Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Hepatol. Aug 27, 2024; 16(8): 1167-1176
Published online Aug 27, 2024. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v16.i8.1167
Published online Aug 27, 2024. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v16.i8.1167
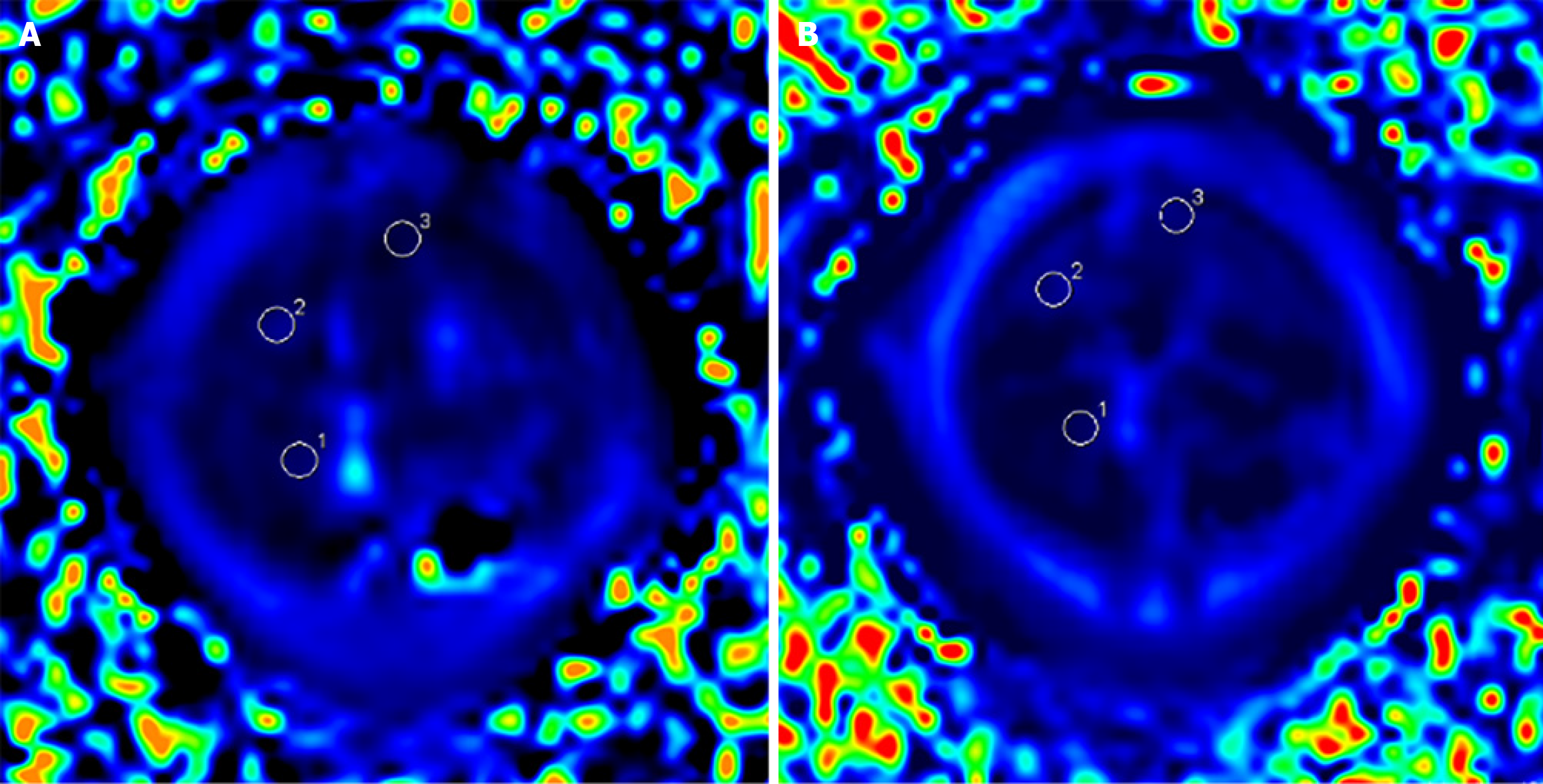
Figure 1 Regions of interest in the same area in the liver parenchyma before and after enhancement in the same C57BL/6 mouse.
A: Before enhancement in the same C57BL/6 mouse; B: After enhancement in the same C57BL/6 mouse. 1The region of interest in the middle hepatic lobe are delineated to avoid blood vessels within the liver parenchyma; 2The region of interest in the right hepatic lobe are delineated to avoid blood vessels within the liver parenchyma; 3The region of interest in the right hepatic lobe are delineated to avoid blood vessels within the liver parenchyma.
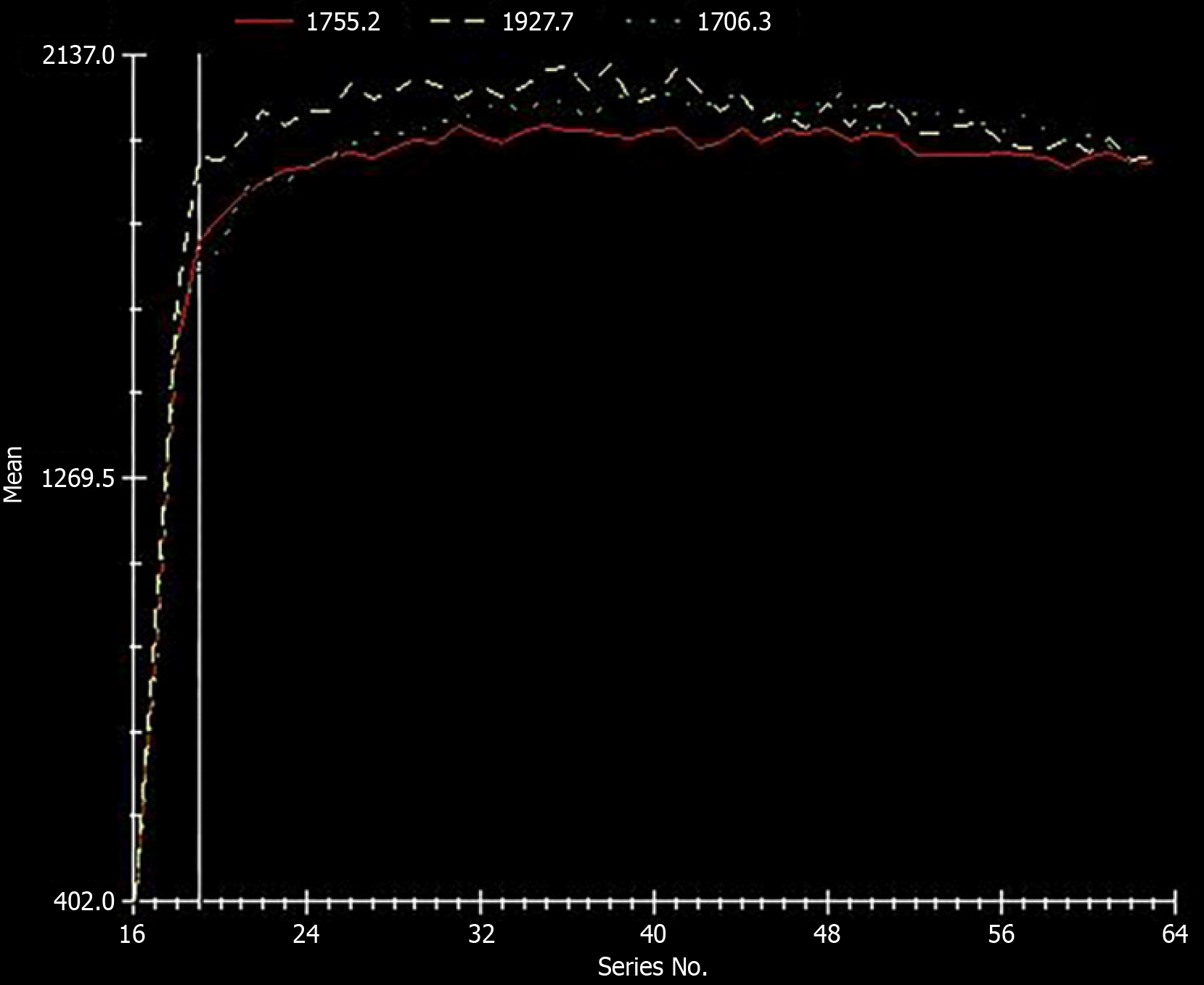
Figure 2 Liver parenchyma time–signal curve: The x axis represents the time axis, and the y axis represents T1 relaxation time, and the slope represents the first rapid enhancement slope percentage.
The three lines represent the values of the three regions of interest (ROIs). We selected the same ROIs in the liver parenchyma for T1 mapping.
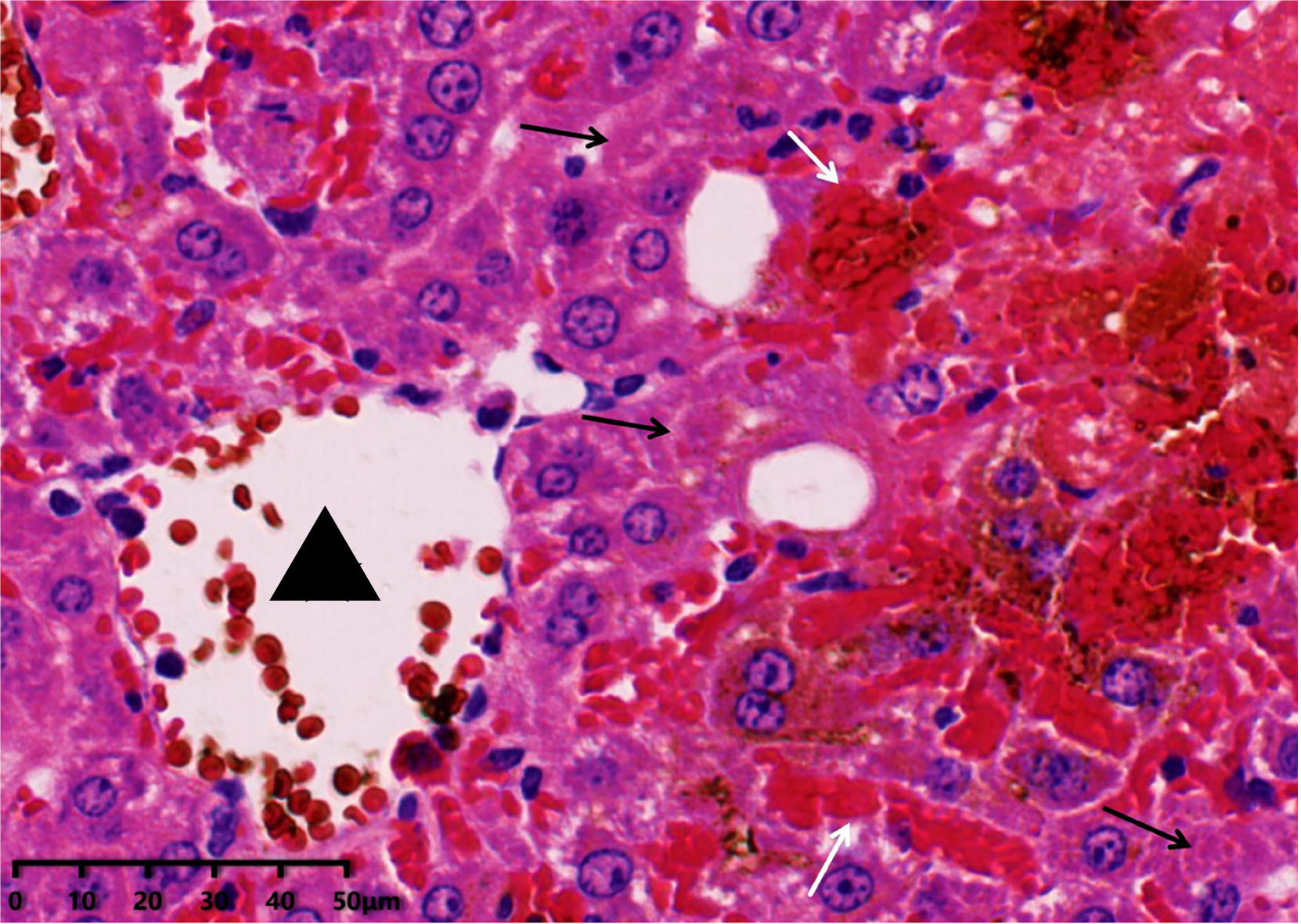
Figure 3 Hematoxylin and eosin staining (400 ×).
Histological findings of monocrotaline mouse models, the liver specimen demonstrates sinusoidal hemorrhage and hepatocytes necrosis, which are characteristic findings of sinusoidal obstruction syndrome. The triangle represents the central vein, the white arrow indicates dilated hepatic sinusoids hemorrhage, and the black arrow indicates hepatocyte necrosis.
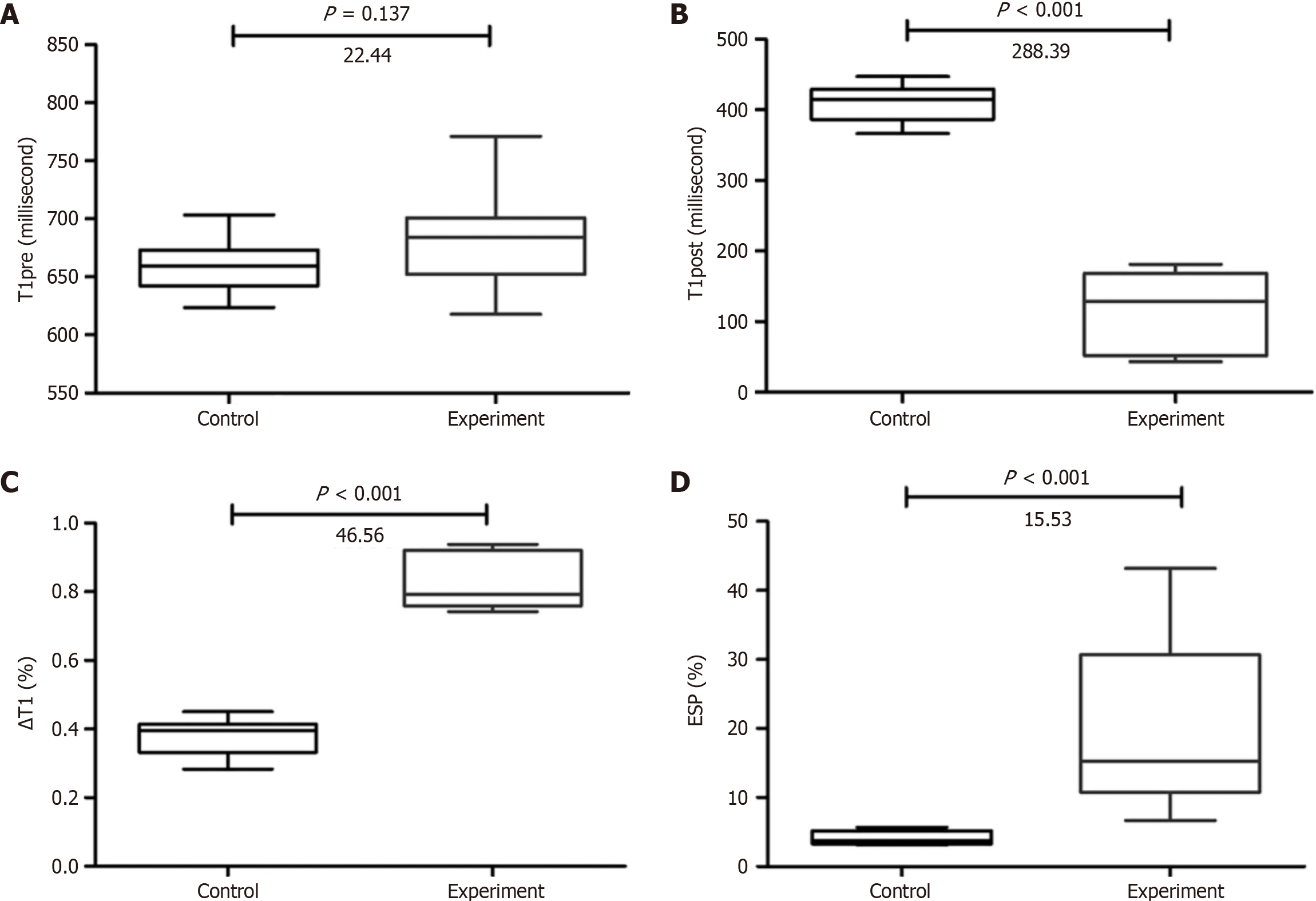
Figure 4 Box plots in control and experimental groups.
A: Box plots of T1 relaxation time before enhancement (T1pre); B: T1 relaxation times 20 minutes after enhancement (T1post); C: The reduction of T1 relaxation time (△T1%); D: The first enhancement slope percentage of the liver parenchyma in control and experimental groups. T1pre: T1 relaxation time before enhancement; T1post: T1 relaxation time 20 minutes after enhancement; △T1%: Reduction rate of T1 relaxation time; ESP: The first enhancement slope percentage in liver parenchyma.
- Citation: Chen YY, Yang L, Li J, Rao SX, Ding Y, Zeng MS. Gadoxetic acid-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in the assessment of hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome in a mouse model. World J Hepatol 2024; 16(8): 1167-1176
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v16/i8/1167.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v16.i8.1167