Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Hepatol. Jun 27, 2014; 6(6): 384-393
Published online Jun 27, 2014. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v6.i6.384
Published online Jun 27, 2014. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v6.i6.384
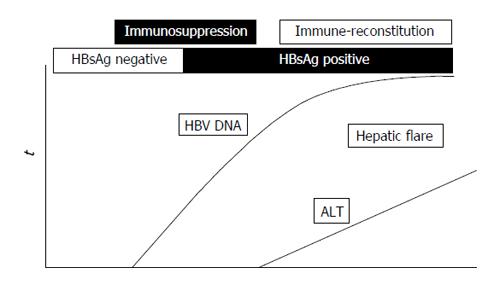
Figure 1 Virological and biochemical dynamics of reactivation of occult hepatitis B infection.
HBV: Hepatitis B virus; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; HBsAg: Hepatitis B surface antigen.
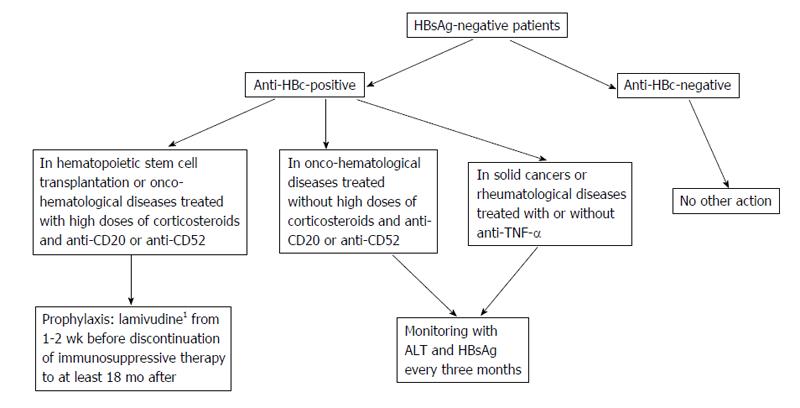
Figure 2 Management of occult hepatitis B infection in hematological and rheumatological diseases and in solid cancers.
1Entecavir instead of Lamivudine, when appropriate. HBsAg: Hepatitis B surface antigen; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; Anti-HBc: Hepatitis B core antigen; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factors-alpha.
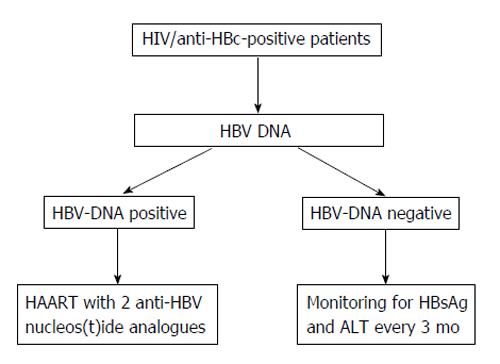
Figure 3 Management of occult hepatitis B infection in anti-human immunodeficiency virus-positive subjects.
HCV: Hepatitis C virus; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; HBV: Hepatitis B virus; HAART: Highly active antiretroviral therapy; HBsAg: Hepatitis B surface antigen.
- Citation: Sagnelli E, Pisaturo M, Martini S, Filippini P, Sagnelli C, Coppola N. Clinical impact of occult hepatitis B virus infection in immunosuppressed patients. World J Hepatol 2014; 6(6): 384-393
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v6/i6/384.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v6.i6.384