Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Jan 15, 2022; 14(1): 75-89
Published online Jan 15, 2022. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v14.i1.75
Published online Jan 15, 2022. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v14.i1.75
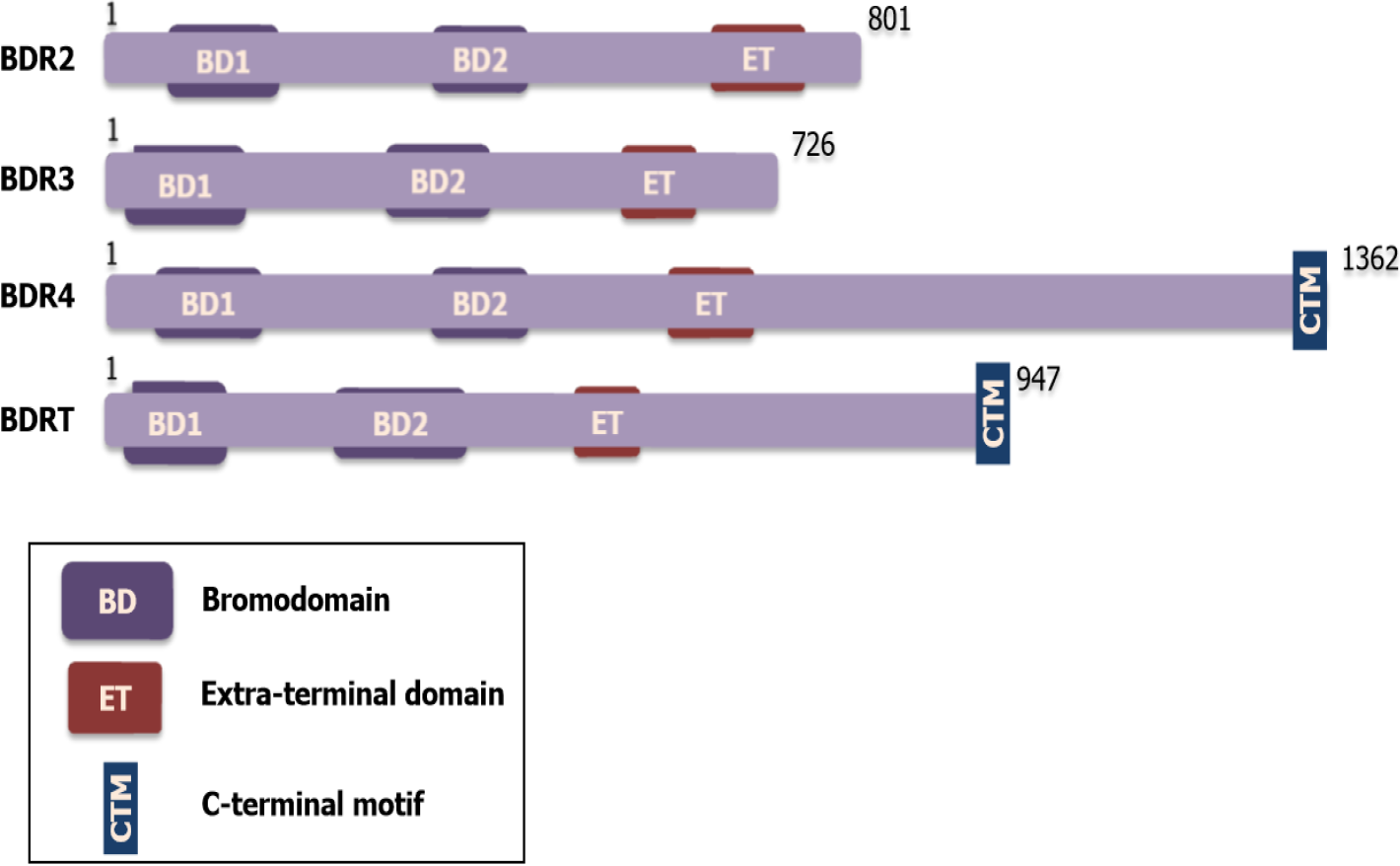
Figure 1 Schematic of basic domain structure of Bromodomain and extra-terminal protein family; BRD2, BRD3, BRD4, and BRDT.
Each Bromodomain and extra-terminal protein has two bromodomains (BD1 and BD2) and one extra-terminal domain. And BRD4 and BRDT specially contain a C-terminal motif. ET: Extra-terminal; BD: Bromodomain.
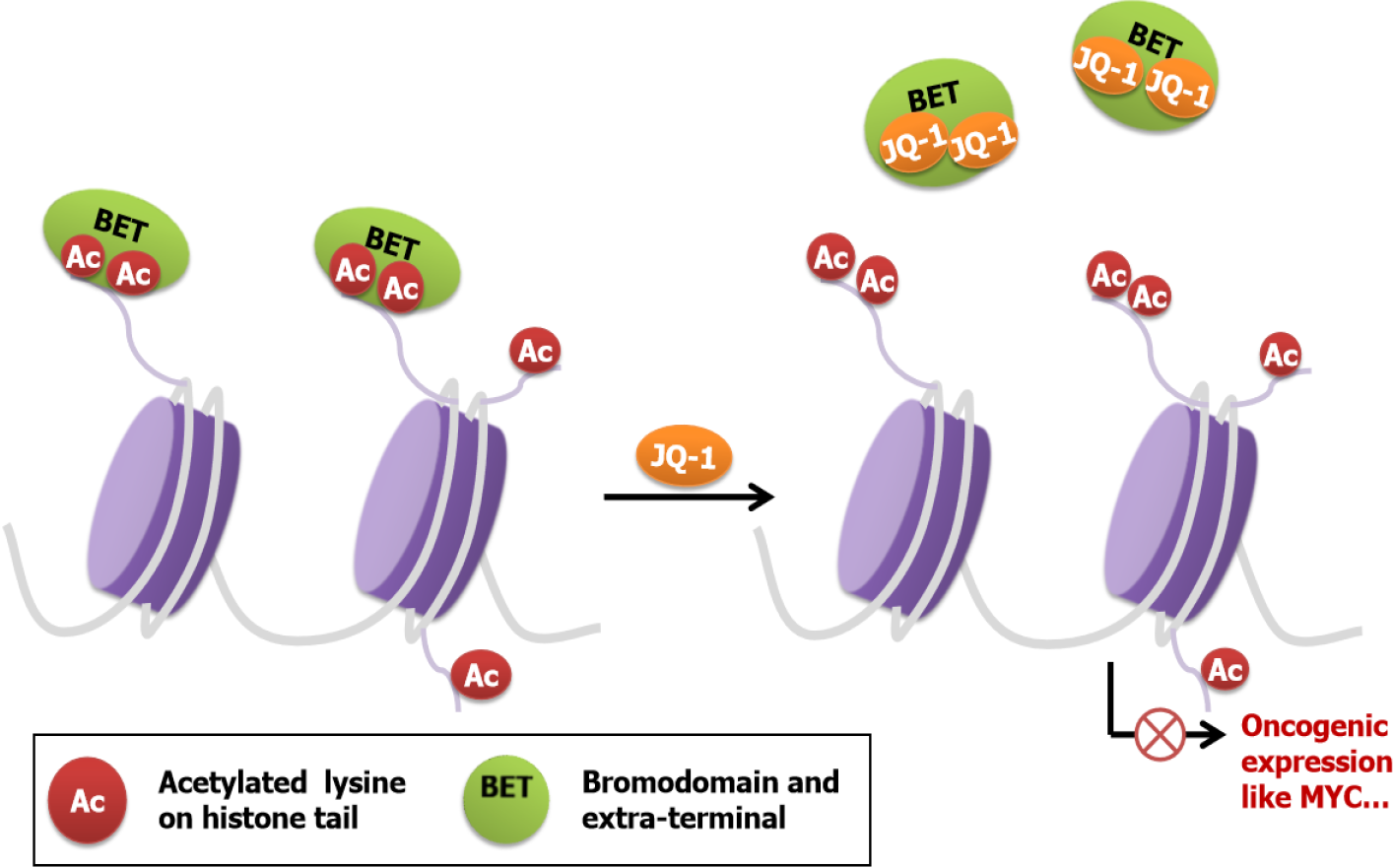
Figure 2 Schematic of the mechanism of the action of Bromodomain and extra-terminal inhibitors.
Upon Bromodomain and extra-terminal (BET) inhibitors binding to Bromodomains, BET proteins are displaced from chromatin. Lacking domains directly interacting with chromatin, BET proteins fail to activate oncogenes, and thus BET inhibitors exert cytotoxic effects on cancer cells. BET: Bromodomain and extra-terminal.
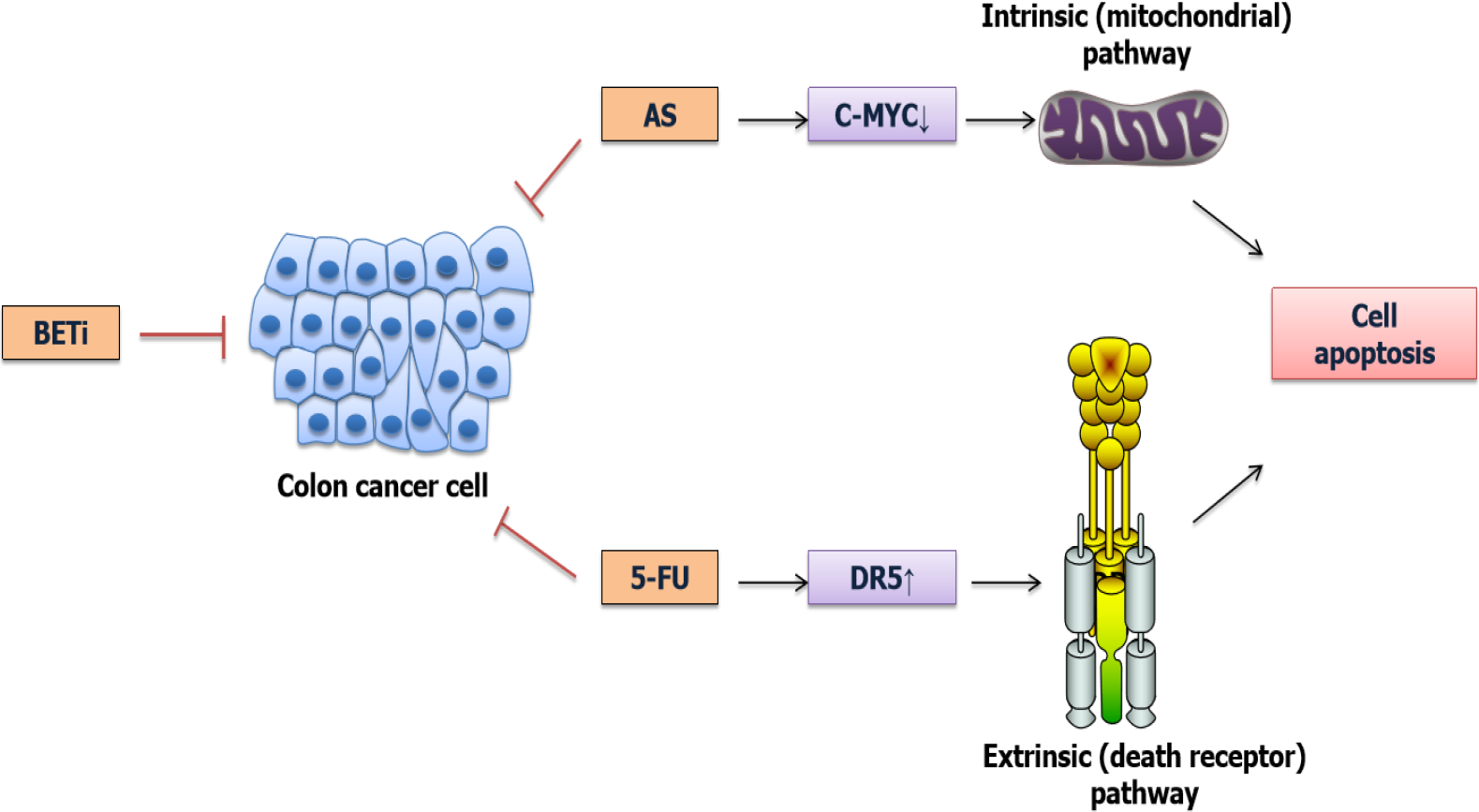
Figure 3 Schematic of Bromodomain and extra-terminal inhibitors enhancing chemotherapy effect through apoptosis induction.
Bromodomain and extra-terminal (BET) inhibitors and arsenic sulfide exert synergistic cytotoxicity via down-regulating c-MYC and induce cell apoptosis in an intrinsic (mitochondrial) pathway; while BET inhibitors in combination with 5-Fluorouracil mediate apoptosis in a death receptor 5-depedent manner which is regulated in extrinsic(death receptor) pathway. BET: Bromodomain and extra-terminal; AS: Arsenic sulfide; 5-FU: 5-fluorouracil; DR5: Death receptor 5; c-MYC: Cellular-myelocytomatosis.
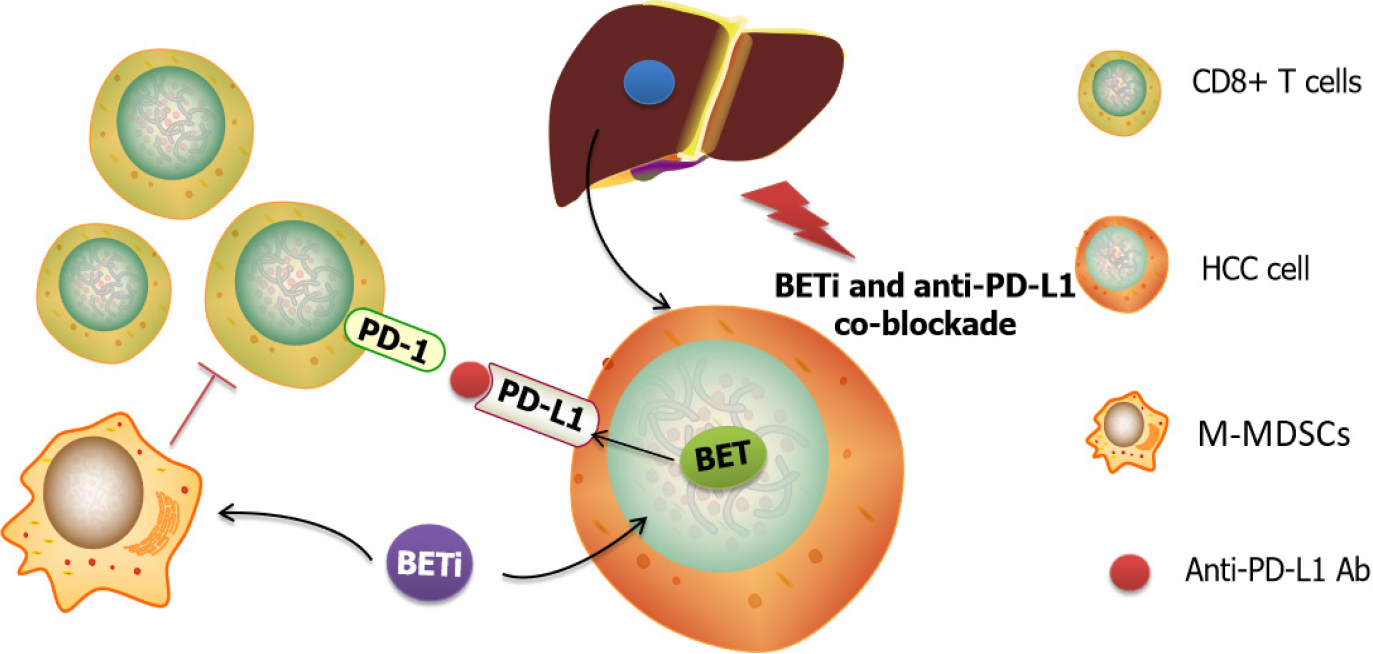
Figure 4 Schematic of Bromodomain and extra-terminal inhibitors combined with anti-programmed death-1-ligand-1 Ab therapeutic effects.
Bromodomain and extra-terminal (BET) inhibitors treatment impacts programmed death-1-ligand-1 (PD-L1) expression, resulting in sensitizing the liver response to anti-PD-L1 blockade. Also, the co-inhibition can inhibit liver-infiltrating monocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells and enhance tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells, which contributes to the elimination of drug resistance. BET: Bromodomain and extra-terminal; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; M-MDSCs: Monocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells; PD-L1: Programmed death-1-ligand-1.
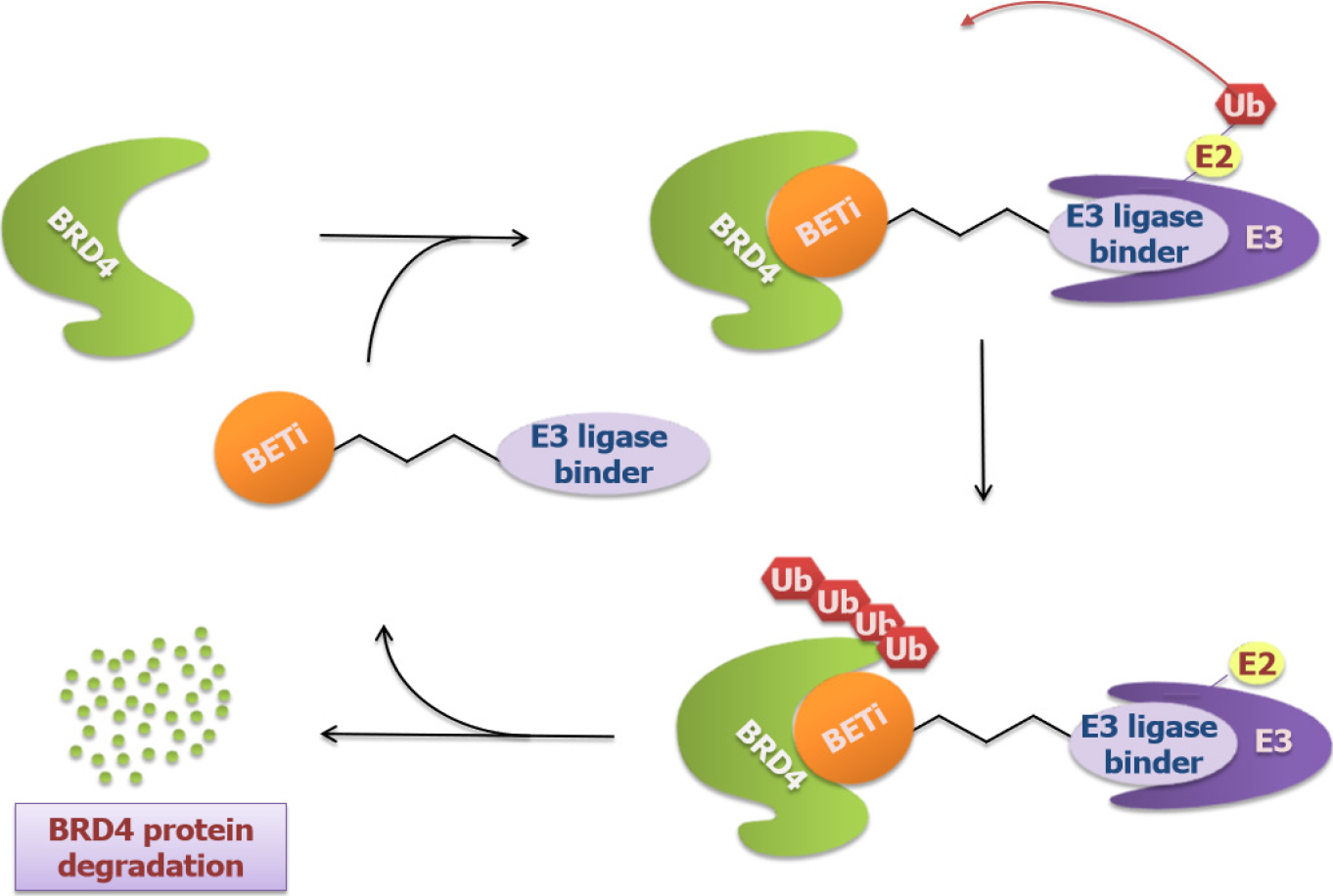
Figure 5 Schematic of new Bromodomain and extra-terminal molecules targeting Bromodomain-containing protein 4 using PROTACs technology.
The bifunctional molecules contain two binders with one (usually bromodomain and extra-terminal inhibitors like JQ-1 or OTX015) targeting Bromodomain-containing protein 4 (BRD4) and the other binding E3 Ligase, which triggers the ubiquitination and degradation of BRD4. BRD4: Bromodomain-containing protein 4.
- Citation: Sun HY, Du ST, Li YY, Deng GT, Zeng FR. Bromodomain and extra-terminal inhibitors emerge as potential therapeutic avenues for gastrointestinal cancers. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2022; 14(1): 75-89
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v14/i1/75.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v14.i1.75