Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Aug 15, 2021; 13(8): 867-878
Published online Aug 15, 2021. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v13.i8.867
Published online Aug 15, 2021. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v13.i8.867
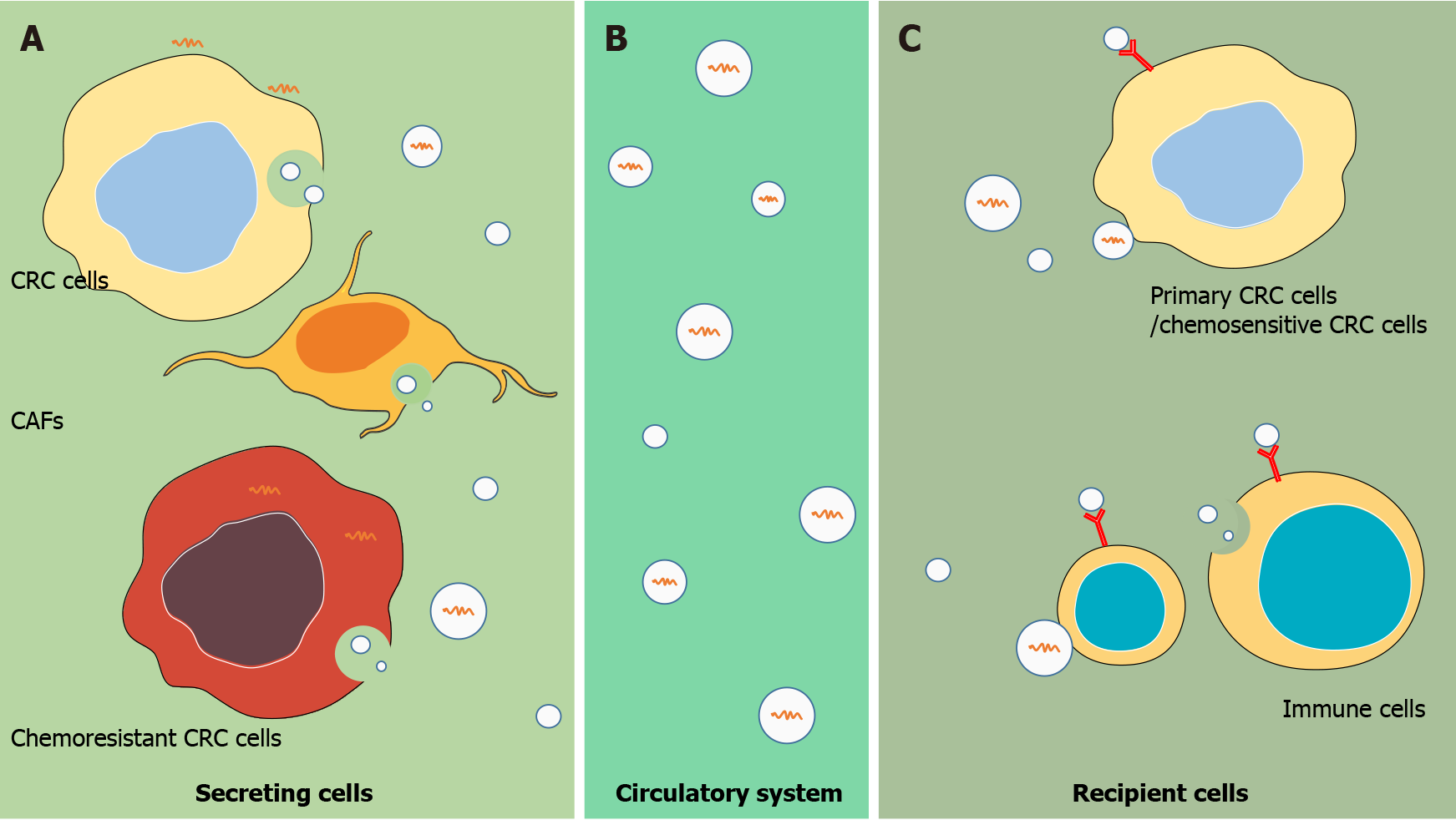
Figure 1 The process of exosomal long non-coding RNAs secretion, transportation, and ingestion.
A: Exosomal long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are secreted by colorectal cancer (CRC) cells, carcinoma-associated fibroblasts, and chemoresistant CRC cells; B: Exosomal lncRNAs are released into circulatory system; C: Exosomal lncRNAs are transferred from the secretory cell into recipient cell to exert their biological function, thereby affecting the progression of tumors. CRC: Colorectal cancer; CAF: Carcinoma-associated fibroblast.
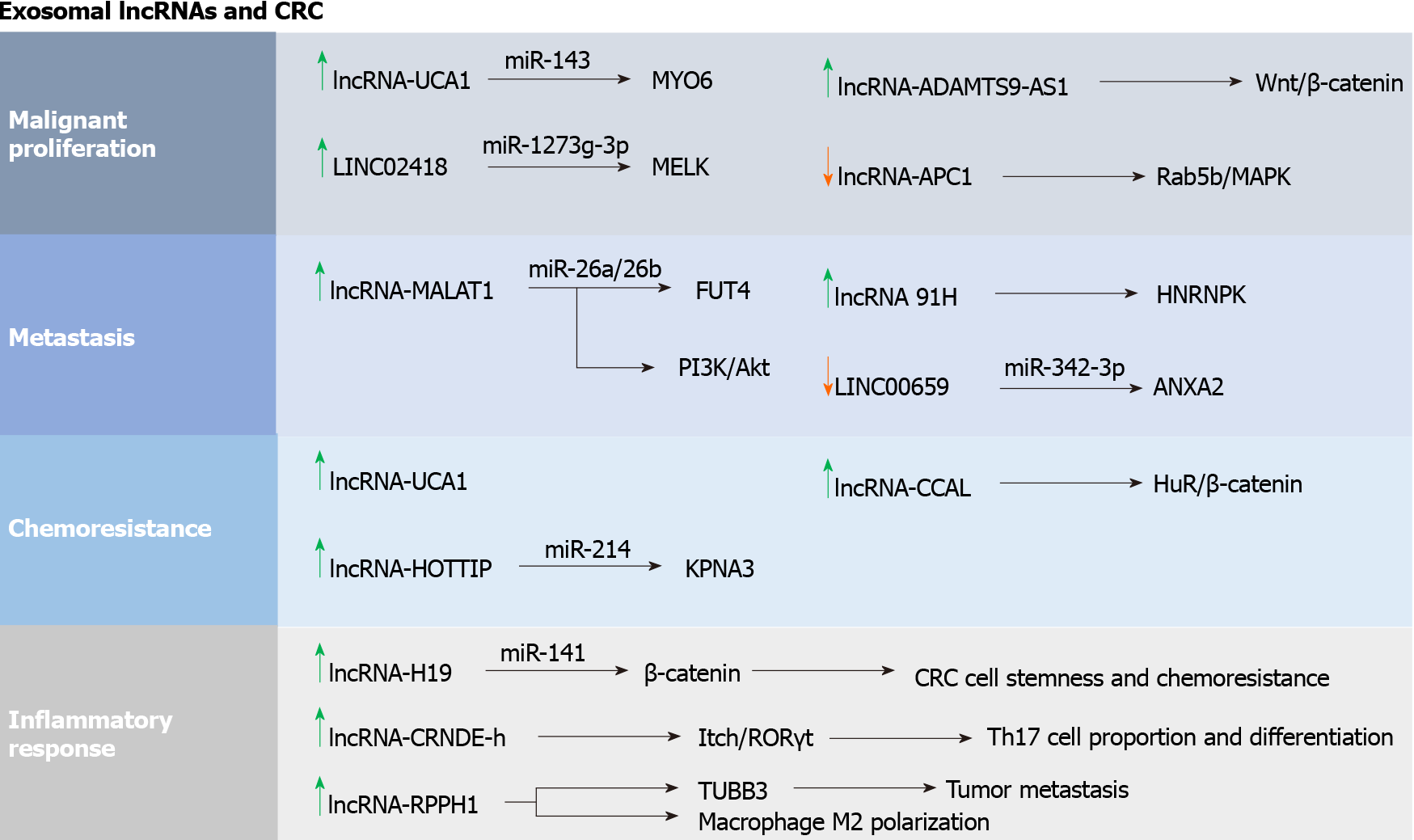
Figure 2 Summary chart of exosomal long non-coding RNAs in colorectal cancer.
Exosomal long non-coding RNAs are closely related to the occurrence and development of tumors, involved in malignant proliferation, invasion and metastasis, chemoresistance, and the inflammatory response. Orange arrows: High expression in colorectal cancer; green arrows: Low expression in colorectal cancer. LncRNA: Long non-coding RNA; CRC: Colorectal cancer; HuR: Human antigen R.
- Citation: Sun R, He XY, Mei C, Ou CL. Role of exosomal long non-coding RNAs in colorectal cancer. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2021; 13(8): 867-878
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v13/i8/867.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v13.i8.867