Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. May 15, 2021; 13(5): 409-423
Published online May 15, 2021. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v13.i5.409
Published online May 15, 2021. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v13.i5.409
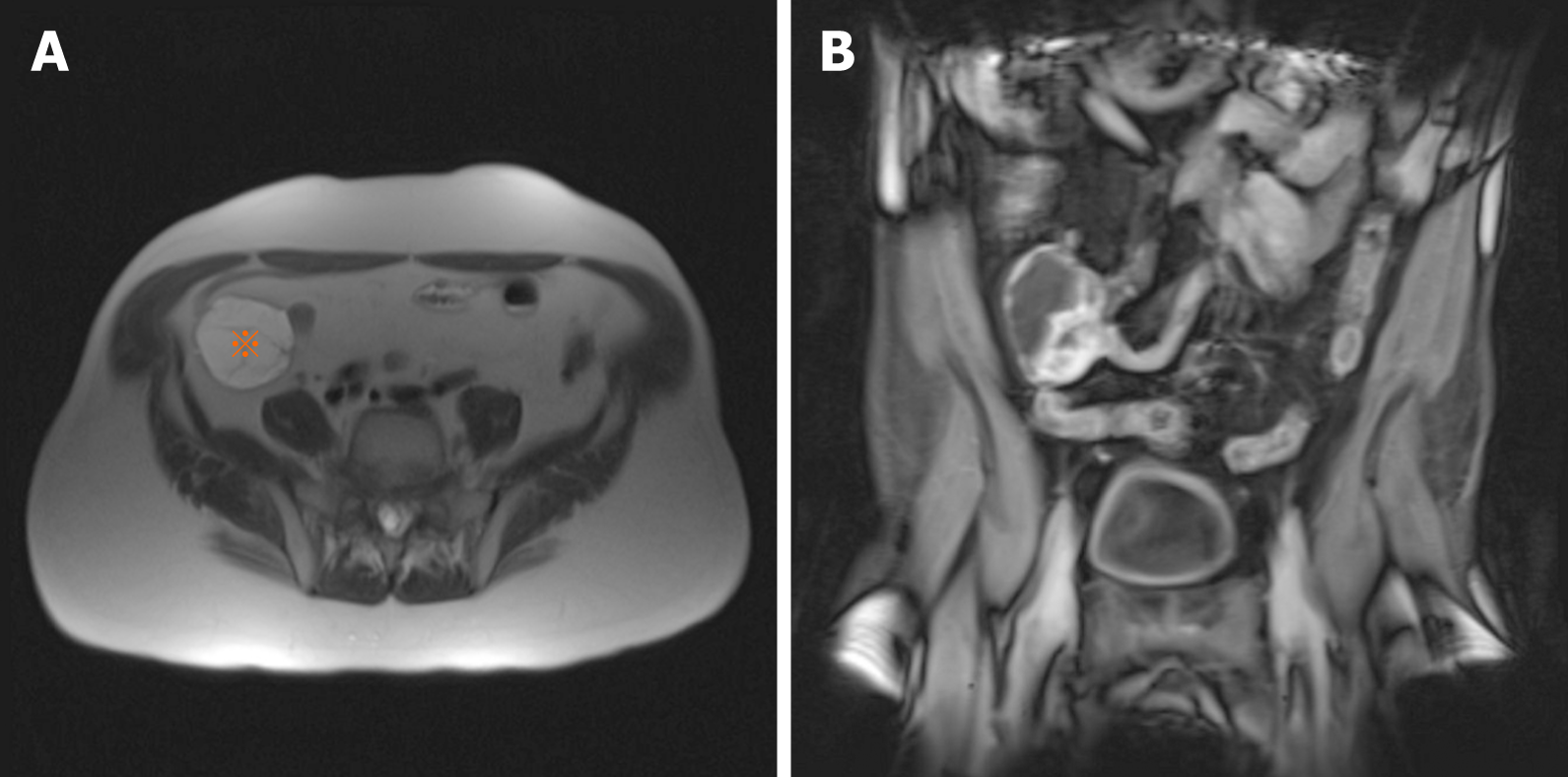
Figure 1 Magnetic resonance imaging of jejunal plexiform fibromyxoma.
A: Plexiform fibromyxoma appears as a well-circumscribed mass (asterisk) in the right lower quadrant; B: Plexiform fibromyxoma shows enhancement with contrast.
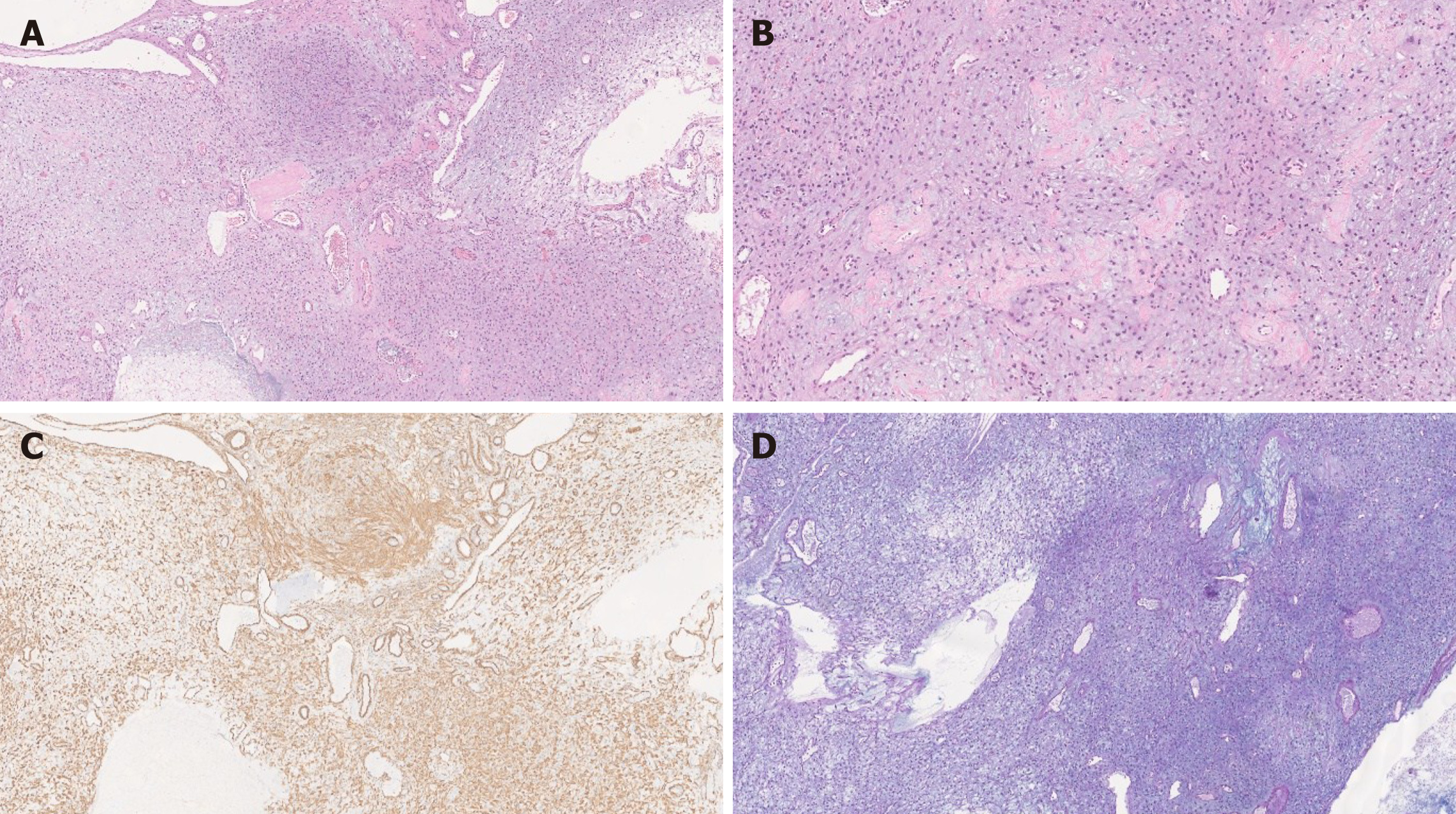
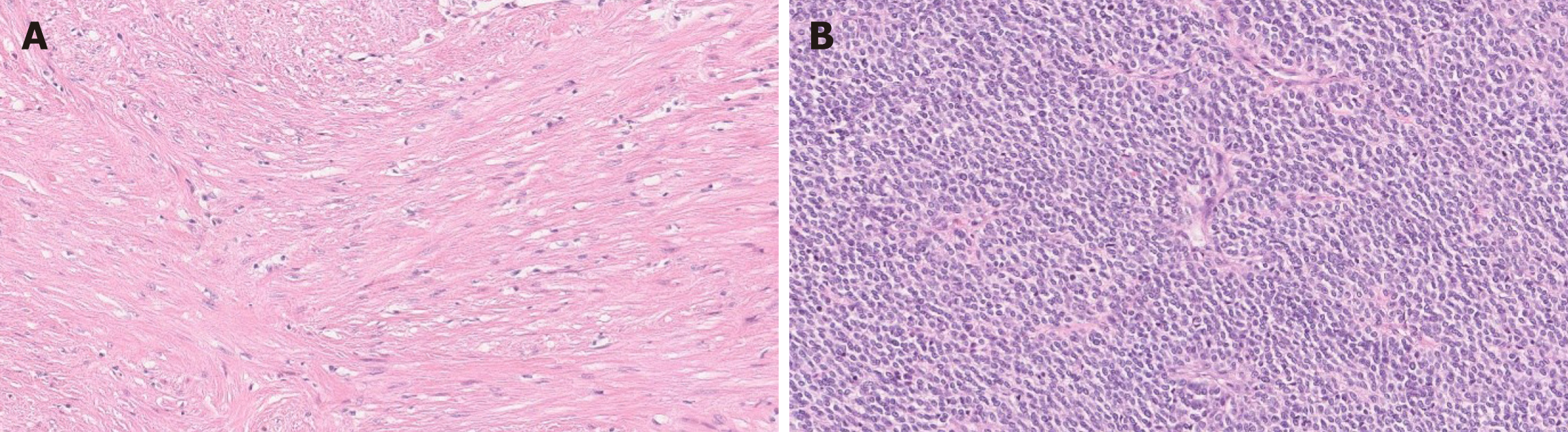
Figure 2 Plexiform fibromyxoma histology.
A: Plexiform fibromyxoma shows characteristic plexiform growth as well as cystic degeneration [hematoxylin and eosin (HE), 50 ×]; B: The tumor is composed of bland spindle to ovoid cells embedded in myxoid stroma, and prominent vasculature (HE, 200 ×); C: The tumor cells are positive for SMA (SMA, 200 ×); D: The myxoid stroma is positive for Alcian Blue (Alcian Blue, 200 ×).
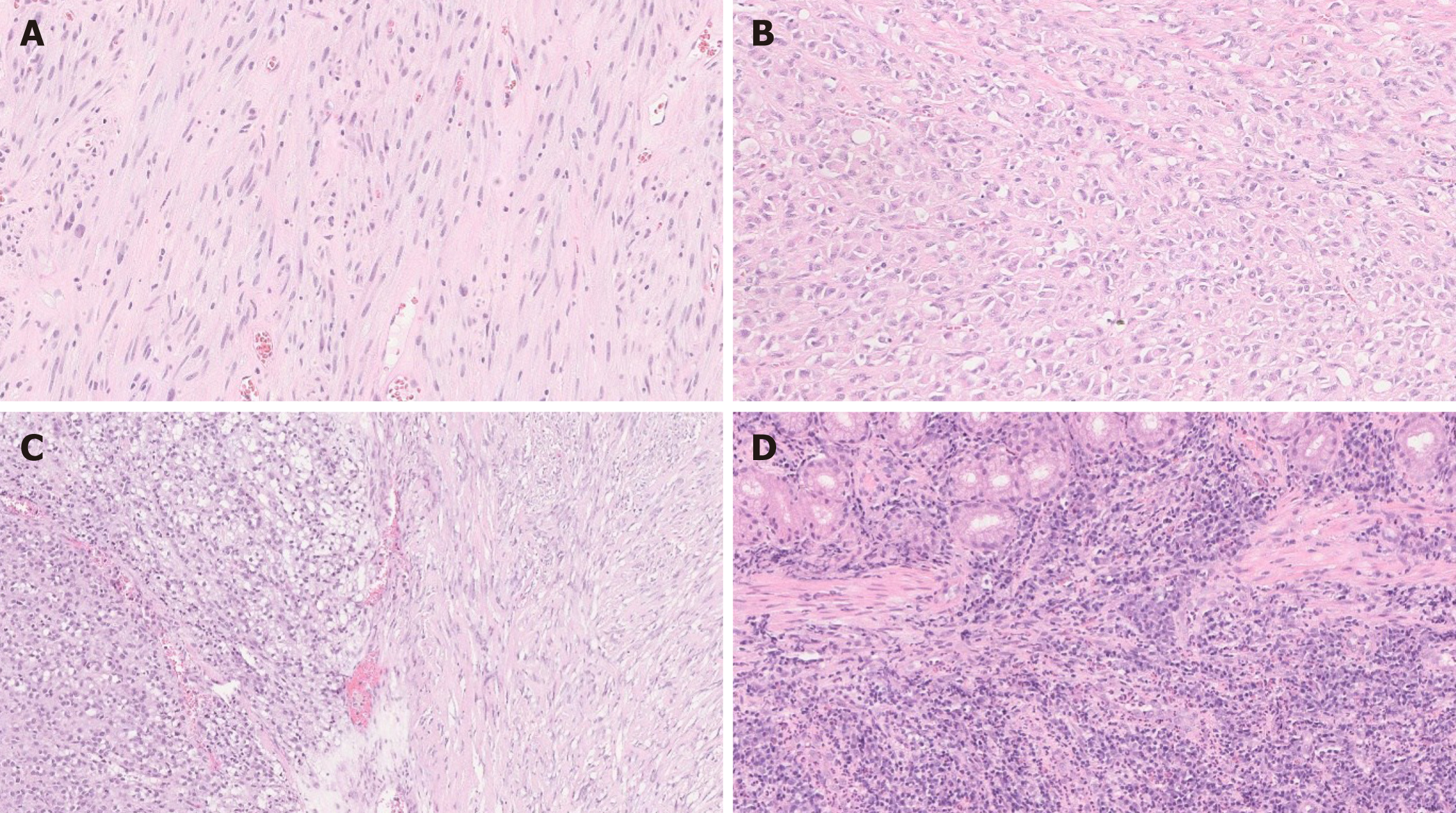
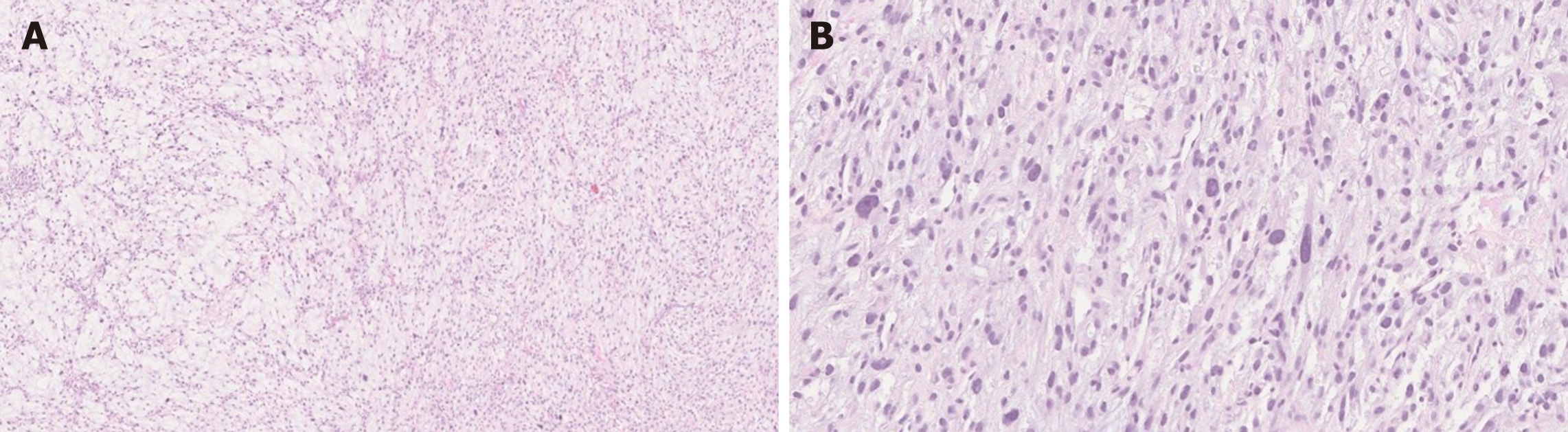
Figure 3 Gastrointestinal stromal tumor.
A: Spindle gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) [hematoxylin and eosin (HE), 200 ×]; B: Epithelioid GIST (HE, 200 ×); C: Spindle and epithelioid GIST (HE, 200 ×); D: Malignant GIST infiltrating muscularis propria of small bowel (HE, 200 ×).
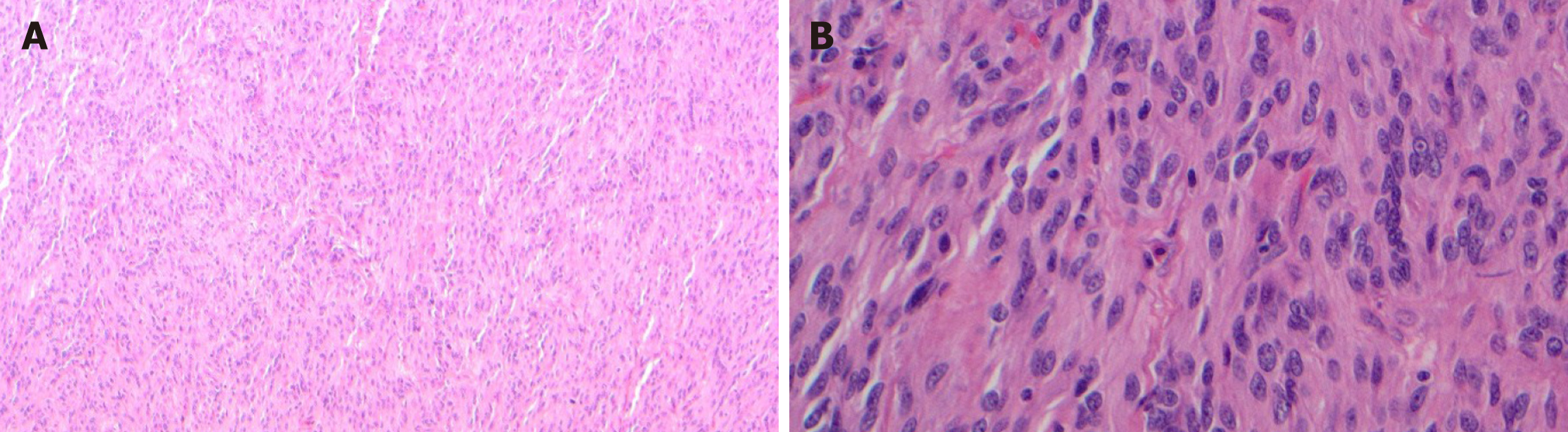
Figure 4 Succinate dehydrogenase-deficient gastrointestinal stromal tumor.
