Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Hepatol. Jul 27, 2025; 17(7): 106795
Published online Jul 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i7.106795
Published online Jul 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i7.106795
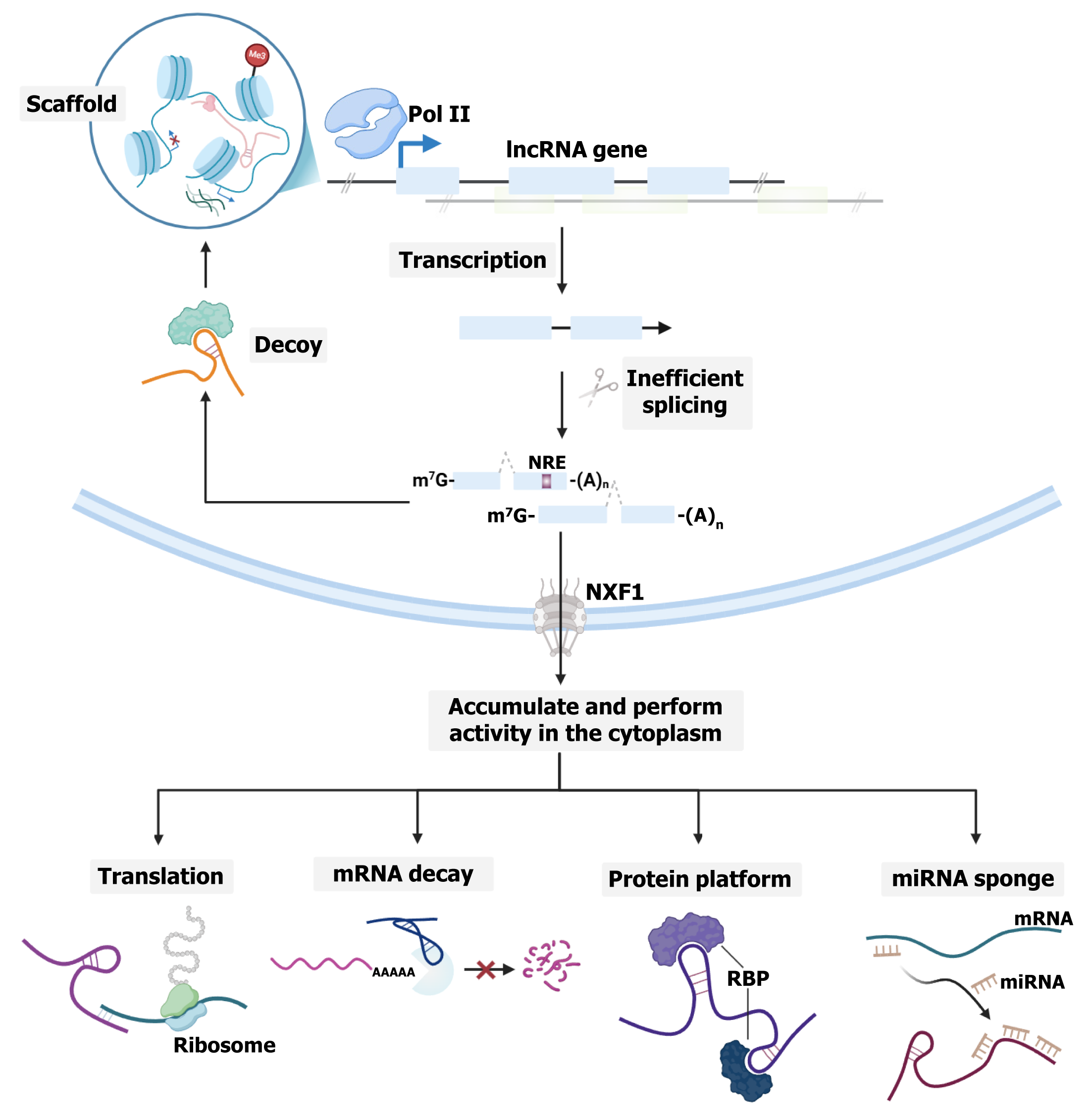
Figure 1 Biogenesis and diverse functions of long noncoding RNAs.
This schematic illustrates how long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) are transcribed, processed, and function. Most lncRNAs are transcribed by RNA polymerase II, undergo 5' capping, 3' polyadenylation, and less efficient splicing. Some lncRNAs localize to the nucleus and act as decoys or scaffolds, while others are exported to the cytoplasm. In the cytoplasm, lncRNAs can regulate gene expression by interacting with proteins or microRNAs. LncRNAs: Long noncoding RNAs; MiRNA: MicroRNAs; NRE: Notopterygium incisum root extract; NXF: Nuclear RNA export factor 1; Pol II: Polymerase II; RBP: RNA-binding protein.
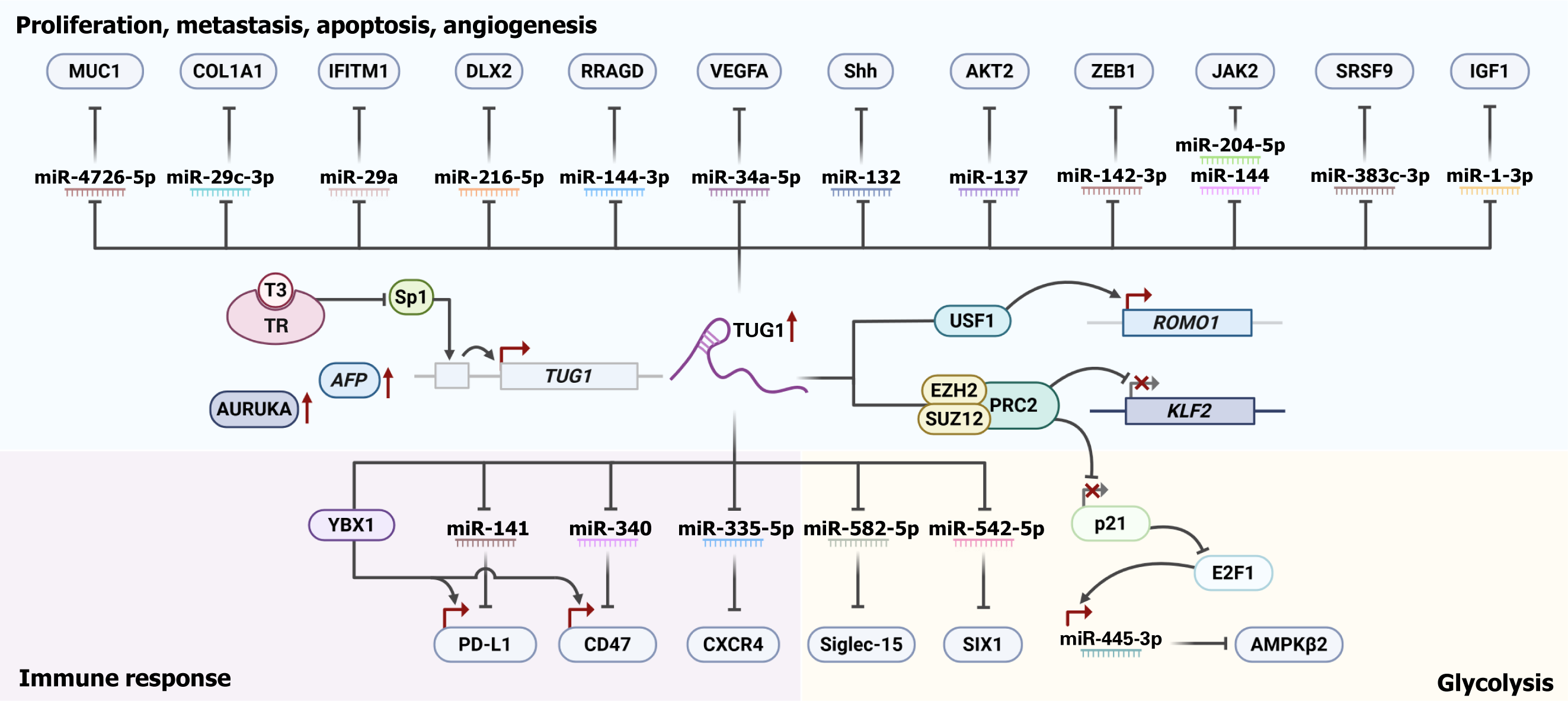
Figure 2 Taurine-upregulated gene 1 regulatory network in hepatocellular carcinoma.
This diagram illustrates the complex interplay between taurine-upregulated gene 1 (TUG1) and various genes, microRNAs (miRNAs), and signaling pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma. TUG1 modulates the expression of oncogenes and tumor suppressors (e.g., mucin 1, collagen type I alpha 1, interferon induced transmembrane protein 1), influencing cellular processes like proliferation, metastasis, and apoptosis. TUG1 acts as a competitive endogenous RNA by sponging miRNAs (e.g., miR-4726-5p, miR-29c-3p), thereby regulating their target genes. Additionally, TUG1 interacts with transcription factors (e.g., triiodothyronine/thyroid hormone receptors, specificity protein 1) and epigenetic modifiers (e.g., polycomb repressive complex 2 complex) to control gene expression. Red arrows indicate activation, and T-bars indicate repression (created in BioRender). AFP: Alpha-fetoprotein; AKT2: Protein kinase B 2; AMPKβ2: AMP-activated protein kinase beta 2; AURKA: Aurora kinase A; CD47: C luster of Differentiation 47; COL1A1: Collagen type I alpha 1; CXCR4: C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 4; DLX2: Distal-less homeobox 2; E2F1: E2F transcription factor 1; EZH2: Enhancer of zeste 2 polycomb repressive complex 2 subunit; IFITM1: Interferon induced transmembrane protein 1; IGF1: Insulin like growth factor 1; JAK2: Janus kinase 2; KLF2: Krüppel-like factor 2; MUC1: Mucin 1; P21: Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1A; PD-L1: Programmed death-ligand 1; PRC2: Polycomb repressive complex 2; ROMO1: Reactive oxygen species modulator 1; RRAGD: Ras related GTP binding D; Shh: Sonic hedgehog; Siglec-15: Sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectin-15; SIX1: SIX homeobox 1; Sp1: Specificity protein 1; SRSF9: Serine and arginine rich splicing factor 9; SUZ12: Suppressor of zeste 12; T3: Triiodothyronine; TR: Thyroid hormone receptors; TUG1: Taurine-upregulated gene 1; USF1: Upstream stimulatory factor 1; VEGFA: Vascular endothelial growth factor A; YBX1: Y-box binding protein 1; ZEB1: Zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 1.
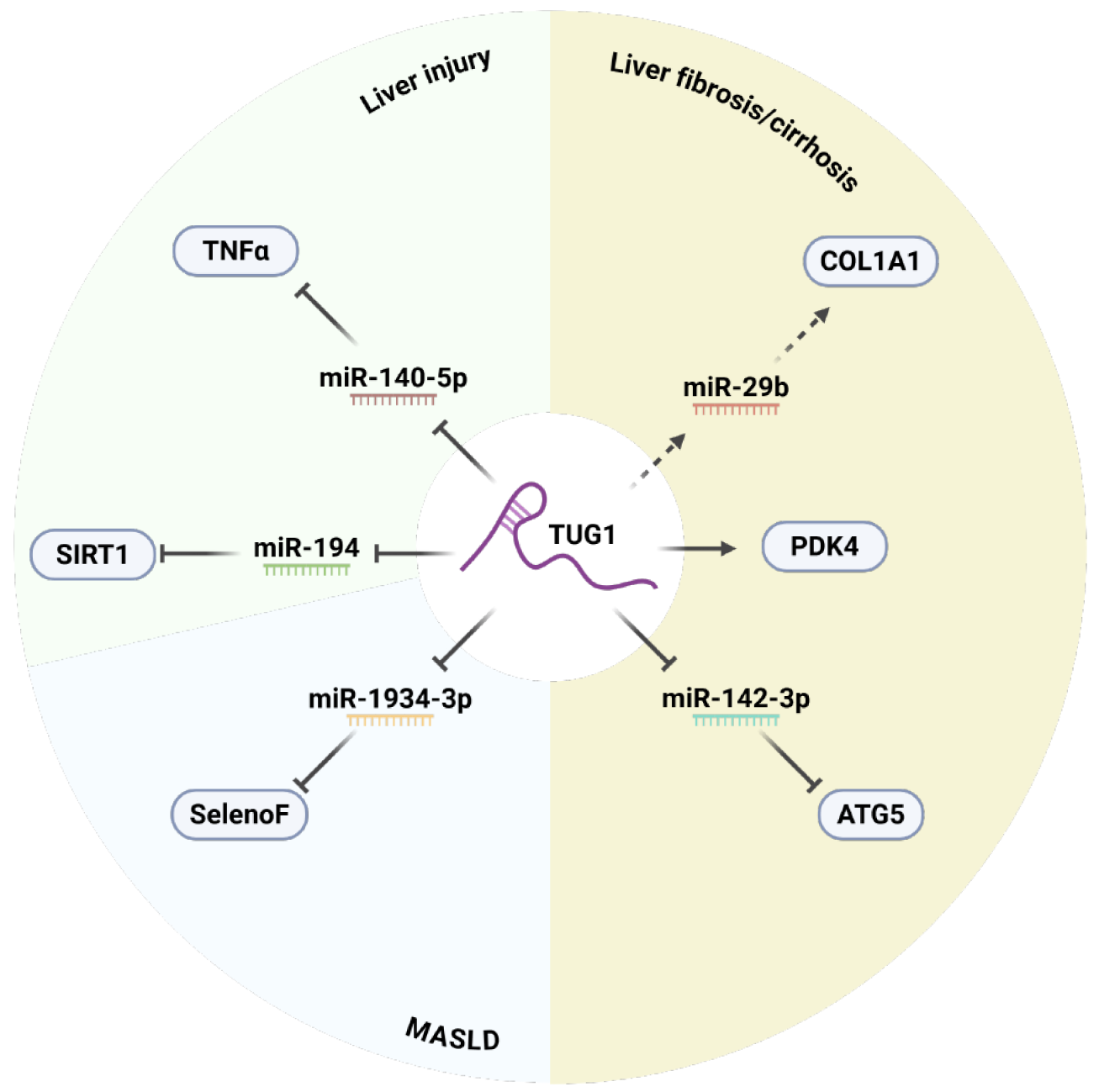
Figure 3 Taurine-upregulated gene 1's involvement in liver pathology.
This diagram illustrates the multifaceted role of taurine-upregulated gene 1 (TUG1) in liver injury, fibrosis/cirrhosis, and metabolic dysfunction–associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD). TUG1 interacts with various molecules, including microRNAs (miRNAs) (miR-140-5p, miR-29b, miR-194, miR-1934-3p, miR-142-3p), proteins [tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, collagen type I alpha 1 (COL1A1), sirtuin 1 (SIRT1), selenoprotein F, pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4 (PDK4), autophagy protein 5 (ATG5)], and cellular processes, contributing to the progression of liver diseases. In liver injury, TUG1 is shown to influence TNF-α signaling and SIRT1 activity. In liver fibrosis/cirrhosis, TUG1 affects the expression of COL1A1. In MASLD, TUG1 modulates the expression of PDK4 and ATG5, which are key players in metabolic pathways. T-bars indicate repression, and arrows indicate activation or positive regulation (created in BioRender). ATG5: Autophagy protein 5; COL1A1: Collagen type I alpha 1; MASLD: Metabolic dysfunction–associated steatotic liver disease; MiRNAs: MicroRNAs; PDK4: Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4; SelenoF: Selenoprotein F; SIRT1: Sirtuin 1; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor alpha; TUG1: Taurine upregulated gene 1.
- Citation: Boonto T, Ariyachet C. Deciphering the role of taurine-upregulated gene 1 in liver diseases: Mechanisms, clinical relevance, and emerging therapeutic opportunities. World J Hepatol 2025; 17(7): 106795
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v17/i7/106795.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v17.i7.106795