Published online Dec 16, 2021. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v13.i12.649
Peer-review started: May 26, 2021
First decision: June 17, 2021
Revised: June 22, 2021
Accepted: June 28, 2021
Article in press: June 28, 2021
Published online: December 16, 2021
Processing time: 201 Days and 17 Hours
Intra-abdominal lymphadenopathy due to tuberculosis (TB) poses a diagnostic challenge due to difficulty in tissue acquisition. Although endoscopic ultrasound guided fine needle aspiration/biopsy (EUS-FNA/B) has shown promise in the evaluation of mediastinal lymph nodes, its role in the evaluation of intra-abdomi
To assess the role of EUS-FNA/B in the evaluation of intra-abdominal lympha
This was a retrospective study where patients with intra-abdominal lymphadenopathy who underwent evaluation with EUS-FNA/B were included. TB was diagnosed if the patient had any one of the following: (1) Positive acid fast bacilli (AFB) stain/TB GeneXpert/TB-polymerase chain reaction/AFB culture of tissue sample; and (2) Positive Mantoux test and response to anti-tubercular therapy. EUS-FNA reports, clinical reports and imaging characteristics of patients were recorded for a detailed analysis of patients with TB.
A total of 149 patients underwent an EUS-FNA/B from lymph nodes (mean age 51 ± 17 years, M:F = 1.2). Benign inflammatory reactive changes were seen in 45 patients (30.2%), while 54 patients (36.2%) showed granulomatous inflammation with/without caseation. Among these, 51 patients (94.4%) were confirmed to have TB as per pre-defined criteria. Patients with TB were more likely to have hypoe
EUS-FNA/B has a high diagnostic yield with a good sensitivity and specificity in the evaluation of intra-abdominal lymphadenopathy due to TB. However, the validity of these findings in populations with low prevalence of TB needs further evaluation.
Core Tip: Intra-abdominal lymphadenopathy due to tuberculosis (TB) poses a significant diagnostic challenge primarily due to difficulty in tissue acquisition. Endoscopic ultrasound guided fine needle aspiration/biopsy (EUS-FNA/B) has shown promise in the evaluation of TB presenting with mediastinal lymph nodes; however, its role in intra-abdominal lymphadenopathy due to TB remains unclear. In this study, a large cohort of patients who underwent EUS-FNA/B were studied. EUS-FNA/B was found to have a sensitivity and specificity of 86% and 93%, respectively, with a high diagnostic accuracy of 88% in the evaluation of intra-abdominal lymphadenitis due to TB. This study provides valuable data on the pivotal role of EUS-FNA/B in the evaluation of this difficult sub-group of patients. However, the validity of these findings in populations with low prevalence of TB needs further evaluation.
- Citation: Rao B H, Nair P, Priya SK, Vallonthaiel AG, Sathyapalan DT, Koshy AK, Venu RP. Role of endoscopic ultrasound guided fine needle aspiration/biopsy in the evaluation of intra-abdominal lymphadenopathy due to tuberculosis. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2021; 13(12): 649-658
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v13/i12/649.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v13.i12.649
Intra-abdominal lymphadenopathy due to tuberculosis (TB) is a common clinical entity in regions endemic for the disease. The presence of concomitant lung paren
Tissue acquisition is usually essential for establishing the diagnosis in patients with intra-abdominal lymphadenopathy. Earlier, tissue acquisition was accomplished by computed tomography guided/laparoscopy assisted biopsy. Currently, these modali
EUS-FNA/B has been shown to be invaluable in the diagnosis of malignancy (primary/metastatic) during evaluation of intra-abdominal lymphadenopathy. There is also a growing body of evidence that highlights the role of EUS-FNA/B in the manage
This was a single center retrospective study conducted in a large tertiary care hospital where patients with intra-abdominal lymphadenopathy referred for EUS-FNA/B between January 1, 2015 and December 31, 2019 were included. Institutional ethics committee clearance for data acquisition and analysis were obtained. All relevant data such as patient demographics (age, gender, comorbidities), procedure details (type of needle, number of passes, size of nodes, echogenicity) and post-procedure complications were noted. On retrospective analysis, TB was diagnosed if the patient had any one of the following: (1) Positive acid fast bacilli (AFB) staining of the tissue sample/ positive TB GeneXpert of the tissue sample/positive TB-polymerase chain reaction (PCR) of the tissue sample; (2) Granulomas with caseation; (3) Positive AFB culture; and (4) Positive Mantoux test and an adequate response to anti-tubercular therapy (ATT). EUS-FNA reports, demographics and imaging characteristics of patients with TB were studied in detail to determine the diagnostic yield of the procedure.
