Published online Nov 27, 2024. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v16.i11.1290
Revised: August 27, 2024
Accepted: October 20, 2024
Published online: November 27, 2024
Processing time: 224 Days and 14.9 Hours
Non-invasive methods to diagnose non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), an inflammatory subtype of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), are currently unavailable.
To develop an integrin αvβ3-targeted molecular imaging modality to differentiate NASH.
Integrin αvβ3 expression was assessed in Human LO2 hepatocytes Scultured with palmitic and oleic acids (FFA). Hepatic integrin αvβ3 expression was analyzed in rabbits fed a high-fat diet (HFD) and in rats fed a high-fat, high-carbohydrate diet (HFCD). After synthesis, cyclic arginine-glycine-aspartic acid peptide (cRGD) was labeled with gadolinium (Gd) and used as a contrast agent in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) performed on mice fed with HFCD.
Integrin αvβ3 was markedly expressed on FFA-cultured hepatocytes, unlike the control hepatocytes. Hepatic integrin αvβ3 expression significantly increased in both HFD-fed rabbits and HFCD-fed rats as simple fatty liver (FL) progressed to steatohepatitis. The distribution of integrin αvβ3 in the liver of NASH cases largely overlapped with albumin-positive staining areas. In comparison to mice with simple FL, the relative liver MRI-T1 signal value at 60 minutes post-injection of Gd-labeled cRGD was significantly increased in mice with steatohepatitis (P < 0.05), showing a positive correlation with the NAFLD activity score (r = 0.945; P < 0.01). Hepatic integrin αvβ3 expression was significantly upregulated during NASH development, with hepatocytes being the primary cells expressing integrin αvβ3.
After using Gd-labeled cRGD as a tracer, NASH was successfully distinguished by visualizing hepatic integrin αvβ3 expression with MRI.
Core Tip: Early identification of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) patients and accurate assessment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease severity are crucial for improving patient outcomes. Currently, no non-invasive method can replace liver biopsy to accurately discern NASH. Hepatic integrin αvβ3 expression significantly increased as simple fatty liver progressed to steatohepatitis. Inflammatory-injured hepatocytes, which might be the primary cells expressing integrin αvβ3 in steatohepatitis, were identified on the basis of steatosis. Utilizing gadolinium-labeled cyclic arginine-glycine-aspartic acid peptide as a contrast agent, steatohepatitis was successfully differentiated by visualizing hepatic integrin αvβ3 expression using a magnetic resonance imaging modality.
- Citation: Huang XQ, Wu L, Xue CY, Rao CY, Fang QQ, Chen Y, Xie C, Rao SX, Chen SY, Li F. Non-invasively differentiate non-alcoholic steatohepatitis by visualizing hepatic integrin αvβ3 expression with a targeted molecular imaging modality. World J Hepatol 2024; 16(11): 1290-1305
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v16/i11/1290.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v16.i11.1290
Currently, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has become the most common cause of chronic liver disease worldwide and is estimated to affect about 25%-30% of the global population[1]. NAFLD encompasses a spectrum of liver disorders, ranging from simple fatty liver (FL) to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), which can ultimately progress to cirrhosis[2]. NASH, an inflammatory subtype of NAFLD, is histologically characterized by hepatic steatosis accompanied by hepatocyte injury (ballooning) and intralobular inflammation, with or without fibrosis[3]. Due to the close association of NAFLD with metabolic disorders such as obesity, hyperlipidemia, and type 2 diabetes, and given the ongoing epidemic of these conditions, the prevalence of NAFLD, along with the proportion of NASH, is projected to continue rising in the coming decade[4]. Compared to the general population and patients with simple FL, a significantly higher proportion of NASH patients can progress to cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), and death[4-6]. Consequently, early identification of NASH and accurate assessment of NAFLD severity are crucial to improving patient outcomes.
Over the past two decades, numerous non-invasive methods have been explored to identify NASH among patients with NAFLD. These methods include conventional imaging examinations, imaging-based evaluation approaches such as magnetic resonance imaging-derived proton density fat fraction (MRI-PDFF), serum biomarkers (e.g., cytokeratin 18), and several complex scoring systems composed of clinical and laboratory values. The characteristics of various non-invasive diagnostic methods are summarized in Table 1. While the diagnosis of FL and advanced liver fibrosis, even cirrhosis, can be made using these methods, none can accurately distinguish NASH, and invasive liver biopsy remains the only accepted method for reliably diagnosing NASH[4,6]. However, performing a liver biopsy on every NAFLD patient is neither feasible nor necessary, as the procedure has limitations, including sampling errors that affect diagnostic accuracy and the risk of operative complications such as bleeding, infection, and, rarely, mortality[6,7]. Therefore, there is an urgent need to develop a novel non-invasive method to accurately distinguish NASH and monitor disease progression.
| Methods | Advantages | Flaws | Patients (n) | AUROC | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | |||
| Imaging modalities | Quantitative ultrasound biomarkers | Ultrasound attenuation coefficient[31] | Low cost and wide availability; High sensitivity and specificity in grading | The diagnostic performance is affected by the presence of fibrosis. | 125 (Excluding liver fibrosis) | S0 vs S1, S2, S3 | 0.951 | 82.1 | 95.5 |
| S0, S1 vs S2, S3 | 0.987 | 94.3 | 93.9 | ||||||
| S0, S1, S2 vs S3 | 0.931 | 94.1 | 85.5 | ||||||
| Ultrasound-derived fat fraction[32] | Low cost and wide availability; Real-time data collection | High interobserver variability | 46 | S0 vs S1, S2, S3 | 0.950 | 90.0 | 94.0 | ||
| S0, S1 vs S2, S3 | 0.980 | ||||||||
| CT | Contrast-enhanced CT[33] | Common in clinical practice; Quantify liver fat without additional radiation exposure | Exposes patients to ionizing radiation | 1204 | Steatosis≥ 5% | 0.669 | 34.0 | 94.2 | |
| Steatosis≥ 10% | 0.854 | ||||||||
| Steatosis ≥ 15% | 0.962 | 75.9 | 95.7 | ||||||
| Non-contrast dual-energy CT[34] | Reliable for detection of moderate steatosis | Influenced by varying contrast bolus and scan timing, cardiac output | 128 | Right lobe | 0.834 | 57.0 | 94.0 | ||
| Left lobe | 0.872 | 68.0 | 90.0 | ||||||
| MR-PDFF[35] | It is used as a reference for testing other clinical or biochemical markers | Expensive; availability-limited; unable to assess liver inflammation, ballooning | 77 | S0 vs S1, S2, S3 | 0.989 | 97 | 100 | ||
| S0, S1 vs S2, S3 | 0.825 | 61 | 90 | ||||||
| S0, S1, S2 vs S3 | 0.893 | 68 | 91 | ||||||
| Serum biomarkers | Laboratory parameter-based model | NAFLD bridge score[36] | Data availability and cost-effectiveness | Unable to differentiate NASH from simple steatosis with high sensitivity and specificity | 422 | With and without NAFLD | 0.880 | 95 | 87 |
Integrins are transmembrane glycoprotein heterodimeric receptors that primarily mediate adhesion between different cells or between cells and the extracellular matrix. They participate in signal transduction related to cell proliferation, activation, movement, and apoptosis, thereby playing a pivotal role in immune regulation, injury repair, tumor infiltration, and other processes[8-10]. A common feature of integrins is their ability to bind endogenous ligands by recognizing the amino acid binding motif arginine-glycine-aspartic acid (RGD)[9,11]. Among the 24 known integrin heterodimers, consisting of 18 α-subunit and 8 β-subunit variants, integrin αvβ3 has been the most studied over the past two decades. Numerous RGD-binding drugs targeting integrin αvβ3 have been developed for the treatment of integrin αvβ3-associated diseases[12-14].
