Copyright
©2010 Baishideng.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Feb 16, 2010; 2(2): 50-53
Published online Feb 16, 2010. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v2.i2.50
Published online Feb 16, 2010. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v2.i2.50
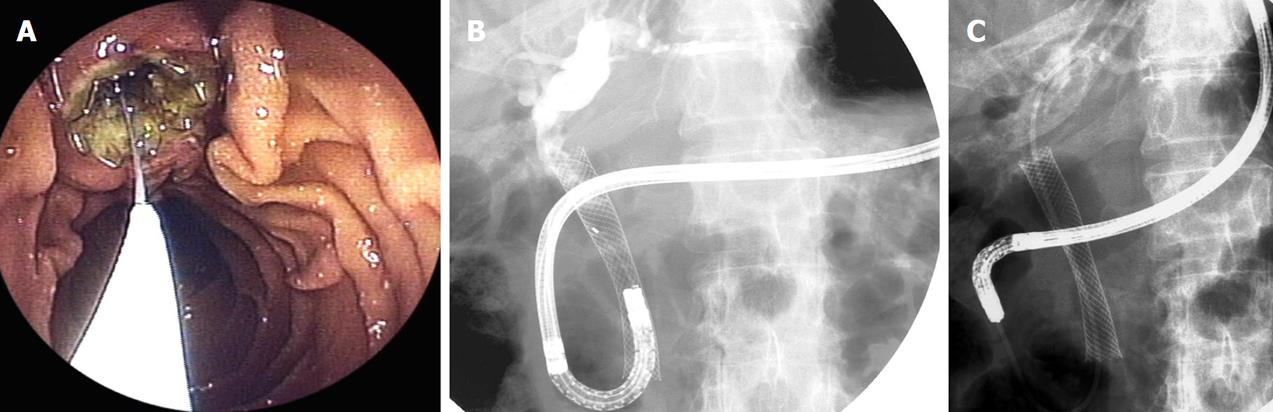
Figure 1 Transnasal endoscopic biliary drainage.
A: Endoscopic image shows biliary cannulation by transnasal endoscopy in patients with placement of self-expandable metallic stent; B: Endoscopic cholangiography showed obstruction of stent; C: Transnasal endoscopic naso-biliary drainage could be performed.
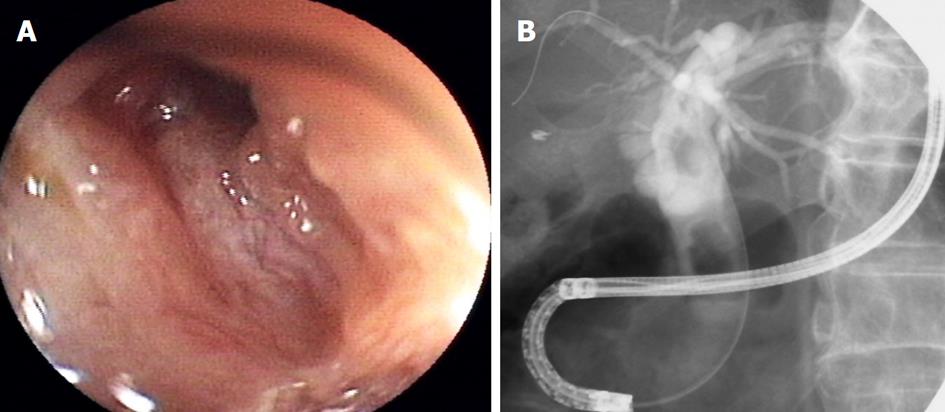
Figure 2 Transnasal endoscopic cholangiography (long scope position).
A: Endoscopic image shows orifice of bile duct in patients with post-sphincterotomy; B: Cholangiography showed bile duct stones.
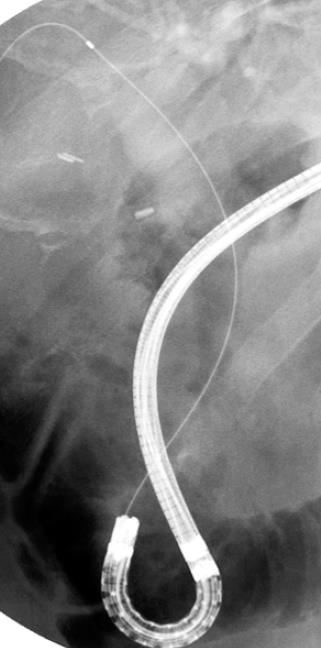
Figure 3 Transnasal endoscopic cholangiography (short scope position).
Bile duct cannulation by transnasal endoscopy at the short scope position.
- Citation: Itoi T, Sofuni A, Itokawa F, Tsuchiya T, Kurihara T, Ishii K, Tsuji S, Ikeuchi N, Moriyasu F. Transnasal endoscopic biliary drainage as a rescue management for the treatment of acute cholangitis. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2010; 2(2): 50-53
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v2/i2/50.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v2.i2.50