Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Mar 15, 2023; 15(3): 464-489
Published online Mar 15, 2023. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v15.i3.464
Published online Mar 15, 2023. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v15.i3.464
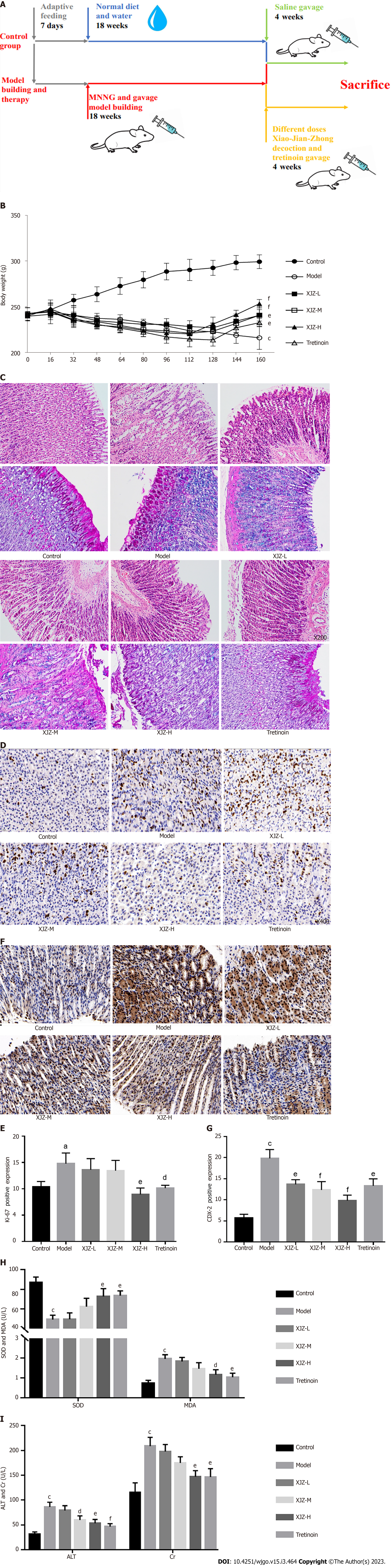
Figure 1 Effects of Xiaojianzhong decoction on body weight, gastric mucosal pathological conditions and liver kidney toxicity in N-methyl-N’-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine-induced gastric precancerous lesions rats.
A: Schematic diagram of model construction and treatment; B: Schematic diagram of weight change in rats; C: Representative images of hematoxylin-eosin and alcian blue-periodic acid-Schiff staining of gastric tissues; D-G: Ki-67 and caudal-type homeobox protein 2 (CDX-2) expression was determined using immunohistochemistry (n = 5); Ki-67 and CDX-2 positive score was determined using Image J; H: Superoxide dismutase and malondialdehyde levels in serum (n = 3); I: Alanine aminotransferase and creatinine levels in serum (n = 3). Data are expressed as mean ± SD. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001 vs control group; dP < 0.05, eP < 0.01, fP < 0.001 vs model group. XJZ-L: Low dose of Xiaojianzhong decoction; XJZ-M: Middle dose of Xiaojianzhong decoction; XJZ-H: High dose of Xiaojianzhong decoction; SOD: Superoxide dismutase; MDA: Malondialdehyde; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; Cr: Creatinine.
