Published online May 27, 2019. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v11.i5.483
Peer-review started: March 7, 2019
First decision: April 11, 2019
Revised: April 25, 2019
Accepted: May 20, 2019
Article in press: May 20, 2019
Published online: May 27, 2019
Processing time: 83 Days and 18.9 Hours
Idiopathic non-cirrhotic portal hypertension (INCPH) is mainly associated with thrombophilia in Western countries. Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) is a rare hematologic disease that manifests with hemolytic anemia, thrombosis, and peripheral blood cytopenias. Portal and hepatic venous thrombosis were reported in PNH. A rare case of INCPH complicating PNH is described.
A 63-year old woman with a 2-year past medical history of PNH without treatment was admitted because of jaundice and refractory ascites requiring large volume paracentesis. Liver histology revealed portal venopathy with portal fibrosis and sclerosis, nodular regenerative hyperplasia, parenchymal ischemic changes, and focal sinusoidal and perivenular fibrosis without bridging fibrosis or cirrhosis, all indicative of INCPH. The flow cytometry confirmed PNH diagnosis and eculizumab treatment was initiated. Her condition was improved gradually, bilirubin was normalized 6 months following initiation of eculizumab, and 1 year later diuretics were stopped.
Eculizumab improved intravascular hemolysis and reversed clinical manifestations of INCPH in a patient with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria.
Core tip Idiopathic non-cirrhotic portal hypertension diagnosis is based on liver histology, the clinical signs of portal hypertension, and the exclusion of chronic liver diseases in the absence of portal and hepatic venous thrombosis. We describe a patient with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria who presented with intravascular hemolysis, jaundice, and refractory ascites. Abdominal portosystemic collaterals were evident in imaging without varices in endoscopy. Liver histology demonstrated portal venopathy, features of nodular regenerative hyperplasia, and ischemic parenchymal changes without cirrhosis, all indicative of idiopathic non-cirrhotic portal hypertension. Eculizumab treatment achieved improvement of hemolysis and reversion of biochemical and clinical manifestations of liver disease.
- Citation: Alexopoulou A, Mani I, Tiniakos DG, Kontopidou F, Tsironi I, Noutsou M, Pantelidaki H, Dourakis SP. Successful treatment of noncirrhotic portal hypertension with eculizumab in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: A case report. World J Hepatol 2019; 11(5): 483-488
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v11/i5/483.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v11.i5.483
Idiopathic non-cirrhotic portal hypertension (INCPH) is evidenced by the presence of an increased portal venous pressure gradient despite the absence of a known cause of chronic liver disease and portal vein thrombosis[1]. In India, INCPH accounts for 23% of portal hypertension cases[2], while in the Western world, it is very rare[3]. The etiology is heterogeneous and varies according to the geographical area and the population studied[4,5]. INCPH is often misdiagnosed as liver cirrhosis, so liver histology is required to differentiate between the two entities[1]. Histological features in liver specimens from patients with INCPH include obliterative portal venopathy, hepatoportal sclerosis, nodular regenerative hyperplasia, and incomplete septal cirrhosis[1]. It has been suggested that obliterative portal venopathy may represent an early stage while nodular regenerative hyperplasia is a late stage of the same disease currently termed porto-sinusoidal vascular disease[6], which may lead to INCPH[7]. Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) is a rare disease[8] and has not been reported so far as a cause of INCPH. We herein describe a case of PNH complicated by INCPH, which was reversed clinically by the administration of eculizumab.
A 63-year old female patient was admitted to the hospital for fatigue, jaundice, and large-volume ascites.
PNH was diagnosed 2 years earlier when she was admitted for anemia, but she was lost to follow-up. Six weeks before current admission, portal vein thrombosis was diagnosed and enoxaparin 60 IU twice daily was initiated.
The abdomen was distended, and the liver was enlarged 4 cm below the right costal margin. The spleen was mildly enlarged.
