Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Feb 15, 2023; 15(2): 332-342
Published online Feb 15, 2023. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v15.i2.332
Published online Feb 15, 2023. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v15.i2.332
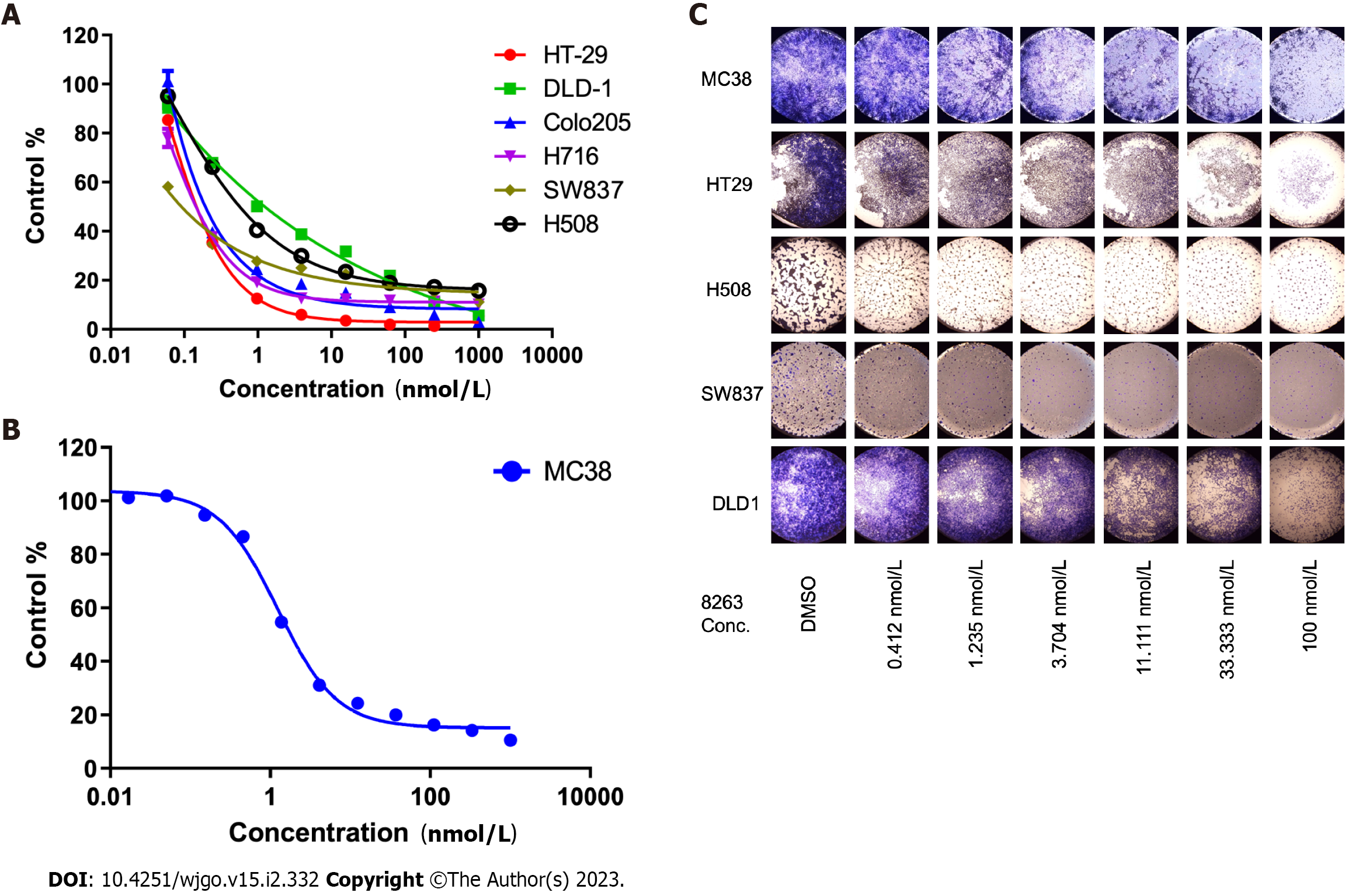
Figure 1 JAB-8263 dose-dependently suppressed colorectal cancer cell proliferation and colony formation in vitro.
A: Human colorectal cancer cell lines including HT29, DLD1, Colo205, H716, SW837 and H508 were treated with JAB-8263 for 6 d, and the proliferation was dose-dependently suppressed; B: The MC38 mouse cell line was treated with JAB-8263 for 6 d, and the proliferation was dose-dependently suppressed; C: The IC50 values of HT-29, DLD-1, Colo205, H716, SW837, H508 and MC38 were 0.15, 1.24, 0.19, 0.09, 0.57, 0.14 and 1.25 μmol/L. Colony formation assays for six colorectal cancer cell lines including MC38, HT29, H508, SW837 and DLD1 were treated with various concentrations of JAB-8263 for 5 d. Cell proliferation in all cell lines was dose-dependently suppressed. All experiments were performed in triplicate. Conc.: Concentration.
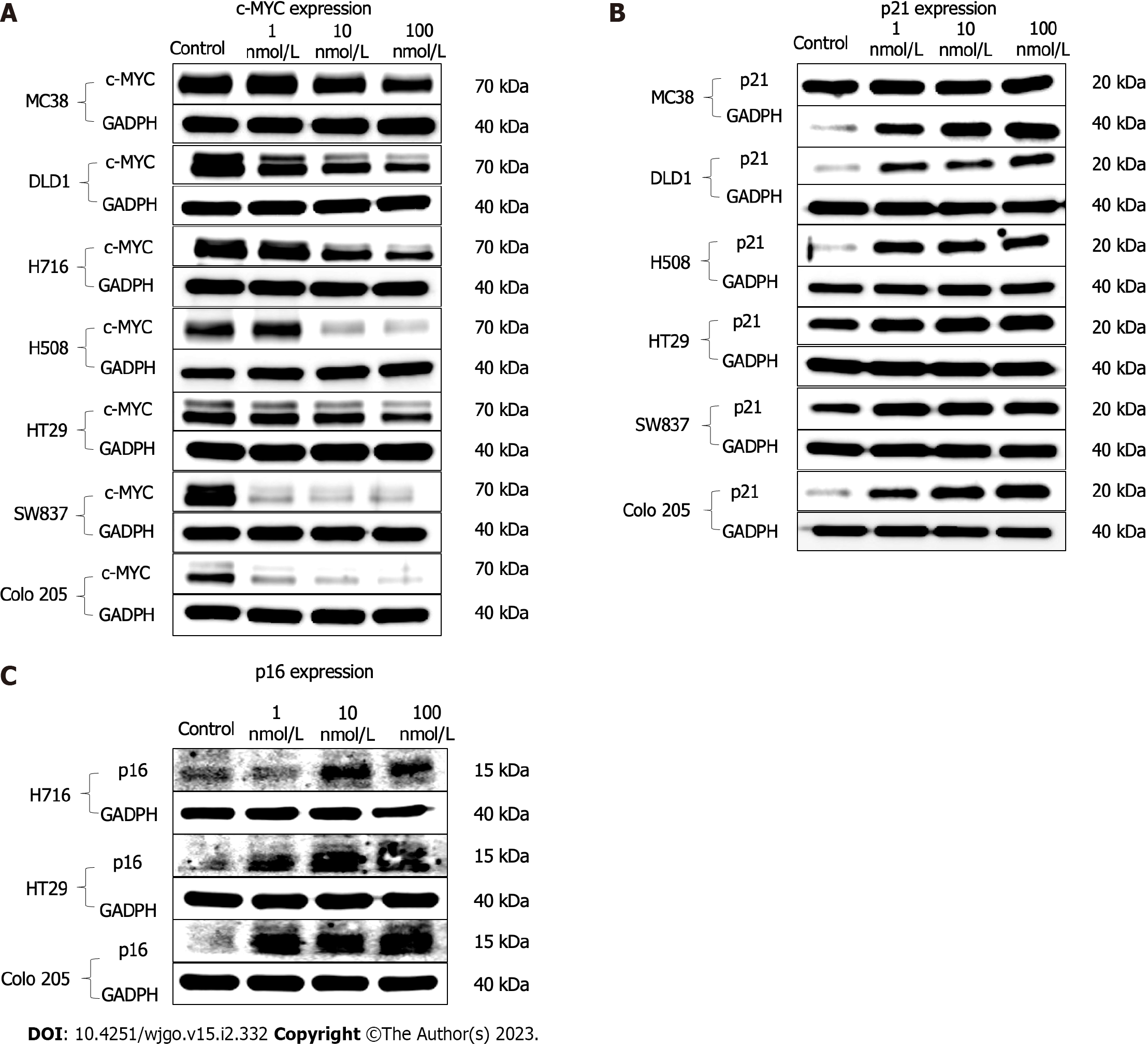
Figure 2 MYC signaling pathway was dose-dependently inhibited by JAB-8263 in human colorectal cancer cell lines.
A-C: Multiple colorectal cancer cell lines were treated with different concentrations of JAB-8263 (1 nmol/L, 10 nmol/L and 100 nmol/L) for 16 h. Western blotting assay was performed to detect levels of MYC, p21 and p16. The expression of MYC were downregulated (A), and the expression of p21 (B) and p16 (C) were upregulated in multiple colorectal cancer cell lines.