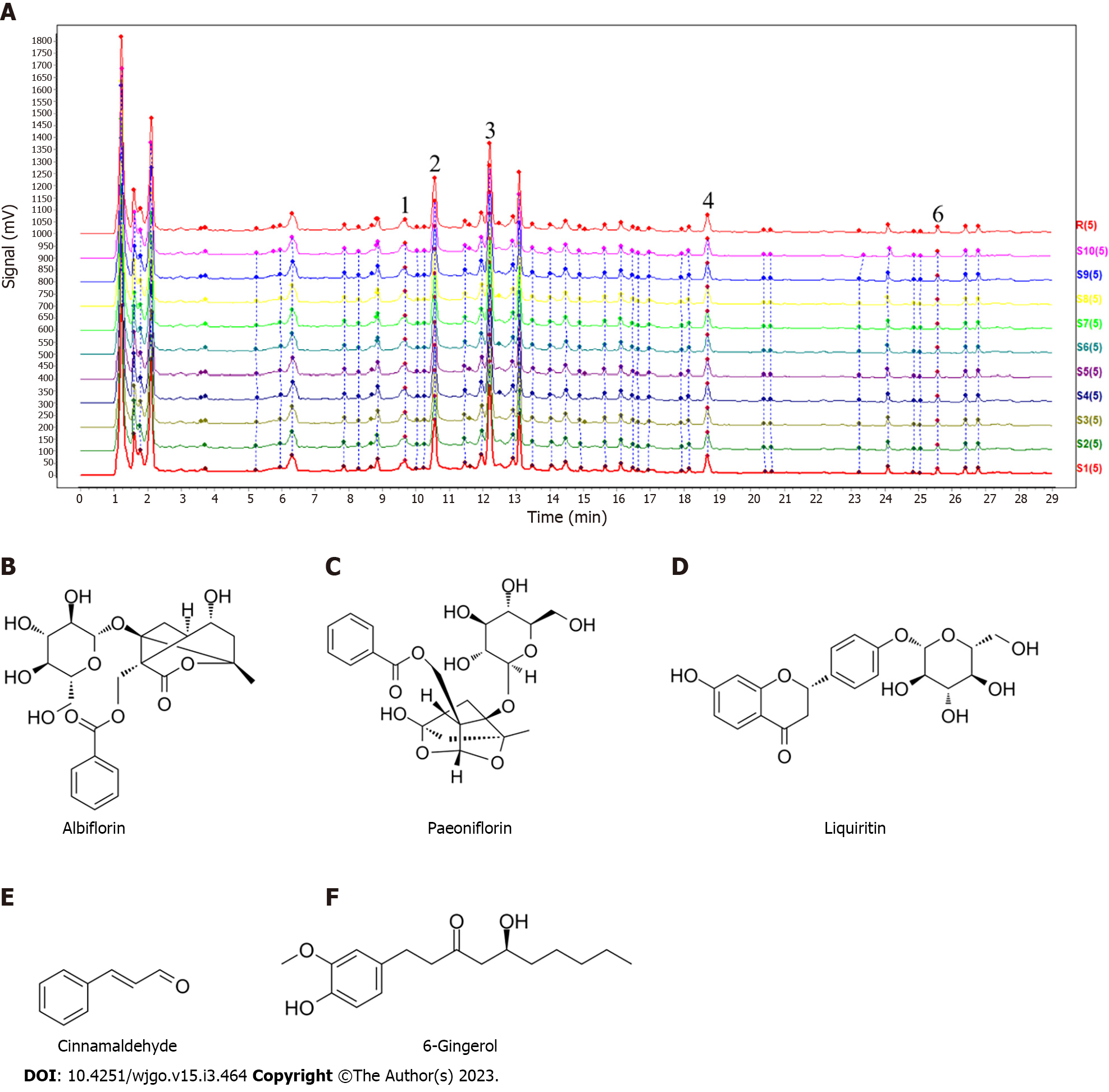
Figure 2 Result of the high-performance liquid chromatography method coupled with triple-quadrupole tandem mass spectrometry assays of the chemical composition of Xiaojianzhong decoction.
A: High-performance liquid chromatography chromatogram; B-F: Compounds contained in Xiaojianzhong decoction.
