Published online Oct 16, 2013. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v5.i10.468
Revised: July 10, 2013
Accepted: August 16, 2013
Published online: October 16, 2013
Processing time: 201 Days and 5.9 Hours
Measuring quality is a current need of medical services either to assess their cost-effectiveness or to identify discrepancies requiring refinement. With the advent of bowel cancer screening and increasing patient awareness of bowel symptoms, there has been an unprecedented increase in demand for colonoscopy. Consequently, there is an expanding open-discussion on missed rates of cancer or precancerous polyps during diagnostic/screening colonoscopy and on the rate of adverse events related to therapeutic colonoscopy. Delivering a quality colonoscopy service is therefore a healthcare priority. Colonoscopy is a multi-step process and therefore assessment of all aspects of the procedure must be addressed. Quality in colonoscopy refers to a combination of many patient-centered technical and non-technical skills and knowledge aiming to patient’s safety and satisfaction through a continuous effort for improvement. The benefits of this endless process are hiding behind small details which can eventually make the difference in colonoscopy. Identifying specific quality metrics help to define and shape an optimal service and forms a secure basis of improvement. Τhis paper does not aim to give technical details on how to perform colonoscopy but to summarize what to measure and when, in accordance with the current identified quality indicators and standards for colonoscopy.
Core tip: With the advent of bowel cancer screening and increasing patient awareness of bowel symptoms, there has been an unprecedented increase in demand for colonoscopy. Delivering a quality colonoscopy service is therefore a healthcare priority. Colonoscopy is a multi-step process and therefore assessment of all aspects of the procedure must be addressed. Quality in colonoscopy refers to a combination of many patient-centered technical and non-technical skills. Identifying specific quality metrics help to define and shape an optimal service.
- Citation: Bourikas LA, Tsiamoulos ZP, Haycock A, Thomas-Gibson S, Saunders BP. How we can measure quality in colonoscopy? World J Gastrointest Endosc 2013; 5(10): 468-475
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v5/i10/468.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v5.i10.468
Colonoscopy is the cornerstone in diagnosis and management of colorectal disease allowing direct optical diagnosis, tissue sampling for histological analysis and therapy of colonic lesions[1]. Quality of colonoscopy practice is highly variable and there is increasing public awareness of missed cancers, incomplete procedures and of adverse events related to colonoscopy which are potentially preventable[2,3]. The establishment of important, measurable quality indicators (metrics) and minimum quality standards is essential to define and shape a quality colonoscopy service.
The current quality indicators and standards for colonoscopy are based on varying levels of evidence, ranging from local perceptions and expert consensus to evidence from randomized controlled trials. The terms “auditable outcome” (an important indicator for which no clear evidence base exists) and “quality standard” (an auditable outcome for which there is an evidence base that can support a minimum standard) have been introduced to help define quality in endoscopy[4]. Τhis paper does not aim to give technical details on how to perform colonoscopy but rather summarizes what to measure and when, in accordance with the current identified quality indicators and standards for colonoscopy.
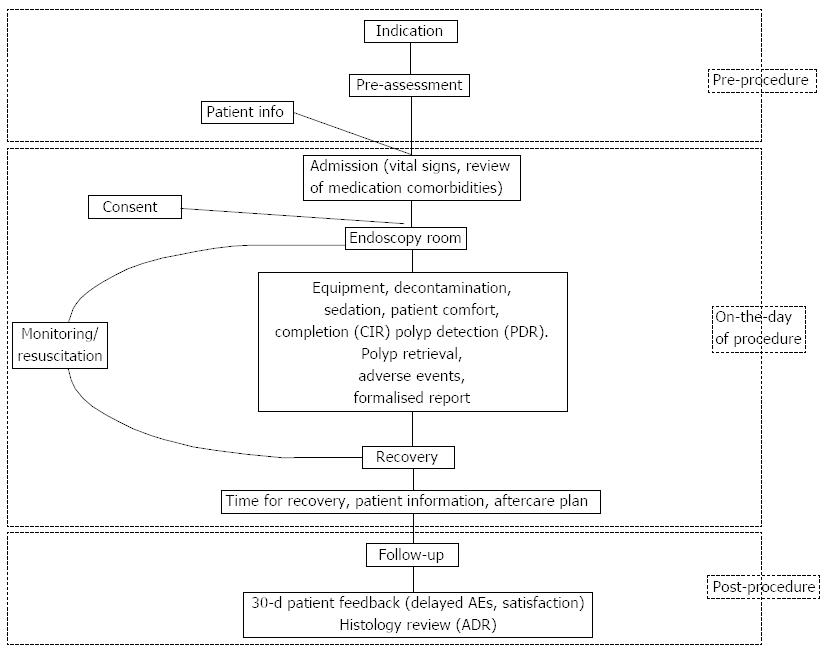
A colonoscopy service can be broken down into three main steps: pre-procedure, on the day of procedure and post-procedure (Figure 1). A high quality colonoscopy service should be patient-centered, evidence-based, cost-effective and adhering to best practice. Quality indicators and standards for each step of the colonoscopy service should be as simple and easy to audit as possible (Table 1).