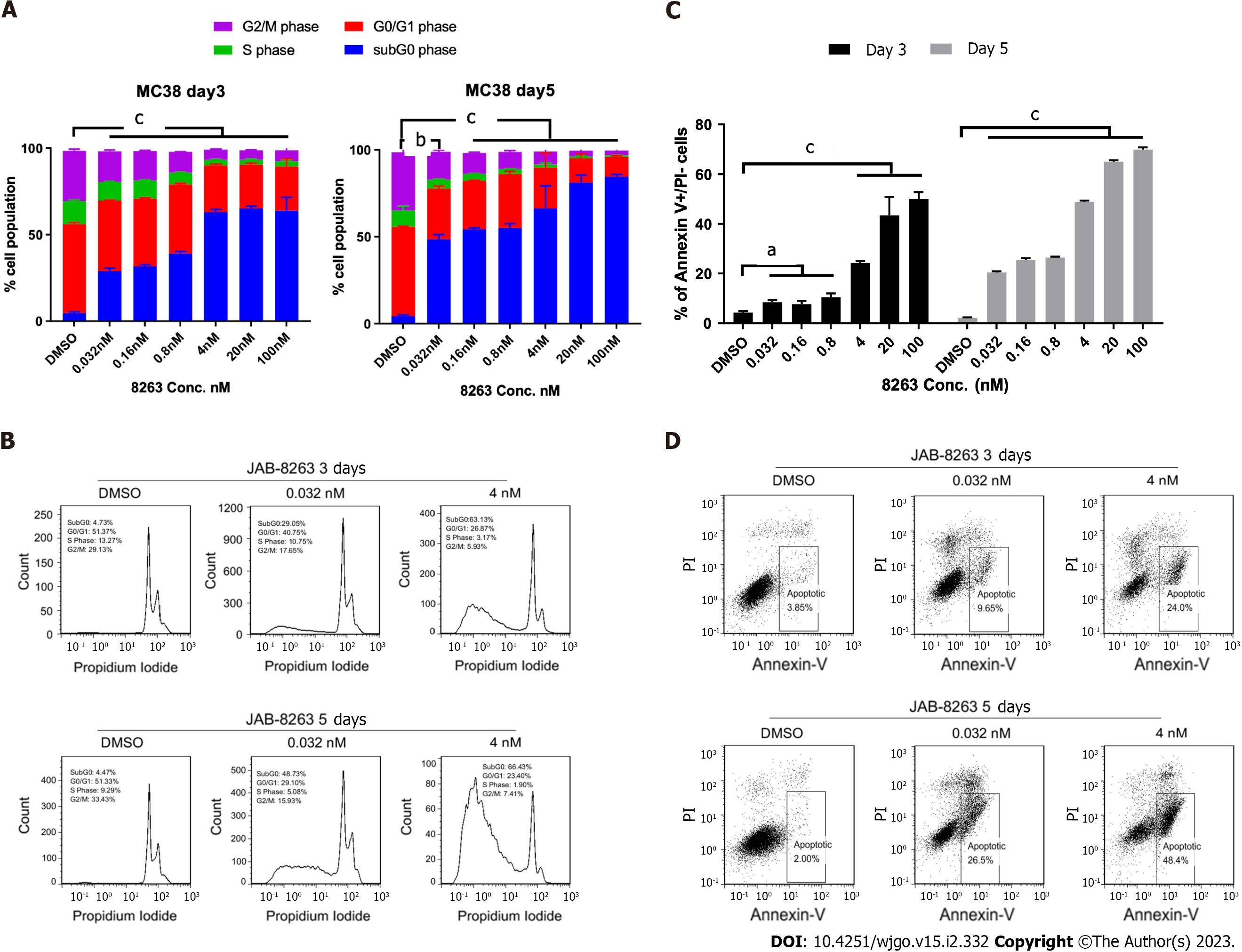
Figure 3 JAB-8263 dose-dependently induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in the MC38 cell line.
After incubation with different concentrations of JAB-8263 (0, 0.032, 0.16, 0.8, 4, 20 and 100 nmol/L) for 3 d and 5 d, MC38 cells were collected and analyzed for cell cycle and apoptosis assays by flow cytometry. A and B: JAB-8263 dose-dependently decreased the G2/M phase ratio and increased the G0 prophase ratio in MC38 cells, indicating that JAB-8263 induced cells to arrest in the G0 phase; C and D: JAB-8263 dose-dependently induced apoptosis in MC38 after treatment for 3 d and 5 d. All experiments were performed in triplicate. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001 vs DMSO control. PI: Propidium iodide.
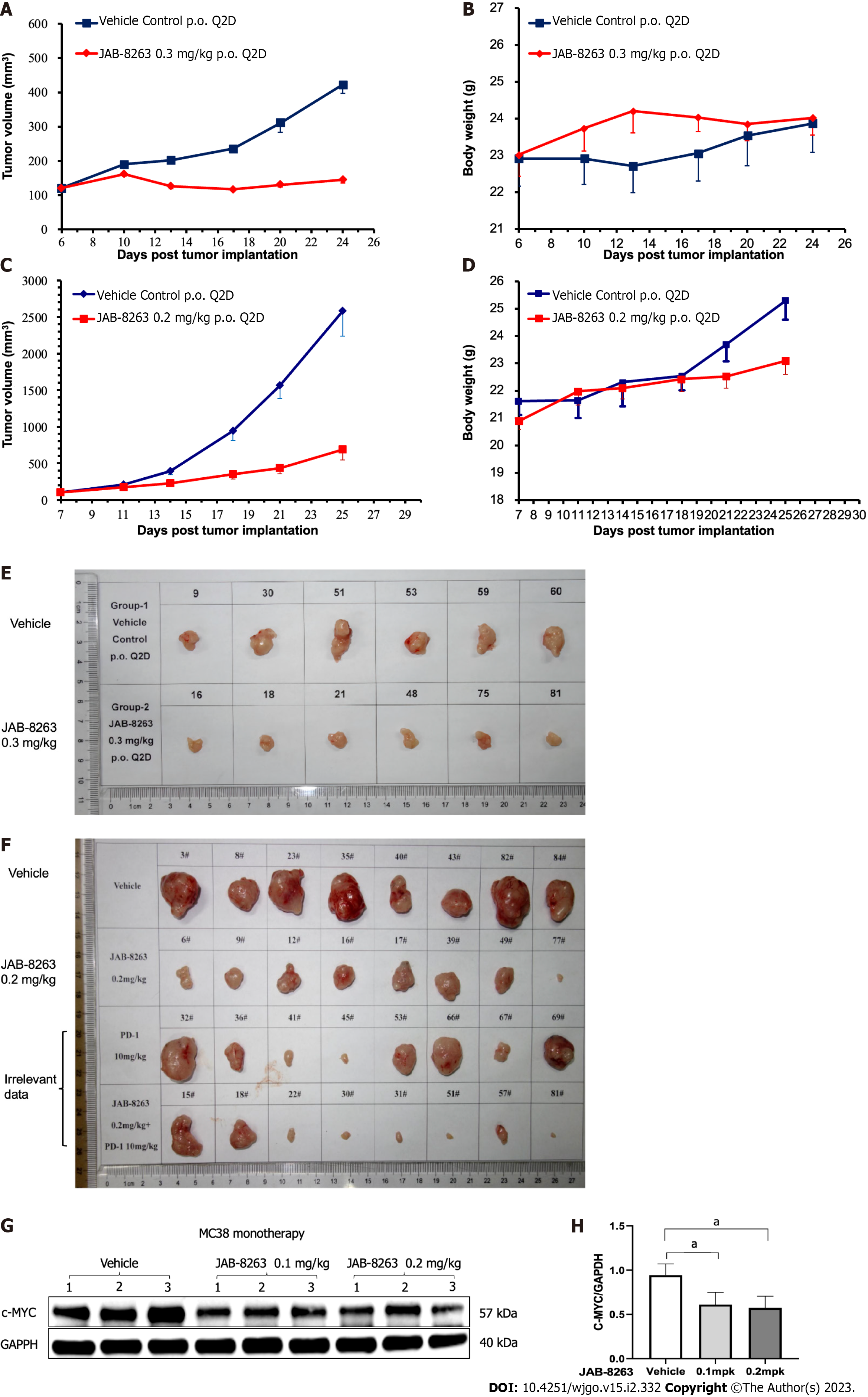
Figure 4 JAB-8263 suppressed tumor growth in colorectal cancer murine xenograft models.
A and E: The SW837 xenograft model (6 mice for each group) was treated with JAB-8263 0.3 mg/kg for 29 d. The average tumor volume was significantly decreased compared to the vehicle control group, P < 0.001; B: There was no significant difference in body weight change between groups; C and F: The MC38 syngeneic murine model (8 mice for each group) was treated with JAB-8263 0.2 mg/kg for 29 d. The average tumor volume was significantly decreased compared to the vehicle control group, P = 0.003; D: There was no significant difference in body weight change between groups; G and H: The tumor tissue of the MC38 syngeneic murine model (3 mice for each group) after a single dose of JAB-8263 treatment was collected for the Western blotting assay. Compared with the control group, the expression of c-MYC in the treatment group was downregulated, aP < 0.05.
- Citation: Liu XM, Xia SY, Long W, Li HJ, Yang GQ, Sun W, Li SY, Du XH. Potent bromodomain and extraterminal domain inhibitor JAB-8263 suppresses MYC expression and exerts anti-tumor activity in colorectal cancer models. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2023; 15(2): 332-342
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v15/i2/332.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v15.i2.332