Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Nov 16, 2016; 8(19): 716-722
Published online Nov 16, 2016. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v8.i19.716
Published online Nov 16, 2016. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v8.i19.716
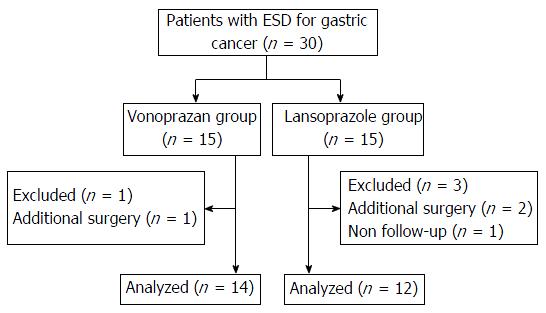
Figure 1 Flow chart of the participants in the study.
Thirty patients were enrolled and four of them were excluded because they needed additional surgery or violated the protocol. Finally, 14 patients in the vonoprazan group and 12 patients in the lansoprazole group were included in the analysis. ESD: Endoscopic submucosal dissection.
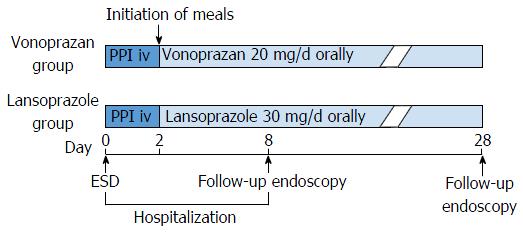
Figure 2 From the day of endoscopic submucosal dissection, intravenous infusion of proton pump inhibitor (lansoprazole 30 mg) was administered to all patients for 2 d.
Then, oral intake was initiated and patients in the vonoprazan group were administered vonoprazan (20 mg daily) and patients in the lansoprazole group were administered lansoprazole (30 mg daily) until 28 d after ESD. Patients underwent follow-up EGD on day 8 and day 28. ESD: Endoscopic submucosal dissection; PPI: Proton pump inhibitor; iv: Intravenous injection.
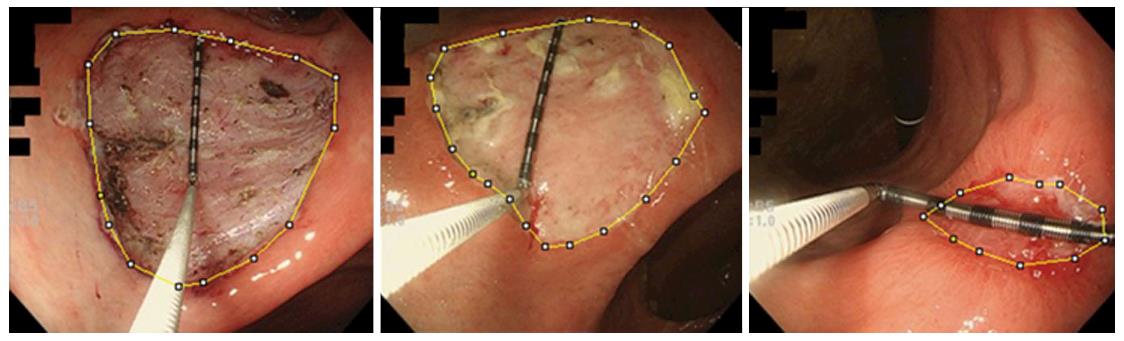
Figure 3 A representative case in the lansoprazole group.
The area inside the yellow line was calculated using ImageJ. We placed measuring forceps on the ulcer base to use as a scale. The ulcer base gradually shrank and there were no adverse events. The shrinking rates on days 8 and 28 were 27.1% and 96.3%, respectively.
- Citation: Takahashi K, Sato Y, Kohisa J, Watanabe J, Sato H, Mizuno K, Hashimoto S, Terai S. Vonoprazan 20 mg vs lansoprazole 30 mg for endoscopic submucosal dissection-induced gastric ulcers. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2016; 8(19): 716-722
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v8/i19/716.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v8.i19.716