Blood analysis revealed hemoglobin of 10.8 g/dL, white blood cell count 5.4 × 109/L, platelets 171 × 109/L, reticulocytes 6.5%, international normalized ratio 1.0, total bilirubin 4 mg/dL, direct bilirubin 2.6 mg/dL, aspartate transaminase 28 IU/L, alanine transaminase 12 IU/L, alkaline phosphatase 456 IU/L, glutamyl transpeptidase 248 IU/L, total protein 6.6 g/dL, albumin 3.3 g/dL, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) 650 U/L, serum haptoglobin < 7 mg/dL, creatinine 1.7 mg/dL, urea 81 mg/dL. Ascitic fluid had a serum-ascites albumin gradient of 1.7 g/dL (ascitic fluid total protein 3 g/dL, albumin 1.6 g/dL). Hepatitis B and C and human immunodeficiency virus serology was negative. Direct globulin test was negative.
In Doppler ultrasonography of splenoportal axis, recanalization of the portal vein and large abdominal portosystemic anastomoses were evident. Hepatic veins were patent. Magnetic resonance imaging showed hepatomegaly and confirmed the above findings. No esophageal or gastric varices were demonstrated in endoscopy. Ascites was refractory to diuretics and multiple large volume paracenteses were required. Due to the absence of a clear etiology of portal hypertension, a liver biopsy was performed.
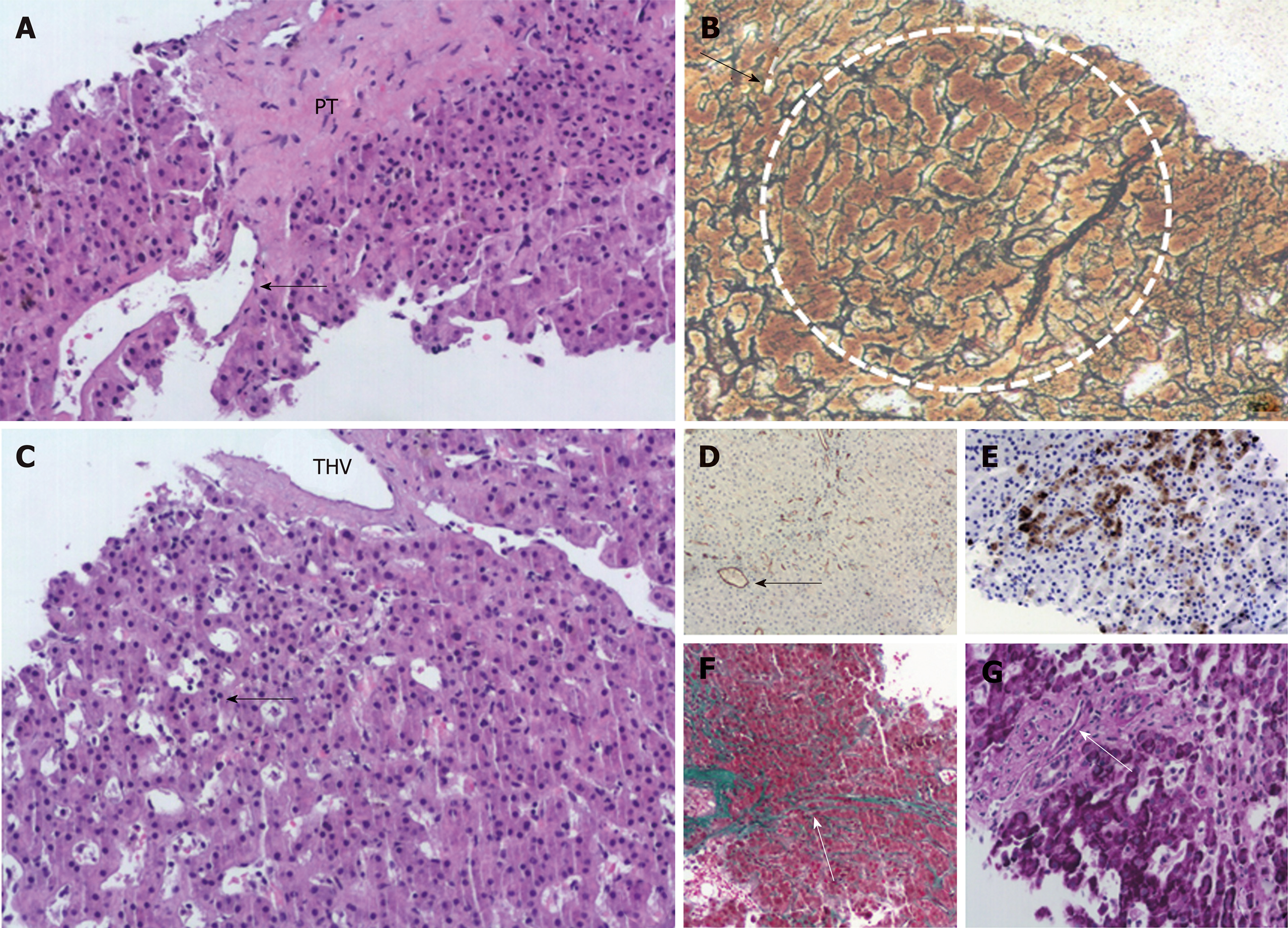
Changes of portal venopathy with portal fibrosis and sclerosis and features of nodular regenerative hyperplasia were demonstrated. A spectrum of portal vein lesions was seen in interlobular portal tracts included in the biopsy, ranging from portal venule herniation in the periportal parenchyma, to slit-like stenosed portal venules and sclerosed portal tracts without a visible portal venule. In addition, parenchymal ischemic changes indicative of decreased venous outflow, mild focal sinusoidal and perivenular fibrosis, mild cholestasis, and mild secondary siderosis were noted. There was no bridging fibrosis or cirrhosis (Figure 1). The overall changes supported the diagnosis of INCPH.
The flow cytometry at this point revealed that 16.5% of her red blood cells were PNH, 4.1% were partially deficient for CD59, and 12.4% lacked CD59 completely; 63% of her granulocytes and 60% of monocytes were PNH.
INCPH complicating PNH was diagnosed.
Paroxysms of abdominal pain, debilitating fatigue, dyspnea, deepening of jaundice (total bilirubin 21 mg/dL, direct bilirubin 14.4 mg/dL), worsening of renal function (creatinine 2.2 mg/dL), anemia (Hb 7.6 g/dL), and thrombocytopenia (80 × 109/L) developed over the next 8 weeks, and the patient became bedridden. Vaccination for Neisseria meningitis was performed as a prophylaxis for future therapy with eculizumab.
Eculizumab was initiated at a regular dosing for patients with PNH (600 mg weekly for the first 5 weeks followed by 900 mg biweekly thereafter).
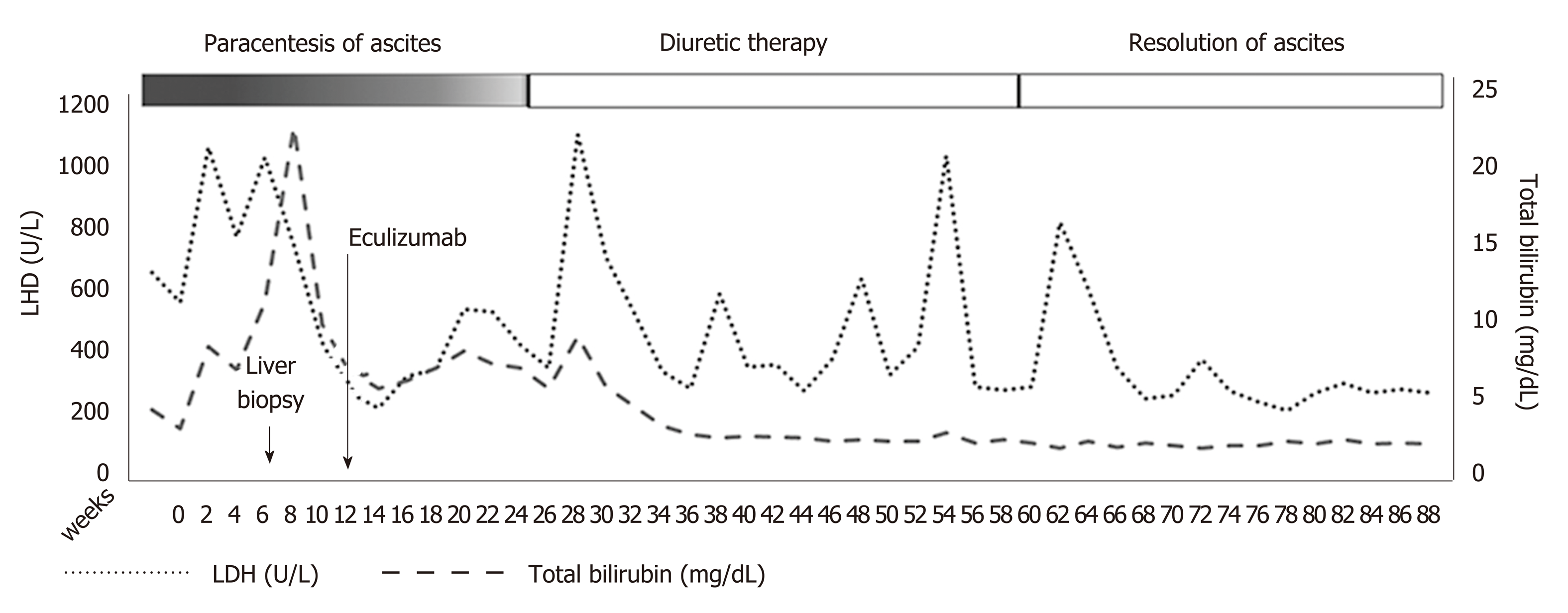
Three months following eculizumab initiation, no more therapeutic paracentesis of ascitic fluid was required and diuretics were administered. Serum bilirubin, LDH, hemoglobin, and reticulocyte count improved gradually (Figure 2). Renal function, serum bilirubin, LDH, and platelets normalized 6 months following initiation of eculizumab. One year later, diuretics were stopped without reappearance of the ascites. No direct antiglobulin test was evident during follow-up. Anticoagulation treatment with enoxaparin was continued during hospitalization and follow-up.
Our patient fulfilled all the criteria for the diagnosis of INCPH, including the clinical signs of portal hypertension (ascites and portovenous collaterals in our case), the exclusion of cirrhosis on histology, the absence of chronic liver diseases causing cirrhosis or other conditions causing INCPH, and the patency of portal and hepatic veins[1]. Although called idiopathic, INCPH has been associated with various conditions, including thrombophilia[9], hematological malignancies[10], infections[11], medication and toxins[12], genetic[13] and immunological disorders[14]. The main symptoms of patients with INCPH are upper gastrointestinal bleeding and splenomegaly[2,15]. Ascites, as in the current case, was present in 50% of cases in a French[16] and in 26% in a Spanish study[17]. Prothrombotic disorders accounted for 48% in the former and 8% in the latter. Our case demonstrated the presence of large abdominal portosystemic collaterals. However, esophageal or gastric varices were not evident, probably due to the early stage of portal hypertension. Chronic ascites may be attributed both to portal hypertension and the concomitant renal failure in keeping with published literature[1]. Kidney disease is a common manifestation of PNH and is a result of tubular damage caused by microvascular thrombosis and renal iron accumulation[8].
From a pathophysiology point of view, in thrombophilia cases of INCPH, increased intrahepatic resistance ensuing from obliteration of the portal venous microcirculation may result in an increase in portal blood pressure[7,18]. High levels of endothelin-1 might further increase vascular resistance and stimulate periportal collagen production[19]. Another hypothesis is that the prothrombotic disorder affects the sinusoidal and portal vein wall causing fibrosis, obstruction, and secondary alterations in hepatic architecture[10]. In the case of PNH, the accumulation of high levels of free hemoglobin, which is a potent nitric oxide scavenger[20], may play a role in increasing vascular resistance. Nitric oxide maintains smooth muscle relaxation and inhibits platelet activation and aggregation[21]. Its deficiency may contribute to smooth muscle tone increase and platelet activation.
In PNH, deficiency of the glycosyl phosphatidylinositol-anchored complement regulatory proteins CD55 and CD59 induces the intravascular hemolysis that is the main clinical manifestation of the disease[22,23]. Thrombotic events occur in about 27% of patients with PNH and are the main cause of mortality, accounting for approximately 40% of deaths[24]. Hepatic and portal veins are considered common sites of thrombosis[25]. Eculizumab is a monoclonal blocking antibody to complement protein C5, which inhibits cleavage to C5a and C5b and impedes terminal complement complex C5b-9[26]. Trials with eculizumab demonstrated a reduction in hemolysis, stabilization of hemoglobin levels, and a reduction in transfusion requirements but also a protection against the complications of hemolytic PNH, such as deteriorating renal function, pulmonary hypertension, and thromboembolism[27].
The patient presented has a large clone (> 50% PNH granulocytes and > 10% PNH red cells) combined with a notably increased LDH as evidence of intravascular hemolysis and a high reticulocyte count. In addition, platelet count was normal and anemia was mild without transfusion requirement, indicating an adequate bone marrow reserve. Thus, she had many chances to benefit from eculizumab treatment as the drug is highly effective in abrogating the intravascular hemolysis of PNH and reducing the risk of thrombosis but does not alleviate bone marrow failure if present[28]. Eculizumab is expensive and should be administered indefinitely for achieving sustained response. It has been stated that the drug has changed the natural course of PNH[29].
In our case, long-term treatment with eculizumab in combination with anticoagulation in a patient with PNH and INCPH resulted in improvement of the symptoms of liver disease, elimination of intravascular hemolysis, gradual resolution of kidney disease, and improvement of quality of life. The beneficial effect of the drug on liver microcirculation may be a result of the elimination of the prothrombotic disorder and the decrease of vascular resistance of the sinusoidal and portal venous walls.
Long-term administration of the monoclonal antibody eculizumab controlled the symptoms and life-threatening complications of PNH. More specifically, it reversed the complications of INCPH, as indicated by the elimination of large ascites and jaundice and normalization of liver function tests. Furthermore, it abrogated the intravascular hemolysis and improved dramatically the quality of life.
Manuscript source: Unsolicited Manuscript
Specialty type: Gastroenterology and hepatology
Country of origin: Greece
Peer-review report classification
Grade A (Excellent): A
Grade B (Very good): B
Grade C (Good): C, C
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Akbulut S, El-Razek AA, Ferraioli G, Garbuzenko DV S-Editor: Cui LJ L-Editor: Filipodia E-Editor: Zhang YL
| 1. | Schouten JN, Garcia-Pagan JC, Valla DC, Janssen HL. Idiopathic noncirrhotic portal hypertension. Hepatology. 2011;54:1071-1081. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 201] [Cited by in RCA: 222] [Article Influence: 15.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Sarin SK, Kumar A, Chawla YK, Baijal SS, Dhiman RK, Jafri W, Lesmana LA, Guha Mazumder D, Omata M, Qureshi H, Raza RM, Sahni P, Sakhuja P, Salih M, Santra A, Sharma BC, Sharma P, Shiha G, Sollano J; Members of the APASL Working Party on Portal Hypertension. Noncirrhotic portal fibrosis/idiopathic portal hypertension: APASL recommendations for diagnosis and treatment. Hepatol Int. 2007;1:398-413. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 128] [Cited by in RCA: 122] [Article Influence: 6.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Wanless IR. Micronodular transformation (nodular regenerative hyperplasia) of the liver: a report of 64 cases among 2,500 autopsies and a new classification of benign hepatocellular nodules. Hepatology. 1990;11:787-797. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 466] [Cited by in RCA: 406] [Article Influence: 11.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Mazumder DN, Das Gupta J, Santra A, Pal A, Ghose A, Sarkar S. Chronic arsenic toxicity in west Bengal--the worst calamity in the world. J Indian Med Assoc. 1998;96:4-7, 18. [PubMed] |
| 5. | Vispo E, Moreno A, Maida I, Barreiro P, Cuevas A, Albertos S, Soriano V. Noncirrhotic portal hypertension in HIV-infected patients: unique clinical and pathological findings. AIDS. 2010;24:1171-1176. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 72] [Cited by in RCA: 72] [Article Influence: 4.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | De Gottardi A, Rautou PE, Schouten J, Rubbia-Brandt L, Leebeek F, Trebicka J, Murad SD, Vilgrain V, Hernandez-Gea V, Nery F, Plessier A, Berzigotti A, Bioulac-Sage P, Primignani M, Semela D, Elkrief L, Bedossa P, Valla D, Garcia-Pagan JC; VALDIG group. Porto-sinusoidal vascular disease: proposal and description of a novel entity. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;4:399-411. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 78] [Cited by in RCA: 180] [Article Influence: 36.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 7. | Elkrief L, Rautou PE. Idiopathic non-cirrhotic portal hypertension: the tip of the obliterative portal venopathies iceberg? Liver Int. 2016;36:325-327. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 10] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Brodsky RA. Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Blood. 2014;124:2804-2811. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 301] [Cited by in RCA: 399] [Article Influence: 36.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Khanna R, Sarin SK. Idiopathic portal hypertension and extrahepatic portal venous obstruction. Hepatol Int. 2018;12:148-167. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 34] [Cited by in RCA: 47] [Article Influence: 6.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Schouten JN, Verheij J, Seijo S. Idiopathic non-cirrhotic portal hypertension: a review. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2015;10:67. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 54] [Cited by in RCA: 81] [Article Influence: 8.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Saifee S, Joelson D, Braude J, Shrestha R, Johnson M, Sellers M, Galambos MR, Rubin RA. Noncirrhotic portal hypertension in patients with human immunodeficiency virus-1 infection. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;6:1167-1169. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 51] [Cited by in RCA: 48] [Article Influence: 2.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Maida I, Garcia-Gasco P, Sotgiu G, Rios MJ, Vispo ME, Martin-Carbonero L, Barreiro P, Mura MS, Babudieri S, Albertos S, Garcia-Samaniego J, Soriano V. Antiretroviral-associated portal hypertension: a new clinical condition? Prevalence, predictors and outcome. Antivir Ther. 2008;13:103-107. [PubMed] |
| 13. | Roulot D, Degott C, Chazouillères O, Oberti F, Calès P, Carbonell N, Benferhat S, Bresson-Hadni S, Valla D. Vascular involvement of the liver in Turner's syndrome. Hepatology. 2004;39:239-247. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 85] [Cited by in RCA: 81] [Article Influence: 3.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Austin A, Campbell E, Lane P, Elias E. Nodular regenerative hyperplasia of the liver and coeliac disease: potential role of IgA anticardiolipin antibody. Gut. 2004;53:1032-1034. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 41] [Cited by in RCA: 51] [Article Influence: 2.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Okuda K, Kono K, Ohnishi K, Kimura K, Omata M, Koen H, Nakajima Y, Musha H, Hirashima T, Takashi M. Clinical study of eighty-six cases of idiopathic portal hypertension and comparison with cirrhosis with splenomegaly. Gastroenterology. 1984;86:600-610. [PubMed] |
| 16. | Hillaire S, Bonte E, Denninger MH, Casadevall N, Cadranel JF, Lebrec D, Valla D, Degott C. Idiopathic non-cirrhotic intrahepatic portal hypertension in the West: a re-evaluation in 28 patients. Gut. 2002;51:275-280. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 226] [Cited by in RCA: 206] [Article Influence: 9.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Siramolpiwat S, Seijo S, Miquel R, Berzigotti A, Garcia-Criado A, Darnell A, Turon F, Hernandez-Gea V, Bosch J, Garcia-Pagán JC. Idiopathic portal hypertension: natural history and long-term outcome. Hepatology. 2014;59:2276-2285. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 99] [Cited by in RCA: 138] [Article Influence: 12.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Cazals-Hatem D, Hillaire S, Rudler M, Plessier A, Paradis V, Condat B, Francoz C, Denninger MH, Durand F, Bedossa P, Valla DC. Obliterative portal venopathy: portal hypertension is not always present at diagnosis. J Hepatol. 2011;54:455-461. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 102] [Cited by in RCA: 120] [Article Influence: 8.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Kamath PS, Carpenter HA, Lloyd RV, McKusick MA, Steers JL, Nagorney DM, Miller VM. Hepatic localization of endothelin-1 in patients with idiopathic portal hypertension and cirrhosis of the liver. Liver Transpl. 2000;6:596-602. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 31] [Cited by in RCA: 25] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Rother RP, Bell L, Hillmen P, Gladwin MT. The clinical sequelae of intravascular hemolysis and extracellular plasma hemoglobin: a novel mechanism of human disease. JAMA. 2005;293:1653-1662. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1105] [Cited by in RCA: 1164] [Article Influence: 58.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Ignarro LJ. Endothelium-derived nitric oxide: actions and properties. FASEB J. 1989;3:31-36. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 479] [Cited by in RCA: 452] [Article Influence: 12.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 22. | Miyata T, Yamada N, Iida Y, Nishimura J, Takeda J, Kitani T, Kinoshita T. Abnormalities of PIG-A transcripts in granulocytes from patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. N Engl J Med. 1994;330:249-255. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 161] [Cited by in RCA: 156] [Article Influence: 5.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 23. | Bessler M, Mason PJ, Hillmen P, Miyata T, Yamada N, Takeda J, Luzzatto L, Kinoshita T. Paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria (PNH) is caused by somatic mutations in the PIG-A gene. EMBO J. 1994;13:110-117. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 270] [Cited by in RCA: 257] [Article Influence: 8.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 24. | Devalet B, Mullier F, Chatelain B, Dogné JM, Chatelain C. Pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: a review. Eur J Haematol. 2015;95:190-198. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 61] [Cited by in RCA: 68] [Article Influence: 6.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 25. | Ziakas PD, Poulou LS, Rokas GI, Bartzoudis D, Voulgarelis M. Thrombosis in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: sites, risks, outcome. An overview. J Thromb Haemost. 2007;5:642-645. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 90] [Cited by in RCA: 90] [Article Influence: 5.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 26. | Hillmen P, Young NS, Schubert J, Brodsky RA, Socié G, Muus P, Röth A, Szer J, Elebute MO, Nakamura R, Browne P, Risitano AM, Hill A, Schrezenmeier H, Fu CL, Maciejewski J, Rollins SA, Mojcik CF, Rother RP, Luzzatto L. The complement inhibitor eculizumab in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:1233-1243. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 855] [Cited by in RCA: 904] [Article Influence: 47.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 27. | Brodsky RA, Young NS, Antonioli E, Risitano AM, Schrezenmeier H, Schubert J, Gaya A, Coyle L, de Castro C, Fu CL, Maciejewski JP, Bessler M, Kroon HA, Rother RP, Hillmen P. Multicenter phase 3 study of the complement inhibitor eculizumab for the treatment of patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Blood. 2008;111:1840-1847. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 417] [Cited by in RCA: 459] [Article Influence: 25.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 28. | Kelly RJ, Hill A, Arnold LM, Brooksbank GL, Richards SJ, Cullen M, Mitchell LD, Cohen DR, Gregory WM, Hillmen P. Long-term treatment with eculizumab in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: sustained efficacy and improved survival. Blood. 2011;117:6786-6792. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 312] [Cited by in RCA: 373] [Article Influence: 26.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 29. | Hillmen P, Muus P, Röth A, Elebute MO, Risitano AM, Schrezenmeier H, Szer J, Browne P, Maciejewski JP, Schubert J, Urbano-Ispizua A, de Castro C, Socié G, Brodsky RA. Long-term safety and efficacy of sustained eculizumab treatment in patients with paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria. Br J Haematol. 2013;162:62-73. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 251] [Cited by in RCA: 294] [Article Influence: 24.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |