Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Mar 15, 2022; 14(3): 607-627
Published online Mar 15, 2022. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v14.i3.607
Published online Mar 15, 2022. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v14.i3.607
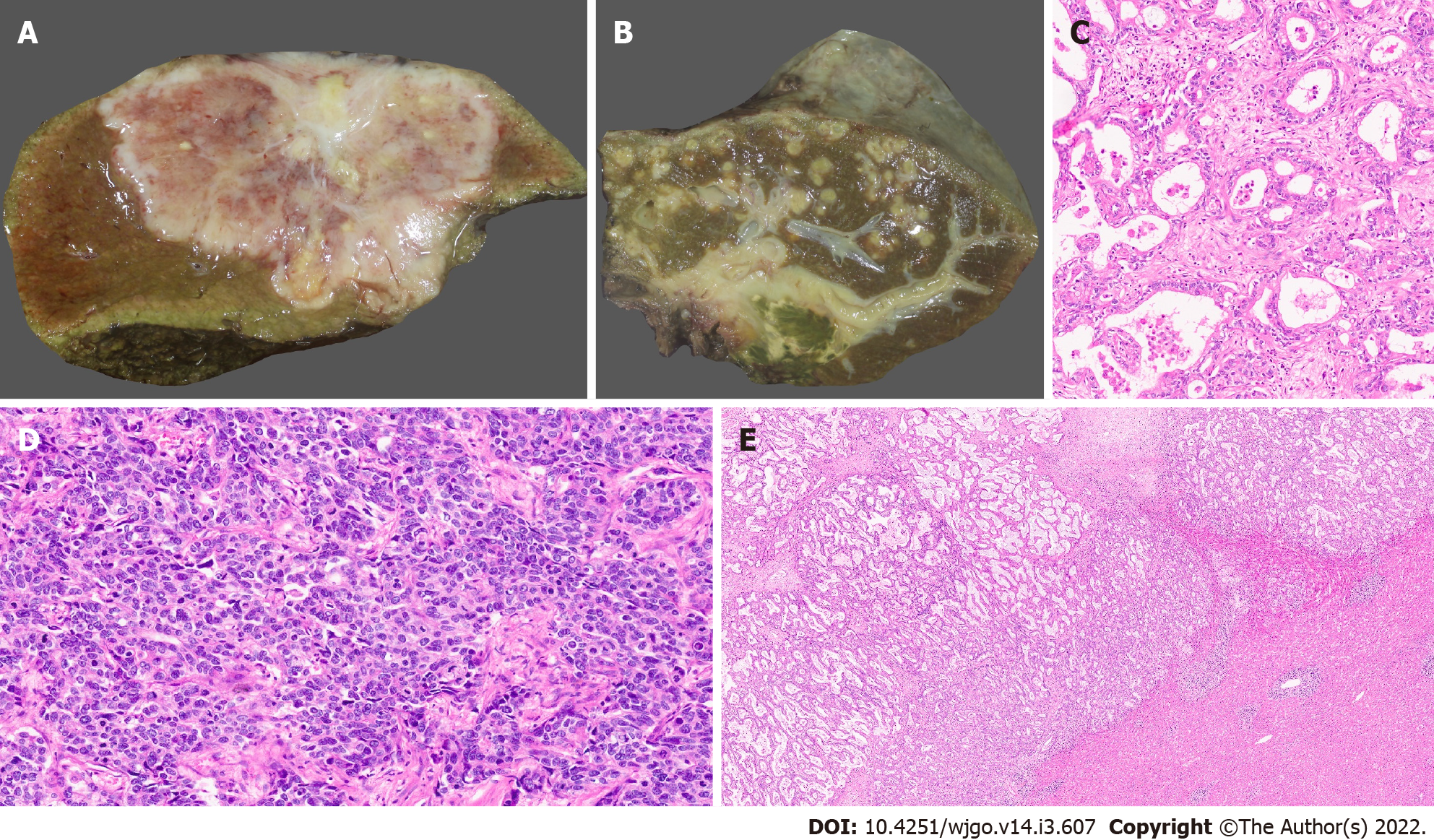
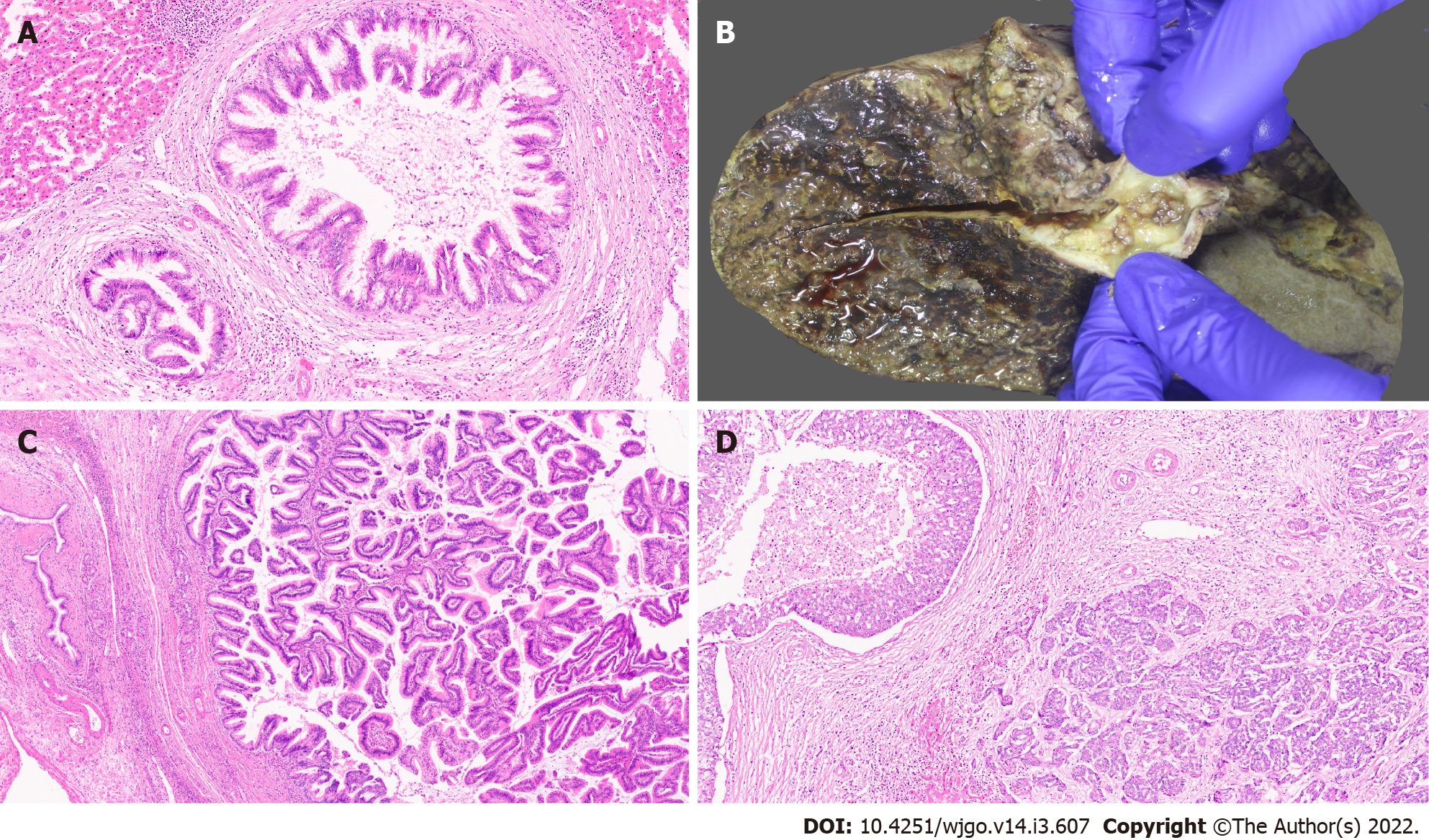
Figure 1 Gross features and morphology of cholangiocarcinoma.
A: Mass forming intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (IHCC); B: Extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma with periductal infiltrating growth (arrow) and markedly greenish liver; C: Well differentiated cholangiocarcinoma [hematoxylin and eosin (H&E, × 25)]; D: Poorly differentiated cholangiocarcinoma (H&E, × 25); E: Large duct variant of IHCC (H&E, × 8).
