Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Oct 15, 2022; 14(10): 1968-1980
Published online Oct 15, 2022. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v14.i10.1968
Published online Oct 15, 2022. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v14.i10.1968
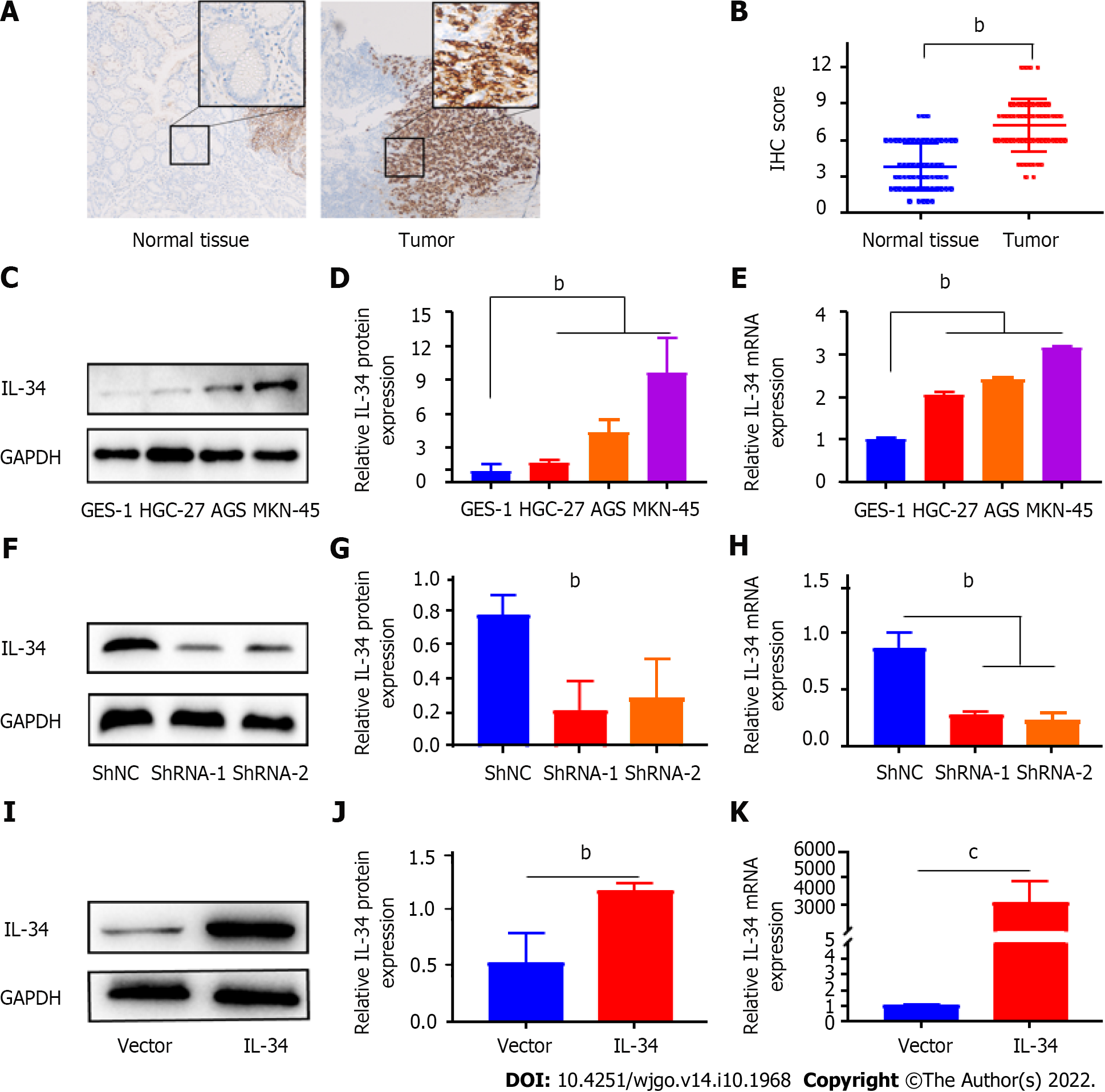
Figure 1 Expression of interleukin-34 in gastric cancer tissues and cell lines, and construction of AGS cell lines with stable knockdown or overexpression of interleukin-34.
A: Representative immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining of interleukin (IL)-34 in adjacent normal tissue, gastric cancer (GC) tissues, (scale bar = 25 μm); B: IHC staining scores were used to evaluate IL-34 expression in GC tissues and adjacent normal tissue; C: Western blotting was used to detect IL-34 protein expression in gastric normal epithelial cells (GES-1) and GC cell lines (AGS, HGC-27, and MKN-45); D: The relative densitometric analysis of protein bands was calculated; E: IL-34 mRNA expression was detected by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR); F and G: Western blotting was used to verify the downregulation of IL-34 in AGS cell lines; H: qRT-PCR was used to verify the downregulation of IL-34 in AGS cell lines; I and J: Western blotting was used to verify the overexpression of IL-34 in AGS cell lines; K: qRT-PCR was used to verify the overexpression of IL-34 in AGS cell lines. bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001.
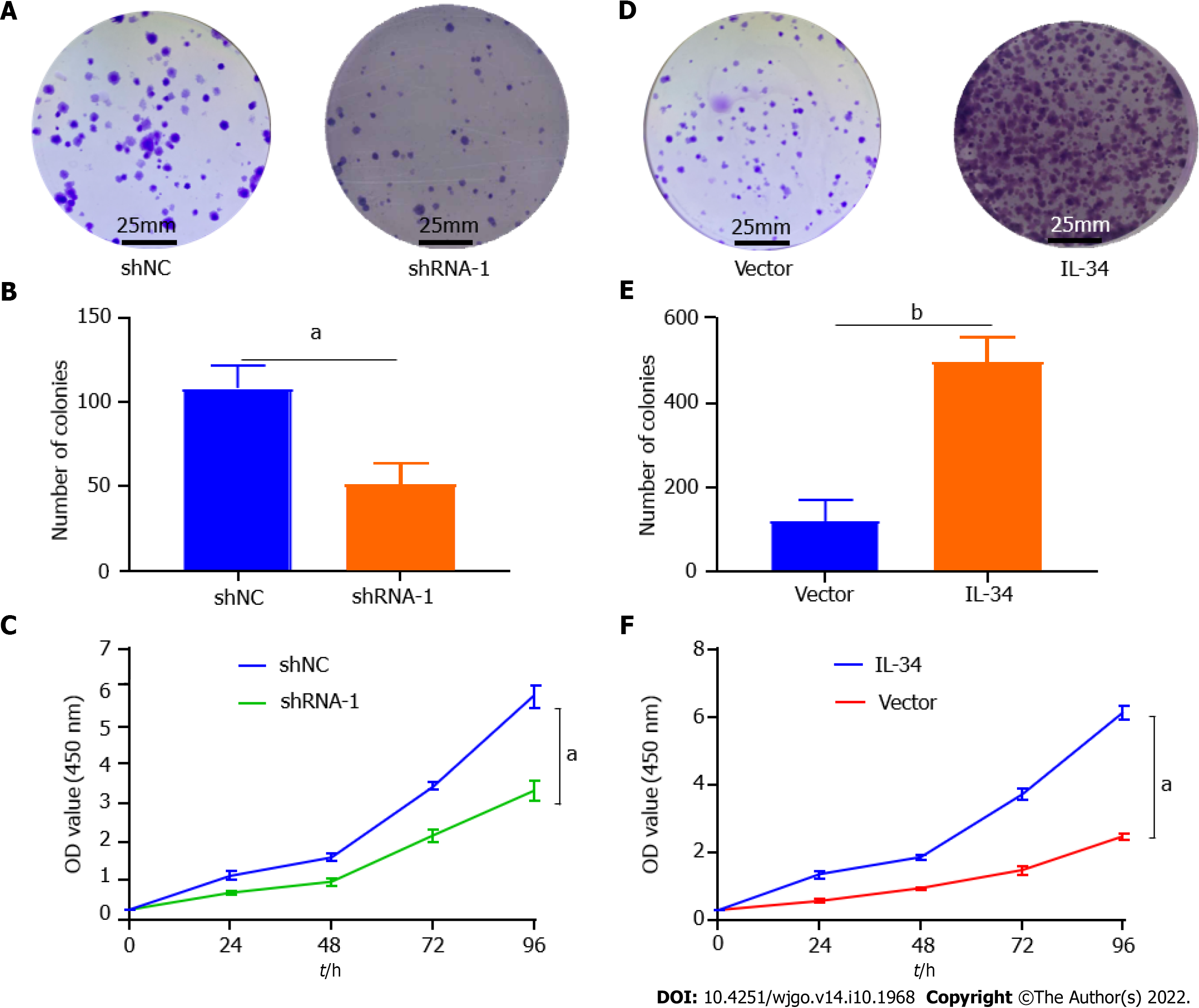
Figure 2 Interleukin-34 modulates clone formation and proliferation in AGS cells.
A and B: Downregulation of endogenous interleukin (IL)-34 reduced the mean colony number in the colony formation assay; C: Downregulation of endogenous IL-34 reduced the mean number of AGS cells in the proliferation assay; D and E: Upregulation of endogenous COL5A2 increased the number of invasion cells in the colony formation assay; F: Upregulation of endogenous IL-34 increased the mean number of AGS cells in the proliferation assay. Data shown on graphs were obtained from three independent replicates of the experiments and expressed as mean ± SD, aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01.
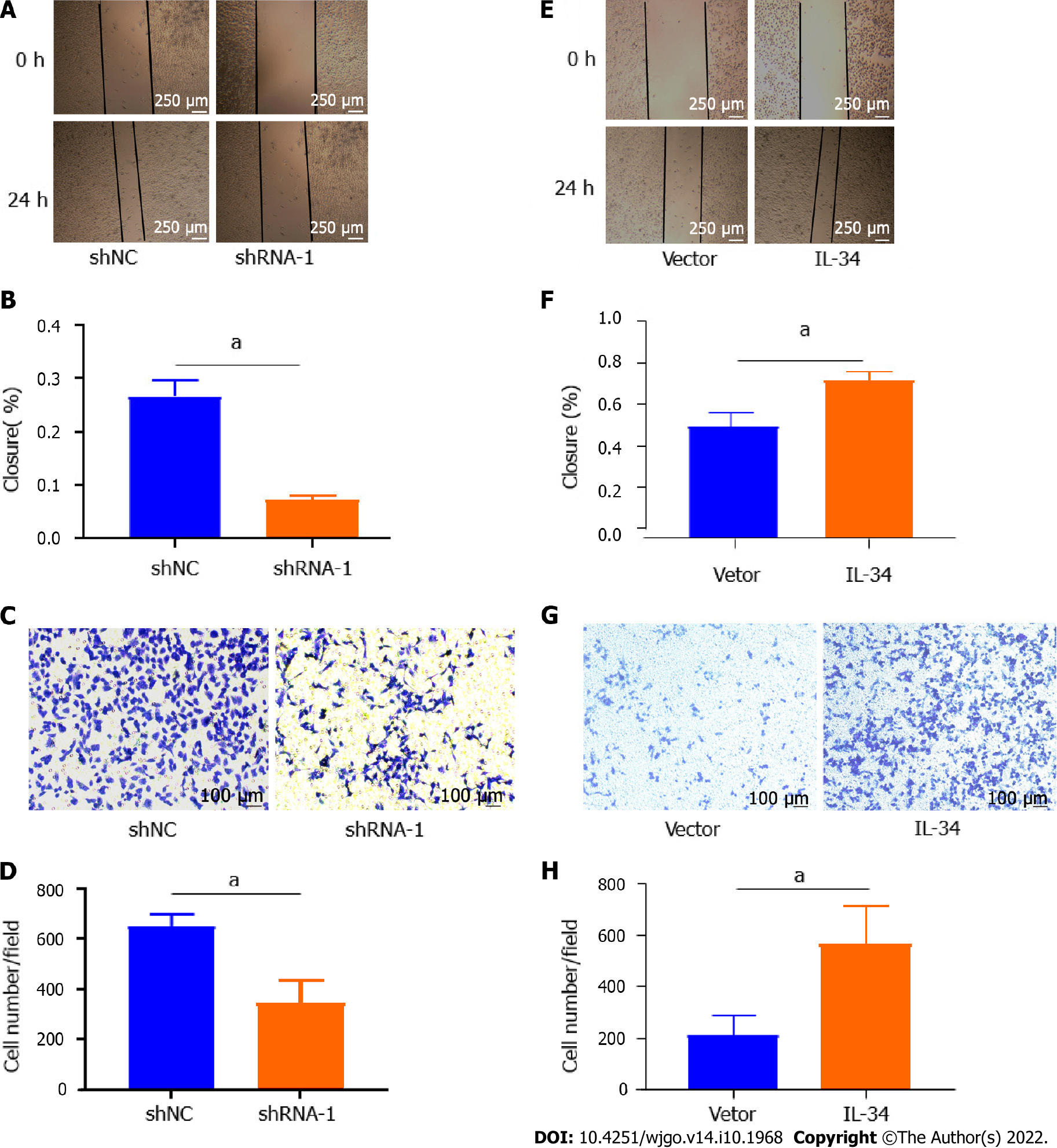
Figure 3 Interleukin-34 regulates the migration and invasiveness of AGS cells.
A and B: Wound-healing assay revealed that downregulation of endogenous interleukin (IL)-34 significantly reduced the migration rate; C and D: Downregulation of endogenous IL-34 reduced the number of invaded cells in the transwell assay; E and F: Wound-healing assay revealed that upregulation of endogenous IL-34 significantly increased the migration rate; G and H: Upregulation of endogenous IL-34 increased the number of invaded cells in the transwell assay. Data derived from three independent experiments performed in triplicate and expressed as mean ± SD, and aP < 0.05.
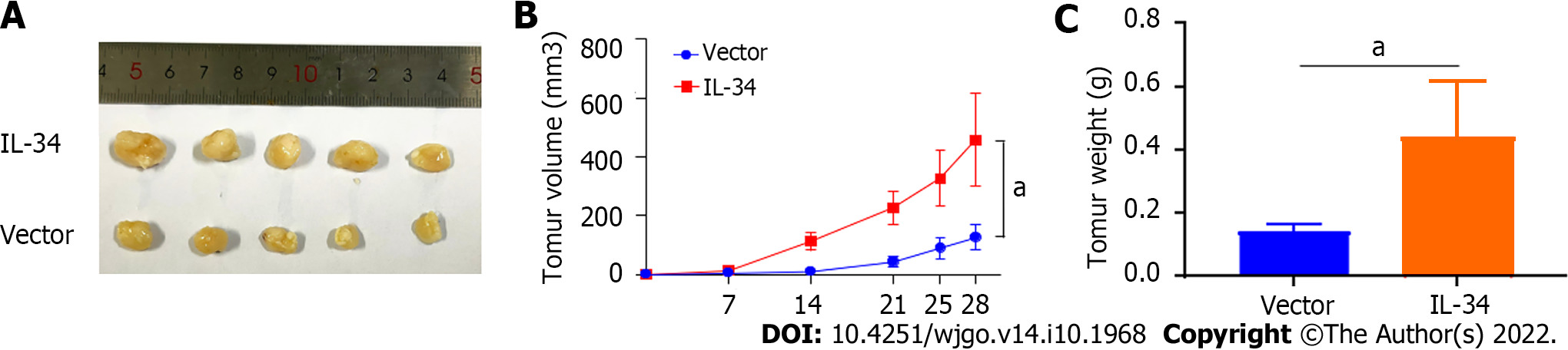
Figure 4 Interleukin-34 regulates the growth of subcutaneous transplantation tumors in nude mice.
A-C: Upregulation of endogenous interleukin-34 promotes the growth of transplanted tumors in nude mice. aP < 0.05.
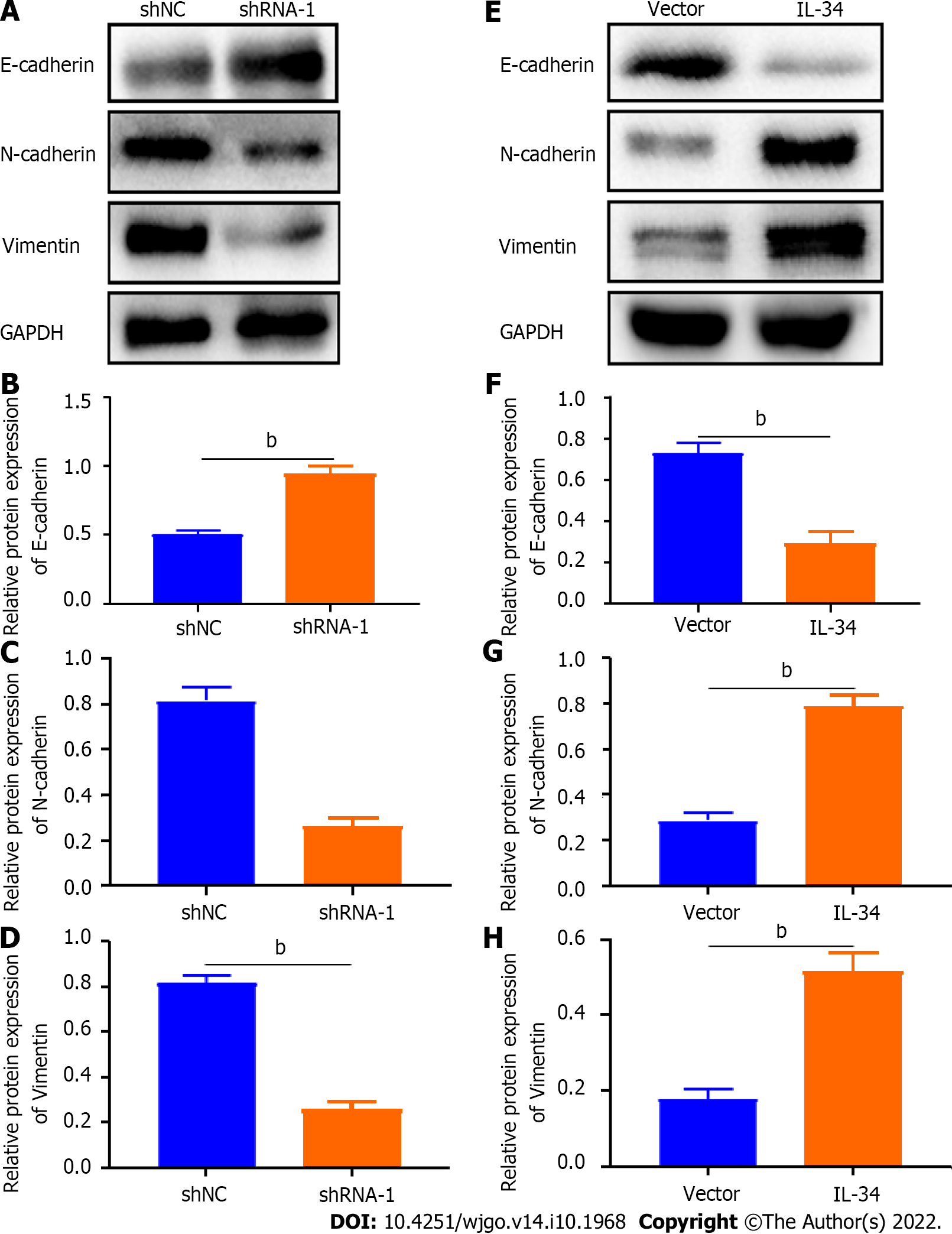
Figure 5 Interleukin-34 regulates the expression of epithelial-mesenchymal transition-related proteins in AGS cells.
A-D: Downregulation of endogenous interleukin (IL)-34 increases E-cadherin expression, and reduces the expression of N-cadherin and vimentin in AGS cells; E-H: Upregulation of endogenous IL-34 reduces the E-cadherin expression, but increases the expression of N-cadherin and vimentin in AGS cells. Data was experiments performed in triplicate and expressed as mean ± standard deviation. bP < 0.01.
- Citation: Li CH, Chen ZM, Chen PF, Meng L, Sui WN, Ying SC, Xu AM, Han WX. Interleukin-34 promotes the proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of gastric cancer cells. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2022; 14(10): 1968-1980
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v14/i10/1968.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v14.i10.1968