Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Feb 15, 2023; 15(2): 352-367
Published online Feb 15, 2023. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v15.i2.352
Published online Feb 15, 2023. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v15.i2.352
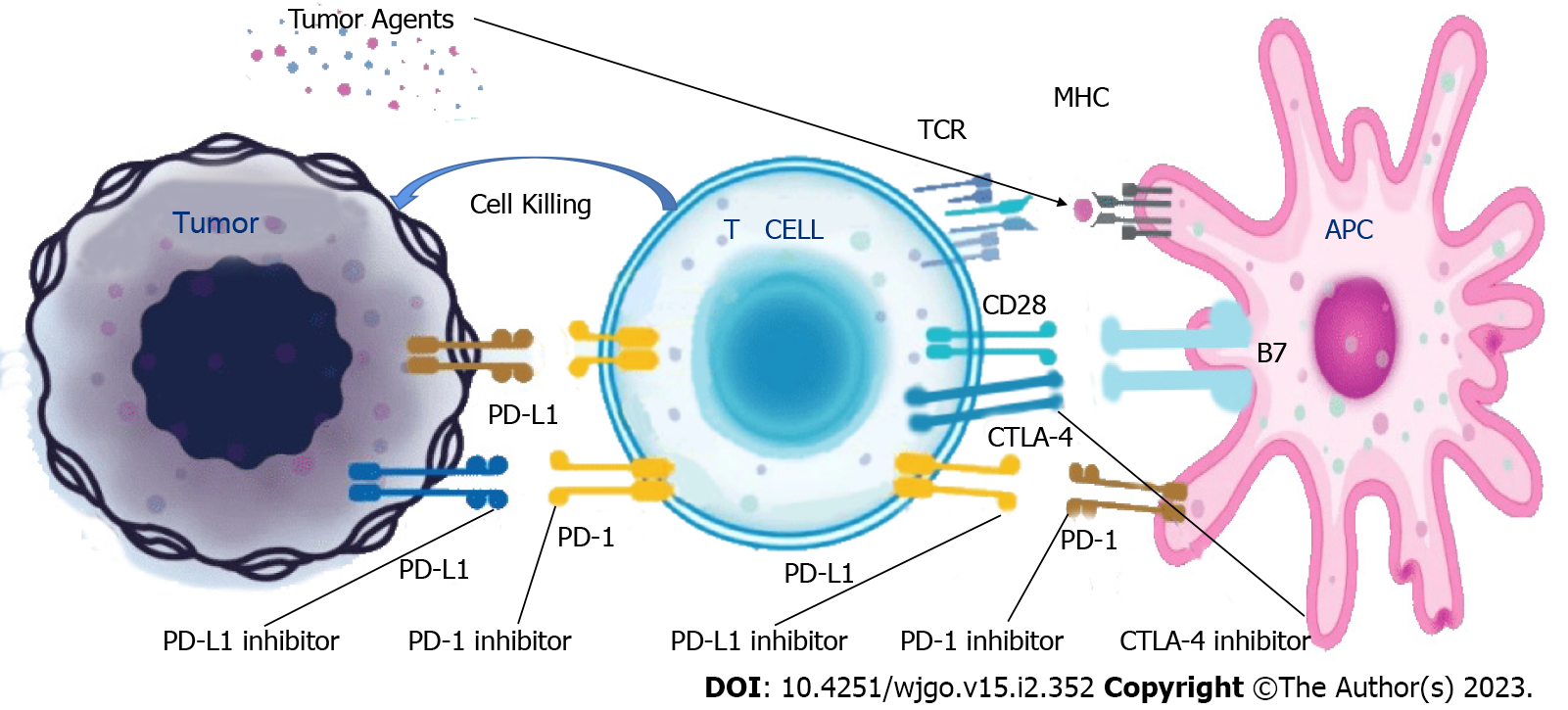
Figure 1 The action mechanism of programmed cell death receptor-1, programmed death receptor-ligand 1, and cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen-4 inhibitors.
PD-1: Programmed cell death receptor-1; PD-L1: Programmed death receptor-ligand 1; CTLA-4: Cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen-4; TCR: T-cell receptor; MHC: Major histocompatibility complex; APC: Antigen-presenting cell.
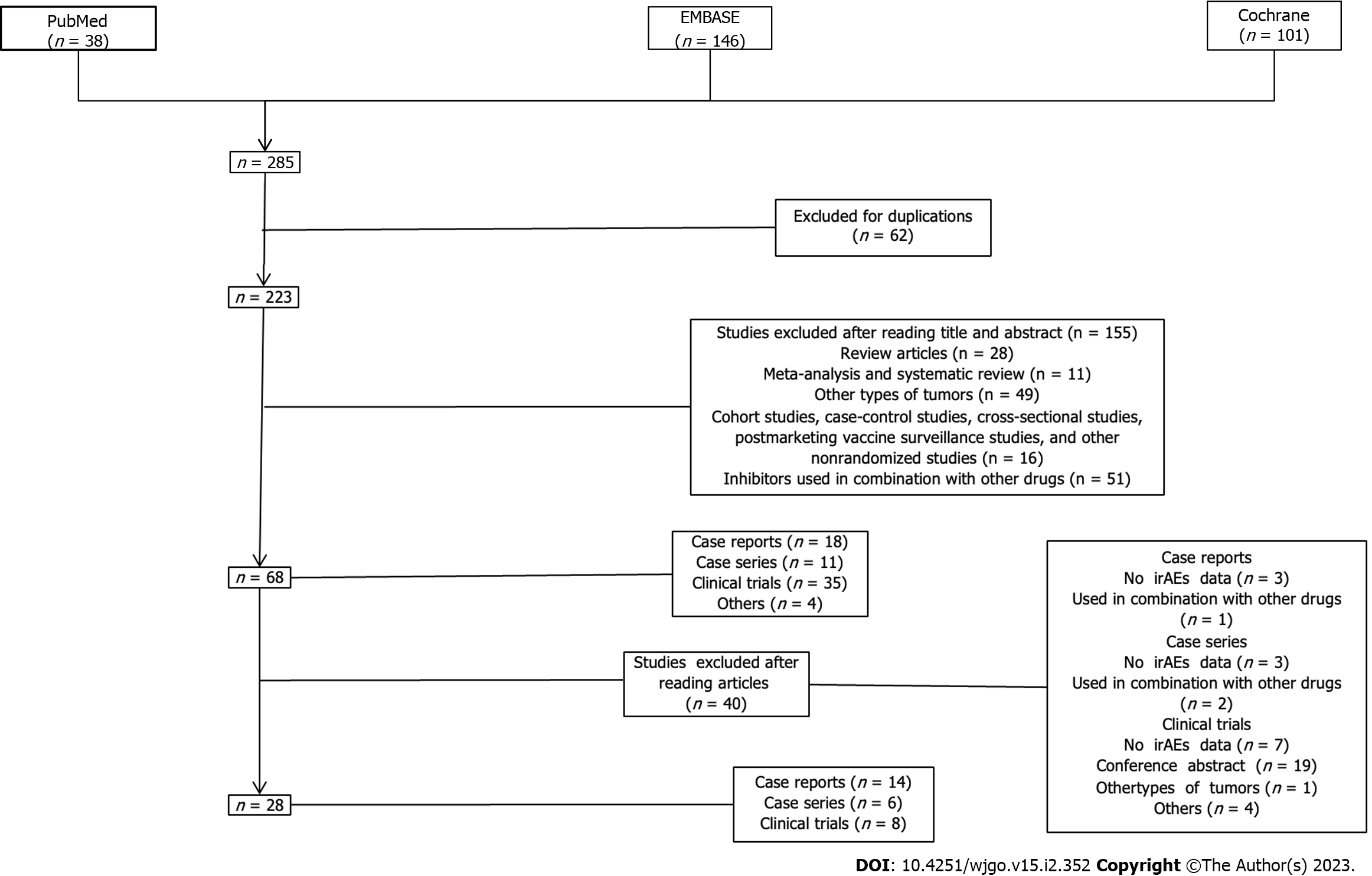
Figure 2 Flowchart of study selection and design.
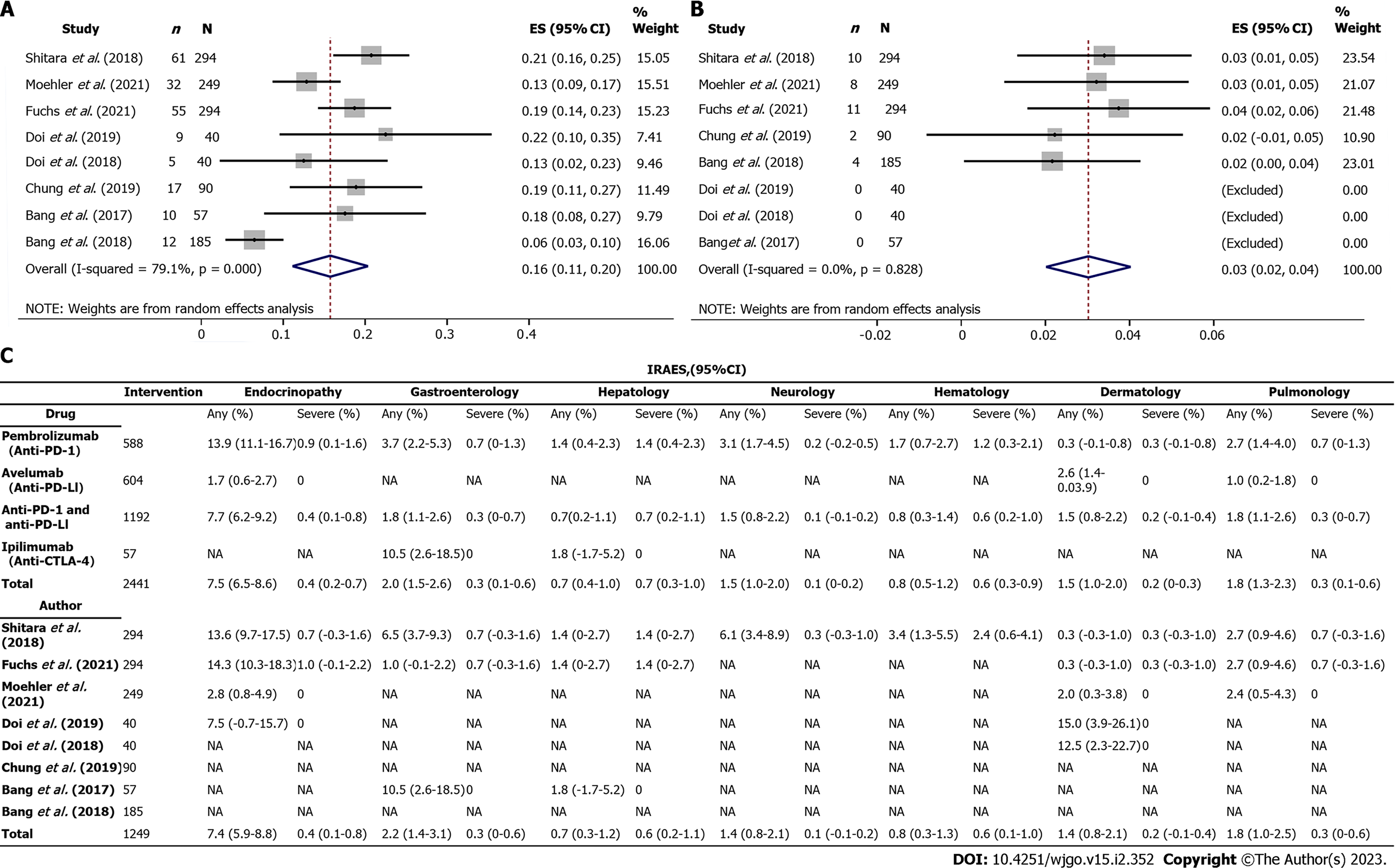
Figure 3 Incidence of global immune-related adverse events associated with anti- programmed cell death receptor-1, anti-programmed death receptor-ligand 1, and anti-cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen-4.
A: All grade; B: Severe grade; C: Incidence of organ specific immune-related adverse events, value are percentage (95% confidence intervals). Any: includes all Common Terms classified by Clinical Adverse Events grades; Severe: includes CTCAE grades 3,4, or 5. NA: Not available; PD-1: Programmed cell death receptor-1; PD-L1: Programmed death receptor-ligand 1; CTLA-4: Cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen-4.
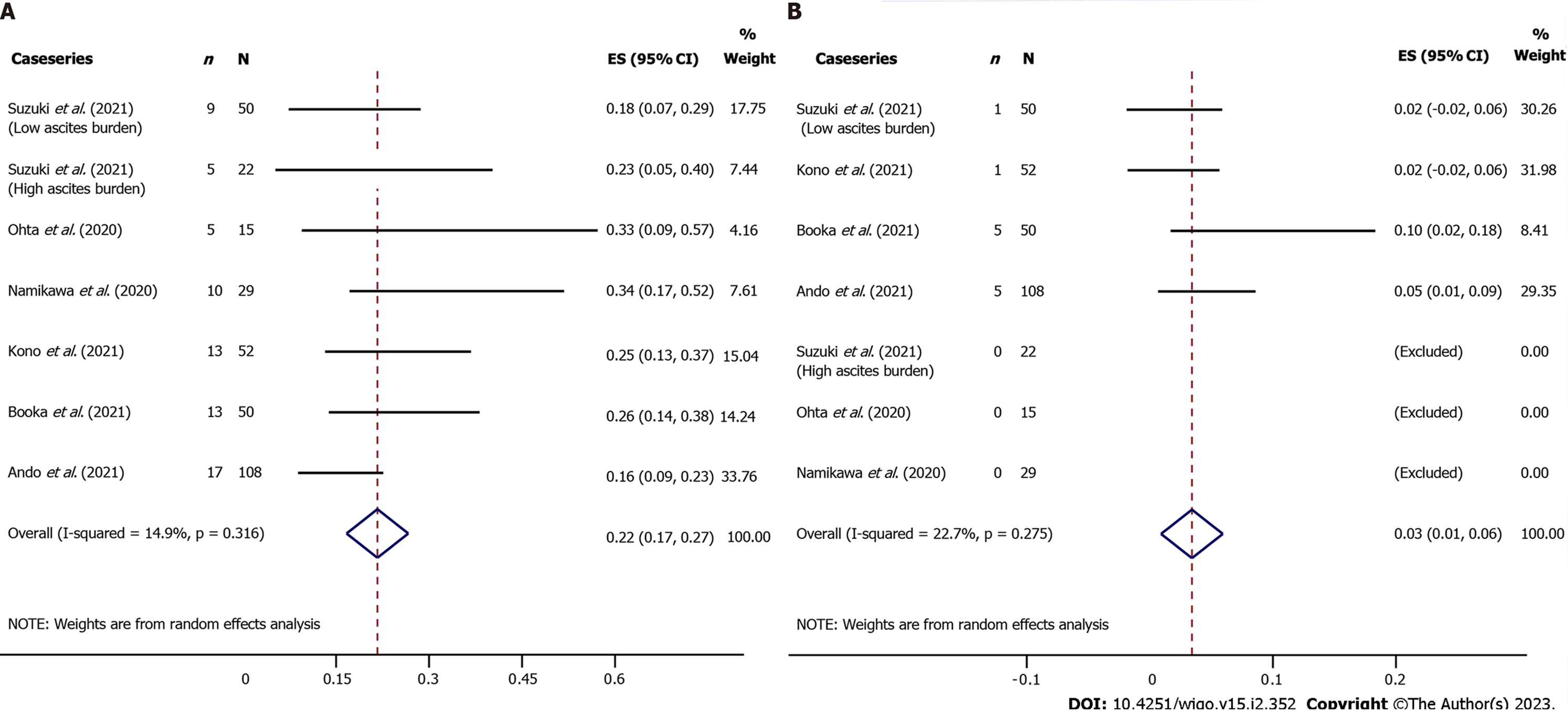
Figure 4 Incidence of immune-related adverse events associated with anti-anti- programmed cell death receptor-1 (nivolumab) in case series.
A: All grade; B: Severe grade.
- Citation: Pei WG, Chen WZ, Wu YK, Tan SX, Jie ZG. Immune-related adverse events associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors for advanced gastric and gastroesophageal junction cancer: A meta-analysis. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2023; 15(2): 352-367
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v15/i2/352.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v15.i2.352