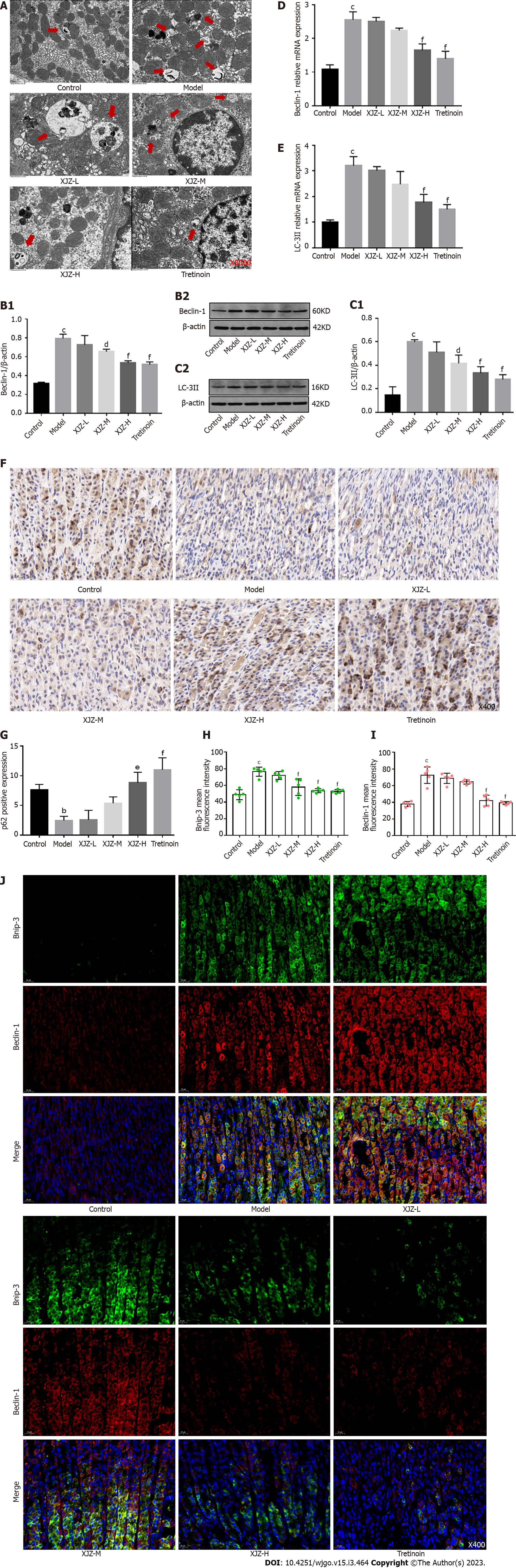
Figure 3 Effects of Xiaojianzhong decoction on autophagy of gastric mucosal epithelial cells in N-methyl-N’-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine-induced gastric precancerous lesions rats.
A: Observation of autophagy in rat gastric epithelial cells by transmission electron microscope (the red arrows in the figure are autophagosomes or autophagolysosomes); B and C: Western blot analysis was performed to detect BCL2-interacting protein 1 (Beclin-1), microtubule associated protein 1 light chain 3 (LC-3) II protein expression (n = 3); D and E: Beclin-1, LC-3II mRNA expression was determined using real-time polymerase chain reaction analysis (n = 3); F and G: p62 expression was determined using immunohistochemistry (n = 5); p62 positive score was determined using Image J; H-J: B cell lymphoma/leukemia-2 and adenovirus E1B19000 interacting protein 3 (Bnip-3), Beclin-1 proteins expression was determined using immunofluorescence (n = 5); Bnip-3, Beclin-1 porteins positive score was determined using ImageJ. Data are expressed as mean ± SD. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001 vs control group; dP < 0.05, eP < 0.01, fP < 0.001 vs model group. XJZ-L: Low dose of Xiaojianzhong decoction; XJZ-M: Middle dose of Xiaojianzhong decoction; XJZ-H: High dose of Xiaojianzhong decoction; Beclin-1: BCL2-interacting protein 1; LC-3: Microtubule associated protein 1 light chain 3.
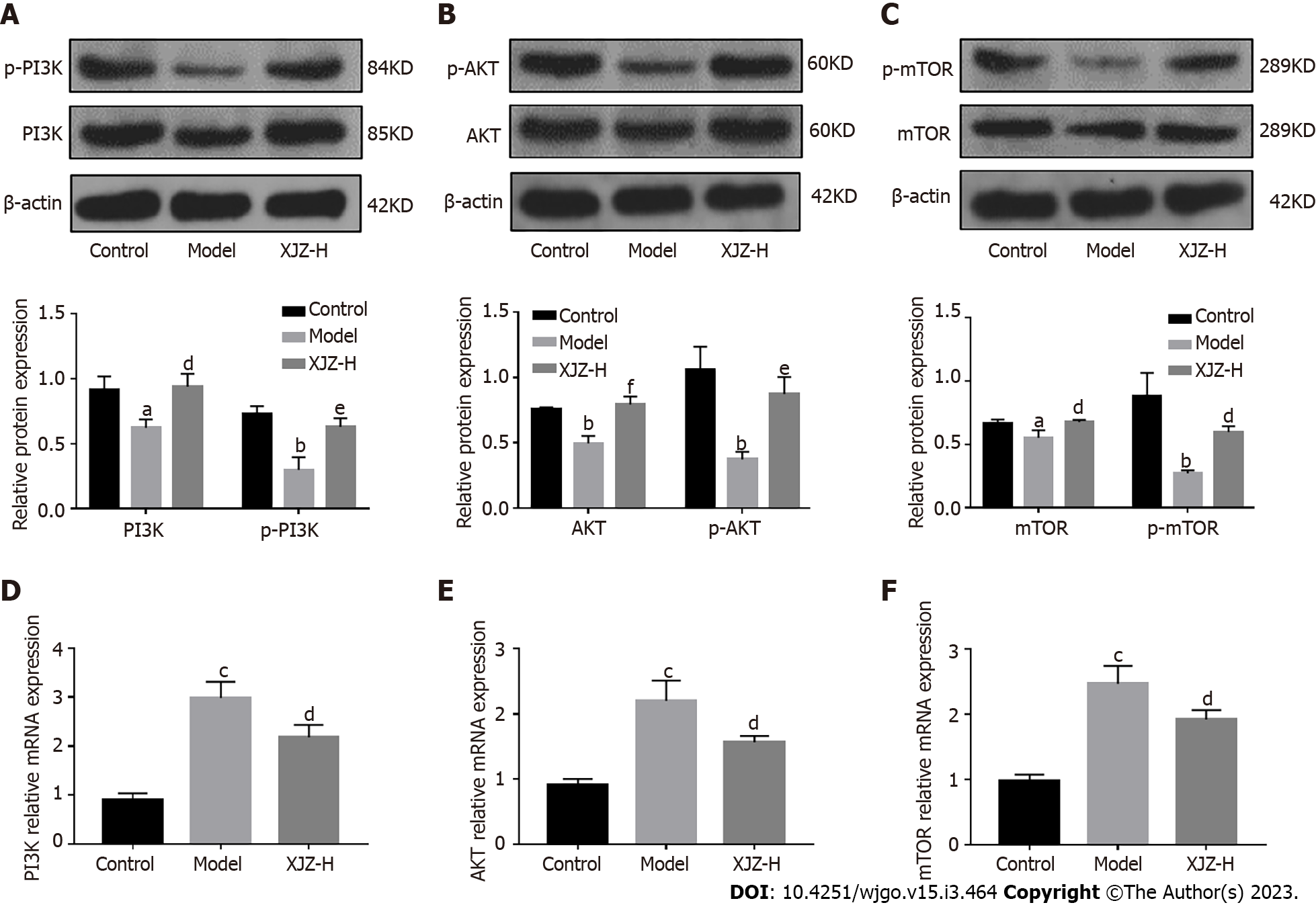
Figure 4 Xiaojianzhong decoction up-regulates phosphatidylinositol 3-kimase/protein kinase B/mammalian target of rapamycin signaling pathway in N-methyl-N’-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine-induced gastric precancerous lesions rats.
A-C: Western blot analysis was performed to detect phosphorylated-phosphatidylinositol 3-kimase (p-PI3K), phosphorylated-protein kinase B (p-AKT), and phosphorylated-mammalian target of rapamycin (p-mTOR) protein expression (n = 3); D-F: PI3K, AKT, and mTOR mRNA expression was determined using real-time polymerase chain reaction analysis (n = 3). Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001 vs control group; dP < 0.05, eP < 0.01, fP < 0.001 vs model group. XJZ-L: Low dose of Xiaojianzhong decoction; XJZ-M: Middle dose of Xiaojianzhong decoction; XJZ-H: High dose of Xiaojianzhong decoction.