A: Succinate dehydrogenase-deficient gastrointestinal stromal tumor shows vaguely nodular growth pattern at low power [hematoxylin and eosin (HE), 100 ×]; B: The cells are epithelioid and spindled without significant atypia (HE, 400 ×). Image courtesy of Abdullah Osme, MD, Resident Physician in Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, University Hospitals, Ohio, United States; used with permission.
Figure 5 Leiomyoma vs Leiomyosarcoma.
A: Leiomyoma shows a spindle cell proliferation. The lesion is hypocellular [hematoxylin and eosin (HE), 200 ×]; B: Epithelioid leiomyosarcoma is composed of epithelioid cells with high nuclear-cytoplasmic ratio. Compared to leiomyoma, it is highly cellular with frequent mitosis (HE, 200 ×).
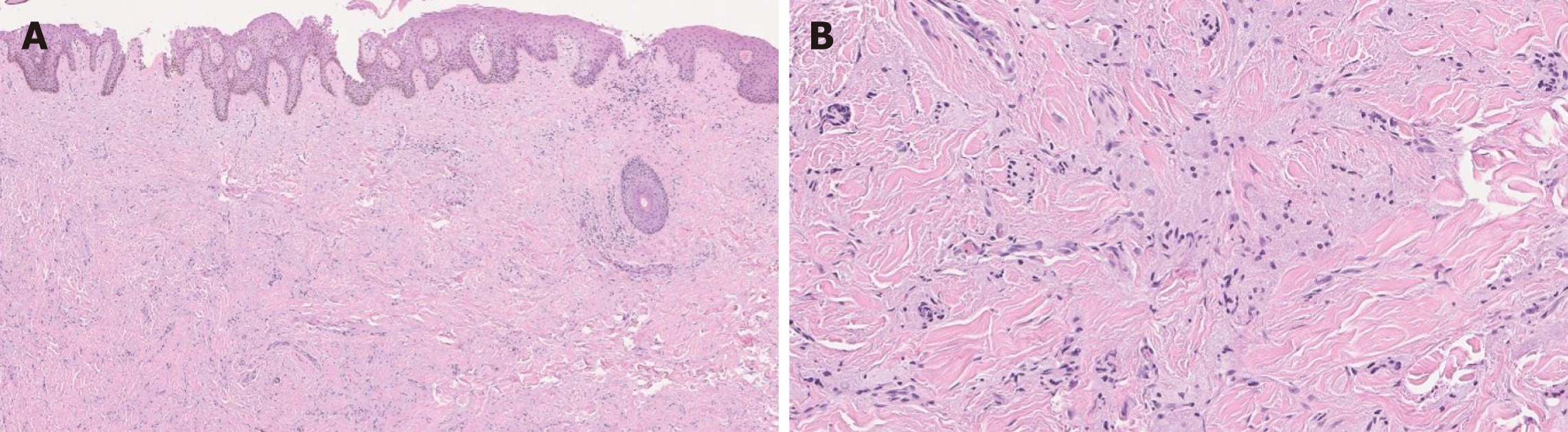
Figure 6 Granular cell tumor.
A: Epithelioid cells with abundant granular cytoplasm are infiltrating the dermis [hematoxylin and eosin (HE), 50 ×]; B: Some tumor cells are spindled with granular cytoplasm (HE, 200 ×).
Figure 7 Gastric schwannoma.
A: Gastric schwannoma exhibits a prominent lymphoid cuff at the periphery [hematoxylin and eosin (HE), 25 ×]; B: Schwannoma is composed of a bland spindle cell proliferation (HE, 200 ×).
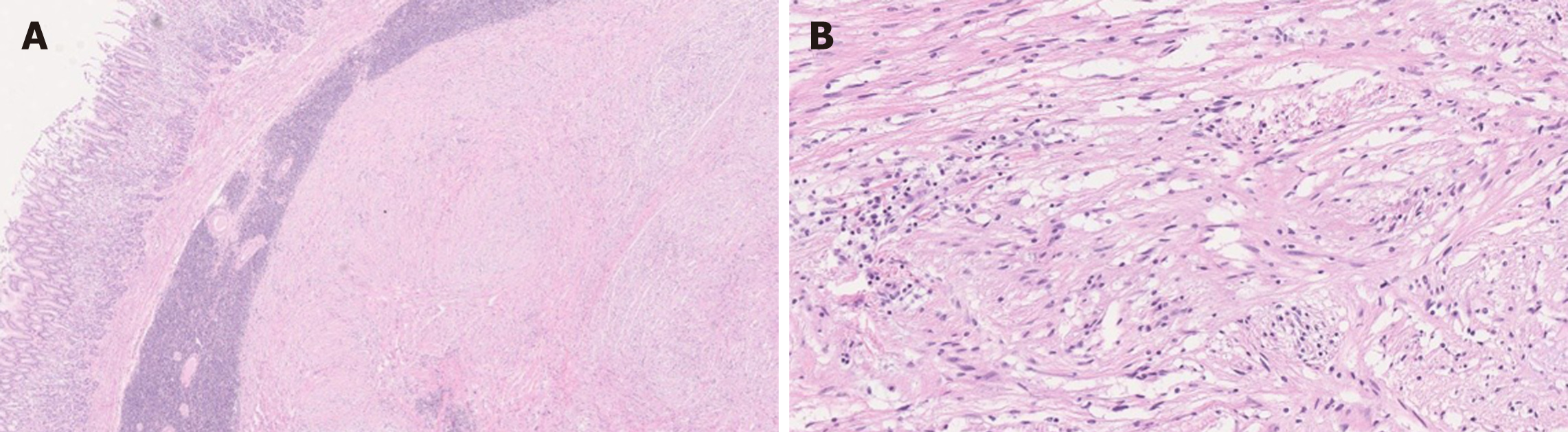
Figure 8 Small bowel neurofibroma.
A: Plexiform neurofibroma shows characteristic multinodular plexiform growth pattern [hematoxylin and eosin (HE), 10 ×]; B; Neurofibroma is composed of wavy spindle cells, fibroblasts, and strands of collagen (HE, 200 ×).
Figure 9 Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor.
A: Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST) shows alternating hypo (left) and hypercellular (right) areas [hematoxylin and eosin (HE), 50 ×]; B: Compared to benign nerve sheath tumors (shown above in Figures 6-8), MPNST exhibits hypercellularity, nuclear hyperchromasia and pleomorphism as well as frequent mitosis (HE, 200 ×).
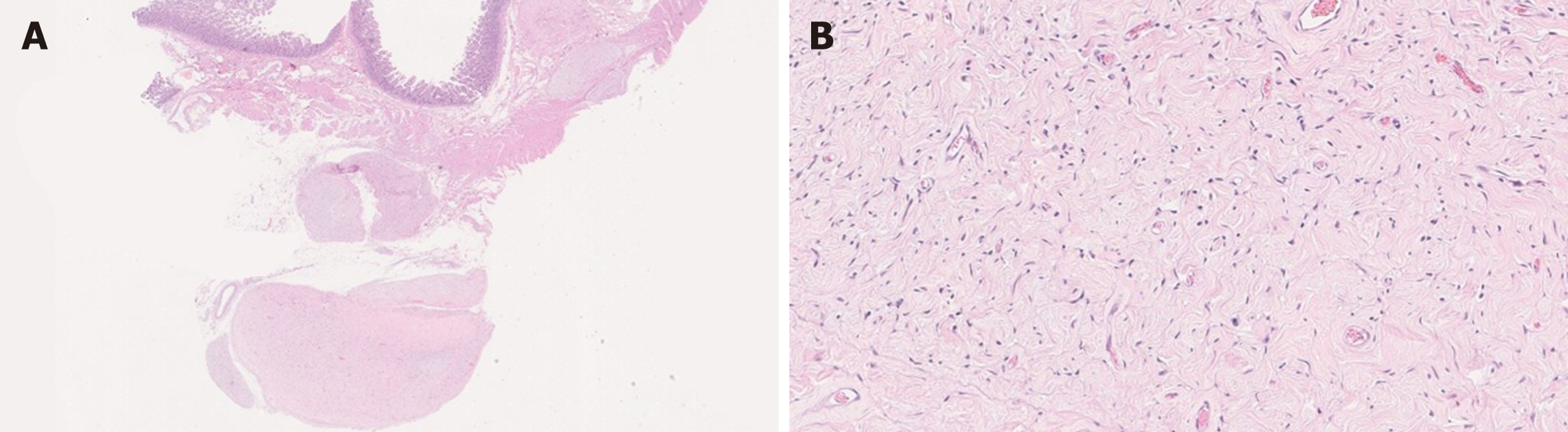
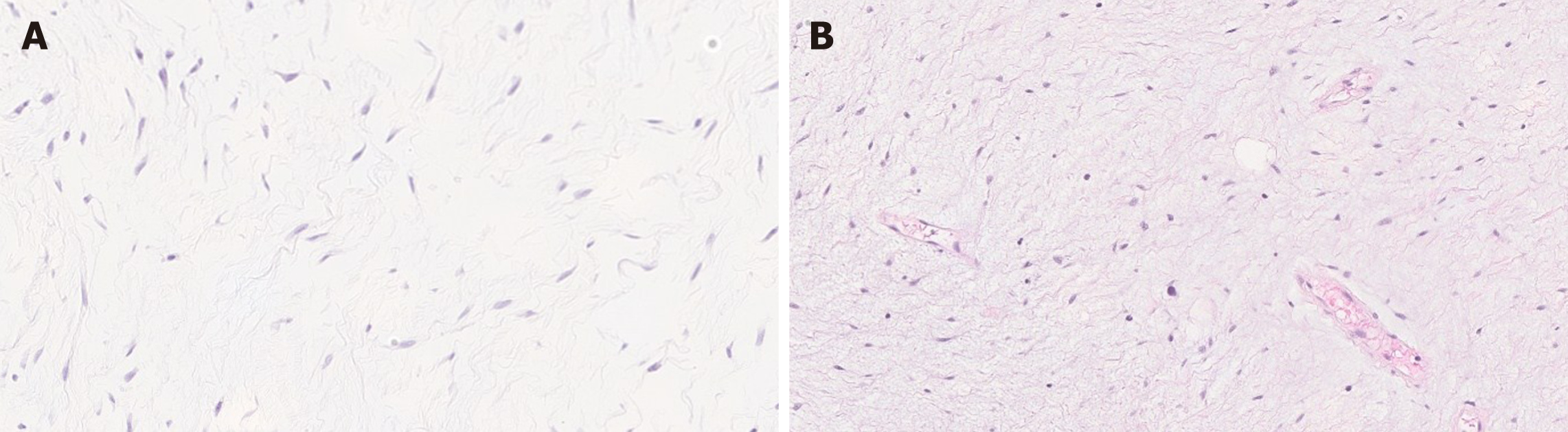
Figure 10 Myxoma vs aggressive angiomyxoma.
A: Myxoma exhibits a proliferation of bland spindle cells within a myxoid stroma. The lesion is paucicellular [hematoxylin and eosin (HE), 200 ×]; B: Aggressive angiomyxoma is also hypocellular and shows a proliferation of spindle and stellate-shaped cells in a myxoid background. Blood vessels varying in caliber may show hyalinization (HE, 200 ×).
- Citation: Arslan ME, Li H, Fu Z, Jennings TA, Lee H. Plexiform fibromyxoma: Review of rare mesenchymal gastric neoplasm and its differential diagnosis. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2021; 13(5): 409-423
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v13/i5/409.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v13.i5.409