All EUS-FNA procedures were performed by an experienced endosonographer. Institutional protocol was followed wherein procedures were performed under moderate or deep sedation which was provided by a dedicated anaesthetist. All patients received prophylactic antibiotics prior to the procedure as per protocol. Initial diagnostic endosonographic evaluation was carried out using a linear array echoendoscope (Olympus GFUCT180, Tokyo, Japan) and upon identification of the lymph nodes, relevant imaging characteristics were noted. Only EUS-FNA/B results of abdominal lymph nodes were analyzed in the study. All procedures were performed with Rapid On-Site Evaluation (ROSE) by a dedicated cytopathologist. Depending upon the site of the nodes, gastric or duodenal approaches were considered. A 22 gauge needle was used for all procedures. A FNA needle (22G Cook EchoTip®, 22G Olympus EZ-shot 3) was used in most cases; while a fine needle biopsy needle (22G Boston Scientific Acquire™) was used in only 10 patients. The needle was passed via the instrument channel and the node was targeted under sonographic guidance. The sharp tip of the needle punctured the node after unlocking the needle apparatus and multiple passes were made into the target node. Suctioning was reserved for cases where the initial few passes were inadequate as assessed by the on-site cytopathologist. The needle was passed multiple times into the node typically for 20-30 s each pass while continuously adjusting the position of the needle in a “fanning” pattern to maximize tissue volume. The needle was then removed from the endoscope, and the tissue was prepared for pathological examination.
All the FNA material was placed onto glass slides and smears were made. Smears for ROSE were fixed in 80% isopropyl alcohol which was then rapidly stained with 1% Toluidine blue. The on-site cytopathologist evaluated the adequacy of tissue in each pass and also gave a preliminary opinion on pathological changes on the slide. The number of passes were determined on the basis of this information until a maximum of 5 passes were made. When staining was complete, all EUS-FNA specimens were evaluated for cytological diagnosis and cellular preservation by a pathologist. These slides were subsequently stained with Papanicolaou stain in the cytology laboratory for further evaluation. Visible core tissue was placed in formalin-alcohol mixture (formalin and 80% isopropyl alcohol in 1:1 ratio) and subsequently paraffin embedded to produce cell blocks. Sections from the cell blocks were stained with hematoxylin and eosin. The slides were meticulously observed to arrive at a final diagnosis.
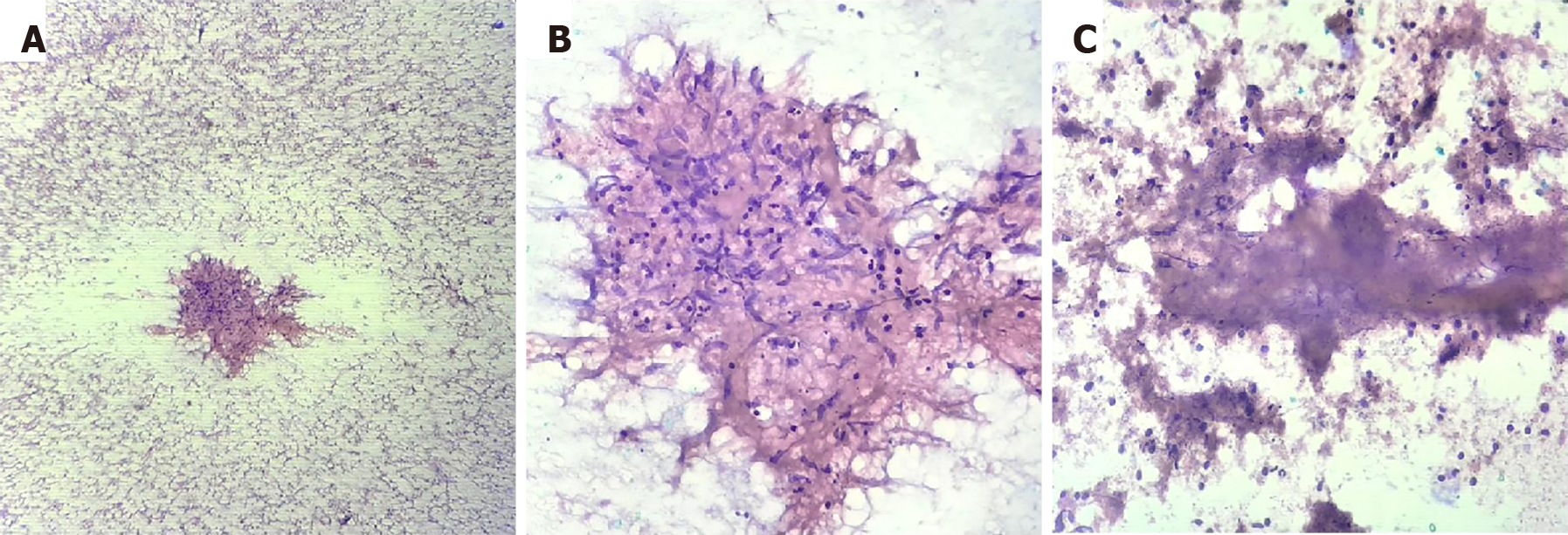
On pathological examination, reactive nodes will exhibit a polymorphous lymphoid population including mature lymphocytes, germinal center cells and tingible body macrophages. Granulomatous inflammation was diagnosed when there were collections of epithelioid histiocytes forming an epithelioid cell granuloma with or without necrosis(Figure 1). In such cases, further sampling was performed with microbiological tests such as AFB staining, GeneXpert and TB culture. Diagnosis of lymphoma was applicable when the lymphoid cells were monomorphic populations of atypical lymphoid cells. Secondary malignant deposits in the node were identified when tumor cells were admixed with a reactive lymphoid population.
