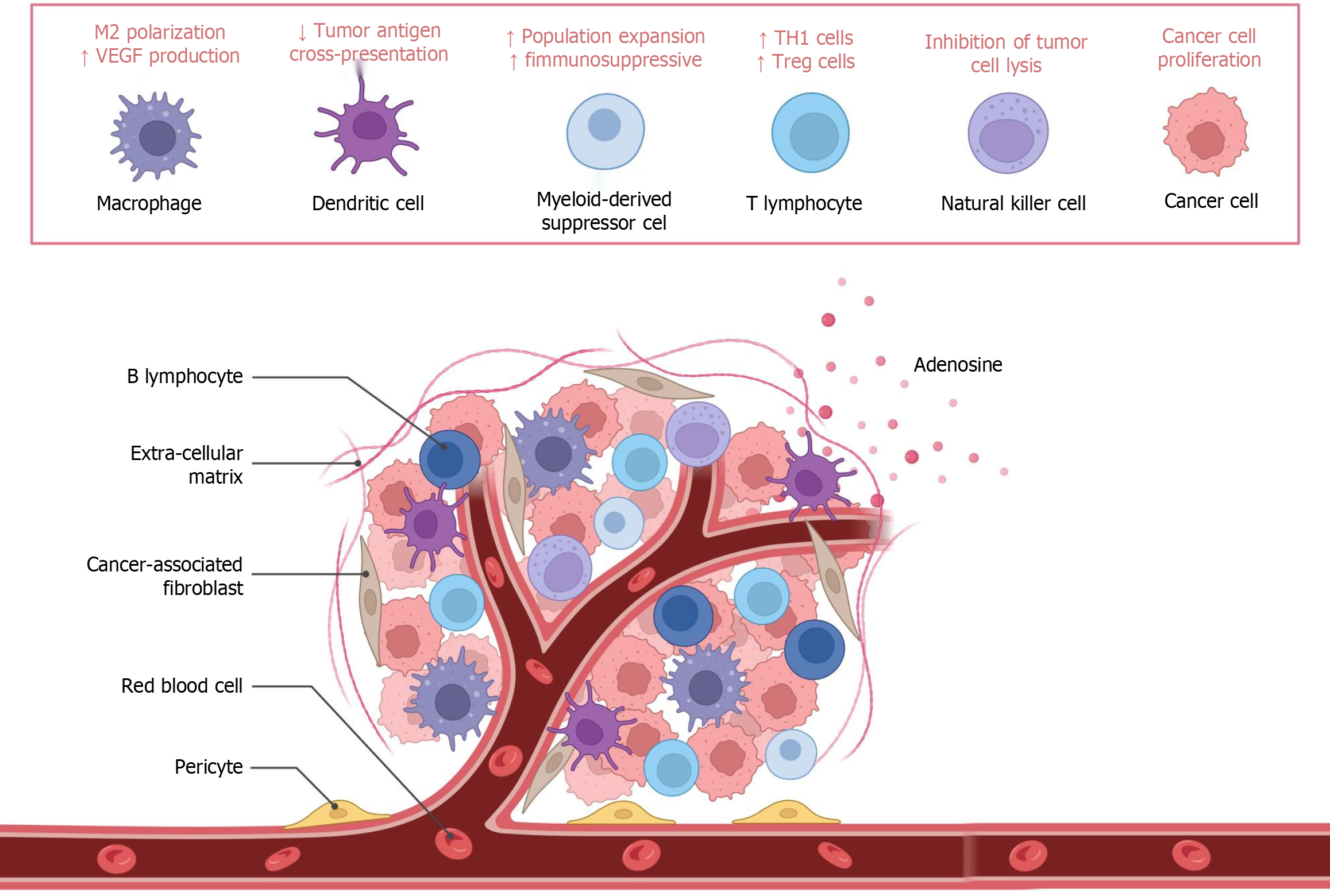
Figure 6 Effects of M2-type polarization from the tumor microenvironment.
VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; Th1: T helper 1; Treg: Regulatory T cell.
- Citation: Fan Q, Fu ZW, Xu M, Lv F, Shi JS, Zeng QQ, Xiong DH. Research progress of tumor-associated macrophages in immune checkpoint inhibitor tolerance in colorectal cancer. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2024; 16(10): 4064-4079
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v16/i10/4064.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v16.i10.4064