In our previous studies, cyclic RGD pentapeptide was prepared and demonstrated to specifically bind to integrin αvβ3 on activated hepatic stellate cells both in vitro and in vivo[15,16]. Additionally, after the synthesized cyclic RGD peptide was directly radiolabeled or used to modify the dendrimer nanoprobe, molecular imaging approaches using single photon emission computed tomography or MRI were developed to non-invasively distinguish the severity of liver fibrosis[15,16]. In this study, hepatic expression of integrin αvβ3 was observed in different animal models of NAFLD. Furthermore, after synthesizing cyclic RGD peptides modified with gadolinium (Gd) and using them as an MRI contrast agent, we aimed to develop a molecular imaging modality to distinguish NASH by visualizing hepatic integrin αvβ3 expression.
Eight-week-old male Sprague-Dawley rats, six-week-old male C57BL/6J mice, and four-month-old male New Zealand white rabbits were obtained from the Experimental Animals Department of Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University (Shanghai, China). All experiments were conducted in accordance with governmental and international guidelines on animal experimentation. The study was reviewed and approved by the Zhongshan Hospital Institutional Review Board, and all experiments were performed following these guidelines.
Cyclic RGD (cRGD) peptide [cyclo (Arg-Gly-Asp-D-Tyr-Lys)] was synthesized and labeled with Gd as previously described[15-17]. Briefly, cRGD was initially synthesized using an Fmoc-protected solid-phase peptide synthesis method and subsequently labeled with Gd through 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid (DOTA) to form cRGD-DOTA-Gd. The molecular weights of cRGD and cRGD-DOTA-Gd were determined using analytical reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography, and their purities were assessed by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. The Gd3+ content of cRGD-DOTA-Gd was determined using a Hitachi P-4010 (Tokyo, Japan). Inductively Coupled Plasma Atomic Emission Spectroscopy system.
Human LO2 hepatocytes (from the Cell Bank of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai, China) were cultured in a medium supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum and 1% penicillin/streptomycin in a 5% CO2 humidified atmosphere at 37 °C.
Firstly, LO2 cells were cultured in a medium containing 100 μmol/L palmitic acid and 200 μmol/L oleic acid (FFA) for 24 hours, after which they were stained with Oil-Red O. LO2 cells cultured in medium without FFA served as controls. Secondly, after being fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde and permeabilized with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) con