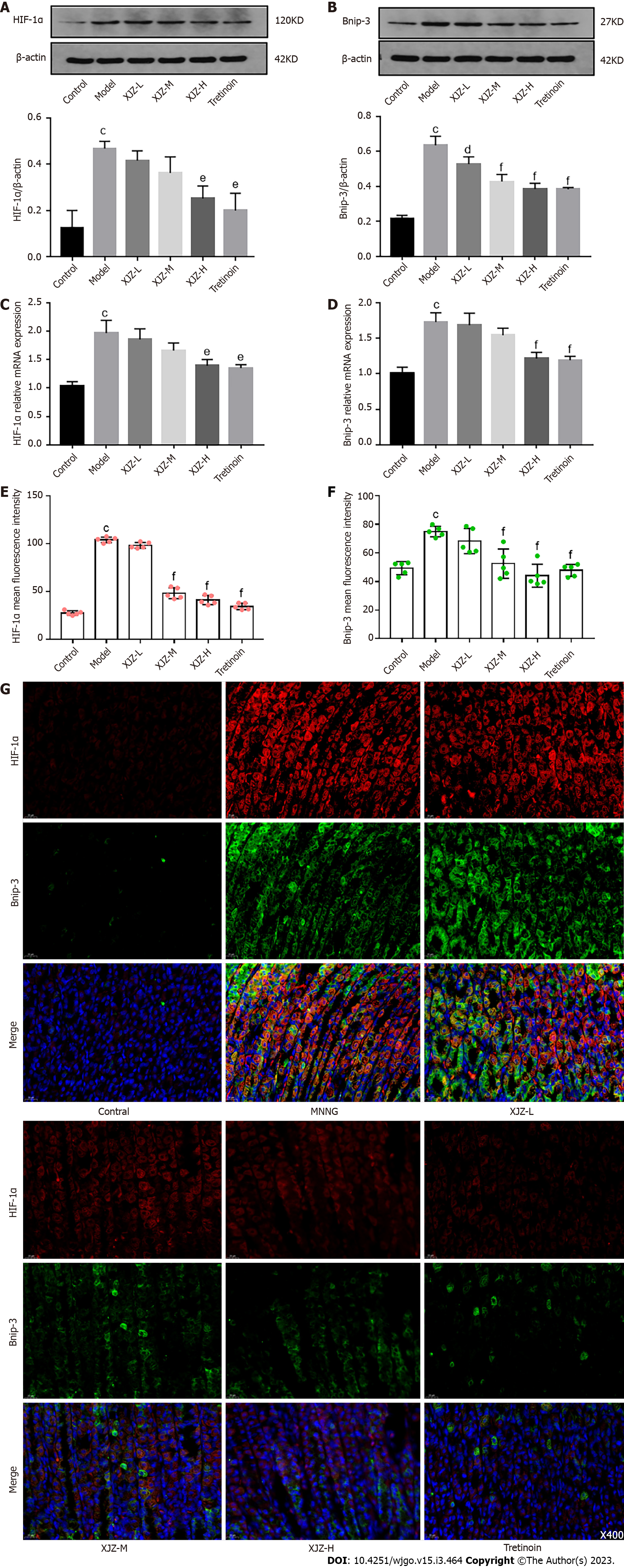
Figure 5 Effects of Xiaojianzhong decoction on gastric mucosal hypoxia in N-methyl-N’-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine-induced gastric precancerous lesions rats.
A and B: Western blot analysis was performed to detect hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α), E1B19000 interacting protein 3 (Bnip-3) protein expression (n = 3); C and D: HIF-1α, Bnip-3 mRNA expression was determined using real-time polymerase chain reaction analysis (n = 3); E-G: Hypoxia-induced autophagy-related protein HIF-1α, Bnip-3 expression was determined using immunofluorescence (n = 5); HIF-1α, Bnip-3 proteins positive score was determined using Image J. Data are expressed as mean ± SD. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001 vs control group; dP < 0.05, eP < 0.01, fP < 0.001 vs model group. XJZ-L: Low dose of Xiaojianzhong decoction; XJZ-M: Middle dose of Xiaojianzhong decoction; XJZ-H: High dose of Xiaojianzhong decoction; HIF-1α: Hypoxia-inducible factor 1α; Bnip-3: B cell lymphoma/Leukemia-2 and adenovirus E1B19000 interacting protein 3.
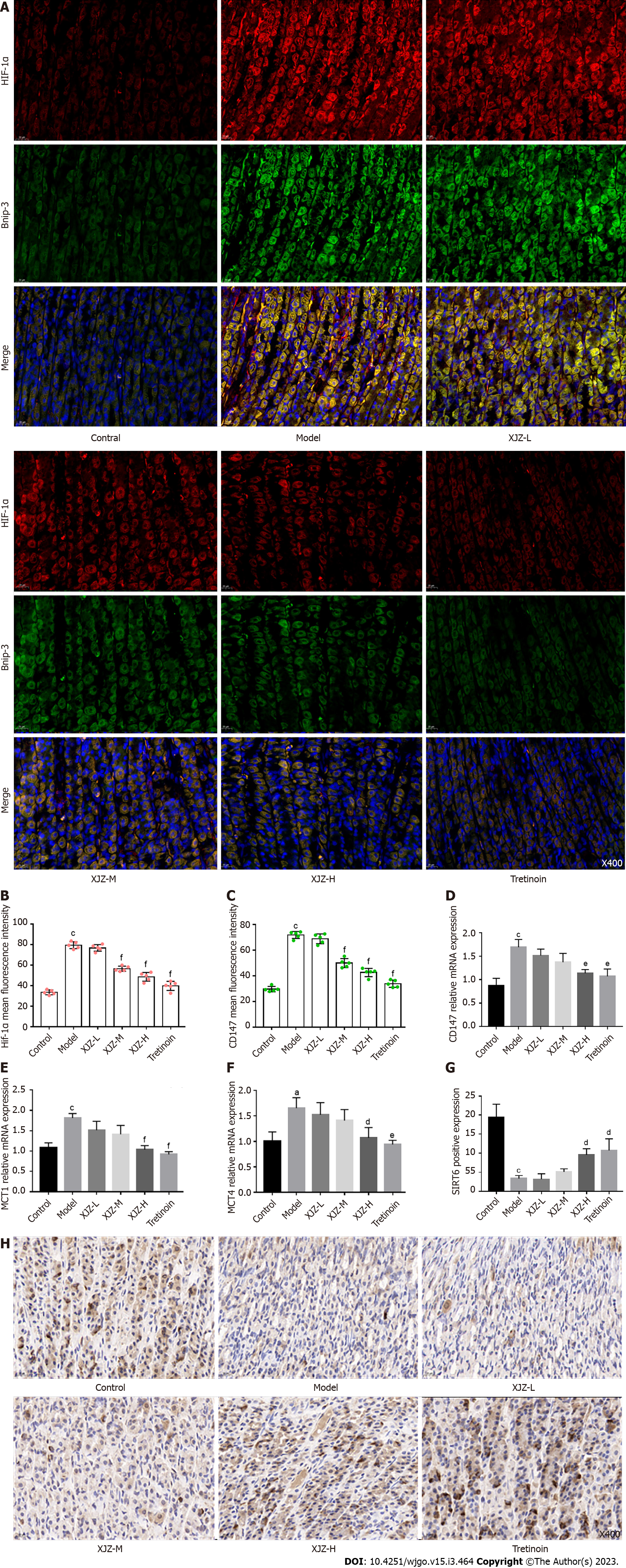
Figure 6 Effects of Xiaojianzhong decoction on hypoxia-induced glycolysis in gastric mucosal epithelial cells.
A-C: Hypoxia-induced glycolysis-related protein hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α), CD147 expression was determined using immunofluorescence (n = 5); HIF-1α, CD147 proteins positive score was determined using Image J; D-F: CD147, monocarboxylate transporter (MCT1), and MCT4 mRNA expression was determined using real-time polymerase chain reaction analysis (n = 3); G and H: Sirtuin 6 (SIRT6) expression was determined using immunohistochemistry (n = 5); SIRT-6 positive score was determined using Image J. Data are expressed as mean ± SD. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001 vs control group; dP < 0.05, eP < 0.01, fP < 0.001 vs model group. XJZ-L: Low dose of Xiaojianzhong decoction; XJZ-M: Middle dose of Xiaojianzhong decoction; XJZ-H: High dose of Xiaojianzhong decoction; HIF-1α: Hypoxia-inducible factor 1α; MCT: Monocarborxylat transporter.
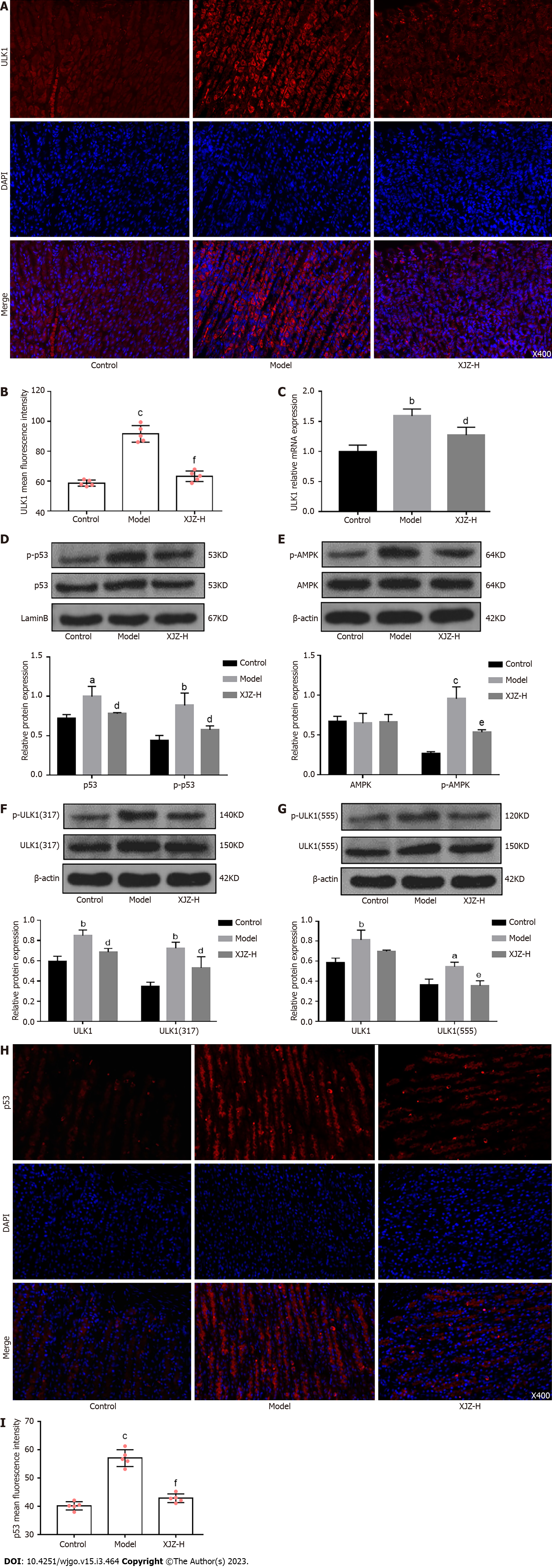
Figure 7 Xiaojianzhong decoction inhibited Unc-51 Like kinase 1 and p53/AMP-activated protein kinase pathway in N-methyl-N’-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine-induced gastric precancerous lesions rats.
A and B: Unc-51 like kinase 1 (ULK1) and p53 protein expression was determined using immunofluorescence (n = 5); ULK1, p53 proteins positive score was determined using Image J; C: ULK1 mRNA expression was determined using real-time polymerase chain reaction analysis (n = 3); D-G: Western blot analysis was performed to detect p-p53, p-AMP-activated protein kinase, p-ULK1 (Ser555), and p-ULK1 (Ser317) protein expression (n = 3); H and I: ULK1 and p53 protein expression was determined using immunofluorescence (n = 5). Data are expressed as mean ± SD. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001 vs control group; dP < 0.05, eP < 0.01, fP < 0.001 vs model group. XJZ-L: Low dose of Xiaojianzhong decoction; XJZ-M: Middle dose of Xiaojianzhong decoction; XJZ-H: High dose of Xiaojianzhong decoction; ULK1: Unc-51 like kinase 1.
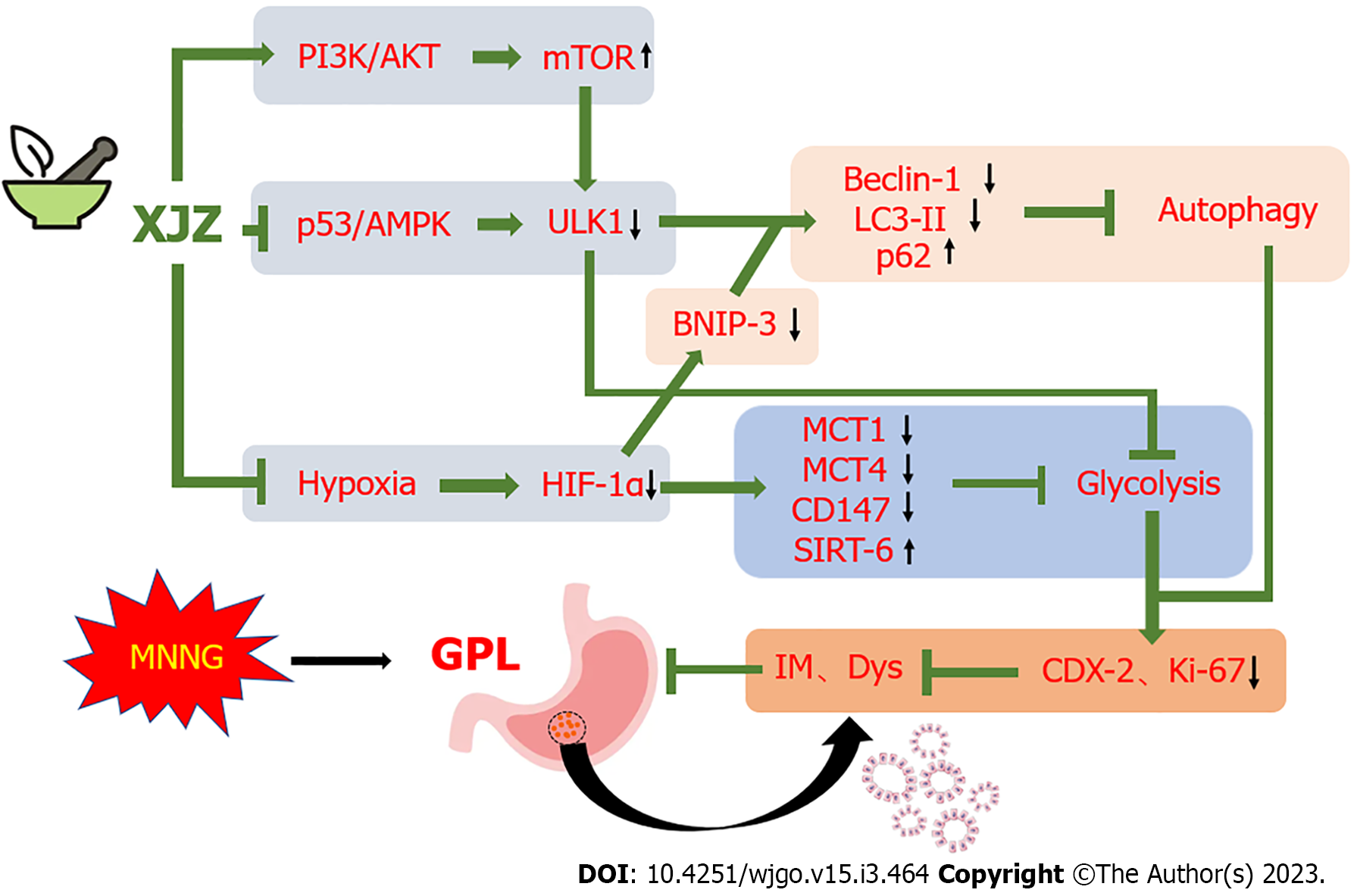
Figure 8 Scheme summarizing the protective effects of Xiaojianzhong decoction on N-methyl-N’-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine-induced gastric precancerous lesions rats via regulation of the p53/AMP-activated protein kinase/Unc-51 like kinase 1, phosphatidylinositol 3-kimase/protein kinase B/mammalian target of rapamycin axis and hypoxia state.
AKT: Protein kinase B; AMPK: AMP-activated protein kinase; Bnip-3: B cell lymphoma/Leukemia-2 and adenovirus E1B19000 interacting protein 3; Dys: Dysplasia; GPL: Gastric precancerous lesions; HIF-1α: Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α; IM: Intestinal metaplasia; MCT: Monocarboxylate transporter; MNNG: N-methyl-N’-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine; PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kimase; mTOR: Mammalian target of rapamycin signaling pathway; SIRT6: Sirtuin 6; ULK1: Unc-51 like kinase 1.
- Citation: Zhang JX, Bao SC, Chen J, Chen T, Wei HL, Zhou XY, Li JT, Yan SG. Xiaojianzhong decoction prevents gastric precancerous lesions in rats by inhibiting autophagy and glycolysis in gastric mucosal cells. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2023; 15(3): 464-489
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v15/i3/464.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v15.i3.464