Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Oct 16, 2021; 13(10): 460-472
Published online Oct 16, 2021. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v13.i10.460
Published online Oct 16, 2021. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v13.i10.460
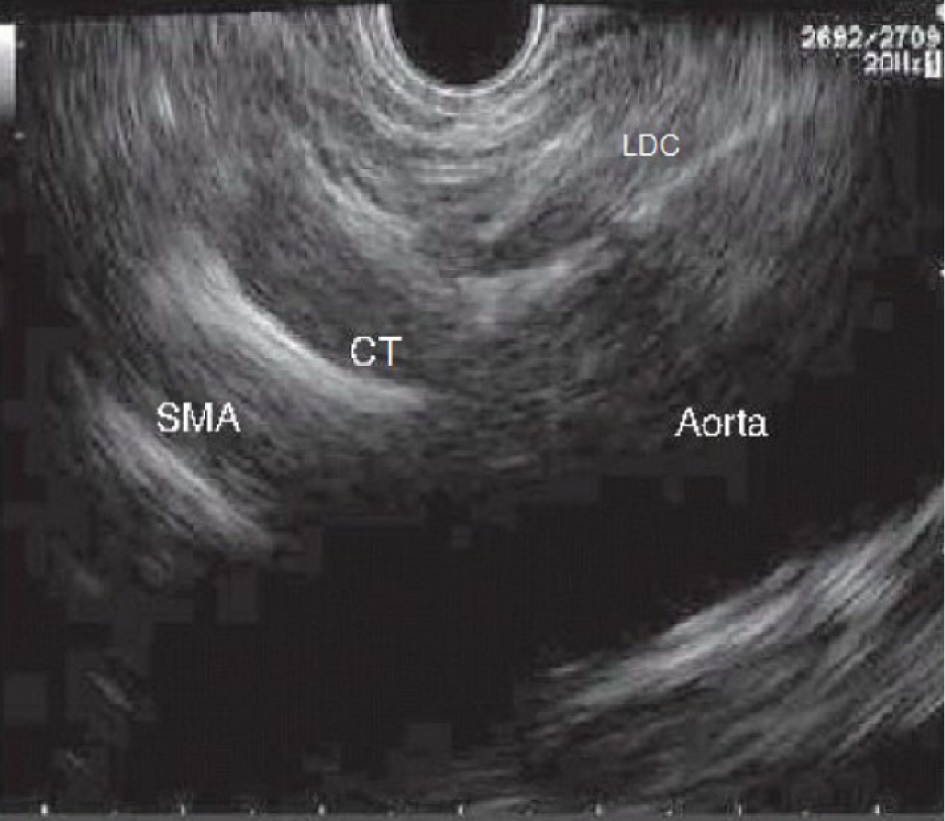
Figure 1 Sagittal plane of the aorta where we can see left diaphragmatic crus, celiac trunk and superior mesenteric artery emerging from Aorta.
SMA: Superior mesenteric artery; LDC: Left diaphragmatic crus; CT: Celiac trunk.
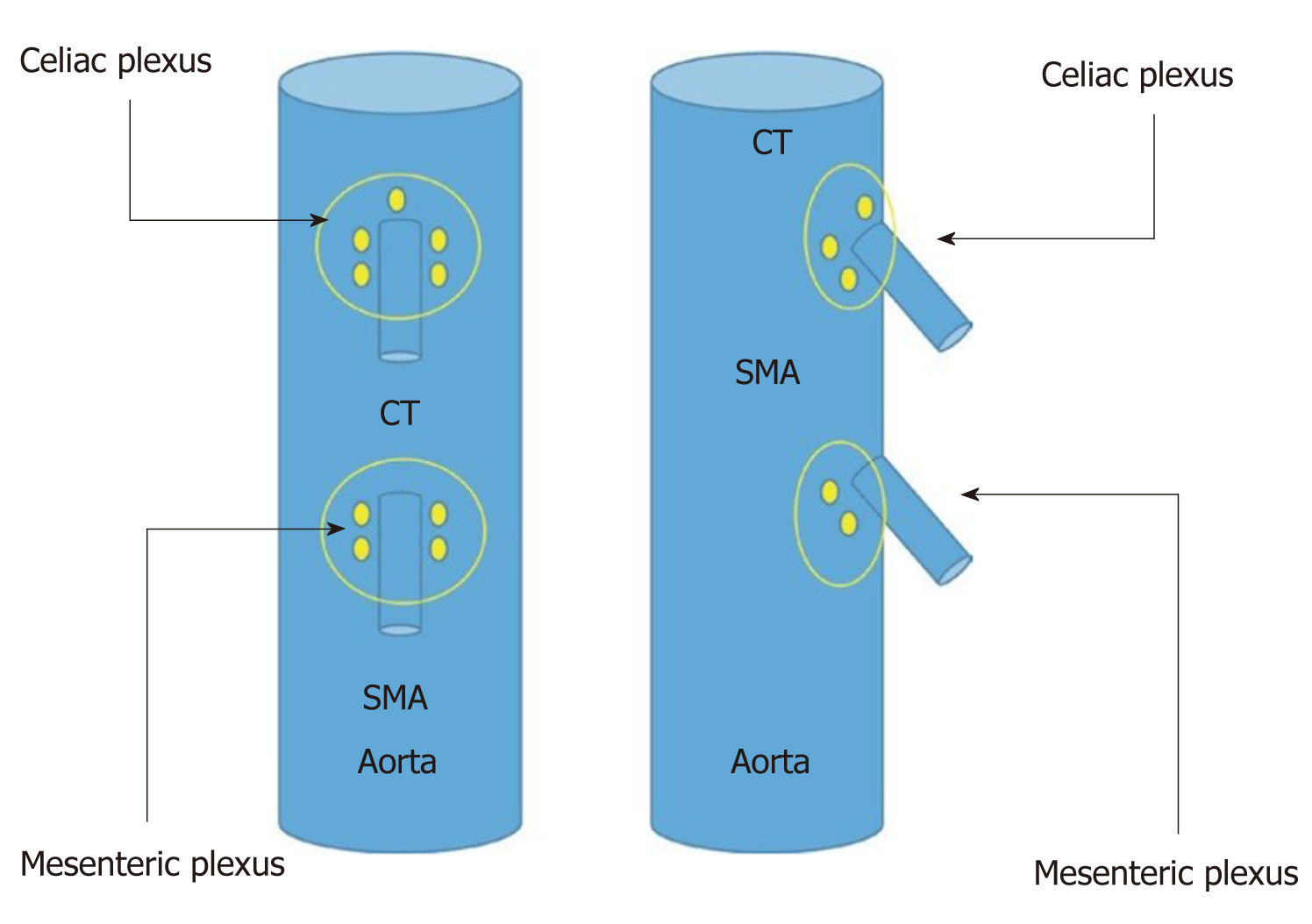
Figure 2 Schematic vision (frontal and lateral) of the situation of celiac and mesenteric plexus.
SMA: Superior mesenteric artery; CT: Celiac trunk.
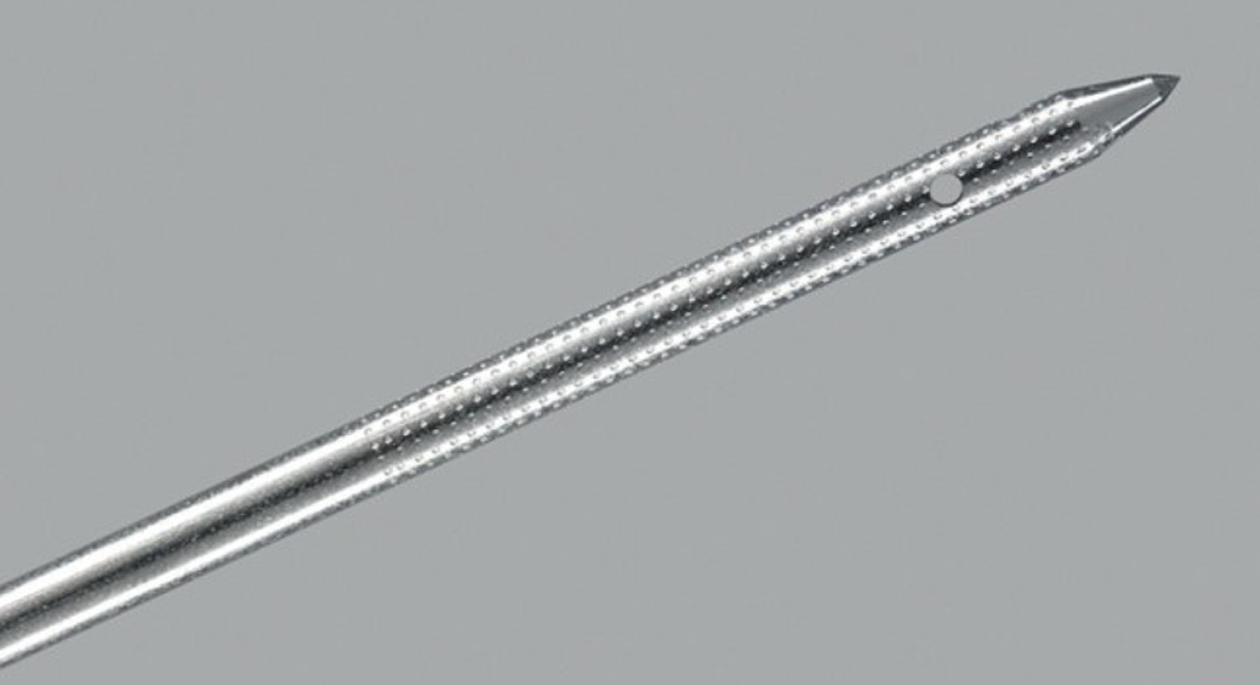
Figure 3 Specific needle designed for endosonography-guided celiac plexus neurolysis (Cook Medical, Limerick, Ireland).
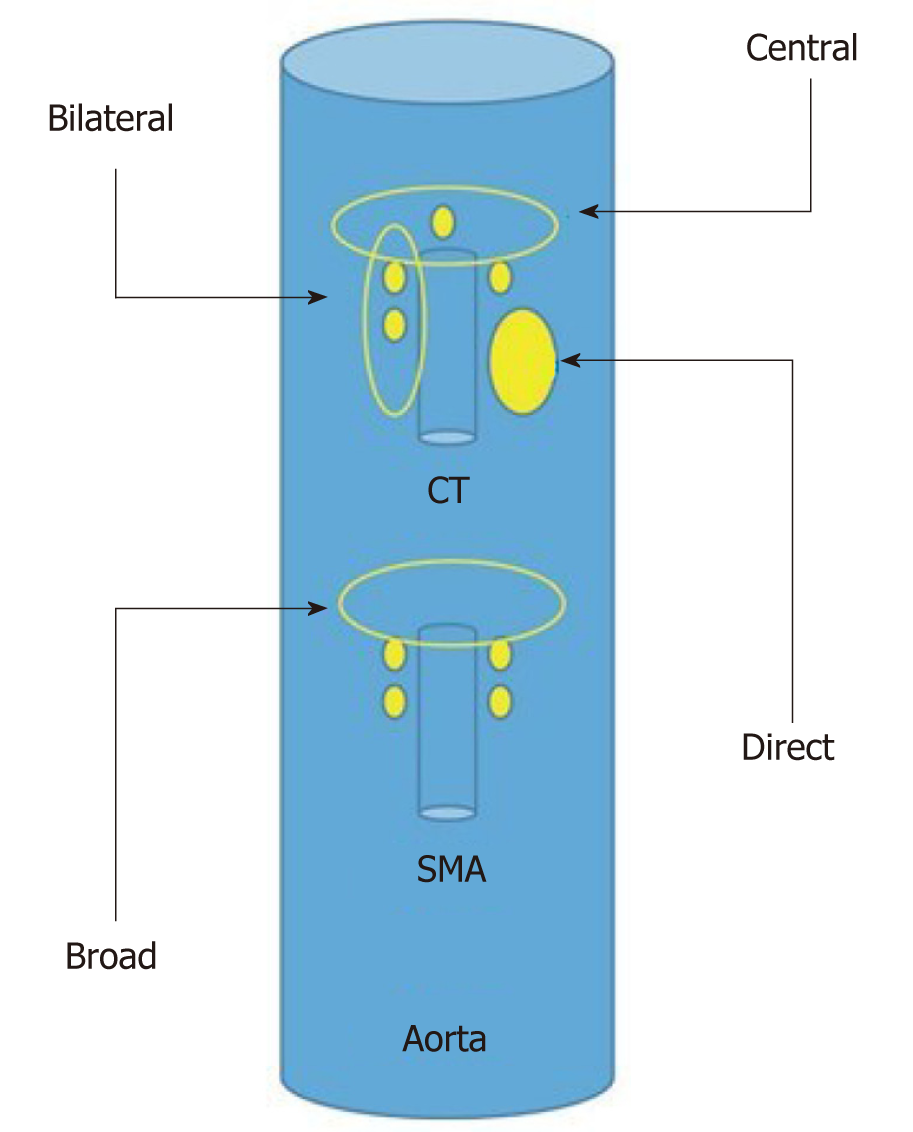
Figure 4 Schematic representation of the different endosonography-guided celiac plexus neurolysis approaches.
SMA: Superior mesenteric artery; CT: Celiac trunk.
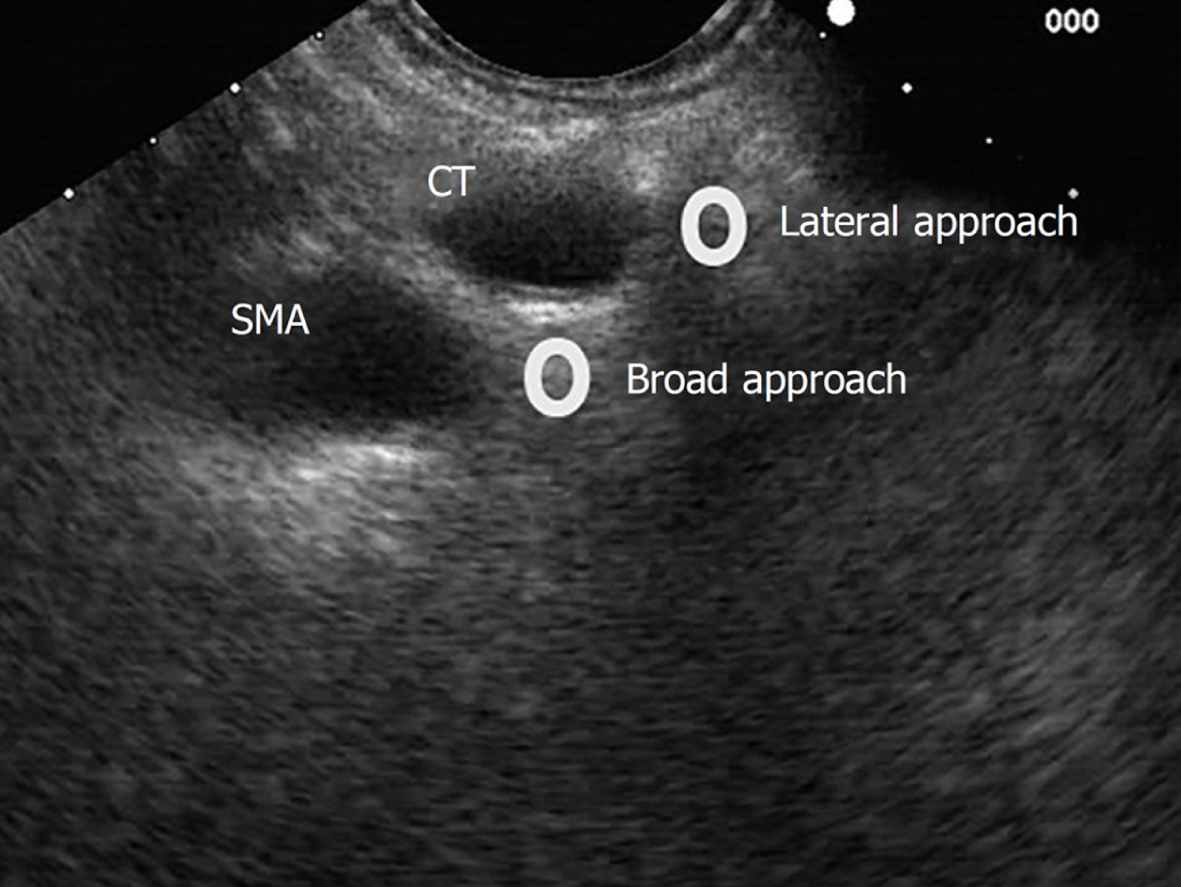
Figure 5 Lateral and broad approaches for endosonography-guided celiac plexus neurolysis.
SMA: Superior mesenteric artery; CT: Celiac trunk.
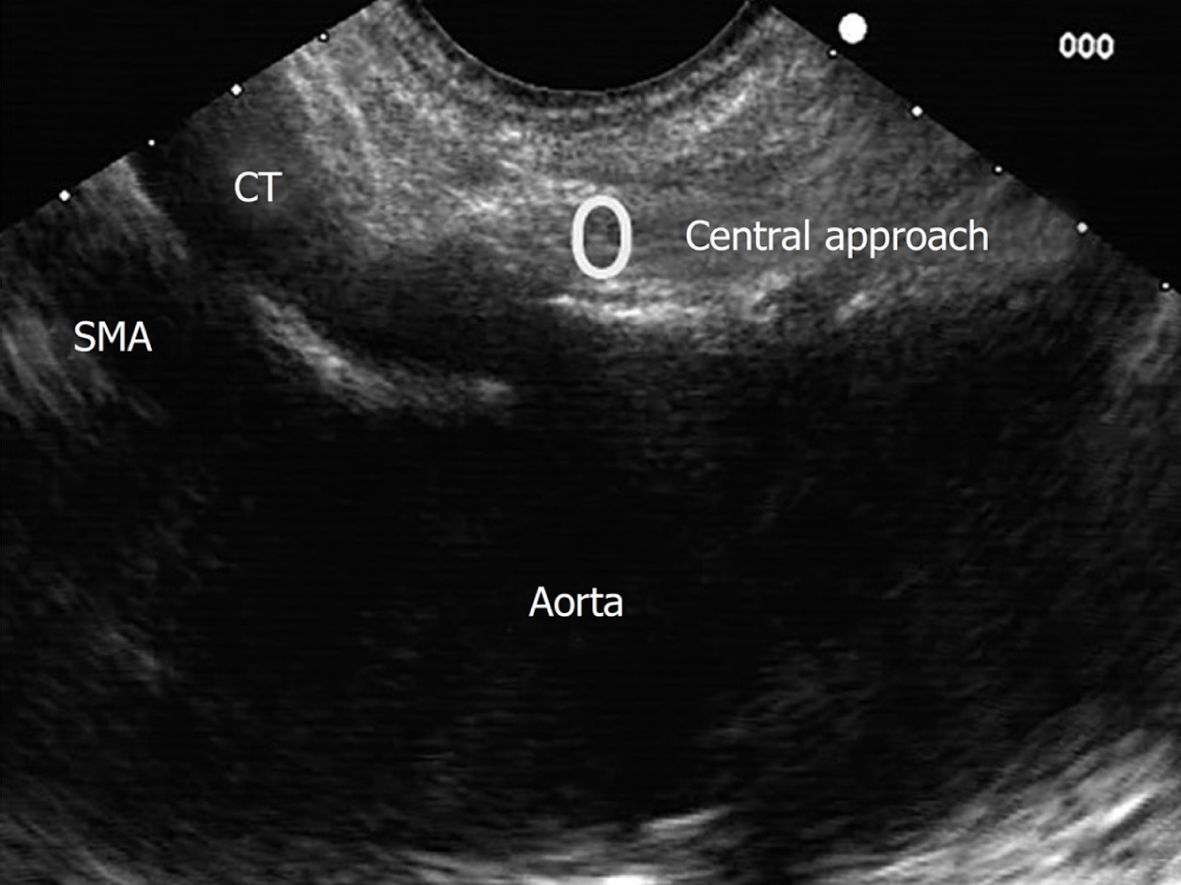
Figure 6 Central approach for endosonography-guided celiac plexus neurolysis.
SMA: Superior mesenteric artery; CT: Celiac trunk.
- Citation: Pérez-Aguado G, de la Mata DMA, Valenciano CML, Sainz IFU. Endoscopic ultrasonography-guided celiac plexus neurolysis in patients with unresectable pancreatic cancer: An update. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2021; 13(10): 460-472
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v13/i10/460.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v13.i10.460