Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Hepatol. Feb 27, 2025; 17(2): 101914
Published online Feb 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i2.101914
Published online Feb 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i2.101914
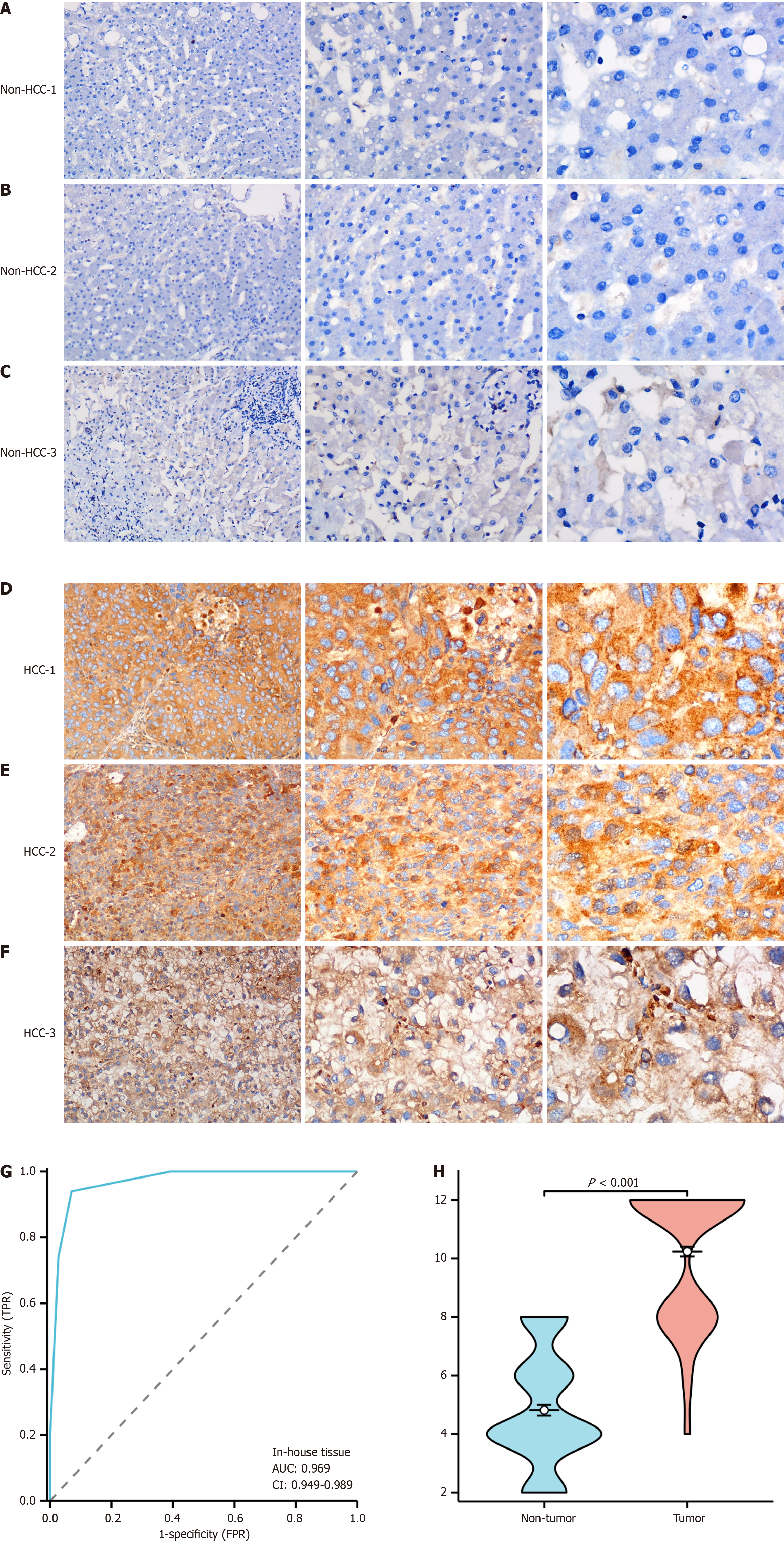
Figure 1 Expression of zinc finger protein 71 protein is elevated in hepatocellular carcinoma tissues compared to non-hepatocellular carcinoma tissues.
A-F: Immunohistochemistry images; G: Receiver operating characteristic curve; H: Violin plot. AUC: Area under the curve; CI: Confidence interval; FPR: False positive rate; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; TPR: True positive rate.
Figure 2 Clinicopathological features of zinc finger protein 71 in hepatocellular carcinoma tissues.
A: Expression of zinc finger protein 71 (ZNF71) in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and non-HCC (P < 0.05); B: Expression of ZNF71 in HCC was based on cancer stage (stage 1/2/3 vs normal, P < 0.05; stage 4 vs normal, P > 0.05); C: Expression of ZNF71 in HCC was based on the tumor grade (P < 0.05); D: Expression of ZNF71 in HCC was based on lymph node metastasis (N0 vs normal, P < 0.05; N1 vs normal, P > 0.05). LIHC: Liver hepatocellular carcinoma; TCGA: The Cancer Genome Atlas.
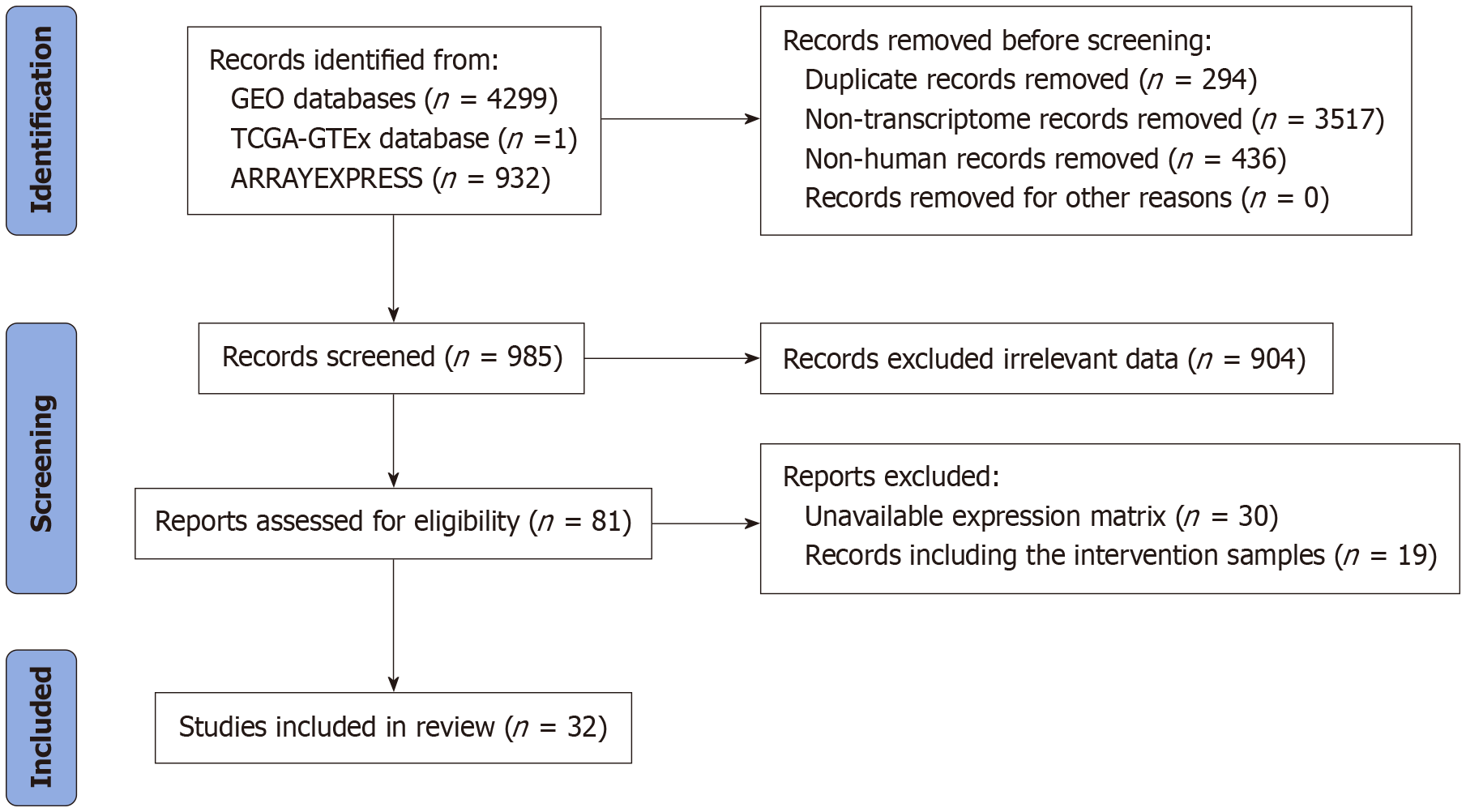
Figure 3 Flowchart of the inclusion analysis process.
GEO: Gene Expression Omnibus; GTEx: Genotype-Tissue Expression project; TCGA: The Cancer Genome Atlas.
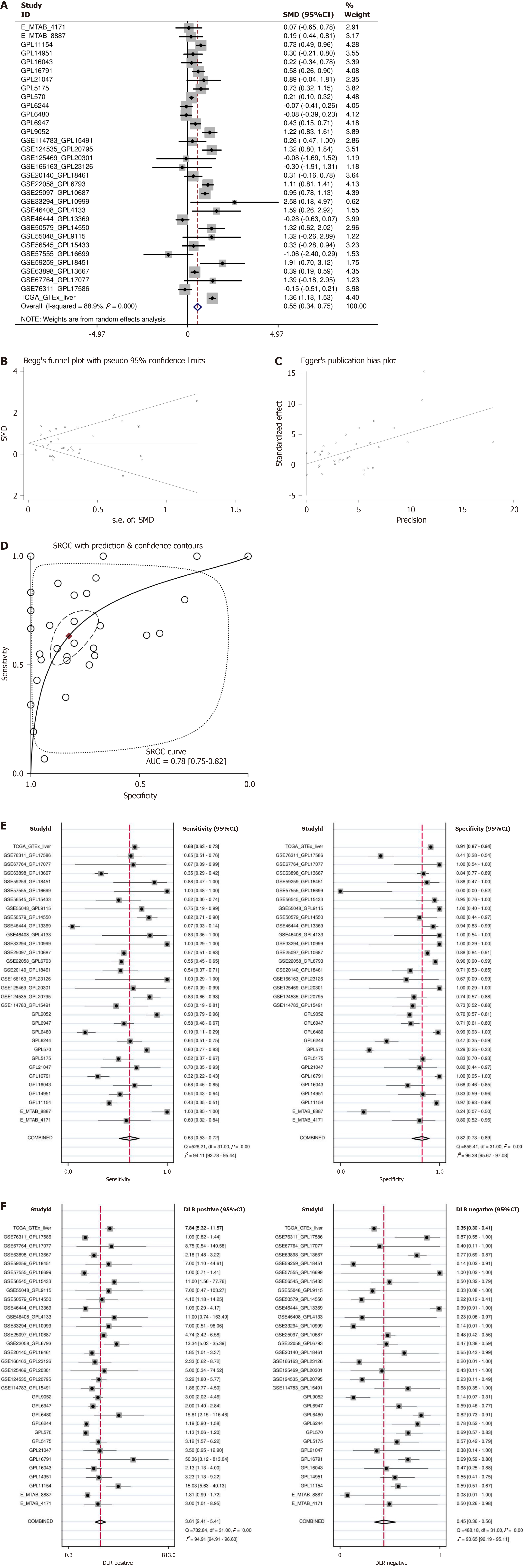
Figure 4 High zinc finger protein 71 mRNA expression levels in hepatocellular carcinoma.
A: Forest plot of the association between zinc finger protein 71 expression and hepatocellular carcinoma; B: Begg’s test for publication bias; C: Egger’s test for publication bias; D: Summary receiver operating characteristic curve; E: Sensitivity and specificity analysis; F: Positive and negative likelihood ratios. AUC: Area under the curve; CI: Confidence interval; SMD: Standardized mean difference; SROC: Summary receiver operating characteristic.
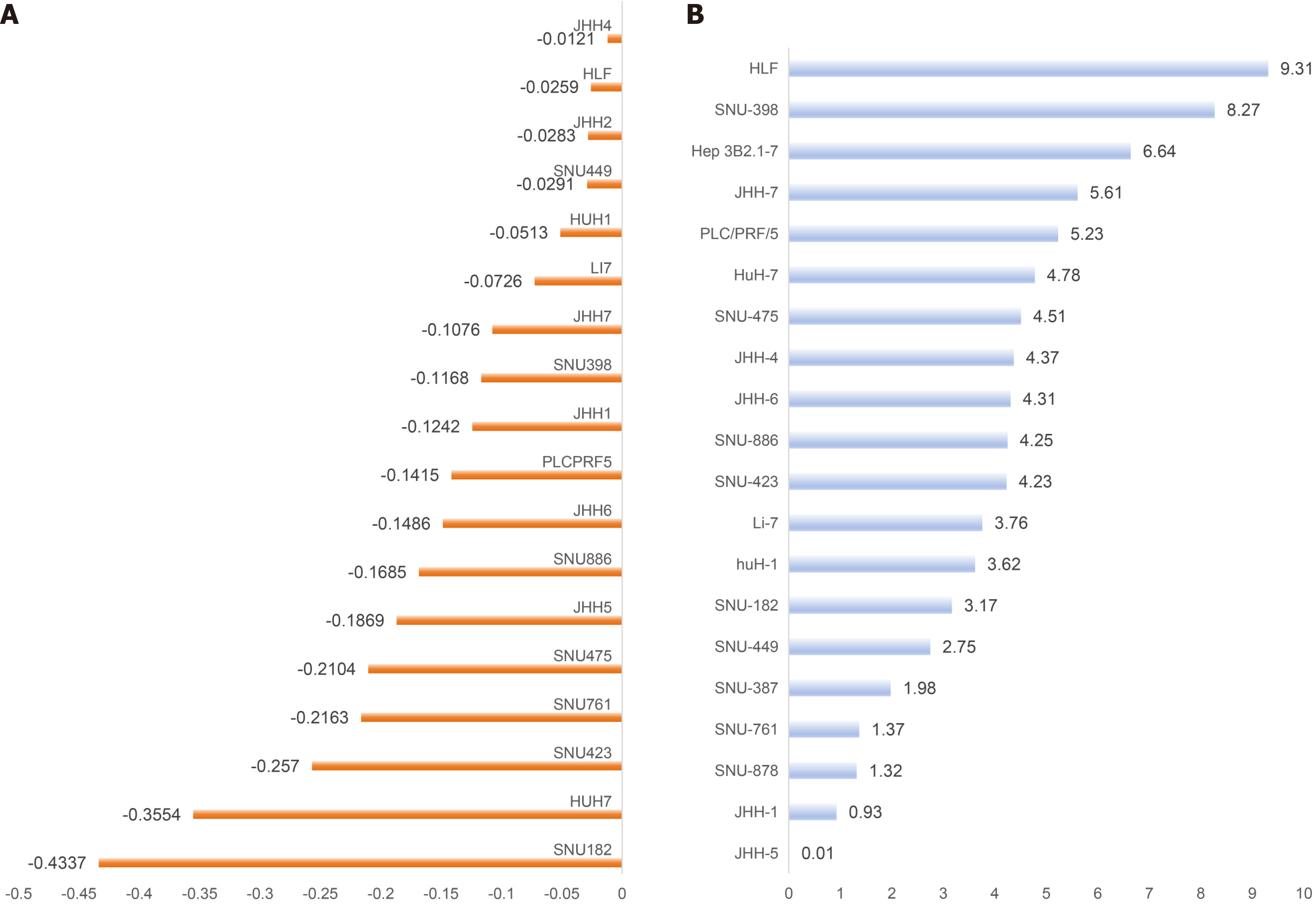
Figure 5 Impact of zinc finger protein 71 on hepatocellular carcinoma cells.
A: Impact of zinc finger protein 71 (ZNF71) gene disruption across 18 hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cell lines (effect score of ZNF71 plotted for each cell line, displayed on the horizontal axis, with cell lines enumerated vertically); B: ZNF71 mRNA expression in HCC cell lines (horizontal axis: ZNF71 mRNA levels in transcripts per million; vertical axis: HCC cell lines).
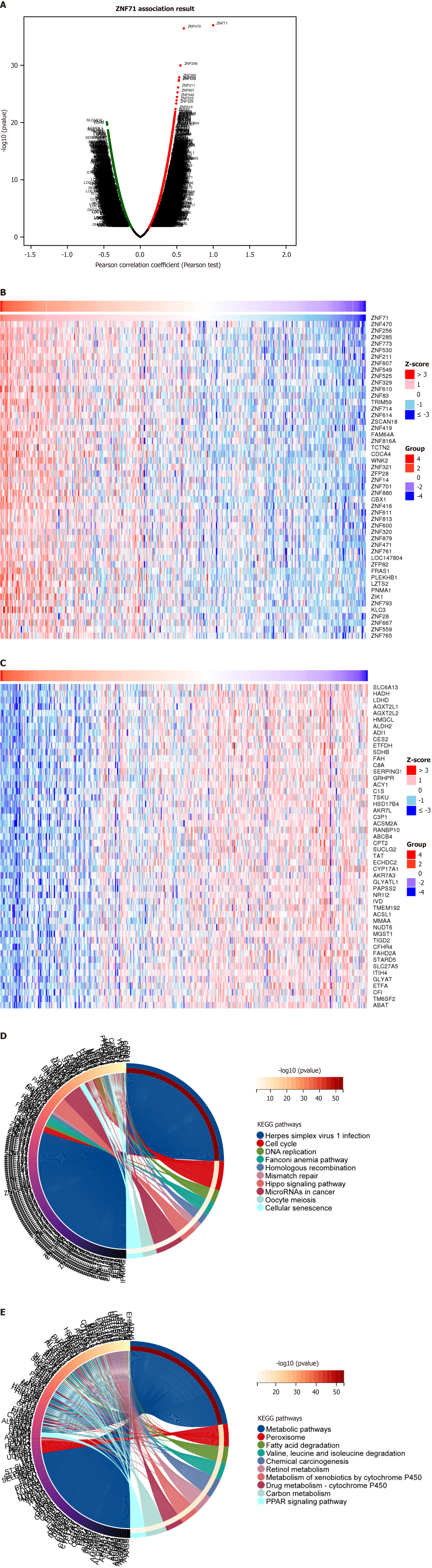
Figure 6 Co-expressed genes and signaling pathways of zinc finger protein 71.
A: Zinc finger protein 71 (ZNF71) co-expressed genes in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC); B: ZNF71 positively correlated co-expressed genes in HCC; C: ZNF71 negatively correlated co-expressed genes in HCC; D: Enrichment analysis of ZNF71 positively correlated co-expressed genes in HCC; E: Enrichment analysis of ZNF71 negatively correlated co-expressed genes in HCC. KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes.
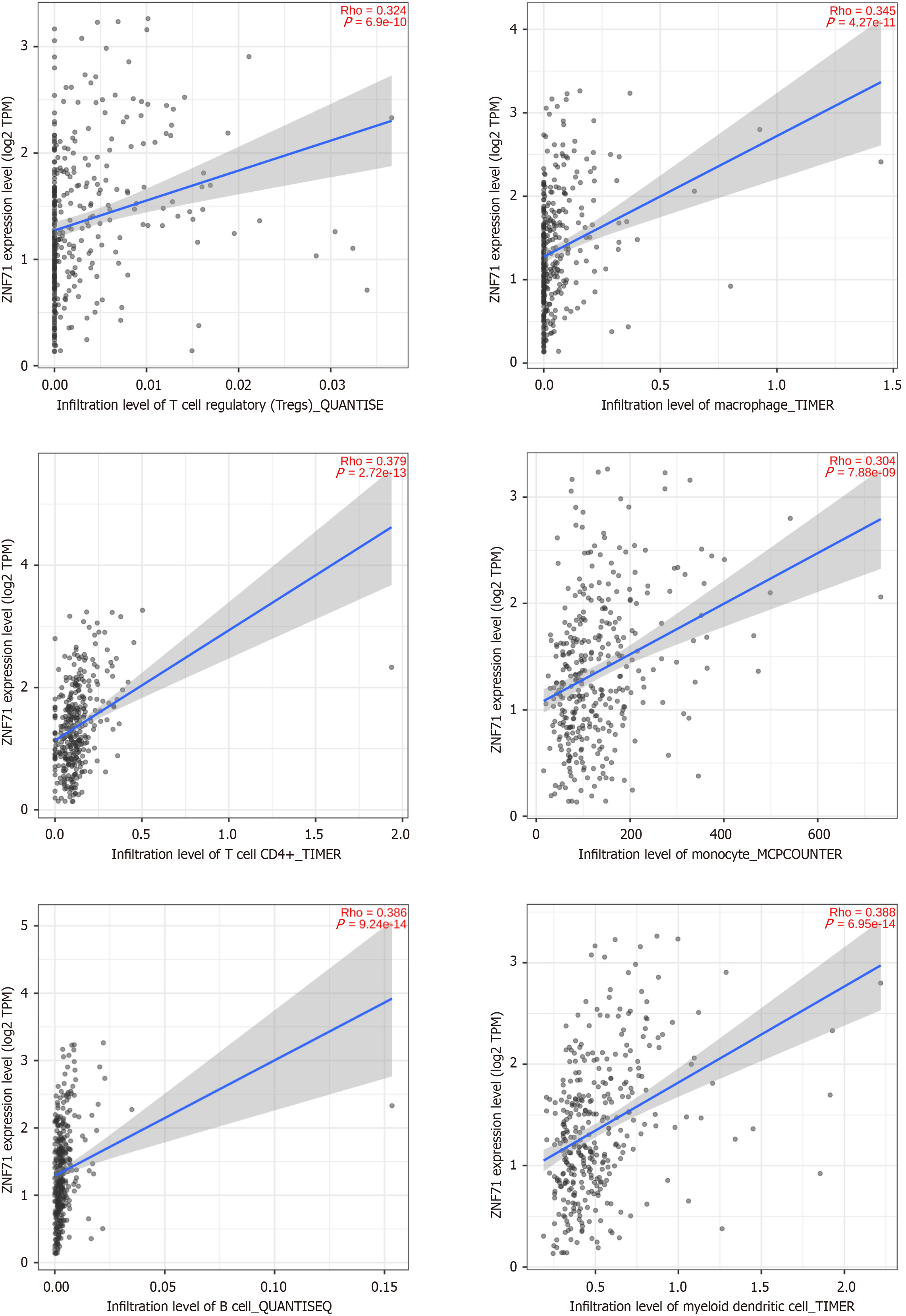
Figure 7 Correlation of zinc finger protein 71 with immune-infiltrating cells (P < 0.
05). TPM: Transcripts per million; ZNF71: Zinc finger protein 71.
- Citation: Qin K, Xiong DD, Qin Z, Li MJ, Li Q, Huang ZG, Tang YX, Li JD, Zhan YT, He RQ, Luo J, Wang HQ, Zhang SQ, Chen G, Wei DM, Dang YW. Overexpression and clinicopathological significance of zinc finger protein 71 in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Hepatol 2025; 17(2): 101914
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v17/i2/101914.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v17.i2.101914