Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Hepatol. Dec 27, 2014; 6(12): 870-879
Published online Dec 27, 2014. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v6.i12.870
Published online Dec 27, 2014. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v6.i12.870
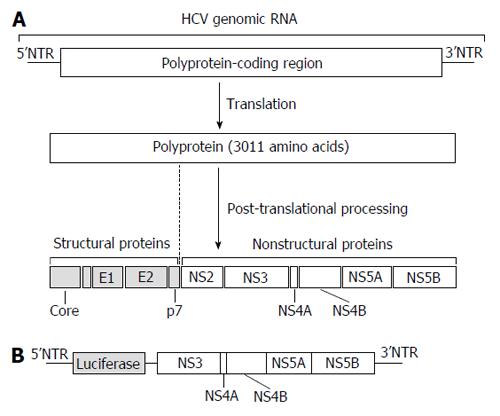
Figure 1 Structure of the hepatitis C virus genome and cell system for anti-hepatitis C virus drug discovery.
A: HCV genomic RNA and viral proteins. HCV genomic RNA encodes a single polyprotein of 3011 amino acids. After being translated, the polyprotein is processed into 4 structural proteins (Core, E1, E2, and p7) and 6 non-structural (NS) proteins (NS2, NS3, NS4A, NS4B, NS5A, and NS5B). The polyprotein-coding region is flanked by 5’ and 3’NTRs. Viral RNA also serves as a template for viral genome replication and both NTRs modulate viral protein synthesis and genome replication; B: The HCV replicon cell system. Huh-7 cells were transfected with the luciferase gene connected with HCV subgenomic RNA including the downstream coding regions of NS3. The expression of HCV subgenomic RNA could be quantified by luciferase activity. HCV: Hepatitis C virus; NTRs: Non-translated regions.
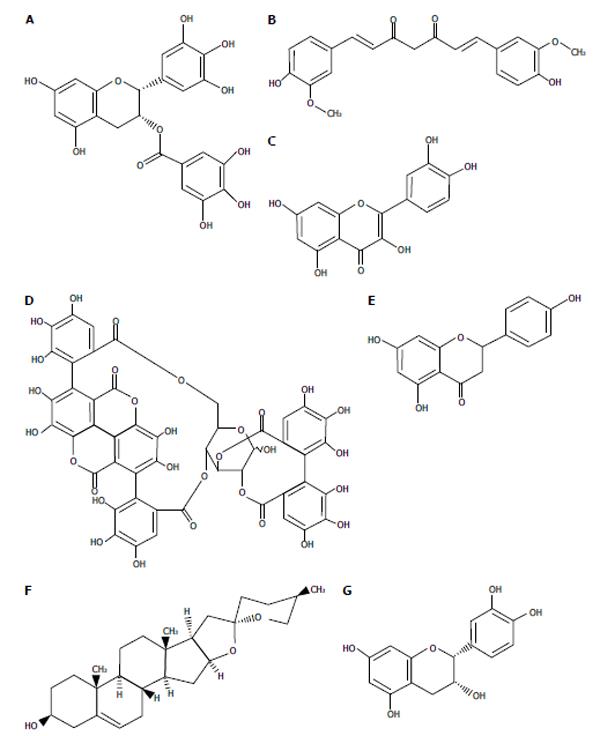
Figure 2 Chemical structure of functional food ingredients with anti-hepatitis C virus activities.
A: Epigallocatechin-3-gallate; B: Curcumin; C: Quercetin; D: Punicalagin; E: Naringenin; F: Diosgenin; G: (-)-epicatechin.
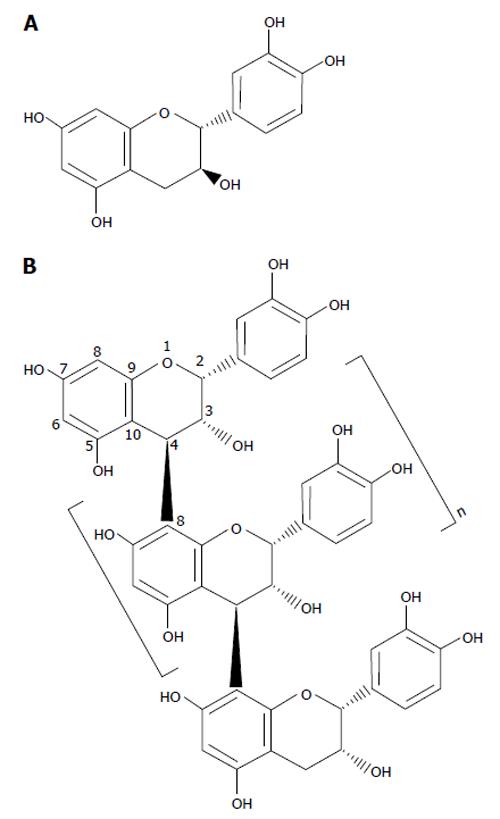
Figure 3 Chemical structures of a flavan-3-ol and proanthocyanidin.
A: (+)-catechin; B: An example of a procyanidin B-type polymer with an (-)-epicatechin based structure.
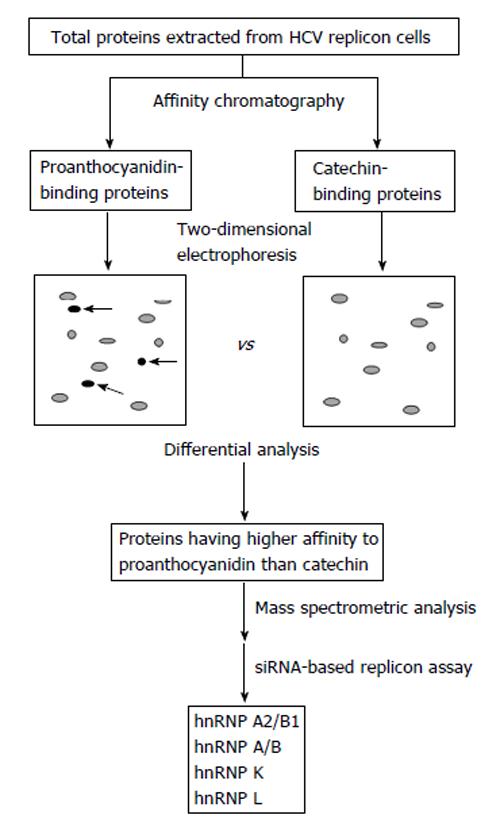
Figure 4 Identification strategy of candidate proteins involved in the proanthocyanidin-mediated inhibition of hepatitis C virus subgenomic expression[13].
Total proteins were extracted from hepatitis C virus (HCV) replicon cells and then proanthocyanidin-binding and catechin-binding proteins were purified by affinity chromatography using sepharose beads coupled with proanthocyanidin and catechin, respectively. Purified proteins were separated by two-dimensional electrophoresis followed by detecting spots of proteins having higher affinity to proanthocyanidin than catechin (arrows). Mass spectrometric analysis and further screening by a siRNA-based replicon assay showed that hnRNP A2/B1, A/B, K, and L are candidate proteins involved in the oligomeric proanthocyanidin-mediated inhibition of HCV subgenomic expression. hnRNP: Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein.
- Citation: Ishida YI, Takeshita M, Kataoka H. Functional foods effective for hepatitis C: Identification of oligomeric proanthocyanidin and its action mechanism. World J Hepatol 2014; 6(12): 870-879
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v6/i12/870.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v6.i12.870