| When to measure | Outcome to measure | Standard |
| Pre-procedure | Appropriateness | 100% indicated |
| Pre-assessment–bowel prep to use | 100% of cases | |
| Patient information | 100% of cases | |
| Awaiting time when positive test | < 4 wk (< 2 wk desirable) | |
| On the day of procedure | Review of comorbidities, check of vital signs | 100% on admission |
| Informed consent | 100% signed | |
| Decontamination of endoscopes | 100% agreement with local policy | |
| Appropriate function and availability of endoscopes/equipment | 100% checked by competent staff | |
| Equipment for resuscitation and monitoring | 100% regular checks | |
| CO2 insufflation | 100% availability | |
| CIR | > 90% unadjusted | |
| Use of reversal agents | < 1/500 cases | |
| Bowel cleansing | good/excellent > 90% | |
| Patient comfort | NA | |
| Polyp detection rate | Dependent on case mix | |
| Polyp retrieval rate | > 90% | |
| Time of scope withdrawal | > 6 min | |
| Complication rates | Bleeding < 1/100 | |
| Perforation < 1/1000 (diagnostic) | ||
| < 1/500 (therapeutic) | ||
| Electronically based endoscopy report | 100% attached to histology request | |
| Aftercare plan | 100% provided at recovery area | |
| Time for recovery | NA | |
| Post-procedure | Annual number of procedures/endoscopist | > 150 ( > 300 desirable) |
| Adenoma detection rate | > 15% unadjusted to race or gender | |
| Time of histopathology report | < 15 d post-colonoscopy | |
| Patient feedback/delayed AEs | 100% at 30 d | |
| Endoscopic Surveillance needed | 100% agreement with guidelines |
An appropriate indication for colonoscopy should be determined in 100% of cases. Guidelines for indications and contraindications for colonoscopy should be used as a filter to avoid unnecessary and potentially hazardous procedures[5,6]. Time-scheduling should be based on priority (surveillance vs symptoms suggestive of CRC) and urgent referrals should be seen more rapidly. In our opinion a 6-wk time limit should be the maximum waiting time for a routine colonoscopy and ≥ 85% of individuals initially offered a colonoscopy should finally undergo a colonoscopy[4].
We recommend nurse-led patient pre-assessment either in a dedicated clinic or by telephone consultation especially when this has not been done by the vetting gastroenterologist. The endoscopist needs to have complete information of patient’s medical history prior to colonoscopy; comorbidities such as clotting disorders, use of anticoagulants or anti-platelet agents, diabetes, allergies, renal function impairment, glaucoma, heart failure and factors related to the risk of endocarditis should be recognised prior to colonoscopy and instructions given to each patient should be driven by current recommendations and local policy[7-10]. The American Society of Anaesthesiologists (ASA) status and factors which could increase the risk and technical difficulty of colonoscopy, such as previous abdominal surgery (i.e., hysterectomy) or diverticular disease should be recorded[7,11].
Patient information leaflets should be available and sent out to patients as a routine, along with a copy of the consent form. Patients must be aware of why the procedure is being organised, what is involved and of the risks related to colonoscopy. They should be informed about the options for sedation in advance and the associated restrictions on travelling home[7].
A clean bowel is a prerequisite for a reliable and efficient examination[12,13]. Clear patient information, reduced fiber diet, regardless of type of bowel preparation used, help to maximise bowel cleansing[14]. PEG-electrolyte is the preparation of choice in patients with renal impairment although it does not eliminate the risk of acute renal failure and it is considered safer for patients with cardiac failure[15,16]. Adequate hydration is vital to protect against adverse events of bowel preparation while timing and in particular PM/AM splitting of administration of the recommended dose and assurance of patient’s understanding of the process also appear to be important[14,17]. Table 2 outlines patients at risk of electrolyte imbalance and documents those who of when should have an assessment of renal function prior to bowel preparation. Those with established renal disease, stage III or greater, should have PEG-electrolyte bowel preparation[18-22]. In our institution we use a combination of 10 senna tablets and 2 doses of sodium picosulfate the day before colonoscopy for morning appointments, while the second dose of sodium picosulfate is taken in the morning of the same day for afternoon colonoscopies. The patient is encouraged to drink at least 2 L of clear fluids daily for 2 d before the procedure and to avoid fiber 2 d before scheduled colonoscopy. We usually use a 2lt PEG solution (MOVIPREP) when needed. Although hospitalisation has been related with poorer bowel cleansing and should be routinely avoided, hospital admission prior to colonoscopy may be required in some cases, especially for patients in whom reduced absorption of regular medications may prove problematic and may need intravenous administration. Fragile patients with multiple comorbidities which are at risk of cardiac or renal failure and should be monitored during bowel prep are often admitted to hospital prior to colonoscopy[23]. Selection of these patients is a matter of careful clinical pre-assesment.
| Candidates for polyethylene glycol bowel preparation for colonoscopy |
| 1GFR < 60 mL/min per 1.73 m2 |
| Electrolyte imbalance |
| Cardiac failure |
| Liver cirrhosis |
| Hypertension with arteriosclerosis |
| Patients on diuretics |
| (when cannot be stopped 24 h prior to colonoscopy) |
| Patients on ACE inhibitors |
| (when cannot be stopped 72 h prior to colonoscopy) |
| Patients on NSAIDs |
| (when cannot be stopped 72 h prior to colonoscopy) |
Colonoscopy in obese patients may prove technically demanding in some cases however, in our practice and according to previous reports, routine colonoscopy is the screening test of choice and can be performed adequately in obese patients when optimal standards are fulfilled[23]. Patients with previous incomplete procedures, multiple comorbidities or on anticoagulant treatment in whom discontinuation can prove catastrophic should be offered a virtual colonoscopy (CT colonography) as an alternative. In these cases virtual colonoscopy may prove an important pre-assessment tool regarding the cost, tolerability and reduced time of the procedure compared with conventional colonoscopy[24,25].