Rabbits were fed a high-fat diet (HFD), which included an additional 20% corn oil in the regular diet containing 3.81% fat, 17.8% protein, and 46.5% carbohydrate (provided by the Experimental Animals Department of Zhongshan Hospital). Based on preliminary experimental results, rabbits fed with HFD for 2, 6, and 8 months were selected for further experiments [referred to as HFD-2 months (M), HFD-6M, and HFD-8M rabbits, respectively]. Rabbits fed with a regular diet for 8 months served as the control group (n = 10 for each group).
Sprague-Dawley rats and C57BL/6J mice were fed a high-fat high-carbohydrate diet (HFCD), which contained 60 kcal% fats, 20 kcal% proteins, and 20 kcal% carbohydrates (D12492, SHUYISHUER bio, Changzhou, China), along with high fructose/glucose (55% fructose and 45% glucose, Sigma, United States) in drinking water at a concentration of 42 g/L. Two months, four months, or six months after the treatment, treated rats and mice were used for further experiments (referred to as HFCD-2M, HFCD-4M, and HFCD-6M rats or mice, respectively). Rats and mice fed with a regular diet for 6 months served as the control group.
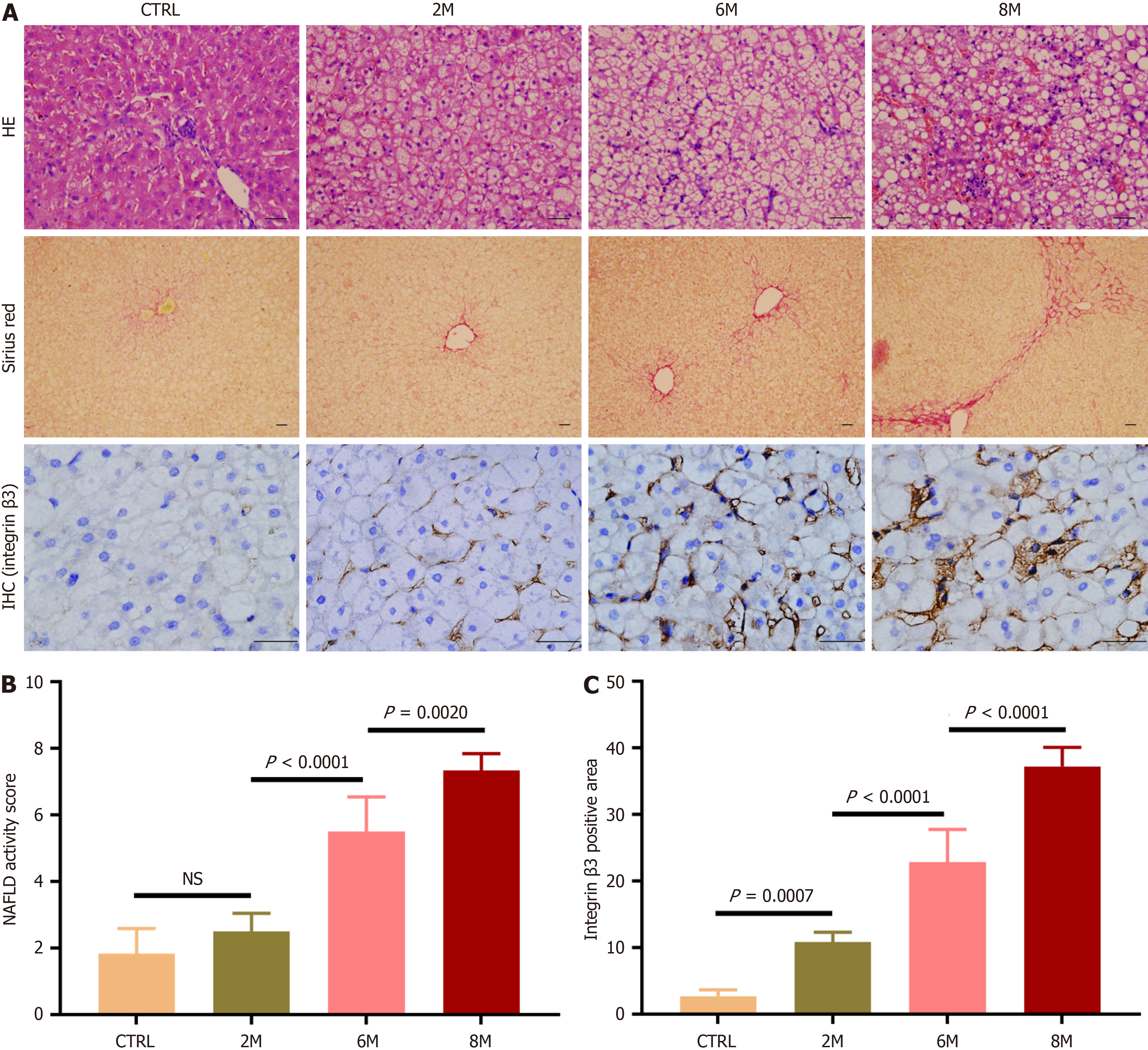
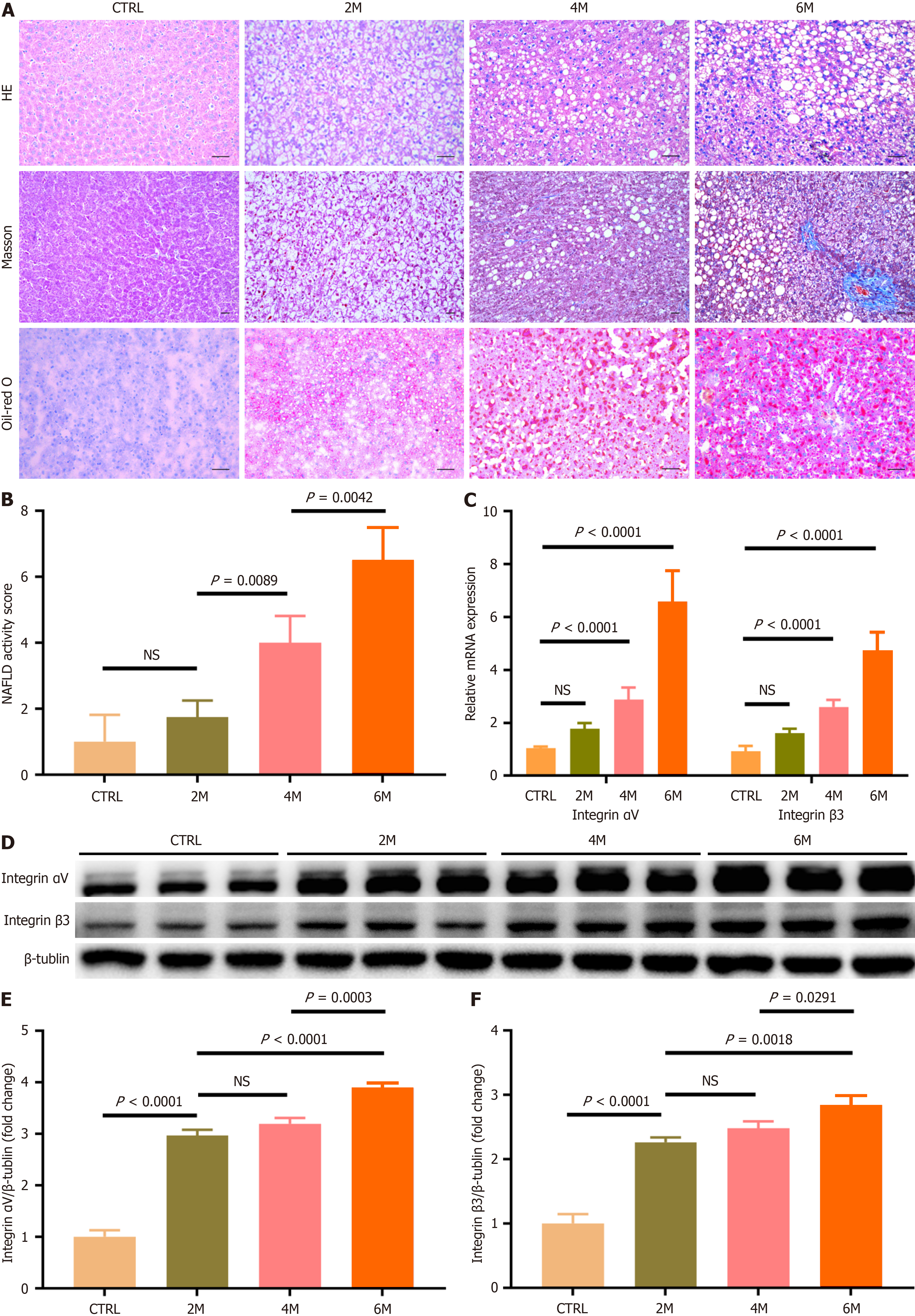
After fixation in neutralized formalin for 48 hours, liver sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Liver sections from rats and mice were stained with Masson, while those from rabbits were stained with Sirius red to assess the degree of liver fibrosis. Additionally, Oil-Red O staining was used to evaluate the degree of hepatic steatosis in frozen liver sections. The severity of NAFLD was semi-quantitatively scored according to the NAFLD activity score, which included steatosis (0-3), lobular inflammation (0-3), and ballooning (0-2)[18]. A score greater than 4 was defined as NASH.
Hepatic expression of integrin αvβ3 was initially assessed in control and HFD-fed rabbits using immunohistochemistry analysis as previously described[17]. Briefly, mouse monoclonal anti-integrin β3 antibody (1:400 in blocking solution, Millipore, Massachusetts, United States, MAB1974) and biotin-conjugated goat polyclonal anti-mouse IgG (1:100 in blocking solution, Abcam, ab6788) were used as the primary and secondary antibodies, respectively. Ten fields (400 × magnification) from each liver section were randomly selected and recorded, and the integrin β3 subunit positive-staining areas were quantified using NIN Image 1.62 software. The percentage of positive-staining areas in each section was then calculated.
Hepatic mRNA levels of integrin αv and integrin β3 subunits in control and HFCD-fed rats were quantified using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction analysis analysis as described previously[15]. The forward primers for integrin αv and integrin β3 subunits were CGAAGCCTTAGCAAGACTGTCCTG and GACTCGGACTGGACTGGCTACTAC, respectively. The reverse primers were CAGTTGAGTTCCAGCCTTCATCGG and ACTTCTCGCAGGTGTCTCCATAGG, respectively. GAPDH was used as the reference, with forward and reverse primers TCCCTCAAGATTGTCAGCAA and AGATCCACAACGGATACATT, respectively. The relative expression of integrin αv and integrin β3 subunits mRNA was analyzed using the comparative cycle threshold method. Additionally, total RNA was extracted from control and FFA-cultured LO2 hepatocytes, and the mRNA expression levels of integrin αv and integrin β3 subunits in these cells were also determined.
The protein amounts of integrin αv and integrin β3 subunits in the livers of control and HFCD-fed rats were determined by western blot analysis. Additionally, protein was extracted from control and FFA-cultured LO2 hepatocytes, and the protein expression levels of integrin αv and integrin β3 subunits in these cells were analyzed. β-tubulin was used as the reference. After chemiluminescent signals were generated and detected on radiographic film, the relative expression of integrin αv and integrin β3 subunits was quantified by scanning densitometry analysis.
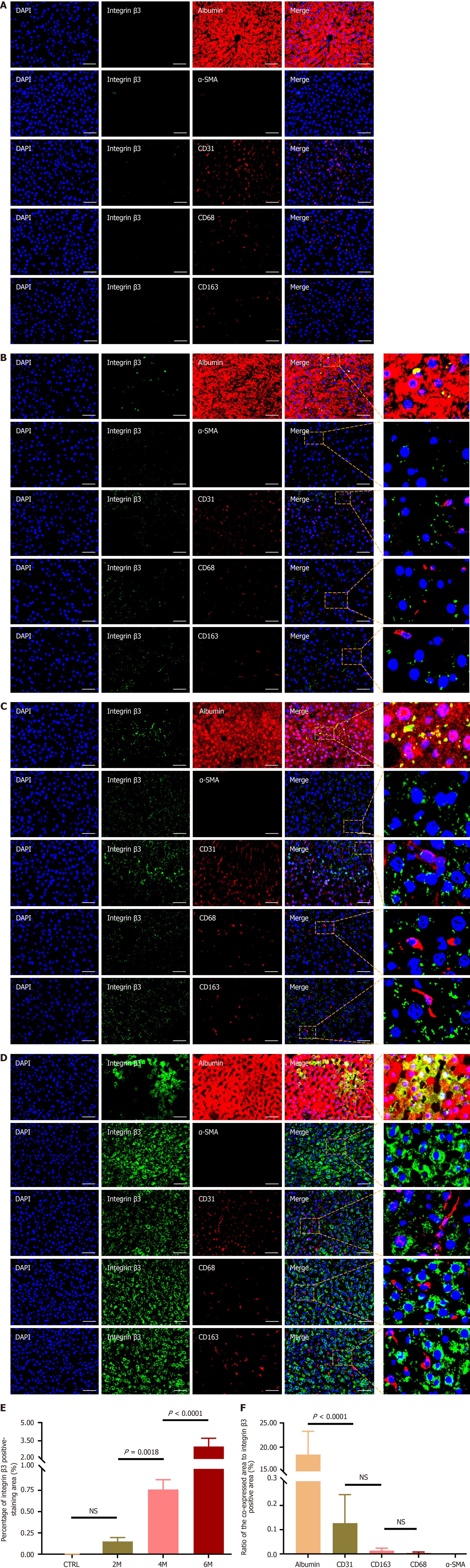
Immunofluorescent staining was performed to reveal the co-localization of integrin β3 subunits with markers of various hepatic cells, including albumin (hepatocytes), α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) (activated hepatic stellate cell), cluster of differentiation (CD) 31 (hepatic sinusoidal endothelial cells), CD68 (macrophages), and CD163 (Kupffer cells), in liver sections of control and HFCD-fed rats as previously described[15]. Primary antibodies against integrin β3 subunit (1:500; Abmart), monoclonal anti-albumin (1:500; Servicebio), monoclonal anti-SMA (1:500, Servicebio, GB111364), monoclonal anti-CD31 (1:500, Servicebio, GB11063-1), monoclonal anti-CD68 (1:500, Servicebio, GB11067), and monoclonal anti-CD163 (1:500, Servicebio, GB11340-1) were used. Secondary antibodies included Alexa Fluor 594-conjugated IgG (1:200, Jackson) and Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated IgG (1:200, Jackson). Multicolored fluorescent staining of liver sections was analyzed, and 10 randomly selected amplifying fields (400 ×) in each section were assessed using Image-Pro Plus version 6.0.0.260. The percentage of integrin β3 subunit-stained green area in each section and the ratio of the merged yellow color area to the total integrin β3 subunit-stained area in each section were calculated.
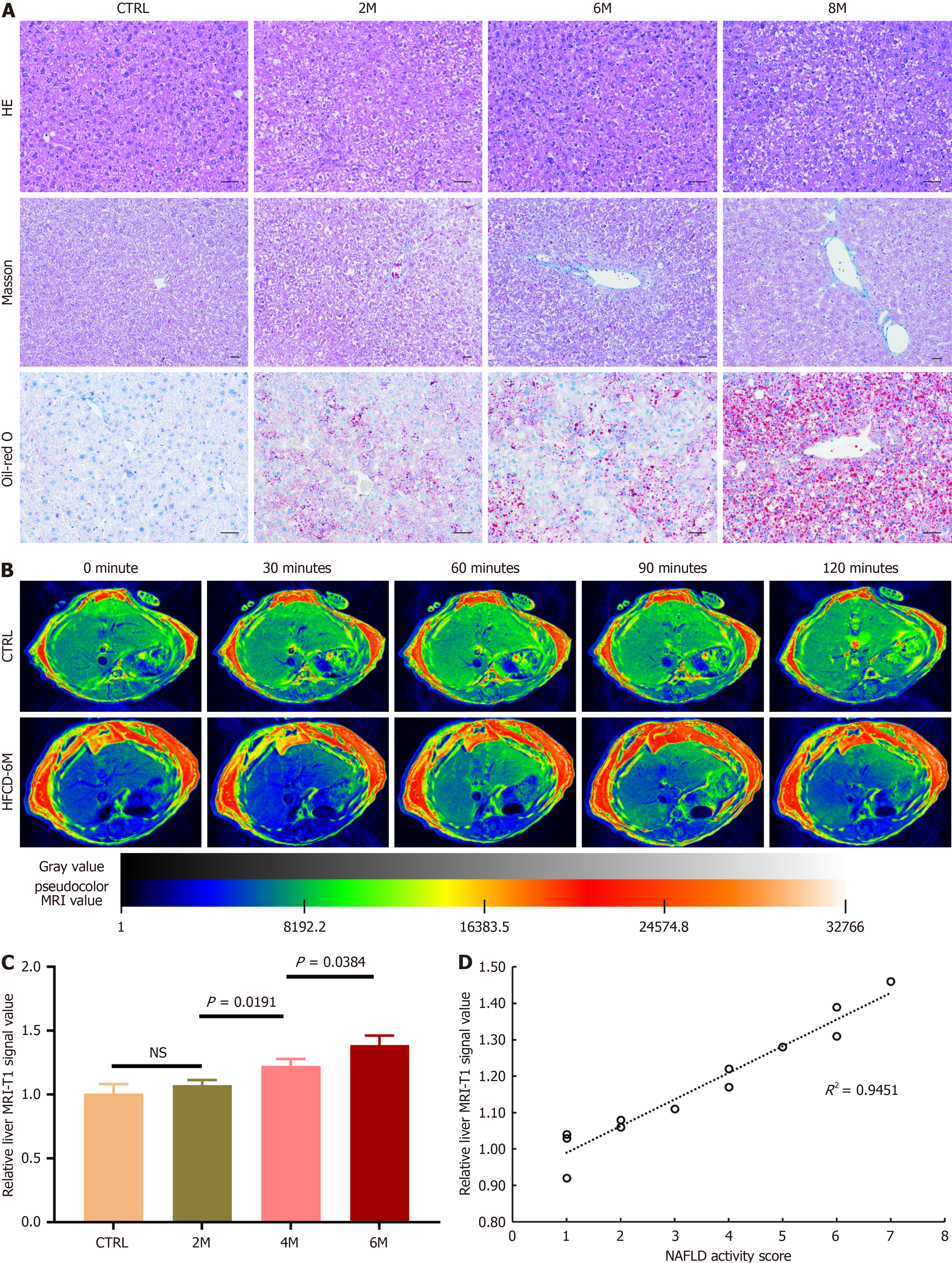
MRI was performed in mice using a Biospec 70/20 MRI scanner (7.0 T, Bruker, Germany) to assess the accumulation of cRGD-DOTA-Gd in livers after cRGD-DOTA-Gd was injected intravenously at a dose of 0.05 mmol/kg [Gd3+] in a total of 0.25 mL PBS solution in the control and HFCD-fed mice, as described previously[16]. Briefly, dynamic T1-weighted MRIs of the liver were collected before and at 30, 60, 90, and 120 minutes after cRGD-DOTA-Gd injection. Cross-sectional images of the liver were acquired using a fast low-angle shot sequence and processed with Weasis software version 3.8.1. The signal intensity of the hepatic region [T1 (liver)] was measured, and the muscle signal intensity [T1 (muscle)] from the region of interest in the same section was used to normalize the hepatic signal intensity. The relative hepatic signal intensity was denoted as T1 (liver)/T1 (muscle). The relative hepatic signal intensity before (T0) and at different time points (Tt) after the injection of cRGD-DOTA-Gd were calculated, and the relative liver MRI-T1 signal value at a specific time point post-injection was determined by subtracting T0 from Tt.
Data were presented as the mean ± SD and analyzed by a one-way analysis of variance followed by the least significant difference test. Statistical product and service solutions 24.0 statistical software (Chicago, United States) was used, and a P value of < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Cyclic peptides (cRGD) were prepared and labeled with Gd (cRGD-DOTA-Gd). The molecular weights of cRGD and cRGD-DOTA-Gd were 623 and 1362 Da, respectively, and their purities exceeded 95%. The Gd3+ content in cRGD-DOTA-Gd was 8.1%.
After LO2 hepatocytes were cultured with FFA for 24 hours, the accumulation of fat droplets was observed in most cells through Oil-Red O staining (Figure 1A), indicating the development of hepatocyte steatosis. Integrin αvβ3 was expressed on FFA-cultured hepatocytes as shown by immunofluorescent staining, but not on the control hepatocytes (Figure 1B and C). Compared to the control cells, the mRNA expression levels and protein amounts of integrin αv and integrin β3 subunits were significantly increased in FFA-cultured hepatocytes (Figure 1B-F, P < 0.05 for all comparisons).
The expression of integrin αvβ3 in NAFLD livers was initially observed in HFD-fed rabbits. After 2 months of HFD feeding, lipid accumulation in hepatocytes was observed, indicating the development of hepatic steatosis. With prolonged HFD feeding for 6 and 8 months, hepatic steatosis worsened, and hepatocyte ballooning became prominent, accompanied by inflammatory cell infiltration in hepatic lobules and the formation of perisinusoidal fibrosis, even bridge fibrosis (Figure 2A). The NAFLD activity score was significantly higher in HFD-6M and HFD-8M rabbits compared to control and HFD-2M rabbits (Figure 2B, P < 0.05 for all comparisons). After immunohistochemical staining of hepatic slices for integrin β3 subunits, abundant positive-staining areas were observed in HFD-6M and HFD-8M rabbits (Figure 2A). The percentage of integrin β3 subunit positive-staining areas in the livers of HFD-6M and HFD-8M rabbits (22.83 ± 4.93 and 37.22 ± 2.88, respectively) was significantly higher than in control (2.68 ± 0.97) and HFD-2M rabbits (10.82 ± 1.48) (Figure 2C, P < 0.05 for all comparisons). These results indicated that hepatic expression of integrin αvβ3 increased consistently with the progression of NAFLD, with a significant increase observed when the condition progressed to NASH.
As shown in Figure 3A, after rats were fed with HFCD, massive fat droplets accumulated in hepatocytes, which was most prominent in HFCD-6M rats. As hepatic steatosis worsened, hepatocyte ballooning and inflammatory cell infiltration became more pronounced in hepatic lobules after 4 months of HFCD feeding. When the HFCD feeding was prolonged to 6 months, perisinusoidal fibrosis was observed in hepatic lobules. Compared to control rats (1.17 ± 0.41) and HFCD-2M rats (1.83 ± 0.75), the NAFLD activity score of hepatic tissue was significantly increased in HFCD-4M and HFCD-6M rats (4.00 ± 0.89 and 6.83 ± 0.75, respectively), with the highest score in HFCD-6M rats (Figure 3B, P < 0.05 for all comparisons). These results indicated that simple FL developed in rats after 2 months of HFCD feeding, progressed to steatohepatitis after 4 months, and further advanced to NASH with liver fibrosis after 6 months.
Hepatic integrin αvβ3 expression during the development and progression of NAFLD was further assessed in HFCD-fed rats. Compared to control and HFCD-2M rats, hepatic mRNA expression levels of integrin αv and integrin β3 subunits were significantly increased after 4 months of HFCD feeding, reaching the highest levels in HFCD-6M rats (Figure 3C, P < 0.05 for all comparisons). Additionally, the protein amounts of integrin αv and integrin β3 subunits in hepatic tissue gradually increased in HFCD-fed rats, with levels significantly higher than those in control rats (Figure 3D-F, P < 0.05 for all comparisons). These results indicated that hepatic integrin αvβ3 expression progressively increased with the development and progression of NAFLD.
To identify the principal cells expressing integrin αvβ3 in livers with NAFLD, double immunofluorescent staining was performed to visualize the co-localization of the integrin β3 subunit with albumin, α-SMA, CD31, CD68, and CD163 in control and HFCD-fed rats. Integrin αvβ3 expression was negligible in the livers of control rats, as no integrin β3 subunit positive-staining (green) areas were found in the liver slices (Figure 4A). In contrast, increasing integrin β3 subunit positive-staining areas were observed in the liver slices of HFCD-fed rats, particularly in HFCD-6M rats (Figure 4B-D). The percentage of integrin β3 subunit positive-staining areas in the liver slices of HFCD-4M and HFCD-6M rats was significantly higher than in control and HFCD-2M rats (Figure 4E, P < 0.05 for all comparisons).
Additionally, in the livers of HFCD-6M rats, the positive staining of the integrin β3 subunit (green) extensively overlapped (yellow) with albumin staining (red) and showed minimal overlap with α-SMA, CD31, CD68, or CD163 staining (Figure 4D). The ratio of the overlapped area of integrin β3 subunit staining with albumin positive-staining was significantly higher than the overlapped staining with other cellular markers (Figure 4F, P < 0.05 for all comparisons).
These findings suggest that hepatic expression of integrin αvβ3 markedly increased as simple FL progressed to steatohepatitis, with hepatocytes being the primary cells expressing integrin αvβ3 in livers with NASH.
After being fed with HFCD for 6 months, the rats became so obese that no suitable coil was available for MRI examination. Therefore, mice were used for in vivo MRI experiments. After the mice were fed with HFCD, similar histopathological findings were observed in their livers: Simple FL developed in HFCD-2M mice and progressed to steatohepatitis in HFCD-4M and HFCD-6M mice (Figure 5A).
A dynamic T1-weighted MRI approach was employed to assess the deposition of cRGD-DOTA-Gd in the livers after the radiotracers were intravenously injected in control and HFCD-fed mice. As shown in Figure 5B, there was no significant change in hepatic signal intensity in control mice before and up to 120 minutes after cRGD-DOTA-Gd in
To date, the development of a non-invasive method that can accurately diagnose NASH and determine the disease severity of NAFLD, thereby replacing the need for liver biopsy, remains one of the urgent unmet needs in the NASH field[4]. Compared to other conventional imaging modalities, such as ultrasound and computed tomography, MRI offers the highest spatial resolution for soft tissues and is considered the most sensitive modality for evaluating hepatic steatosis[19]. While these imaging modalities can also detect advanced liver fibrosis and cirrhosis, none can accurately distinguish NASH. Recently, several MRI-based imaging modalities, such as MRI-PDFF and magnetic resonance elastography (MRE), have been developed for NAFLD diagnosis. MRI-PDFF is currently the gold standard for diagnosing and quantifying hepatic steatosis, showing excellent accuracy in detecting dynamic changes in steatosis, but it fails to provide information on steatohepatitis and fibrosis[20,21]. Conversely, MRE is recognized as the most accurate imaging modality for diag
Many animal models are currently available for basic and translational research on NAFLD, primarily grouped into two categories: specific gene knockout models and special diet-induced models. Compared to gene knockout NAFLD models, the animal models induced by special diets, particularly high-fat (± high-carbohydrate) diets, more comprehensively mimic the spectrum of metabolic and histological features of human NAFLD[24]. In the present study, the HFD-induced NAFLD rabbit model was initially used to observe the expression of integrin αvβ3 in the liver with NAFLD. However, significant individual variability in hepatic histopathological manifestations was found in HFD-fed rabbits. Therefore, HFCD-induced NAFLD murine models were used to further assess hepatic integrin αvβ3 expression and conduct in vivo MRI examinations. With prolonged HFCD feeding, hepatic steatosis developed and progressed to steatohepatitis in most rats and mice, as demonstrated histologically.
In our previous study, it was found that integrin αvβ3 in fibrotic livers was primarily expressed on activated hepatic stellate cells, and its expression level strongly correlated with the degree of liver fibrosis, while it was scarcely expressed on hepatocytes[15,25]. Additionally, Rokugawa et al[26] recently reported quantitatively evaluating hepatic integrin αvβ3 expressed on activated hepatic stellate cells using positron emission tomography imaging in rats with NASH[26,27]. However, in the present study, hepatocytes - not activated hepatic stellate cells-were found to be the primary cells expressing integrin αvβ3 in NASH livers. In the in vivo study, hepatic expression of integrin αvβ3 was significantly increased in NASH livers, with no expression in normal livers and mild expression in livers with simple FL. More importantly, most integrin αvβ3 was found to be expressed on hepatocytes in NASH livers, as demonstrated by double immunofluorescent staining for integrin αvβ3 and markers of various hepatic cells. In the in vitro study, integrin αvβ3 was markedly expressed on hepatocytes cultured with palmitic acid and FFA, but not on normal control hepatocytes. It has been demonstrated that hepatocytes develop not only steatosis, but also inflammatory injury and apoptosis after being cultured with palmitic acid and FFA[28]. These results indicate that on the basis of steatosis, hepatocytes injured by inflammation express abundant integrin αvβ3 in NASH livers. Additionally, based on these results, we speculate that integrin αvβ3 might play a role in the pathogenesis of NASH, which needs to be further elucidated in future studies.
In this study, hepatic integrin αvβ3 expression significantly increased as simple FL progressed to steatohepatitis, with or without fibrosis, which correlated with the increased NAFLD activity score. Therefore, we aimed to visualize hepatic integrin αvβ3 expression during the development and progression of NAFLD using an MRI-based molecular imaging modality. After Gd-labeled cRGD, targeted to integrin αvβ3, was injected, the hepatic signal markedly intensified at 60 minutes post-injection compared to pre-injection levels, and the relative liver MRI-T1 signal value at 60 minutes post-injection was significantly increased in mice with NASH compared to control mice and those with simple FL, showing a linear correlation with the NAFLD activity score. These results indicated that the binding amount of Gd-labeled cRGD in the liver significantly increased secondary to elevated hepatic integrin αvβ3 expression during the development of NASH. Thus, NASH was successfully differentiated from simple FL in NAFLD by visualizing hepatic integrin αvβ3 expression with the targeted molecular imaging modality.
Recently, it has been found that long-term outcomes, including overall mortality in patients with NAFLD, are strongly associated with the severity of liver fibrosis but not with the NAFLD activity score[29]. However, non-NASH NAFLD seldom progresses to significant fibrosis, indicating that steatohepatitis is a cornerstone in the development and progression of liver fibrosis in NAFLD[4-6]. More importantly, HCC has been found to develop in NASH patients without liver cirrhosis[30]. Consequently, it is essential to discern NASH early and regularly monitor the progression of NAFLD, but invasive liver biopsy, the only currently accepted method for diagnosing NASH, fails to achieve this goal. In contrast, non-invasive molecular imaging modalities could potentially be utilized for routine screening and regular follow-up of NASH in the NAFLD population. Over the past decades, numerous molecular imaging modalities have been developed for diagnosing tumors and their metastases, especially those with integrin αvβ3-positive expression[14]. Furthermore, in our previous studies, two molecular imaging modalities were explored to diagnose liver fibrosis by visualizing hepatic αvβ3 expression in the development and progression of fibrosis[15,16]. All these developments will aid in promoting the clinical application of integrin αvβ3-targeted molecular imaging modalities in NASH diagnosis.
However, the availability and cost-effectiveness of MRI are still worth considering. There is no doubt that MRI is more expensive than ultrasound or computed tomography-based imaging modalities and tends to be more time-consuming. Nevertheless, the reliability of MRI is widely accepted, and other non-invasive methods are often compared with MRI-based methods like MRI-PDFF, which are limited in assessing inflammation, to evaluate their potential in clinical applications. In this study, we developed an RGD-based MRI contrast agent to differentiate steatohepatitis by visualizing hepatic integrin αvβ3 expression, which could counteract the interference of inflammation in MRI detection. This approach holds promise for future development and use.
In conclusion, this study demonstrated that hepatic integrin αvβ3 expression significantly increased as simple FL progressed to NASH. Hepatocytes, injured by inflammation on the basis of hepatic steatosis, were the primary cells expressing integrin αvβ3 in NASH livers. After cyclic RGD peptides were labeled with Gd and used as a contrast agent, NASH was successfully distinguished by visualizing hepatic integrin αvβ3 expression with an MRI modality.
The authors would like to acknowledge Pang ZY (Shanghai East Hospital) for valuable assistance with fluorescence microscopy and MRI analysis.
| 1. | Younossi Z, Tacke F, Arrese M, Chander Sharma B, Mostafa I, Bugianesi E, Wai-Sun Wong V, Yilmaz Y, George J, Fan J, Vos MB. Global Perspectives on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Hepatology. 2019;69:2672-2682. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1415] [Cited by in RCA: 1317] [Article Influence: 219.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Pouwels S, Sakran N, Graham Y, Leal A, Pintar T, Yang W, Kassir R, Singhal R, Mahawar K, Ramnarain D. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): a review of pathophysiology, clinical management and effects of weight loss. BMC Endocr Disord. 2022;22:63. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 52] [Cited by in RCA: 455] [Article Influence: 151.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 3. | Chalasani N, Younossi Z, Lavine JE, Charlton M, Cusi K, Rinella M, Harrison SA, Brunt EM, Sanyal AJ. The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2018;67:328-357. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3544] [Cited by in RCA: 4954] [Article Influence: 707.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (9)] |
| 4. | Cotter TG, Rinella M. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease 2020: The State of the Disease. Gastroenterology. 2020;158:1851-1864. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 411] [Cited by in RCA: 842] [Article Influence: 168.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (2)] |
| 5. | Rinella ME, Neuschwander-Tetri BA, Siddiqui MS, Abdelmalek MF, Caldwell S, Barb D, Kleiner DE, Loomba R. AASLD Practice Guidance on the clinical assessment and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2023;77:1797-1835. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 252] [Cited by in RCA: 1172] [Article Influence: 586.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 6. | Sheka AC, Adeyi O, Thompson J, Hameed B, Crawford PA, Ikramuddin S. Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: A Review. JAMA. 2020;323:1175-1183. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 473] [Cited by in RCA: 999] [Article Influence: 199.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Ajmera V, Loomba R. Imaging biomarkers of NAFLD, NASH, and fibrosis. Mol Metab. 2021;50:101167. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 24] [Cited by in RCA: 135] [Article Influence: 33.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Xu S, Zhang T, Cao Z, Zhong W, Zhang C, Li H, Song J. Integrin-α9β1 as a Novel Therapeutic Target for Refractory Diseases: Recent Progress and Insights. Front Immunol. 2021;12:638400. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 12] [Article Influence: 3.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Slack RJ, Macdonald SJF, Roper JA, Jenkins RG, Hatley RJD. Emerging therapeutic opportunities for integrin inhibitors. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2022;21:60-78. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 36] [Cited by in RCA: 326] [Article Influence: 81.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | De Marco R, Tolomelli A, Juaristi E, Gentilucci L. Integrin Ligands with α/β-Hybrid Peptide Structure: Design, Bioactivity, and Conformational Aspects. Med Res Rev. 2016;36:389-424. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 20] [Cited by in RCA: 31] [Article Influence: 3.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Ruoslahti E. My scientific journey to and through extracellular matrix. Matrix Biol. 2024;133:57-63. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Sani S, Messe M, Fuchs Q, Pierrevelcin M, Laquerriere P, Entz-Werle N, Reita D, Etienne-Selloum N, Bruban V, Choulier L, Martin S, Dontenwill M. Biological Relevance of RGD-Integrin Subtype-Specific Ligands in Cancer. Chembiochem. 2021;22:1151-1160. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 15] [Cited by in RCA: 42] [Article Influence: 8.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Bhatwadekar AD, Kansara V, Luo Q, Ciulla T. Anti-integrin therapy for retinovascular diseases. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2020;29:935-945. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 14] [Cited by in RCA: 38] [Article Influence: 7.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Li ZH, Zhou Y, Ding YX, Guo QL, Zhao L. Roles of integrin in tumor development and the target inhibitors. Chin J Nat Med. 2019;17:241-251. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 23] [Cited by in RCA: 28] [Article Influence: 4.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Li F, Song Z, Li Q, Wu J, Wang J, Xie C, Tu C, Wang J, Huang X, Lu W. Molecular imaging of hepatic stellate cell activity by visualization of hepatic integrin αvβ3 expression with SPECT in rat. Hepatology. 2011;54:1020-1030. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 39] [Cited by in RCA: 49] [Article Influence: 3.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Li F, Yan H, Wang J, Li C, Wu J, Wu S, Rao S, Gao X, Jin Q. Non-invasively differentiating extent of liver fibrosis by visualizing hepatic integrin αvβ3 expression with an MRI modality in mice. Biomaterials. 2016;102:162-174. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 21] [Cited by in RCA: 26] [Article Influence: 2.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Wu L, Huang XQ, Li N, Xie C, Rao SX, Chen SY, Li F. A magnetic resonance imaging modality for non-invasively distinguishing progression of liver fibrosis by visualizing hepatic platelet-derived growth factor receptor-beta expression in mice. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;36:3448-3456. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Kleiner DE, Brunt EM, Van Natta M, Behling C, Contos MJ, Cummings OW, Ferrell LD, Liu YC, Torbenson MS, Unalp-Arida A, Yeh M, McCullough AJ, Sanyal AJ; Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Clinical Research Network. Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2005;41:1313-1321. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 6807] [Cited by in RCA: 8248] [Article Influence: 412.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (5)] |
| 19. | Selvaraj EA, Mózes FE, Jayaswal ANA, Zafarmand MH, Vali Y, Lee JA, Levick CK, Young LAJ, Palaniyappan N, Liu CH, Aithal GP, Romero-Gómez M, Brosnan MJ, Tuthill TA, Anstee QM, Neubauer S, Harrison SA, Bossuyt PM, Pavlides M; LITMUS Investigators. Diagnostic accuracy of elastography and magnetic resonance imaging in patients with NAFLD: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Hepatol. 2021;75:770-785. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 80] [Cited by in RCA: 210] [Article Influence: 52.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Caussy C, Reeder SB, Sirlin CB, Loomba R. Noninvasive, Quantitative Assessment of Liver Fat by MRI-PDFF as an Endpoint in NASH Trials. Hepatology. 2018;68:763-772. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 209] [Cited by in RCA: 350] [Article Influence: 50.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Xia T, Du M, Li H, Wang Y, Zha J, Wu T, Ju S. Association between Liver MRI Proton Density Fat Fraction and Liver Disease Risk. Radiology. 2023;309:e231007. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in RCA: 15] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 22. | Castera L, Friedrich-Rust M, Loomba R. Noninvasive Assessment of Liver Disease in Patients With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology. 2019;156:1264-1281.e4. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 619] [Cited by in RCA: 1037] [Article Influence: 172.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 23. | Ozturk A, Olson MC, Samir AE, Venkatesh SK. Liver fibrosis assessment: MR and US elastography. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2022;47:3037-3050. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 16] [Cited by in RCA: 74] [Article Influence: 24.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 24. | Jahn D, Kircher S, Hermanns HM, Geier A. Animal models of NAFLD from a hepatologist's point of view. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2019;1865:943-953. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 68] [Cited by in RCA: 141] [Article Influence: 20.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 25. | Zhong L, Zhao J, Huang L, Liu Y, Pang X, Zhan K, Li S, Xue Q, Pan X, Deng L. Runx2 activates hepatic stellate cells to promote liver fibrosis via transcriptionally regulating Itgav expression. Clin Transl Med. 2023;13:e1316. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in RCA: 17] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 26. | Rokugawa T, Konishi H, Ito M, Iimori H, Nagai R, Shimosegawa E, Hatazawa J, Abe K. Evaluation of hepatic integrin αvβ3 expression in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) model mouse by (18)F-FPP-RGD(2) PET. EJNMMI Res. 2018;8:40. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 18] [Article Influence: 2.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 27. | Hiroyama S, Rokugawa T, Ito M, Iimori H, Morita I, Maeda H, Fujisawa K, Matsunaga K, Shimosegawa E, Abe K. Quantitative evaluation of hepatic integrin α(v)β(3) expression by positron emission tomography imaging using (18)F-FPP-RGD(2) in rats with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. EJNMMI Res. 2020;10:118. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 8] [Article Influence: 1.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 28. | Zhang M, Bai X, Du Q, Xu J, Wang D, Chen L, Dong K, Chen Z, Yang J. The Different Mechanisms of Lipid Accumulation in Hepatocytes Induced by Oleic Acid/Palmitic Acid and High-Fat Diet. Molecules. 2023;28. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 29. | Ekstedt M, Hagström H, Nasr P, Fredrikson M, Stål P, Kechagias S, Hultcrantz R. Fibrosis stage is the strongest predictor for disease-specific mortality in NAFLD after up to 33 years of follow-up. Hepatology. 2015;61:1547-1554. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1353] [Cited by in RCA: 1703] [Article Influence: 170.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 30. | Shah PA, Patil R, Harrison SA. NAFLD-related hepatocellular carcinoma: The growing challenge. Hepatology. 2023;77:323-338. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 49] [Cited by in RCA: 133] [Article Influence: 66.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 31. | Gao J, Zapata I, Chen J, Erpelding TN, Adamson C, Park D. Quantitative Ultrasound Biomarkers to Assess Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J Ultrasound Med. 2023;42:1675-1688. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 32. | Zalcman M, Barth RA, Rubesova E. Real-time ultrasound-derived fat fraction in pediatric population: feasibility validation with MR-PDFF. Pediatr Radiol. 2023;53:2466-2475. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 14] [Article Influence: 7.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 33. | Pickhardt PJ, Blake GM, Graffy PM, Sandfort V, Elton DC, Perez AA, Summers RM. Liver Steatosis Categorization on Contrast-Enhanced CT Using a Fully Automated Deep Learning Volumetric Segmentation Tool: Evaluation in 1204 Healthy Adults Using Unenhanced CT as a Reference Standard. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2021;217:359-367. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 35] [Cited by in RCA: 43] [Article Influence: 10.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 34. | Zhang PP, Choi HH, Ohliger MA. Detection of fatty liver using virtual non-contrast dual-energy CT. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2022;47:2046-2056. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in RCA: 16] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 35. | Tang A, Tan J, Sun M, Hamilton G, Bydder M, Wolfson T, Gamst AC, Middleton M, Brunt EM, Loomba R, Lavine JE, Schwimmer JB, Sirlin CB. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: MR imaging of liver proton density fat fraction to assess hepatic steatosis. Radiology. 2013;267:422-431. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 310] [Cited by in RCA: 422] [Article Influence: 35.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 36. | Yip TC, Ma AJ, Wong VW, Tse YK, Chan HL, Yuen PC, Wong GL. Laboratory parameter-based machine learning model for excluding non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in the general population. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2017;46:447-456. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 143] [Cited by in RCA: 129] [Article Influence: 16.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |