Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Jan 15, 2022; 14(1): 265-277
Published online Jan 15, 2022. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v14.i1.265
Published online Jan 15, 2022. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v14.i1.265
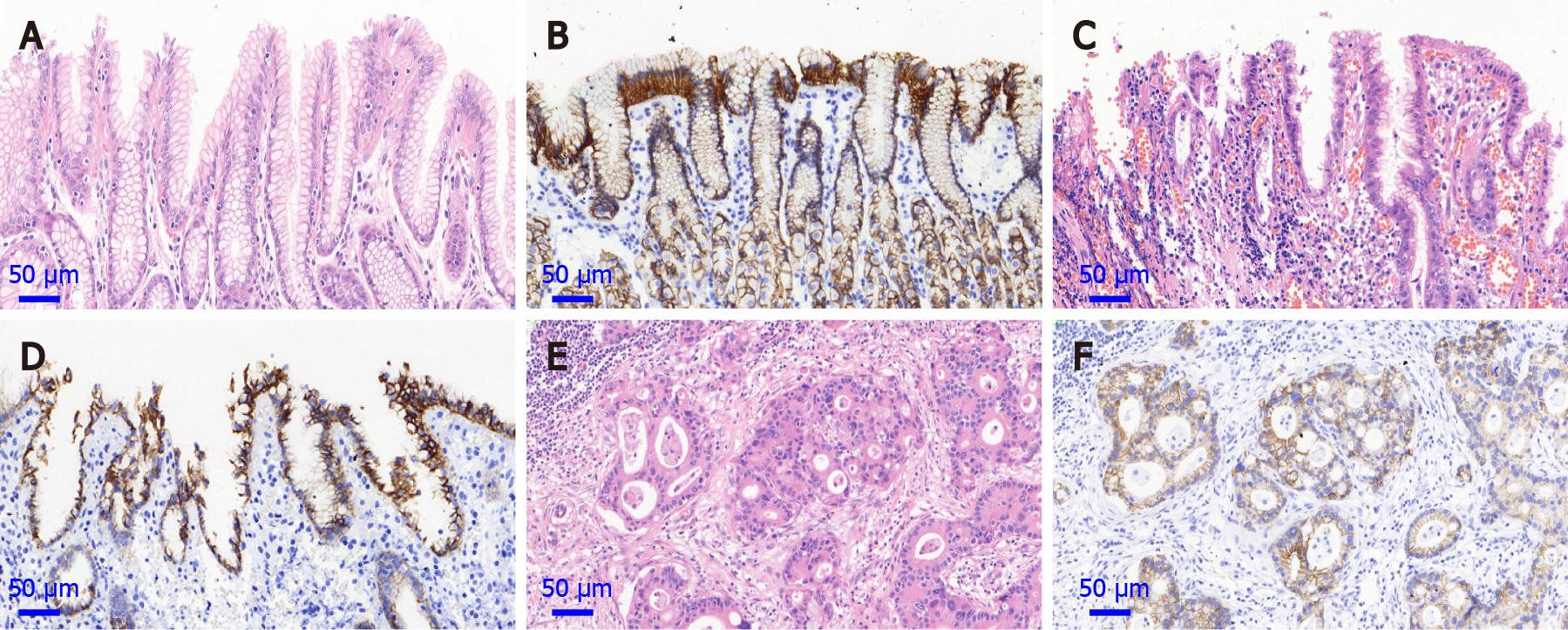
Figure 1 Hematoxylin and eosin staining sections and expression of E-cadherin of normal gastric cardia mucosa, dysplasia and gastric cardia adenocarcinoma (magnification, 400 ×).
A: Hematoxylin and eosin staining (HE) section of normal gastric cardia mucosa; B: Positive protein expression of E-cadherin in normal gastric cardia mucosa; C: HE section of dysplasia (DYS); D: Positive protein expression of E-cadherin in DYS tissue; E: HE section of gastric cardia adenocarcinoma (GCA) tissue; F: Positive protein expression of E-cadherin in GCA.
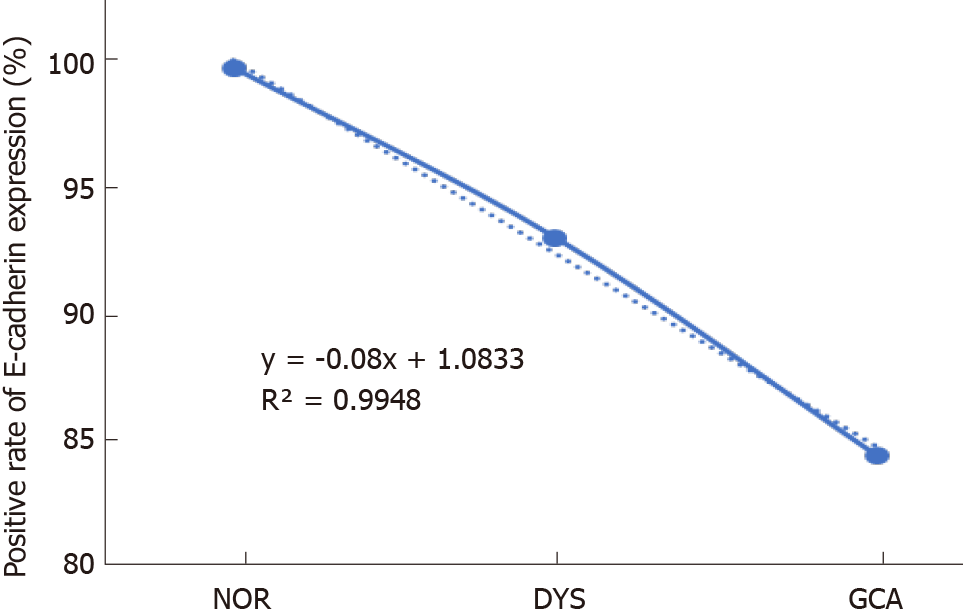
Figure 2 The linear analysis of E-cadherin protein expression in normal gastric cardia mucosa, dysplasia and gastric cardia adenocarcinoma.
With the lesions progressed from normal gastric cardia mucosa to dysplasia and gastric cardia adenocarcinoma, the positive immunostaining rates for E-cadherin decreased significantly from 100% to 93.0% and 84.1%, respectively (y = - 0.08x + 1.0833, R2 = 0.9948).
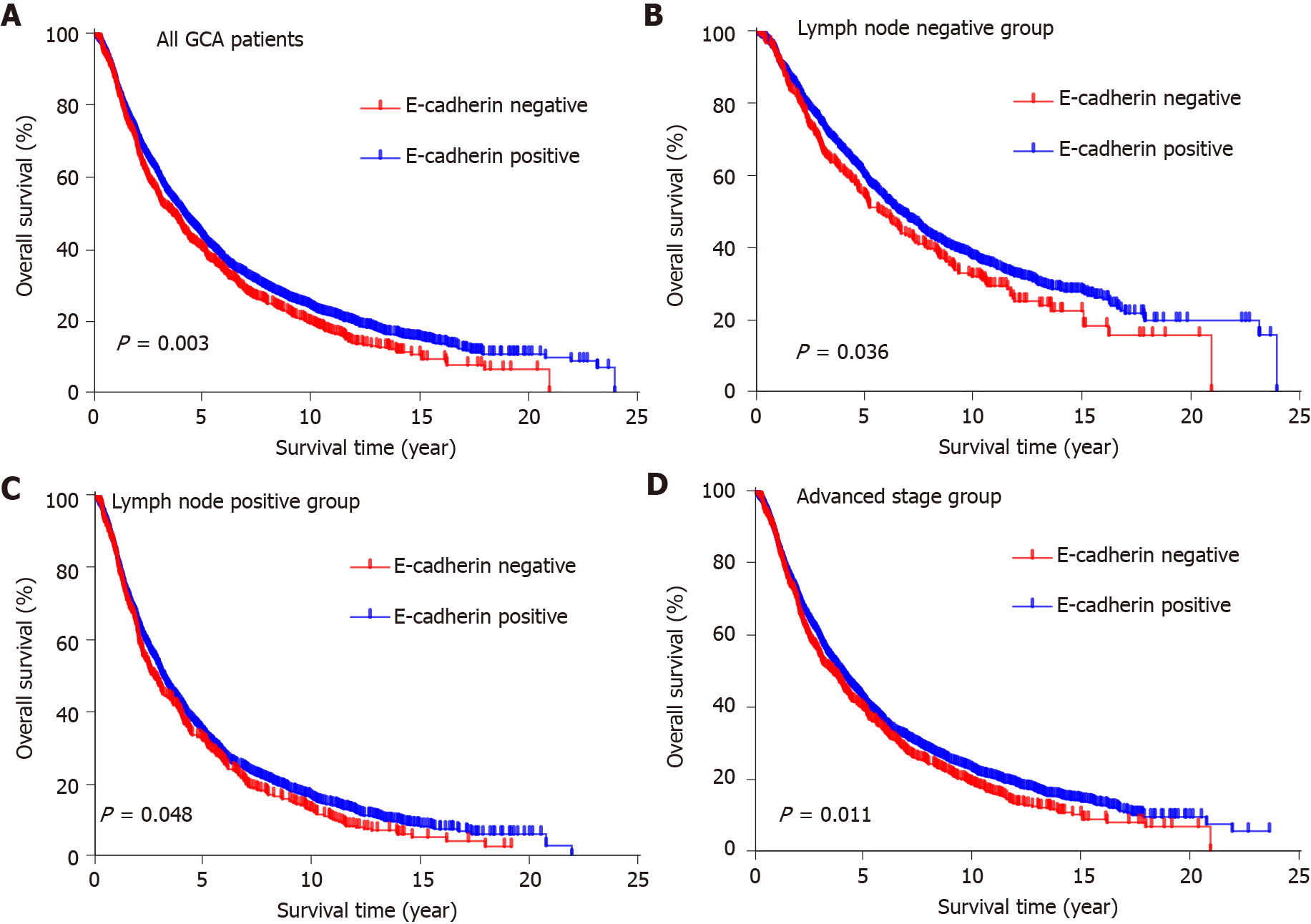
Figure 3 Kaplan–Meier analysis of the effect of E-cadherin expression on survival of gastric cardia adenocarcinoma patients.
A: Kaplan-Meier curves of overall survival according to the E-cadherin expression in gastric cardia adenocarcinoma (GCA) patients (n = 4651; P = 0.003); B: Kaplan–Meier curves of overall survival in GCA patients with negative lymph node metastasis (n = 1637; P = 0.036); C: Kaplan–Meier curves of overall survival in GCA patients with positive lymph node metastasis (n = 2924; P = 0.048); D: Kaplan–Meier curves of overall survival in GCA patients with advanced stage (n = 4370; P = 0.011). GCA: Gastric cardia adenocarcinoma.
- Citation: Wang HL, Zhao XK, Zhou FY, Song X, Li LY, Huang GR, Bao QD, Lei LL, Yang HJ, Li L, Xu RH, Li AL, Wang XZ, Han WL, Ren JL, Wang LD. Characterization of E-cadherin expression in normal mucosa, dysplasia and adenocarcinoma of gastric cardia and its influence on prognosis. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2022; 14(1): 265-277
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v14/i1/265.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v14.i1.265