Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Hepatol. Jul 27, 2024; 16(7): 1018-1028
Published online Jul 27, 2024. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v16.i7.1018
Published online Jul 27, 2024. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v16.i7.1018
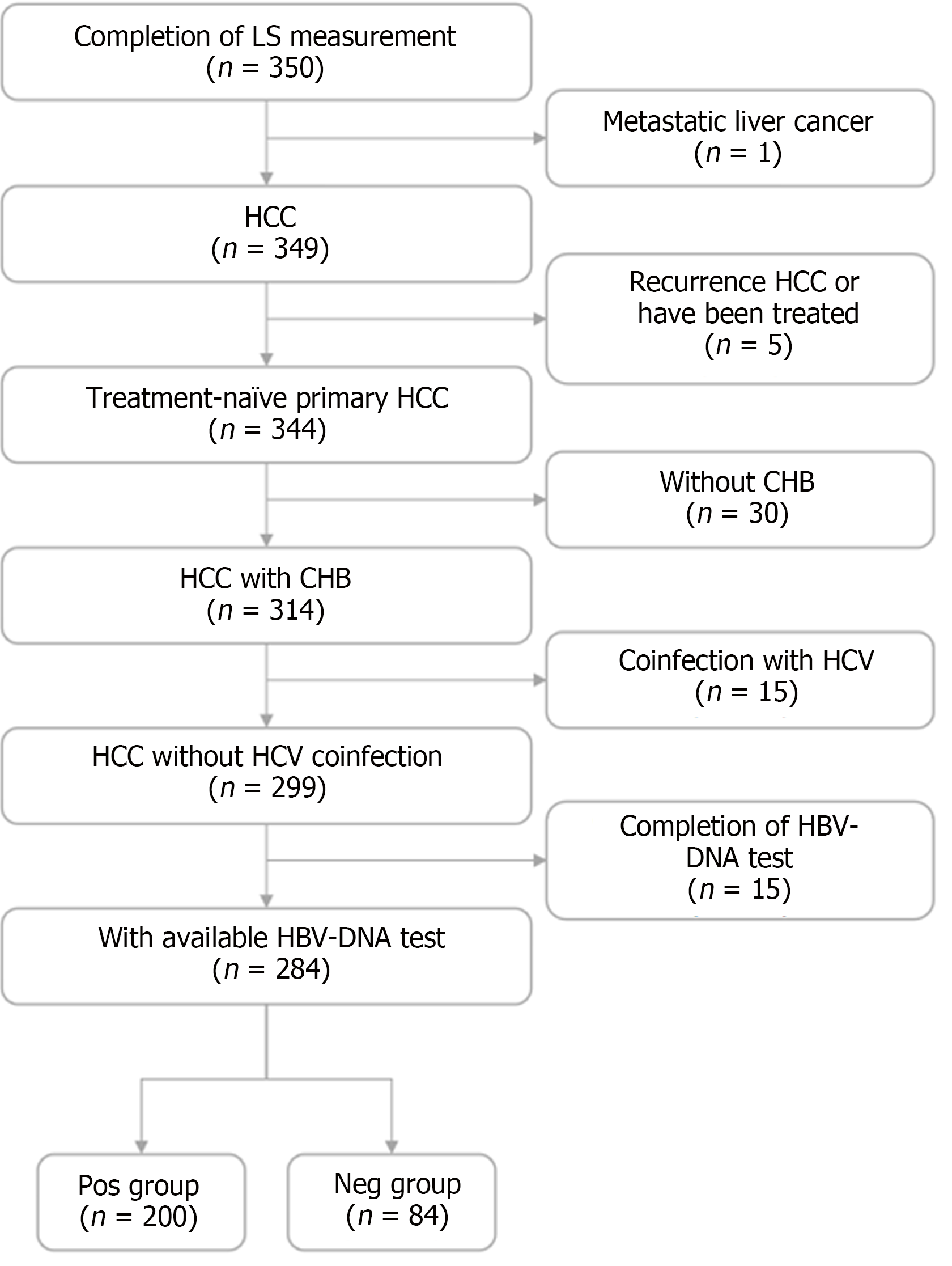
Figure 1 Flow chart of recruitment of patients.
LS: Liver stiffness; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; CHB: Chronic hepatitis B; HCV: Hepatitis C virus; HBV: Hepatitis B virus; Pos group: HBV-DNA positive group; Neg group: HBV-DNA negative group.
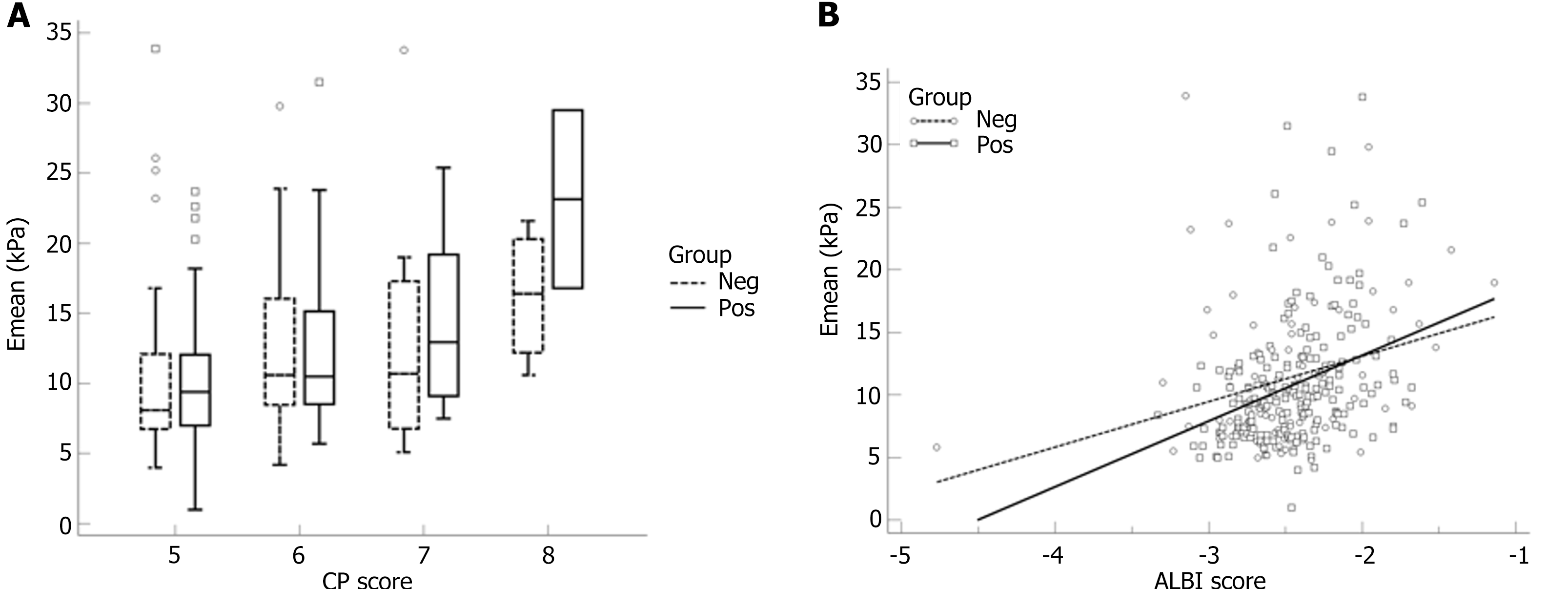
Figure 2 Correlation between Emean and liver condition.
A: Box plot of the correlation between Emean and Child-Pugh score; B: Line graph of the correlation between Emean and albumin-bilirubin score. HBV: Hepatitis B virus; Pos group: HBV-DNA positive group; Neg group: HBV-DNA negative group; CP: Child-Pugh; ALBI: Albumin-bilirubin.
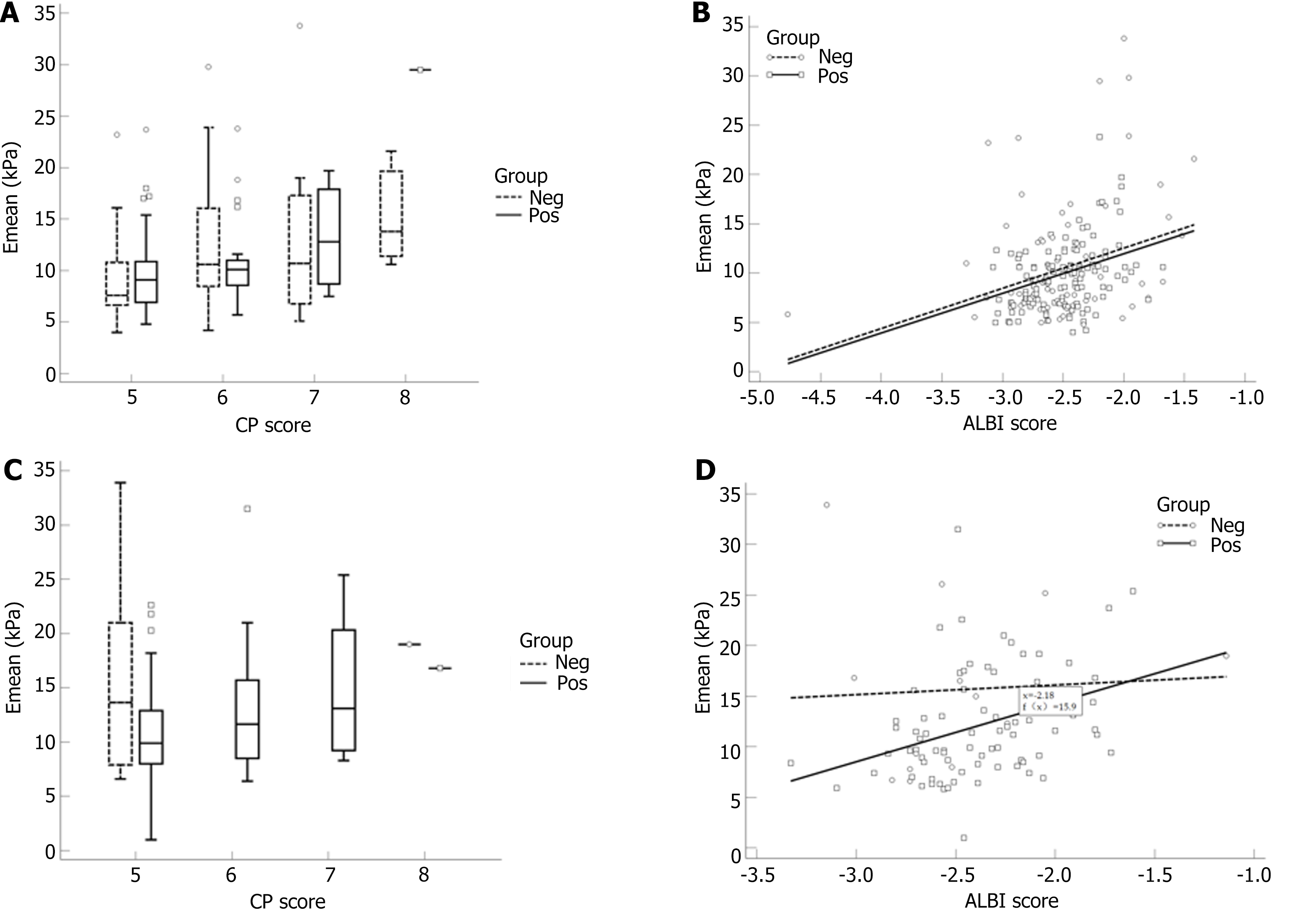
Figure 3 Correlation between Emean and liver condition in patients with different levels of alanine aminotransferase.
A: Box plot of the correlation between Emean and Child-Pugh score in patients with normal alanine aminotransferase (ALT); B: Line graph of the correlation between Emean and albumin-bilirubin (ALBI) score in patients with normal ALT; C: Box plot of the correlation between Emean and Child-Pugh score in patients with increased ALT; D: Line graph of the correlation between Emean and ALBI score in patients with increased ALT. HBV: Hepatitis B virus; Pos group: HBV-DNA positive group; Neg group: HBV-DNA negative group; CP: Child-Pugh; ALBI: Albumin-bilirubin.
- Citation: Huang JY, Peng JY, Long HY, Zhong X, Xie YH, Yao L, Xie XY, Lin MX. Liver stiffness in hepatocellular carcinoma and chronic hepatitis patients: Hepatitis B virus infection and transaminases should be considered. World J Hepatol 2024; 16(7): 1018-1028
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v16/i7/1018.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v16.i7.1018