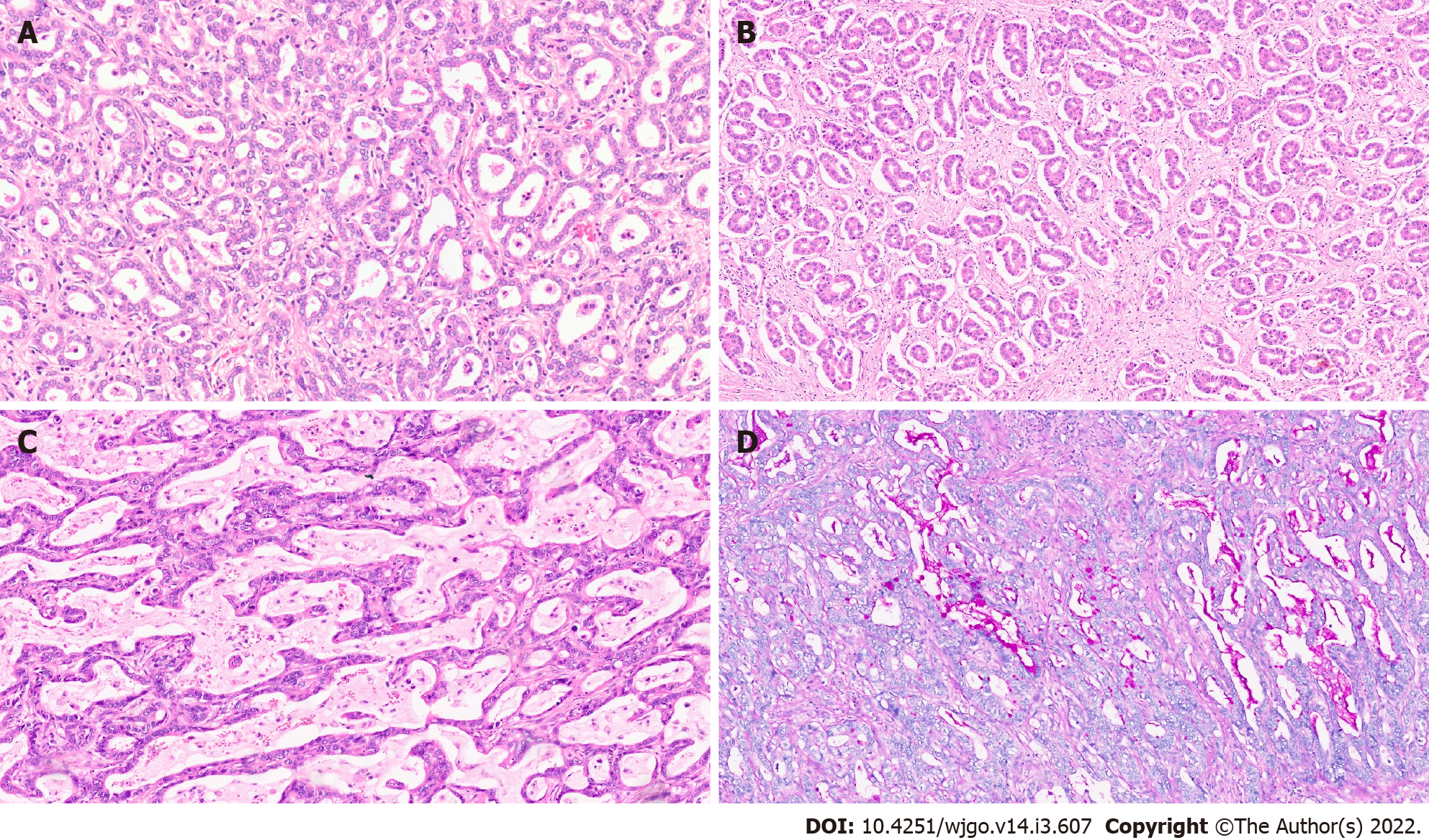
Figure 2 Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma.
A: Small duct variant of Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (IHCC) (SD-IHCC) with closely packed small glands [hematoxylin and eosin (H&E, × 15)]; B: SD-IHCC with desmoplastic stroma (H&E, × 15); C: Large duct variant of IHCC (LD-IHCC) with mucin production (H&E, × 20); D: LD-IHCC with mucin [Periodic acid Schiff after diastase, × 15].
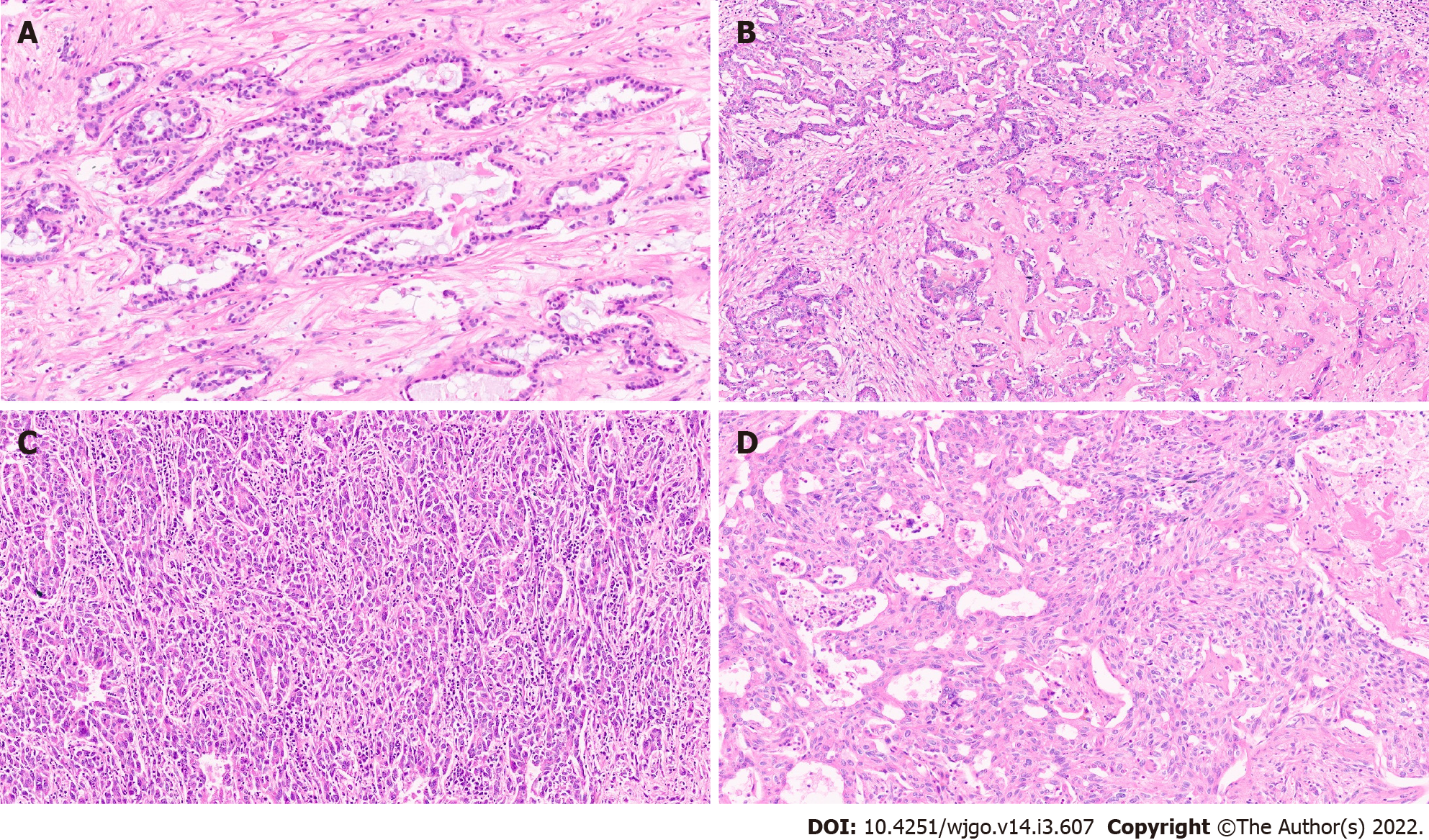
Figure 3 Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma.
A: Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (IHCC) with ductal plate malformation phenotype [hematoxylin and eosin (H&E, × 20)]; B: Cholangiocellular or bile ductular type of IHCC (H&E, × 20); C: IHCC lymphoepithelioma subtype (H&E, × 20); D: IHCC with sarcomatoid areas (H&E, × 20).
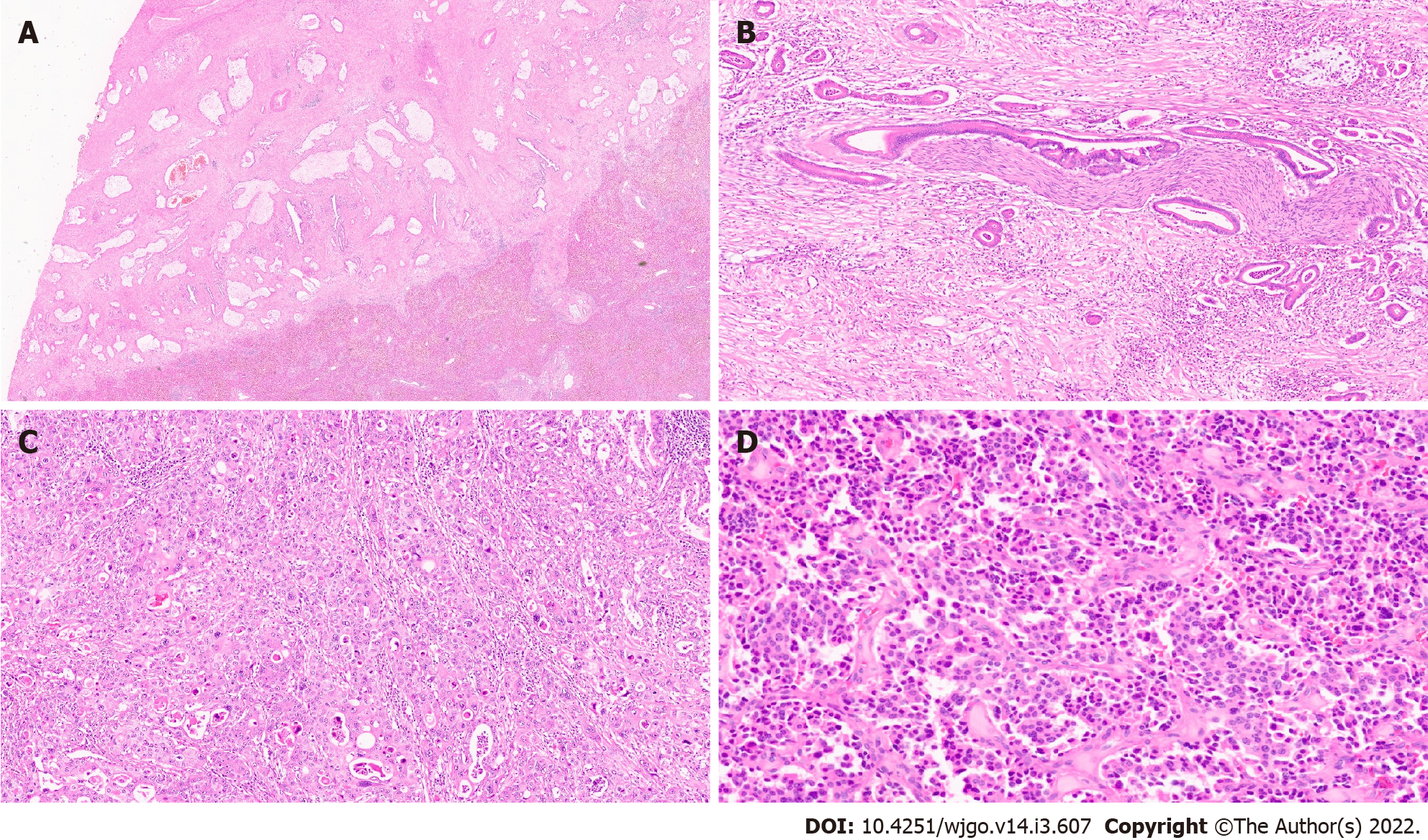
Figure 4 Extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma.
A: Extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (EHCC) with large mucin producing malignant glands and abundant desmoplastic stroma [haematoxylin and eosin (H&E, × 8)]; B: EHCC with perineural invasion (H&E, × 20); C: EHCC adenosquamous subtype (H&E, × 15); D: Well differentiated neuroendocrine tumour of the bile duct (H&E, × 20).
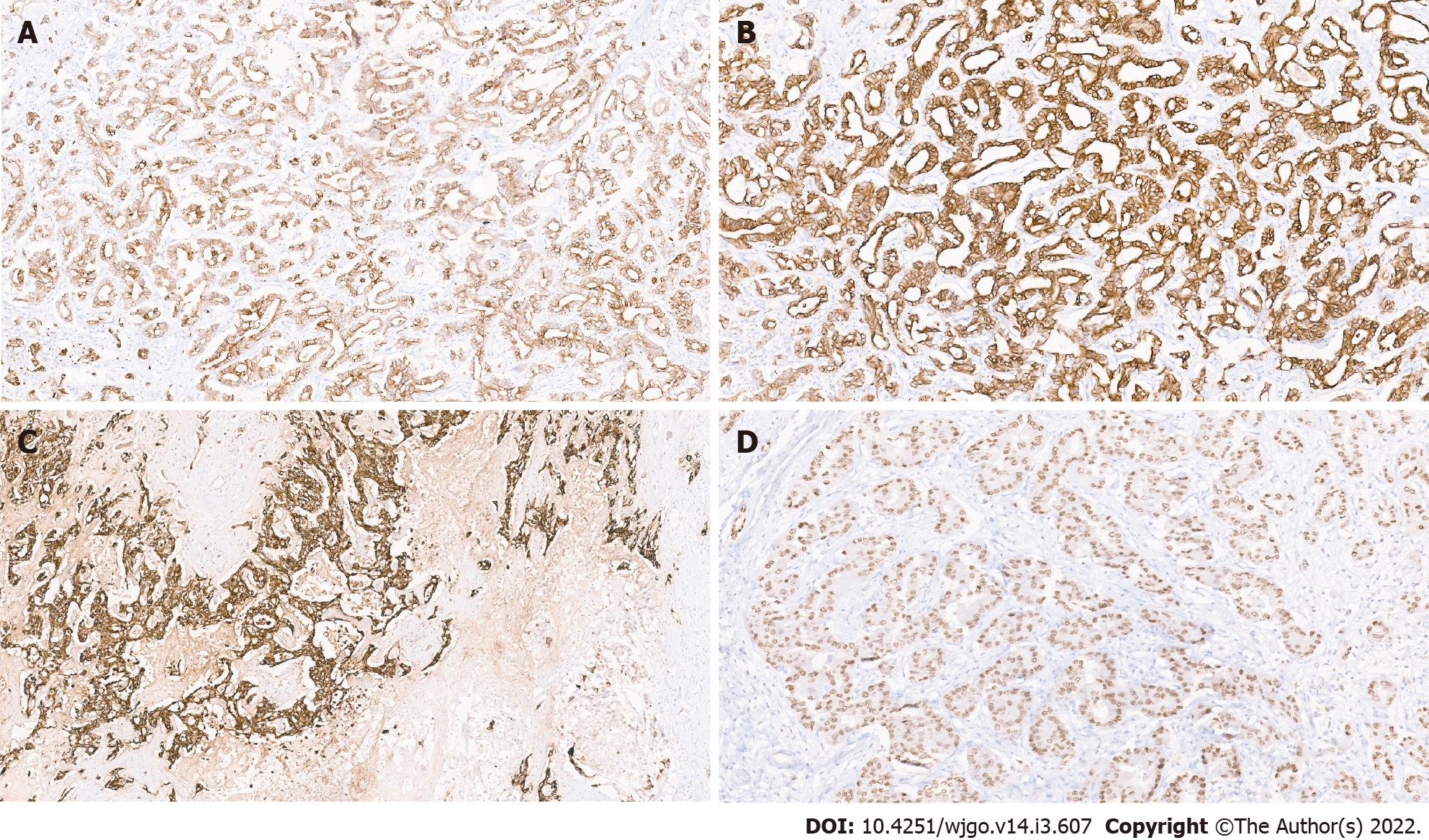
Figure 5 Immunohistochemistry in cholangiocarcinoma.
A: Positive CK7 immunostaining; B: Positive CK19 immunostaining; C: Positive epithelial membrane antigen immunostaining; D: Hepatocyte nuclear factor-1 β nuclear immunostaining in a small duct variant of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma.
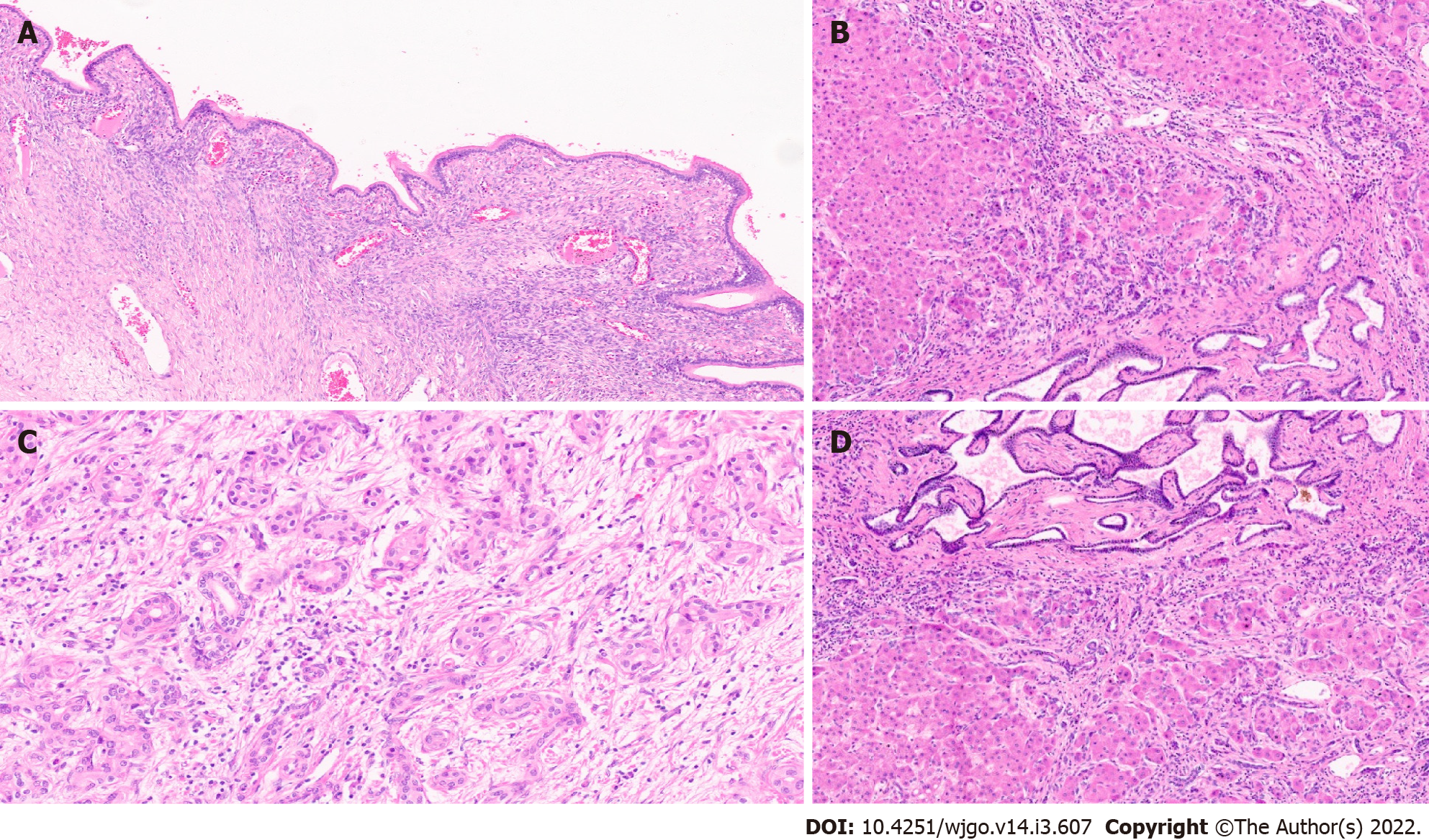
Figure 6 Precursor lesions of cholangiocarcinoma.
A: Biliary intraepithelial neoplasia with low grade dysplasia [haematoxylin and eosin (H&E, × 15)]; B: Intraductal papillary neoplasm of the bile duct (IPNB) (arrow); C: IPNB pancreaticobiliary subtype (H&E, × 10); D: Intraductal tubulopapillary neoplasms of the bile duct with invasive carcinoma (H&E, × 10).
Figure 7 Other precursor lesions.
A: Hepatobiliary mucinous cystic neoplasm with mucinous lining epithelial and ovarian stroma [haematoxylin and eosin (H&E, × 10)]; B: Von Mayenberg complex (H&E, × 20); C: Bile duct adenoma (H&E, × 20).
- Citation: Vij M, Puri Y, Rammohan A, G G, Rajalingam R, Kaliamoorthy I, Rela M. Pathological, molecular, and clinical characteristics of cholangiocarcinoma: A comprehensive review. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2022; 14(3): 607-627
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v14/i3/607.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v14.i3.607