Patients with features of lymphoma or metastatic malignancy were treated with an appropriate chemotherapy regimen as per hospital protocol by the oncologist. Patients with TB as defined above, received ATT for 6 mo. Patients with sarcoidosis were treated with steroids. All patients were followed up 15 d after the procedure to discuss biopsy findings and treatment plan. All patients were followed up clinically every month for symptomatic improvement or drug side effects.
Statistical analysis was carried out using IBM SPSS software version 20.0. The pathology reports were correlated with clinical diagnosis in order to determine the diagnostic validity of EUS-FNA in the evaluation of intra-abdominal lymph nodes resulting from TB. A descriptive analysis of all patients with TB was carried out. Comparisons of means for continuous variables were carried out using the indepen
A total of 149 patients underwent EUS-FNA/B of lymph nodes. The mean age of these patients was 51 ± 17 years with a male to female ratio of 1.2. The most common clinical presentation was fever of unknown origin [78 patients (52.3%)], whereas, 48 patients (32.2%) underwent EUS-FNA of lymph nodes for staging of malignancy and the remaining 23 patients (15.5%) were incidentally detected to have abdominal lymphadenopathy. A total of 91 patients (61.1%) had only abdominal lymphadenopathy and the remaining 58 patients (38.9%) had both mediastinal as well as abdominal lymphadenopathy. Most of the patients (n = 139) underwent EUS-FNA using a 22G aspiration needle (22G Cook EchoTip®, 22G Olympus EZ-shot 3), while only 10 patients (6.7%) underwent the procedure using a 22G biopsy needle (22G Boston Scientific Acquire™). No differences in patient characteristics and procedures results were observed between the two needle types. All patients had adequate cellularity to make a diagnosis, from the samples taken from abdominal lymph nodes, as assessed by the on-site cytopathologist, in this study. The cytology results showed only reactive changes in 45 patients (30.2%), while 54 patients (36.2%) showed granulomatous inflammation with or without caseation. Malignant cells were seen in a total of 50 patients (33.6%), of which, features suggestive of lymphoma were seen in 11 patients (22%) and metastatic deposits were seen in 39 patients (78%) (Table 1). Among the 54 patients with granulomatous inflammation on EUS-FNA cytology, 51 patients (94.4%) were confirmed to have TB on the basis of confirmatory tests or response to ATT on follow-up; and 3 patients (5.55%) had elevated angiotensin I-converting enzyme levels along with systemic symptoms of sarcoidosis which was managed accordingly. On follow-up of patients with reactive changes on EUS-FNA cytology (n = 45), 30 patients (66.67%) showed non-specific inflammation which was managed conservatively, 8 patients (17.78%) had TB and were treated accordingly, 1 patient (2.22%) was diagnosed with sarcoidosis, while 3 patients (6.66%) showed malignant cells as per the surgical histopathology report; 3 patients (6.66%) were lost to follow-up.
| Baseline characteristics | Overall (n = 149) |
| Age (mean ± SD) in yr | 51 ± 17 |
| Gender, n (%) | |
| Male | 84 (56.38) |
| Female | 65 (43.62) |
| Clinical presentation, n (%) | |
| Fever of unknown origin | 78 (52.3) |
| Staging of malignancy | 48 (32.2) |
| Incidental | 23 (15.5) |
| Cytology, n (%) | |
| Granulomatous inflammation | 54 (36.2) |
| Reactive changes | 45 (30.2) |
| Malignant cells | 50 (33.6) |
| Final clinical diagnosis, n (%) | |
| Tuberculosis | 59 (39.59) |
| Primary lymphoid malignancy (lymphoma) | 11 (7.38) |
| Secondary malignant deposits | 39 (26.17) |
| Sarcoidosis | 3 (2.01) |
| Benign inflammatory lymphadenopathy | 37 (24.8) |
A total of 59 patients were diagnosed with TB during follow-up and were treated with standard anti-tubercular drugs. The baseline characteristics of these patients are shown in Table 2. Isolated abdominal lymphadenopathy was seen in 31 patients (52.5%), while 28 patients (47.4%) had both mediastinal and abdominal lymphadenopathy. All the patients presented with fever of unknown origin and a majority of them also had systemic symptoms such as weight loss and night sweats [40 patients (67.7%)].
| Baseline characteristics | Overall (n = 59) |
| Age (mean ± SD) in yr | 45 ± 18 |
| Gender, n (%) | |
| Male | 31 (52.5) |
| Female | 28 (47.4) |
| Echogenicity, n (%) | |
| Hypoechoic node | 37 (62.7) |
| Heteroechoic node | 22 (37.3) |
| Matting of lymph nodes, n (%) | |
| Yes | 40 (67.7) |
| No | 19 (32.2) |
| Cytology, n (%) | |
| Granulomatous inflammation with or without caseation | 51 (86.4) |
| Reactive changes only | 8 (13.5) |
| TB GeneXpert, n (%), n = 34 | |
| Positive | 14 (41.1) |
| Negative | 20 (58.9) |
| TB culture, n (%), n = 38 | |
| Growth | 12 (31.6) |
| No growth | 26 (68.4) |
| Fine needle aspiration (22 Gauge needle) (%) | |
| Sensitivity | 86 |
| Specificity | 93 |
| Accuracy | 88 |
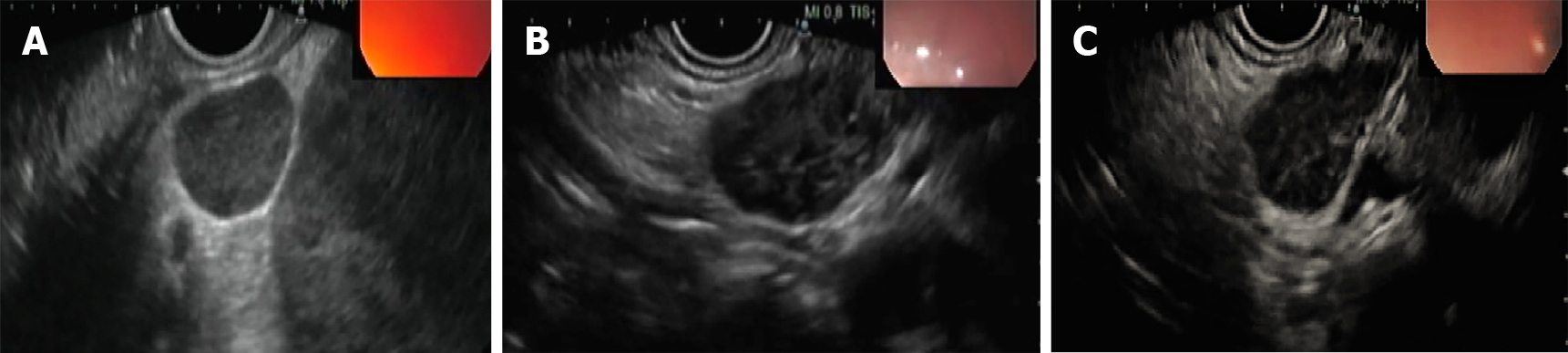
Patients with TB were more likely to have hypoechoic nodes [37 patients (62.7%)], while 22 patients (37.3%) had heteroechoic nodes on endosonographic examination (Figure 2). A majority of these patients also had matted nodes forming a conglomerate lymphnodal mass [40 patients (67.7%)]. All patients underwent EUS-FNA using an aspiration needle except for 2 patients (3.4%) in whom a biopsy needle was used. TB GeneXpert of the biopsy sample was performed in a total of 34 patients (57.6%), of which only 14 patients (41.1%) had a positive result and the remaining 20 patients (58.9%) had a false negative result. Samples from a total of 38 patients were sent for TB culture. Of these, only 12 samples (31.6%) grew Mycobacterium tuberculosis, while the remaining 26 samples (68.4%) did not show any growth of organisms.
Among the patients with confirmed TB, EUS-FNA/B showed granulomatous inflammation with or without caseation in 51 patients (86.4%), while the remaining patients showed non-specific reactive changes [8 patients (13.5%)]. EUS-FNA/B was found to have a sensitivity and specificity of 86% and 93%, respectively, with a diagnostic accuracy of 88% in the evaluation of mesenteric lymphadenitis due to TB.
Extrapulmonary TB accounts for 15%-20% of all cases of TB[11,12]. TB presenting with isolated lymphadenopathy is common in endemic areas and poses a significant diagnostic challenge[13]. In the absence of characteristic symptoms or pathognomic radiographic features, isolation of the bacilli and/or identification of caseous granu
EUS-FNA/B has seen tremendous progress in the last decade with improved image resolution, increased experience with therapeutic interventions and unique biopsy needles that can increase the quantum of tissue obtained and thereby potentially address existing pitfalls of FNA cytology in establishing a diagnosis of TB. EUS-FNA has also already been evaluated for mediastinal lymphadenopathy with an overall accuracy of 93%, sensitivity of 71% and specificity of 100% for the diagnosis of TB in the Indian population[7]. However, the role of EUS-FNA/B in the evaluation of intra-abdominal lymphadenopathy due to TB remains an area that merits further evalua
In general, the quantum of tissue samples obtained from lymph nodes after EUS-FNA have been found to be sufficient in most indications[4]. Ancillary techniques such as applying suction and slow withdrawal have been evaluated in the setting of pancreatic lesions. However, the utility of these techniques in the setting of lymph nodes needs further clarity. In our experience, we have found no added benefit with these ancillary techniques. A thorough endosonographic evaluation prior to FNA with emphasis on choosing an ideal node that is adequately enlarged and with sharp borders, with/without matting is essential to ensure a high yield. Particular attention should be paid to the morphology of the lymph node wherein hypoechoic areas which might indicate necrosis should be avoided. Sampling of peripheral tissue within the node has yielded better tissue samples in our experience. However, this requires further validation in larger studies.
There are a few limitations in the present study. This study was performed in an area endemic for TB. Therefore, the pre-test probability of TB would be high and as such, the findings of this study would be applicable only in similar demographic groups. In addition, a definitive diagnosis of TB requires a positive culture/GeneXpert and/or PCR for tubercular bacilli. A proportion of our study population could not undergo these tests due to financial considerations and poor patient compliance. Empirical ATT is a practice followed in most regions endemic for TB, but carries with it a high risk of treatment failure and can even pose a risk for the emergence of resistant organisms. Tissue acquisition in these cases can provide valuable information and dictate therapy. Moreover, a high pre-test probability of TB, a positive Mantoux test and granulomas on the FNA sample has been shown to be a reasonable approach to start a patient on ATT[18]. Moreover, all the patients who were treated with ATT using this approach showed good response to treatment on follow-up.
In conclusion, EUS-FNA/B has a high diagnostic yield with a good sensitivity and specificity in the evaluation of intra-abdominal lymphadenopathy in patients with a clinical suspicion of TB. The procedure is safe, performed with moderate sedation and can potentially prevent further invasive testing in this subgroup of patients. However, the utility of this procedure in populations with a low prevalence of TB needs more clarity. In addition, a protocol-based approach with additional tests such as TB culture, AFB stain, TB-PCR or GeneXpert in specific subgroups of patients at risk for TB needs to be developed and evaluated in future studies.
Intra-abdominal lymphadenopathy due to tuberculosis (TB) poses a diagnostic challenge due to difficulty in tissue acquisition.
Endoscopic ultrasound guided fine needle aspiration/biopsy (EUS-FNA/B) has shown excellent results in patients with mediastinal lymphadenopathy. However, its role in the evaluation of abdominal lymphadenopathy due to TB needs further clarity.
The utility of EUS-FNA/B in the evaluation of intra-abdominal lymphadenopathy was assessed by evaluating the diagnostic yield in patients with confirmed TB.
This was a single center retrospective study conducted in a large tertiary care hospital where patients with intra-abdominal lymphadenopathy referred for EUS-FNA/B were studied. The diagnosis of TB was confirmed and EUS-FNA/B results including cytology, pathological diagnosis, ancillary test findings (TB culture, GeneXpert) and demographics in these patients were carefully analyzed.
This study showed that EUS-FNA/B has a high diagnostic yield with good sensitivity (86%), specificity (93%) and diagnostic accuracy (88%) in the evaluation of intra-abdominal lymphadenopathy in patients with a clinical suspicion of TB. Morphological findings on EUS evaluation of intra-abdominal lymphadenopathy include hypoechoic/heteroechoic nodes, with sharp borders, with/without matting.
EUS-FNA/B is a viable, reliable and safe procedure, which can be performed with moderate sedation and can potentially prevent further invasive testing in this subgroup of patients.
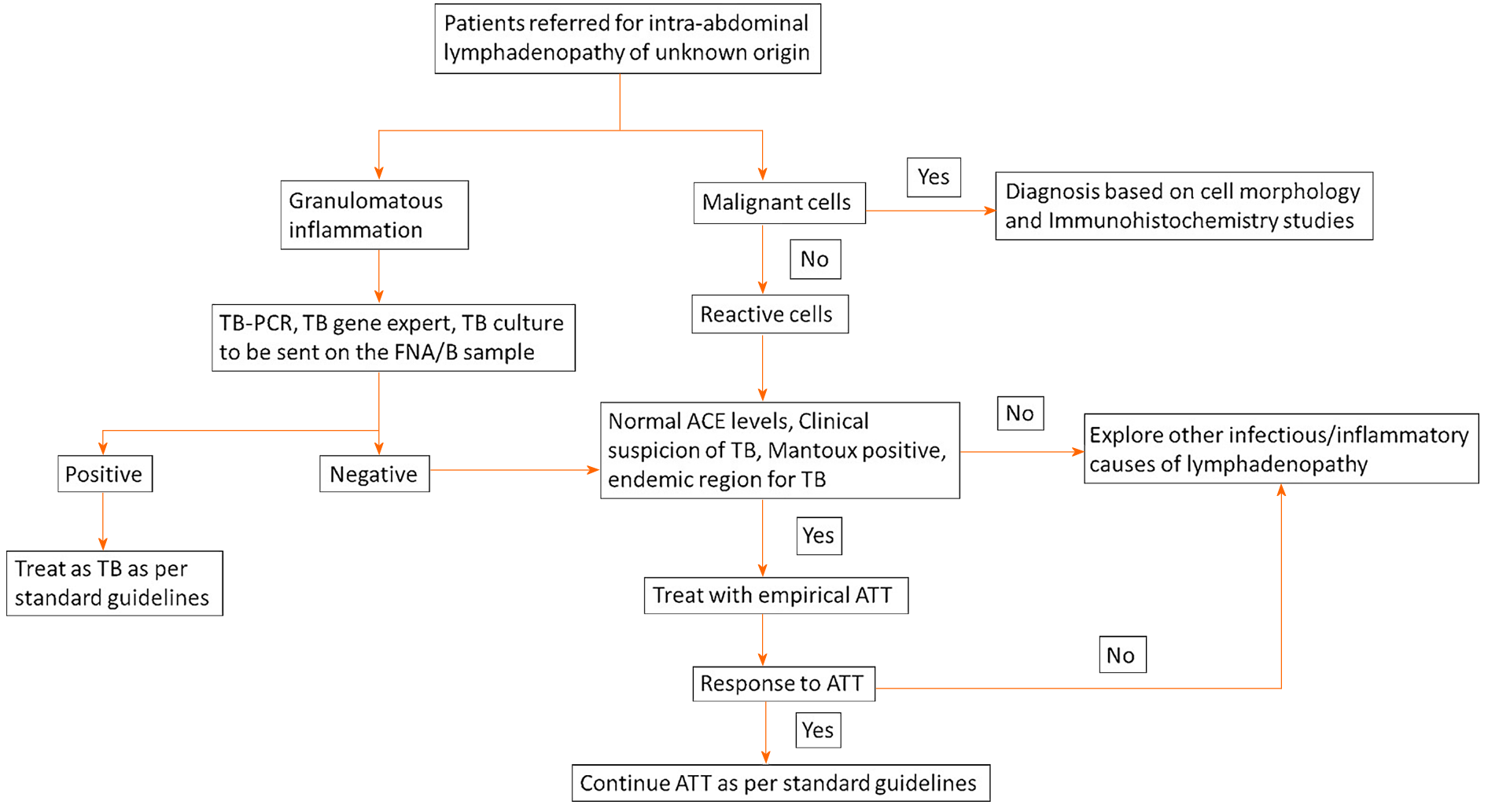
This study provides vital information that can guide the approach and management of patients with intra-abdominal lymphadenopathy. A management algorithm that highlights key points during the management of these patients is provided. However, the utility of this procedure in populations with a low prevalence of TB needs more clarity. In addition, a protocol-based approach with additional tests such as TB culture, acid fast bacilli stain, TB-polymerase chain reaction or GeneXpert in specific subgroups of patients at risk for TB needs to be developed and evaluated in future studies.
Provenance and peer review: Unsolicited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Specialty type: Gastroenterology and hepatology
Country/Territory of origin: India
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): B
Grade C (Good): 0
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Sugimoto M S-Editor: Fan JR L-Editor: Webster JR P-Editor: Guo X
| 1. | Sharma SK, Mohan A. Extrapulmonary tuberculosis. Indian J Med Res. 2004;120:316-353. [PubMed] |
| 2. | Tanisaka Y, Ryozawa S, Kobayashi M, Harada M, Kobatake T, Omiya K, Iwano H, Arai S, Nonaka K, Mashimo Y. Usefulness of endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration for lymphadenopathy. Oncol Lett. 2018;15:4759-4766. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Yasuda I, Tsurumi H, Omar S, Iwashita T, Kojima Y, Yamada T, Sawada M, Takami T, Moriwaki H, Soehendra N. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy for lymphadenopathy of unknown origin. Endoscopy. 2006;38:919-924. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 107] [Cited by in RCA: 116] [Article Influence: 6.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Li C, Shuai Y, Zhou X. Endoscopic ultrasound guided fine needle aspiration for the diagnosis of intra-abdominal lymphadenopathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2020;55:114-122. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 10] [Article Influence: 2.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Gaddey HL, Riegel AM. Unexplained Lymphadenopathy: Evaluation and Differential Diagnosis. Am Fam Physician. 2016;94:896-903. [PubMed] |
| 6. | Sharma M, Ecka RS, Somasundaram A, Shoukat A, Kirnake V. Endoscopic ultrasound in mediastinal tuberculosis. Lung India. 2016;33:129-134. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Puri R, Vilmann P, Sud R, Kumar M, Taneja S, Verma K, Kaushik N. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration cytology in the evaluation of suspected tuberculosis in patients with isolated mediastinal lymphadenopathy. Endoscopy. 2010;42:462-467. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 42] [Cited by in RCA: 51] [Article Influence: 3.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Vilmann P. Endoscopic ultrasonography-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy of lymph nodes. Gastrointest Endosc. 1996;43:S24-S29. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 43] [Cited by in RCA: 45] [Article Influence: 1.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Detterbeck FC, Jantz MA, Wallace M, Vansteenkiste J, Silvestri GA; American College of Chest Physicians. Invasive mediastinal staging of lung cancer: ACCP evidence-based clinical practice guidelines (2nd edition). Chest. 2007;132:202S-220S. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 477] [Cited by in RCA: 457] [Article Influence: 25.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Chin YK, Iglesias-Garcia J, de la Iglesia D, Lariño-Noia J, Abdulkader-Nallib I, Lázare H, Rebolledo Olmedo S, Dominguez-Muñoz JE. Accuracy of endoscopic ultrasound-guided tissue acquisition in the evaluation of lymph nodes enlargement in the absence of on-site pathologist. World J Gastroenterol. 2017;23:5755-5763. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 15] [Cited by in RCA: 12] [Article Influence: 1.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | National survey of tuberculosis notifications in England and Wales in 1983: characteristics of disease. Report from the Medical Research Council Tuberculosis and Chest Diseases Unit. Tubercle. 1987;68:19-32. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 38] [Cited by in RCA: 40] [Article Influence: 1.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Pitchenik AE, Fertel D, Bloch AB. Mycobacterial disease: epidemiology, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. Clin Chest Med. 1988;9:425-441. [PubMed] |
| 13. | Codecasa LR, Besozzi G, De Cristofaro L, Miradoli A, Sabolla L, Tagliaferri B. Epidemiological and clinical patterns of intrathoracic lymph node tuberculosis in 60 human immunodeficiency virus-negative adult patients. Monaldi Arch Chest Dis. 1998;53:277-280. [PubMed] |
| 14. | Gupta SK, Chugh TD, Sheikh ZA, al-Rubah NA. Cytodiagnosis of tuberculous lymphadenitis. A correlative study with microbiologic examination. Acta Cytol. 1993;37:329-332. [PubMed] |
| 15. | Fanny ML, Beyam N, Gody JC, Zandanga G, Yango F, Manirakiza A, Rigouts L, Pierre-Audigier C, Gicquel B, Bobossi G. Fine-needle aspiration for diagnosis of tuberculous lymphadenitis in children in Bangui, Central African Republic. BMC Pediatr. 2012;12:191. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 17] [Cited by in RCA: 16] [Article Influence: 1.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Derese Y, Hailu E, Assefa T, Bekele Y, Mihret A, Aseffa A, Hussien J, Ali I, Abebe M. Comparison of PCR with standard culture of fine needle aspiration samples in the diagnosis of tuberculosis lymphadenitis. J Infect Dev Ctries. 2012;6:53-57. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 34] [Cited by in RCA: 36] [Article Influence: 2.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Radhika S, Gupta SK, Chakrabarti A, Rajwanshi A, Joshi K. Role of culture for mycobacteria in fine-needle aspiration diagnosis of tuberculous lymphadenitis. Diagn Cytopathol. 1989;5:260-262. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 29] [Cited by in RCA: 31] [Article Influence: 0.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Verma K, Kapila K. Aspiration cytology for diagnosis of tuberculosis--perspectives in India. Indian J Pediatr. 2002;69 Suppl 1:S39-S43. [PubMed] |