A brief review of the cardiorespiratory function including blood pressure, pulse rate and oxygen saturation in addition to documentation of adverse events related to bowel preparation or any medication given prior to colonoscopy (i.e., antibiotic prophylaxis) should be performed on the day of the procedure and before the patient’s entrance into the endoscopy room.
A signed informed consent should be obtained by 100% of patients prior to colonoscopy, ideally in a separate area rather than the endoscopy room where a patient’s privacy can be assured. Consent for colonoscopy must include a clear and realistic explanation of the procedure, possible attendant discomfort, the benefits and a clear discussion of risks and potential adverse events including sedation reactions, bleeding (immediate and delayed), perforation and missed pathology. Patient’s right to withdraw consent at any stage of the colonoscopy process should be understood by all members of the team[4,26]. Some institutions having the patient consented in clinic by the requesting consultant as well as giving the prescription for bowel preparation and patient leaflets and thus alleviating the need for postal issue for the same. This practice can prove beneficial acting as an indirect vetting as well of high risk patients.
The appropriateness, availability and functionality of the endoscopy room and equipment used during colonoscopy (including equipment used for patient monitoring) should be ensured through regular checks. Cleansing and decontamination of endoscopes should conform to current National or International guidelines[27].
Monitoring of vital signs (blood pressure, pulse and oxygen saturation) and regular checks of patient’s comfort and ability for verbal communication should be routinely used during colonoscopy. The use of CO2 capnography is recommended to identify hypoventilation and hypoxia if heavy sedation required[28].
Patient’s comfort during colonoscopy is a critical quality outcome which refers to public acceptance rate of the procedure as a screening tool[29]. Levels of patient discomfort (no or minimal, mild, moderate, severe) should be recorded during colonoscopy.
The use of CO2 insufflation, instead of air, is currently a quality standard to maximize comfort during unsedated colonoscopy and flexible sigmoidoscopy and permits reliable radiologic examination at the same day following colonoscopy[7,30]. Moreover, since carbon dioxide is an inert gas that cannot form a combustible mixture with hydrogen and methane, CO2 insufflation avoids the very rare risk of explosion during colonoscopy with electrocautery and reduces post-polypectomy admissions after removal of large polyps[31,32]. Insufflation of CO2 should be avoided in patients with COPD, known CO2 retention or severely reduced pulmonary function.
The use of sedation improves patient tolerance of colonoscopy. A “titrated” (administrated gradually during procedure) low dose of an anxiolytic, such as midazolam (1.25-5 mg), given alone or combined with an opiate like pethidine (12.5-100 mg) or fentanyl (25-100 μg) are usually sufficient to achieve conscious sedation during colonoscopy[33], however, thresholds of pain and over-sedation remain undistinguishable and variable between individuals. Dosage reduction should be considered for older patients (> 70)[33-35]. Nitrous oxide/oxygen inhalation (Entonox) should be an alternative for people that cannot have intravenous sedation[36]. The type and dose of medications used the level of sedation (minimal-anxiolysis, moderate-conscious, deep or general anaesthesia) and the use of reversal drugs should be recorded at every colonoscopy and should be an auditable safety outcome.
The adequacy of colonic cleansing is an important outcome related to the reliability and completion rates of colonoscopy and should be reported at each procedure. Valid scales for assessment of quality bowel preparation have been made according to the presence of solid or semisolid stool and the relative limitation to achieving adequate visualization[37,38]. Excellent or adequate bowel preparation documented in > 90% of cases has been considered as a standard of bowel preparation efficacy[4,7].
Intubation of the most proximal part of the colon is a prerequisite to achieving complete examination. Intubation of the terminal ileum (TI) is not required if there is not specific indication while obtaining biopsies from normal TI is discouraged secondary to the relative concern of variant Creutzfeldt - Jakob disease’s transmission[39]. Caecal intubation rate (CIR) is a key quality indicator that reflects the performance skills of each colonoscopist, but can be affected by a variety of factors that can make the insertion of the scope difficult or impossible[40]. The main conflict in measuring the CIR of each colonoscopist is whether it should be adjusted for bowel preparation, obstructive lesions or for symptomatic patients. Overall, an unadjusted CIR > 90% can be used as the quality standard of colonoscopy, regardless of case[7].
The routine use of photodocumentation or videorecording is an emerging necessity in relation to the medicolegal risks of missed pathology or adverse events (AEs) following colonoscopy[41]. Photographic evidence of the appendix orifice and/or the ileocaecal valve has been considered as a standard practice to achieve completion[7]. Unarguably, additional pictures of the ileal mucosa provide strong evidence of completion[42]. Rectal retroversion has been considered as an established diagnostic technique to improve detection of lesions abutting the dental line[43,44] however an adequate examination can also be performed by tip manipulation in the forward view.
The incidence of colorectal cancer (CRC) can be significantly reduced through detection and appropriate removal of adenomatous polyps during colonoscopy[1]. The polyp detection rate (PDR) is defined as the number of colonoscopies at which one or more polyps were found (regardless of histological type) divided by the total number of colonoscopies performed (in the same time period). Counting polyps or polypectomy rates is easy during colonoscopy but is not as important parameter as adenoma detection rate (see later). A high retrieval rate (> 90%) of polyps removed is a recognized quality standard in the United Kingdom BCS program and can be affected by polyp size and cold snare technique of polypectomy[45]. The number and size of adenomatous polyps removed at colonoscopy should be recorded as this defines the risk of CRC and determines endoscopic surveillance[4,46,47].
Time spent on withdrawal (WT) is an important quality outcome and should be recorded during colonoscopy. A time for scope withdrawal of more than 6 min has been well-correlated with increased detection of adenomas and thus is considered as an important quality standard to be followed by each endoscopist[48]. Longer WT has been related with increased detection of proximal and serrated polyps[49,50]. Probably adequate withdraw technique and high technical endoscopist’s skills are more important to increase detection rate when appropriate WT (> 6 min) has been spent, but this is a matter of proper training and accreditation in colonoscopy that exceeds the purposes of this paper[51,52].
AEs in colonoscopy are uncommon but can be life threatening. Appropriate documentation of AEs related to colonoscopy is a substantial outcome of safety of the procedure. A Lexicon has been previously developed to provide clear definitions for AEs and levels of severity, including the minimum threshold at which an AE should be documented and reported[53]. Early AEs (bleeding, perforation, oversedation, vasovagal attacks), whether they have been adequately resolved during the procedure (i.e., use of haemostatic equipment or reversal drugs, hydration) or whether further actions are required, have to be clearly documented.
The endoscopist should be competent with the function of all supplementary equipment used during the procedure. Therapeutic colonoscopists should be technically competent to identify and safely remove high-risk lesions and be comfortable with techniques of endoscopic haemostasis[54,55]. Around 90% of post-polypectomy bleeding should be amenable to conservative management without the need for surgical intervention. According to current recommendations based on data from retrospective studies, the incidence of bleeding for colonoscopies where polypectomy is performed should not exceed 1/100[4]. However, this is a cut -off point that needs to be adjusted according to the time (immediate or delayed) and severity of bleeding, patients’ comorbidities and complexity of the procedure (i.e., EMR or simple polypectomy). Future analysis of risk factors for delayed bleeding should be possible and would optimally permit individualization of the risk of bleeding between patients. Risk of perforation should not exceed 1/1000 procedures, but may have to be adjusted to 1/500 for therapeutic colonoscopies with polypectomy[4]. In cases of therapeutic colonoscopy, the final report should include a clear description of “alarm post procedural symptoms” symptoms such as rectal bleeding, fever or abdominal pain that can be associated with delayed AEs requiring immediate medical support[4,56,57].
An increased number of AEs (ie bleeding or perforation) during therapeutic procedures always raise issues about the adequacy of therapeutic skills of each endoscopist. The European guidelines for quality assurance in colorectal cancer screening and diagnosis have proposed 5 levels of competency in colonoscopy related to the interventional armamentarium of each colonoscopist. According to this consensus colonoscopists should be able at least to remove lesions < 10 mm in order to avoid additional endoscopic procedures. We recommend that basic EMR technique for sessile polyps 1-2 cm in size, or for small flat adenomas smaller than 1 cm, should be within the armamentarium of all colonoscopists.
Standard protocols for monitoring and for emergencies should be available in the recovery area. Checks of availability and proper function of resuscitation and monitoring equipment should be regularly updated. Time of recovery is an important auditable outcome and should be recorded. After recovering from sedation and before leaving the endoscopy unit, patients need to be told about the outcome of their procedure in a simple and comprehensive way. Breaking bad news regarding suspicion of cancer should be done according to the established local policy. The average waiting time for the histopathology report and the aftercare plan should be provided and supported by a detailed written report of the procedure that includes a contact telephone number (24 h/d, 7 d/wk) in case of a procedure-related complication. An electronically based and formalized endoscopy report is essential for further interpretation of outcomes.
A copy of the endoscopy report should be attached to any histology request and should be as detailed as possible to provide accurate description of suspicious lesions including their location, their estimated size, their nature according to accredited classification systems (i.e., Paris or Lateral Spreading Tumors - LST - classification)[58], whether they are ulcerated and in case of excision whether this was completed or not.
Adenoma detection rate (ADR) is currently the benchmark of quality in colonoscopy and represents the number of colonoscopies at which one or more histologically confirmed adenomas were found divided by the total number of colonoscopies performed in the same time period[59]. ADR reflects a colonoscopist’s technical skills and care to achieve visualization of the entire colon during the procedure. High ADRs reduce the probability of interval cancer by correctly identify surveillance intervals[60]. The overall prevalence of CRC, polyps and adenomas may differ between patient populations according to gender, race, diet or environmental factors and subsequently ADRs may vary[61]. Measurement of ADR is greatly assisted by a direct link between the databases of the endoscopy and pathology departments, but this is not available everywhere[62]. Polypectomy rates can potentially provide an ADR estimate based on previous ADRs but polyp detection rate (PDR) should be used cautiously for polyps of the left colon[63-66]. Previous reports argue that reliability of ADR is much higher when refers to a sufficient volume of colonoscopies (> 150/year in our BCSP) while the number and features (size, histology or grade of dysplasia) of adenomas detected per procedure is not included when counting ADR[67,68]. The mean number of adenomas per procedure (MAP) (defined as the total number of adenomas detected divided by the number of procedures) and the mean number of adenomas per positive procedure (MAP +) (defined as the total number of adenomas detected divided by the number of procedures in which one or more adenomas were detected) can provide additional information for endoscopist’s performance[44,69,70]. We recommend an ADR > 15% as the minimum outcome unadjusted for gender or race.
Τhe reliability of a colonoscopy service is dependent on a well-organized aftercare system. This should provide patients with easy-access to further care pathways deemed necessary by colonoscopy such as appropriate time for follow-up colonoscopy (indicated by current guidelines) need for radiological or surgical examination or referral to local Multi-Disciplinary-Team (MDT) meeting. This network should ensure that no patient is lost to follow-up and it requires good communication between relevant departments (Gastroenterology, Radiology, Histopathology and Surgery).
A routine policy of contacting patients within a defined period of time (30 d) following colonoscopy is recommended to check for delayed adverse events related to the procedure and to obtain the overall patient’s feedback for the service. A simple quality questionnaire for each part of colonoscopy service is useful to detect problems with the service. We recommend a routine 30-d check for every patient having a colonoscopy while patients should also be encouraged to report any AE in the meantime. Regular reviews of complications and 30-d mortality is an essential part of quality assurance. Records of adverse events should be kept active. Clusters of AEs should instigate a formal review of individual cases.
Quality in colonoscopy encompasses optimal collaboration of various professionals with clearly defined processes. Quality assurance in colononoscopy should be based on measurement of simple and reproducible outcomes which permit regular checks on each step of the colonoscopy service. CIR and ADR are the key elements of personal endoscopic performance and their value is maximized when standards of patient’s safety, comfort and satisfaction are adequately monitored and reviewed.
P- Reviewers Bordas JM, George A S- Editor Wen LL L- Editor A E- Editor Liu XM
| 1. | Winawer SJ, Zauber AG, Ho MN, O’Brien MJ, Gottlieb LS, Sternberg SS, Waye JD, Schapiro M, Bond JH, Panish JF. Prevention of colorectal cancer by colonoscopic polypectomy. The National Polyp Study Workgroup. N Engl J Med. 1993;329:1977-1981. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3107] [Cited by in RCA: 3118] [Article Influence: 97.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 2. | Postcolonoscopy colorectal cancers are preventable: a population-based study. Gut. 2013;Epud ahead of print. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 236] [Cited by in RCA: 264] [Article Influence: 24.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Erichsen R, Baron JA, Stoffel EM, Laurberg S, Sandler RS, Sørensen HT. Characteristics and survival of interval and sporadic colorectal cancer patients: a nationwide population-based cohort study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2013;108:1332-1340. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 66] [Cited by in RCA: 76] [Article Influence: 6.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | NHS Cancer Screening Programmes. Great Britain. National Health Service. Quality assurance guidelines for colonoscopy. Sheffield: NHS Cancer Screening Programmes 2011; Available from: http://www.cancerscreening.nhs.uk/bowel/publications/nhsbcsp06.pdf. |
| 5. | Khashab MA, Rex DK. Indications and Contraindications. Colonoscopy: Wiley-Blackwell 2009; 165-177. |
| 6. | Carrion S, Marin I, Lorenzo-Zuniga V, Moreno De Vega V, Boix J. Appropriateness of colonoscopy indications according to the new EPAGE II criteria. Gastroenterología y Hepatología. 2010;33:484-489. [RCA] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 10] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Segnan N, Patnick J, Von Karsa L. European guidelines for quality assurance in colorectal cancer screening and diagnosis-1st ed. Luxembourg: Publications Office of the European Union 2010; . |
| 8. | ASGE Standards of Practice Committee, Anderson MA, Ben-Menachem T, Gan SI, Appalaneni V, Banerjee S, Cash BD, Fisher L, Harrison ME, Fanelli RD, Fukami N, Ikenberry SO, Jain R, Khan K, Krinsky ML, Lichtenstein DR, Maple JT, Shen B, Strohmeyer L, Baron T, Dominitz JA. Management of antithrombotic agents for endoscopic procedures. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009;70:1060-1070. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 378] [Cited by in RCA: 352] [Article Influence: 22.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Ginzburg L, Greenwald D, Cohen J. Complications of endoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2007;17:405-432. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 15] [Cited by in RCA: 15] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | ASGE Standards of Practice Committee, Banerjee S, Shen B, Baron TH, Nelson DB, Anderson MA, Cash BD, Dominitz JA, Gan SI, Harrison ME, Ikenberry SO, Jagannath SB, Lichtenstein D, Fanelli RD, Lee K, van Guilder T, Stewart LE. Antibiotic prophylaxis for GI endoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2008;67:791-798. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 277] [Cited by in RCA: 213] [Article Influence: 12.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Bernstein C, Thorn M, Monsees K, Spell R, O’Connor JB. A prospective study of factors that determine cecal intubation time at colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005;61:72-75. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 138] [Cited by in RCA: 143] [Article Influence: 7.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Froehlich F, Wietlisbach V, Gonvers JJ, Burnand B, Vader JP. Impact of colonic cleansing on quality and diagnostic yield of colonoscopy: the European Panel of Appropriateness of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy European multicenter study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005;61:378-384. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 642] [Cited by in RCA: 698] [Article Influence: 34.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Rex DK, Imperiale TF, Latinovich DR, Bratcher LL. Impact of bowel preparation on efficiency and cost of colonoscopy. Am J Gastroenterol. 2002;97:1696-1700. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 395] [Cited by in RCA: 470] [Article Influence: 20.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Hassan C, Bretthauer M, Kaminski MF, Polkowski M, Rembacken B, Saunders B, Benamouzig R, Holme O, Green S, Kuiper T. Bowel preparation for colonoscopy: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) guideline. Endoscopy. 2013;45:142-150. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 290] [Cited by in RCA: 310] [Article Influence: 25.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 15. | Choi NK, Lee J, Chang Y, Jung SY, Kim YJ, Lee SM, Lee JH, Kim JY, Song HJ, Park BJ. Polyethylene glycol bowel preparation does not eliminate the risk of acute renal failure: a population-based case-crossover study. Endoscopy. 2013;45:208-213. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 22] [Cited by in RCA: 21] [Article Influence: 1.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Parikh K, Weitz H. Can a bowel preparation exacerbate heart failure? Cleve Clin J Med. 2011;78:157-160. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 10] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Belsey J, Epstein O, Heresbach D. Systematic review: oral bowel preparation for colonoscopy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2007;25:373-384. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 162] [Cited by in RCA: 135] [Article Influence: 7.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Lawrance IC, Willert RP, Murray K. Bowel cleansing for colonoscopy: prospective randomized assessment of efficacy and of induced mucosal abnormality with three preparation agents. Endoscopy. 2011;43:412-418. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 61] [Cited by in RCA: 62] [Article Influence: 4.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Gurudu SR, Ratuapli S, Heigh R, DiBaise J, Leighton J, Crowell M. Quality of bowel cleansing for afternoon colonoscopy is influenced by time of administration. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010;105:2318-2322. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 45] [Cited by in RCA: 46] [Article Influence: 3.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Longcroft-Wheaton G, Bhandari P. Same-day bowel cleansing regimen is superior to a split-dose regimen over 2 d for afternoon colonoscopy: results from a large prospective series. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2012;46:57-61. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 53] [Cited by in RCA: 39] [Article Influence: 3.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Nguyen DL, Wieland M. Risk factors predictive of poor quality preparation during average risk colonoscopy screening: the importance of health literacy. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2010;19:369-372. [PubMed] |
| 22. | Cohen LB. Split dosing of bowel preparations for colonoscopy: an analysis of its efficacy, safety, and tolerability. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010;72:406-412. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 62] [Cited by in RCA: 68] [Article Influence: 4.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 23. | Bhandari P, Agrawal A, Lim C, Manjunath S, Murphy S, Rembacken B, Robb J. Bowel preparation before colonoscopy: get it right first time. London: BMJ Group 2012; 1-8. |
| 24. | van Dam L, de Wijkerslooth TR, de Haan MC, Stoop EM, Bossuyt PM, Fockens P, Thomeer M, Kuipers EJ, van Leerdam ME, van Ballegooijen M. Time requirements and health effects of participation in colorectal cancer screening with colonoscopy or computed tomography colonography in a randomized controlled trial. Endoscopy. 2013;45:182-188. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 25. | Gomes M, Aldridge RW, Wylie P, Bell J, Epstein O. Cost-effectiveness analysis of 3-D computerized tomography colonography versus optical colonoscopy for imaging symptomatic gastroenterology patients. Appl Health Econ Health Policy. 2013;11:107-117. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 8] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 26. | Available from: http://www.bsg.org.uk/pdf_word_docs/consent.pdf. |
| 27. | Beilenhoff U, Neumann CS, Rey JF, Biering H, Blum R, Cimbro M, Kampf B, Rogers M, Schmidt V. ESGE-ESGENA Guideline: cleaning and disinfection in gastrointestinal endoscopy. Endoscopy. 2008;40:939-957. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 97] [Cited by in RCA: 93] [Article Influence: 5.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 28. | Deitch K, Miner J, Chudnofsky CR, Dominici P, Latta D. Does end tidal CO2 monitoring during emergency department procedural sedation and analgesia with propofol decrease the incidence of hypoxic events? A randomized, controlled trial. Ann Emerg Med. 2010;55:258-264. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 149] [Cited by in RCA: 137] [Article Influence: 8.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 29. | Condon A, Graff L, Elliot L, Ilnyckyj A. Acceptance of colonoscopy requires more than test tolerance. Can J Gastroenterol. 2008;22:41-47. [PubMed] |
| 30. | Hussein AM, Bartram CI, Williams CB. Carbon dioxide insufflation for more comfortable colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 1984;30:68-70. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 76] [Cited by in RCA: 73] [Article Influence: 1.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 31. | Ladas SD, Karamanolis G, Ben-Soussan E. Colonic gas explosion during therapeutic colonoscopy with electrocautery. World J Gastroenterol. 2007;13:5295-5298. [PubMed] |
| 32. | Bassan MS, Holt B, Moss A, Williams SJ, Sonson R, Bourke MJ. Carbon dioxide insufflation reduces number of postprocedure admissions after endoscopic resection of large colonic lesions: a prospective cohort study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2013;77:90-95. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 58] [Cited by in RCA: 62] [Article Influence: 5.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 33. | British Society of Gastroenterology (BSG) Guidelines on Safety and Sedation During Endoscopic Procedures. London: BSG 2003; . |
| 34. | Lord DA, Bell GD, Gray A, Quine A, Bowles J, Romaya C, De La Iglesia B, Reynolds A, Rayward-Smith VJ. Sedation for Gastrointestinal Endoscopic Procedures in the Elderly: Getting Safer but Still Not Nearly Safe Enough. London: BSG 2006; Available from: http://www.bsg.org.uk/pdf_word_docs/sedation_elderly.pdf. |
| 35. | National Guideline C. ASGE guideline: modifications in endoscopic practice for the elderly. Gastrointest Endosc. 2006;63:566-569. |
| 36. | Aboumarzouk OM, Agarwal T, Syed Nong Chek SA, Milewski PJ, Nelson RL. Nitrous oxide for colonoscopy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011;. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 22] [Cited by in RCA: 22] [Article Influence: 1.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 37. | Rostom A, Jolicoeur E. Validation of a new scale for the assessment of bowel preparation quality. Gastrointest Endosc. 2004;59:482-486. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 308] [Cited by in RCA: 341] [Article Influence: 16.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (2)] |
| 38. | Lai EJ, Calderwood AH, Doros G, Fix OK, Jacobson BC. The Boston bowel preparation scale: a valid and reliable instrument for colonoscopy-oriented research. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009;69:620-625. [PubMed] |
| 39. | Powell N, Hayee BH, Yeoh DP, Rowbotham DS, Saxena V, McNair A. Terminal ileal photography or biopsy to verify total colonoscopy: does the endoscope agree with the microscope? Gastrointest Endosc. 2007;66:320-325. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 14] [Cited by in RCA: 14] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 40. | Church JM. Complete colonoscopy: how often? And if not, why not? Am J Gastroenterol. 1994;89:556-560. [PubMed] |
| 41. | Rex DK. Avoiding and defending malpractice suits for postcolonoscopy cancer: advice from an expert witness. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;11:768-773. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 23] [Cited by in RCA: 28] [Article Influence: 2.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 42. | Powell N, Knight H, Dunn J, Saxena V, Mawdsley J, Murray C, Hoare J, Teare J, McNair A. Images of the terminal ileum are more convincing than cecal images for verifying the extent of colonoscopy. Endoscopy. 2011;43:196-201. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 16] [Cited by in RCA: 19] [Article Influence: 1.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 43. | Reddy AB, Palardy LG, Reddy KB. The utility of rectal retroflexion. Am J Gastroenterol. 2011;106:1008-1011. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 0.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 44. | Lee TJ, Rutter MD, Blanks RG, Moss SM, Goddard AF, Chilton A, Nickerson C, McNally RJ, Patnick J, Rees CJ. Colonoscopy quality measures: experience from the NHS Bowel Cancer Screening Programme. Gut. 2012;61:1050-1057. [RCA] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 209] [Cited by in RCA: 249] [Article Influence: 19.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 45. | Komeda Y, Suzuki N, Sarah M, Thomas-Gibson S, Vance M, Fraser C, Patel K, Saunders BP. Factors associated with failed polyp retrieval at screening colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2013;77:395-400. [PubMed] |
| 46. | Rex DK, Petrini JL, Baron TH, Chak A, Cohen J, Deal SE, Hoffman B, Jacobson BC, Mergener K, Petersen BT. Quality indicators for colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2006;63:S16-S28. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 390] [Cited by in RCA: 383] [Article Influence: 20.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 47. | Results of the first round of a demonstration pilot of screening for colorectal cancer in the United Kingdom. BMJ. 2004;329:133. [PubMed] |
| 48. | Barclay RL, Vicari JJ, Doughty AS, Johanson JF, Greenlaw RL. Colonoscopic withdrawal times and adenoma detection during screening colonoscopy. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:2533-2541. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 911] [Cited by in RCA: 945] [Article Influence: 49.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 49. | de Wijkerslooth TR, Stoop EM, Bossuyt PM, Tytgat KM, Dees J, Mathus-Vliegen EM, Kuipers EJ, Fockens P, van Leerdam ME, Dekker E. Differences in proximal serrated polyp detection among endoscopists are associated with variability in withdrawal time. Gastrointest Endosc. 2013;77:617-623. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 104] [Cited by in RCA: 117] [Article Influence: 9.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 50. | Lee TJ, Blanks RG, Rees CJ, Wright KC, Nickerson C, Moss SM, Chilton A, Goddard AF, Patnick J, McNally RJ. Longer mean colonoscopy withdrawal time is associated with increased adenoma detection: evidence from the Bowel Cancer Screening Programme in England. Endoscopy. 2013;45:20-26. [PubMed] |
| 51. | Barclay RL, Vicari JJ, Greenlaw RL. Effect of a time-dependent colonoscopic withdrawal protocol on adenoma detection during screening colonoscopy. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;6:1091-1098. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 190] [Cited by in RCA: 199] [Article Influence: 11.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 52. | Coe SG, Crook JE, Diehl NN, Wallace MB. An endoscopic quality improvement program improves detection of colorectal adenomas. Am J Gastroenterol. 2013;108:219-226; quiz 227. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 134] [Cited by in RCA: 151] [Article Influence: 12.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 53. | Cotton PB, Eisen GM, Aabakken L, Baron TH, Hutter MM, Jacobson BC, Mergener K, Nemcek A, Petersen BT, Petrini JL. A lexicon for endoscopic adverse events: report of an ASGE workshop. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010;71:446-454. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1238] [Cited by in RCA: 1834] [Article Influence: 122.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 54. | Saunders B, Ginsberg GG, Bjorkman DJ. How I do it: Removing large or sessile colonic polyps. Munich: OMED 2008; . |
| 55. | Riley SA. Colonoscopic Polypectomy and Endoscopic Mucosal Resection: A Practical Guide. 2008. Available from: http://www.bsg.org.uk/clinical-guidance/endoscopy/colonoscopic-polypectomy-and-endoscopic-mucosal-resection-a-practical-guide.html. |
| 56. | Rabeneck L, Paszat LF, Hilsden RJ, Saskin R, Leddin D, Grunfeld E, Wai E, Goldwasser M, Sutradhar R, Stukel TA. Bleeding and perforation after outpatient colonoscopy and their risk factors in usual clinical practice. Gastroenterology. 2008;135:1899-1906, 1906.e1. [PubMed] |
| 57. | Gatto NM, Frucht H, Sundararajan V, Jacobson JS, Grann VR, Neugut AI. Risk of perforation after colonoscopy and sigmoidoscopy: a population-based study. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2003;95:230-236. [PubMed] |
| 58. | The Paris endoscopic classification of superficial neoplastic lesions: esophagus, stomach, and colon: November 30 to December 1, 2002. Gastrointest Endosc. 2003;58:S3-43. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1117] [Cited by in RCA: 1315] [Article Influence: 59.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (4)] |
| 59. | Millan MS, Gross P, Manilich E, Church JM. Adenoma detection rate: the real indicator of quality in colonoscopy. Dis Colon Rectum. 2008;51:1217-1220. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 68] [Cited by in RCA: 83] [Article Influence: 4.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 60. | Kaminski MF, Regula J, Kraszewska E, Polkowski M, Wojciechowska U, Didkowska J, Zwierko M, Rupinski M, Nowacki MP, Butruk E. Quality indicators for colonoscopy and the risk of interval cancer. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:1795-1803. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1287] [Cited by in RCA: 1462] [Article Influence: 97.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 61. | Diamond SJ, Enestvedt BK, Jiang Z, Holub JL, Gupta M, Lieberman DA, Eisen GM. Adenoma detection rate increases with each decade of life after 50 years of age. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011;74:135-140. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 59] [Cited by in RCA: 60] [Article Influence: 4.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 62. | Greene MA, Butterly LF, Goodrich M, Onega T, Baron JA, Lieberman DA, Dietrich AJ, Srivastava A. Matching colonoscopy and pathology data in population-based registries: development of a novel algorithm and the initial experience of the New Hampshire Colonoscopy Registry. Gastrointestinal endoscopy. 2011;74:334-340. [RCA] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 36] [Cited by in RCA: 38] [Article Influence: 2.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 63. | Williams JE, Le TD, Faigel DO. Polypectomy rate as a quality measure for colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011;73:498-506. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 49] [Cited by in RCA: 58] [Article Influence: 4.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 64. | Francis DL, Rodriguez-Correa DT, Buchner A, Harewood GC, Wallace M. Application of a conversion factor to estimate the adenoma detection rate from the polyp detection rate. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011;73:493-497. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 89] [Cited by in RCA: 102] [Article Influence: 7.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 65. | Patel NC, Islam RS, Wu Q, Gurudu SR, Ramirez FC, Crowell MD, Faigel DO. Measurement of polypectomy rate by using administrative claims data with validation against the adenoma detection rate. Gastrointest Endosc. 2013;77:390-394. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 32] [Cited by in RCA: 36] [Article Influence: 3.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 66. | Boroff ES, Gurudu SR, Hentz JG, Leighton JA, Ramirez FC. Polyp and adenoma detection rates in the proximal and distal colon. Am J Gastroenterol. 2013;108:993-999. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 69] [Cited by in RCA: 86] [Article Influence: 7.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 67. | Do A, Weinberg J, Kakkar A, Jacobson BC. Reliability of adenoma detection rate is based on procedural volume. Gastrointest Endosc. 2013;77:376-380. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 64] [Cited by in RCA: 78] [Article Influence: 6.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 68. | Greenspan M, Rajan KB, Baig A, Beck T, Mobarhan S, Melson J. Advanced adenoma detection rate is independent of nonadvanced adenoma detection rate. Am J Gastroenterol. 2013;108:1286-1292. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 48] [Cited by in RCA: 48] [Article Influence: 4.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 69. | Denis B, Sauleau EA, Gendre I, Piette C, Bretagne JF, Perrin P. Measurement of adenoma detection and discrimination during colonoscopy in routine practice: an exploratory study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011;74:1325-1336. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 31] [Cited by in RCA: 28] [Article Influence: 2.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 70. | Wang HS, Pisegna J, Modi R, Liang LJ, Atia M, Nguyen M, Cohen H, Ohning G, van Oijen M, Spiegel BM. Adenoma detection rate is necessary but insufficient for distinguishing high versus low endoscopist performance. Gastrointest Endosc. 2013;77:71-78. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 109] [Cited by in RCA: 111] [Article Influence: 9.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |