Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Hepatol. Dec 27, 2014; 6(12): 930-938
Published online Dec 27, 2014. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v6.i12.930
Published online Dec 27, 2014. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v6.i12.930
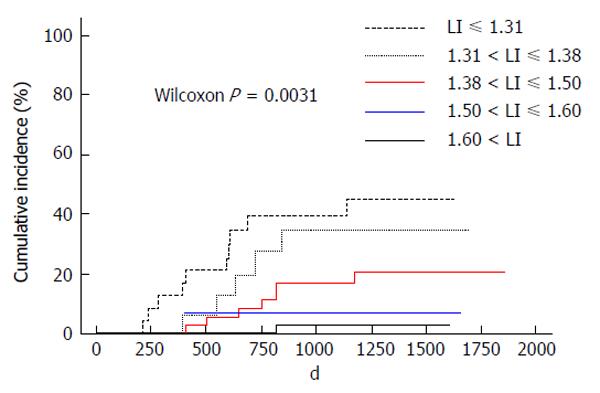
Figure 1 Cumulative incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma occurrence stratified by liver-intervertebral disc ratio.
Cumulative occurrence rates increased gradually in an LI-independent manner. LI: Liver-intervertebral disc ratio.
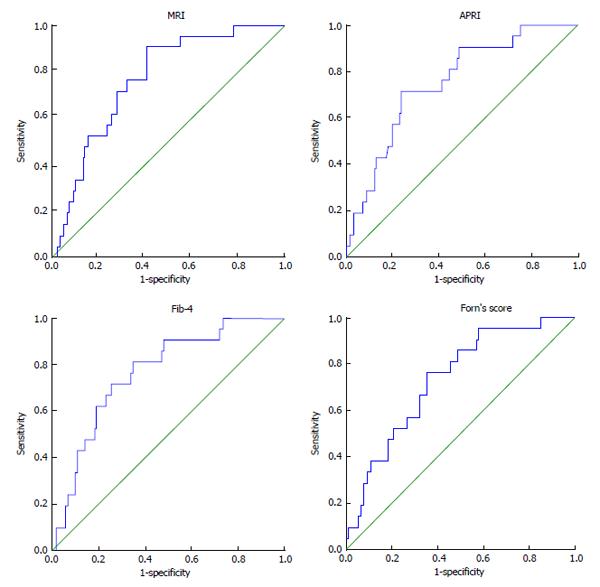
Figure 2 Receiver operating characteristic curve evaluating the cumulative incidence of liver-intervertebral disc ratio, aspartate amino transferase-to-platelet ratio index, Fib-4, and Forn’s index.
APRI: Aspartate amino transferase-to-platelet ratio index; MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging.
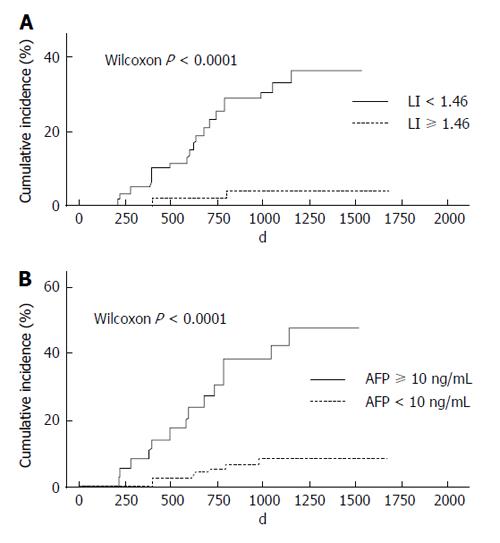
Figure 3 Relationship between cumulative occurrence rates and liver-intervertebral disc ratio (A), cumulative occurrence rates and serum α-fetoprotein level (B).
A: Occurrence rates with LI < 1.46 were significantly higher than those with LI ≥ 1.46; B: Occurrence rates with serum AFP ≥ 10 ng/mL were significantly higher than in those with serum AFP < 10 ng/mL. LI: Liver-intervertebral disc ratio; AFP: α-fetoprotein.
- Citation: Nojiri S, Fujiwara K, Shinkai N, Endo M, Joh T. Evaluation of hepatocellular carcinoma development in patients with chronic hepatitis C by EOB-MRI. World J Hepatol 2014; 6(12): 930-938
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v6/i12/930.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v6.i12.930